【数据结构】线性表之链表
目录
- 前言
- 一、链表的定义
- 二、链表的分类
-
- 1. 单向和双向
- 2. 带头和不带头
- 3. 循环和不循环
- 4. 常用(无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表)
- 三、无头单向非循环链表的接口及实现
-
- 1. 单链表的接口
- 2. 接口的实现
- 四、带头双向循环链表接口的及实现
-
- 1. 双向链表的接口
- 2. 接口的实现
- 五、带头双向循环链表VS无头单向非循环链表
-
- 1. 带头双向循环链表
-
- 1.1 带头双向循环链表的优点:
- 1.2 带头双向循环链表的缺点:
- 2. 无头单向非循环链表
-
- 2.1 无头单向非循环链表的优点:
- 2.2 无头单向非循环链表的缺点:
- 3. 小结
- 六、链表VS顺序表
-
- 1. 带头双向循环链表
-
- 1.1 链表的优点:
- 2. 链表的缺点:
- 2. 顺序表
-
- 2.1顺序表的优点
- 2.2顺序表的缺点
- 结尾
前言
上一篇文章讲述了线性表中的顺序表,这篇文章讲述关于链表的定义、类别、实现、多种不同链表的优缺点和链表与顺序表的优缺点。
关于上一篇文章的链接:线性表之顺序表
一、链表的定义
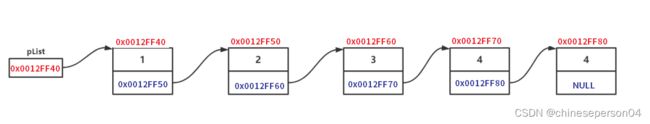
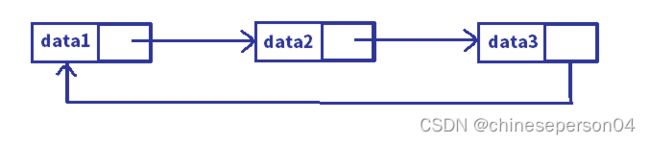
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
二、链表的分类
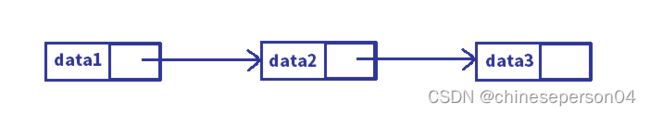
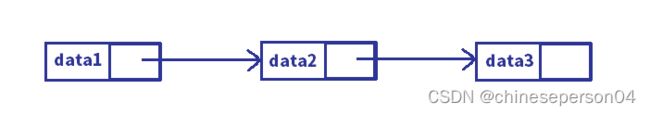
1. 单向和双向
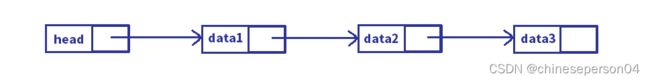
2. 带头和不带头
3. 循环和不循环
4. 常用(无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表)
三、无头单向非循环链表的接口及实现
1. 单链表的接口
#pragma once
#include 2. 接口的实现
#include "slist.h"
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
{
//创造新节点
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
//新节点初始化
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
//这里使用二级指针的原因是:
//若链表为空,需要改变的就是结构体指针,需要结构体指针的地址
//若传入的是一级指针,这里传入的只是临时拷贝,无法改变函数外的变量
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = BuySListNode(x);
}
//若不为空,需要改变的是结构体,只需要结构体的指针
else
{
SListNode* tail = *pplist;
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
void SListPrint(SListNode* plist)
{
while (plist)
{
printf("%d->", plist->data);
plist = plist->next;
}
printf("NULL");
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
//这里使用二级指针的原因是:每次头删都需要改变头节点
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}
//无头单链表尾删删除节点的时候有三种情况
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist)
{
//没有节点
assert(*pplist);
//一个节点
if ((*pplist)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pplist);
*pplist = NULL;
}
//多个节点
else
{
//尾删既可以找尾找尾的前一个节点,也可以创造一个变量记录尾节点的前一个节点
//创造一个变量记录尾节点的前一个节点
// SListNode* tail = *pplist;
// SListNode* prev = NULL;
// while (tail->next)
// {
// prev = tail;
// tail = tail->next;
// }
// free(prev->next);
// prev->next = NULL;
//找尾找尾的前一个节点
SListNode* tail = *pplist;
while (tail->next->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next = NULL;
}
}
//无头单链表头删删除节点的时候有三种情况,但只有一个节点和多个节点的情况可以合并
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist)
{
//无节点时
assert(*pplist);
//有节点时
SListNode* del = *pplist;
*pplist = del->next;
free(del);
}
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{
//断言:在pos后面插入一个节点,最差的情况是pos为尾节点,但不能为NULL
assert(pos);
SListNode* cur = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (cur == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return;
}
cur->data = x;
cur->next = pos->next;
pos->next = cur;
}
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{
//需要删除节点的前一个节点不能为NULL,删除节点也不能为NULL
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
SListNode* next = pos->next;
pos->next = next->next;
free(next);
}
void SListDestroy(SListNode* plist)
{
SListNode* del = NULL;
while (plist)
{
del = plist;
plist = plist->next;
free(del);
}
}
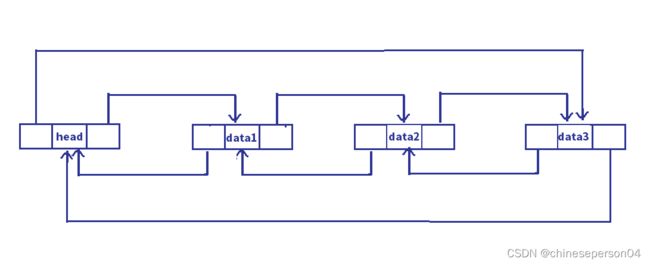
四、带头双向循环链表接口的及实现
1. 双向链表的接口
#pragma once
#include 2. 接口的实现
#include "list.h"
// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate()
{
ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (phead == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
//让头的 next 和 prev 都指向自己
//则双向链表为空
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
// 创造新节点
ListNode* BuyTLNode(LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
return newnode;
}
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
/*ListNode* tail = pHead->prev;
ListNode* newnode = BuyTLNode(x);
newnode->next = pHead;
newnode->prev = tail;
tail->next = newnode;
pHead->prev = newnode;*/
ListInsert(pHead, x); //复用
}
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead)
{
printf("header <--> ");
//打印的时候,由于头内的 data 的值没用
//则从头的的下一个节点开始打印
//并且在循环到头的时候打印结束
ListNode* cur = pHead ->next;
while (cur != pHead)
{
printf("%d <--> ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 判断双向链表是否为空
bool LTEmpty(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
return pHead->next == pHead;
}
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!(LTEmpty(pHead)));
/*ListNode* first = pHead->next;
ListNode* second = first->next;
pHead->next = second;
second->prev = pHead;
free(first);*/
ListErase(pHead->next); //复用
}
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
/*ListNode* next = pHead->next;
ListNode* newnode = BuyTLNode(x);
newnode->next = next;
newnode->prev = pHead;
next->prev = newnode;
pHead->next = newnode;*/
ListInsert(pHead->next, x);//复用
}
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead)
{
assert(pHead);
assert(!(LTEmpty(pHead)));
/*ListNode* tail = pHead->prev;
ListNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;
tailPrev->next = pHead;
pHead->prev = tailPrev;
free(tail);*/
ListErase(pHead->prev); //复用
}
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x)
{
ListNode* cur = pHead ->next;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* newnode = BuyTLNode(x);
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
newnode->next = pos;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
posPrev->next = newnode;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
ListNode* posNext = pos->next;
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;
free(pos);
}
五、带头双向循环链表VS无头单向非循环链表
1. 带头双向循环链表
1.1 带头双向循环链表的优点:
- 可以自由地在链表中任意位置插入和删除节点,这是因为双向链表可以方便地找到前驱和后继节点。
- 可以支持双向遍历,即可以从前往后或从后往前遍历链表。
- 可以更加高效地实现某些特殊的操作,比如在链表中删除指定节点,需要同时修改其前驱和后继节点的指针,双向链表则可以直接完成这个操作,而单向链表则需要遍历到前驱节点才能完成。
1.2 带头双向循环链表的缺点:
- 因为每个节点都要额外存储一个前驱节点的指针,所以需要更多的内存空间。
- 因为需要维护前驱和后继节点的指针,所以在插入和删除节点时需要更多的操作,导致时间复杂度较高。
2. 无头单向非循环链表
2.1 无头单向非循环链表的优点:
- 因为每个节点只需存储一个后继节点的指针,所以需要较少的内存空间。
- 在插入和删除节点时,只需要修改前一个节点的指针,不需要修改后一个节点的指针,操作相对简单,导致时间复杂度较低。
2.2 无头单向非循环链表的缺点:
- 无法实现双向遍历,即无法从后往前遍历链表。
- 在删除指定节点时,需要先遍历到其前驱节点,才能完成删除操作,导致删除效率较低。
3. 小结
总之,选择哪种链表数据结构应该根据具体的应用场景和需要做的操作来决定。如果需要频繁地插入和删除节点,且需要支持双向遍历,可以选择带头双向循环链表;如果需要占用较少的内存空间,且不需要双向遍历,可以选择无头单向非循环链表。
六、链表VS顺序表
1. 带头双向循环链表
1.1 链表的优点:
- 动态内存分配:链表可以在运行时动态地分配内存,因此可以根据实际需要灵活地增加或减少节点数。
- 插入和删除操作高效:由于链表中的元素不必在连续的内存空间中存储,所以插入和删除操作非常高效,只需要修改指针,而不需要移动所有后续元素。
- 大小不受限制:链表的大小不受限制,可以根据实际需要进行扩展。
2. 链表的缺点:
- 随机访问低效:由于链表中的元素不是按顺序存储的,因此随机访问某个元素的效率比较低,需要从头开始遍历
O(N)。 - 存储空间开销大:链表每个节点都需要额外的指针来指向下一个节点,这样会增加存储空间的开销。
- 缓存不友好:由于链表中的元素不是按顺序存储的,因此可能会导致缓存未命中,降低访问效率。
2. 顺序表
2.1顺序表的优点
- 随机访问高效:下标的随机访问效率高
O(1)。 - 尾删尾插高效:顺序表的尾插尾删不需要移动数据,效率高。
- 缓存友好:由于链表中的元素是按顺序存储的,缓存命中率高,访问效率高。
2.2顺序表的缺点
- 部分插入删除操作低效:由于顺序表中的元素是物理结构上是连续的,当数据插入删除前面顺序表的时候需要移动数据,效率低
O(N)。 - 内存大小受限:当顺序表内存存满后需要扩容,扩容需要代价,并且顺序表通常会有内存的浪费情况。
结尾
如果有什么建议和疑问,或是有什么错误,希望大家能够提一下。
希望大家以后也能和我一起进步!!
如果这篇文章对你有用的话,希望能给我一个小小的赞!