一起刷算法与数据结构-链表篇1
| 大家好,我是工藤学编程 | 大二在读 |
|---|---|
| 作业侠系列最新文章 | Java实现聊天程序 |
| 一起备战ccf-csp与蓝桥杯系列最新文章 | 一起备战蓝桥杯与CCF-CSP之大模拟炉石传说 |
| 一起刷算法与数据结构最新文章 | 一起刷算法与数据结构-链表篇1 |
一起刷算法与数据结构专栏说明:
由于博主数据结构与算法能力处于普通水平,就和大多数同学一样,本专栏会按照每个知识点整理题目,同时,为了节约大家的时间,为大家去掉了很简单的题,整理出了适合我们思考的难度的题目,题目来源均为Acwing或者lc,如果大家对想刷数据结构和算法但又不知道重合下手,那大家可以按照我为大家整理的题目来,每个题目都为大家准备了通俗易懂解题思路和参考代码,准备面试什么的非常适合
接下来进入的开始篇:
一起刷算法与数据结构-链表篇1
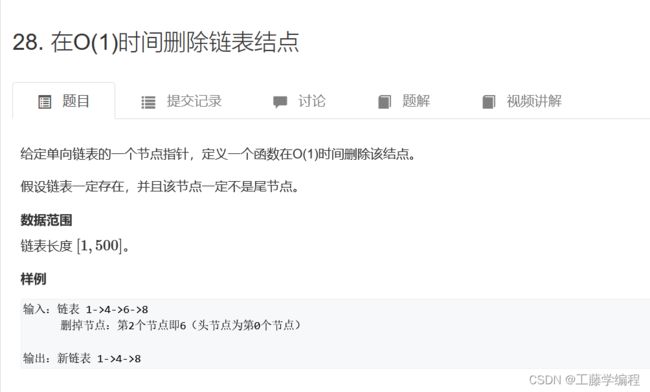
题目1.在O(1)时间删除链表节点
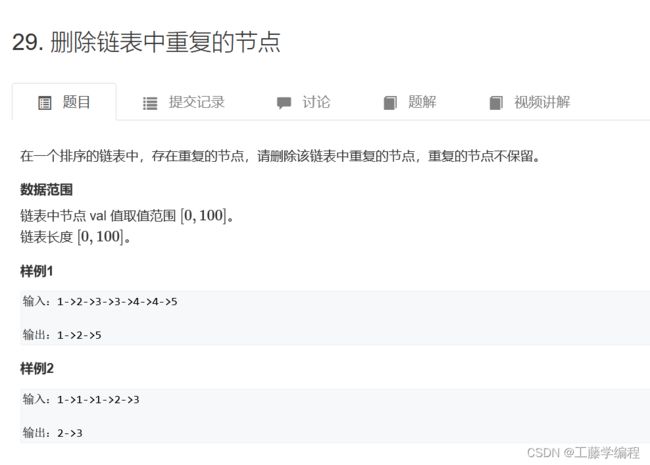
题目2.删除链表中重复的节点
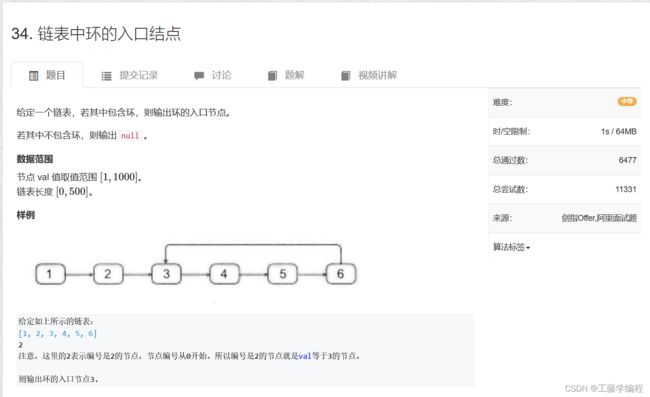
题目3.链表中环的入口节点
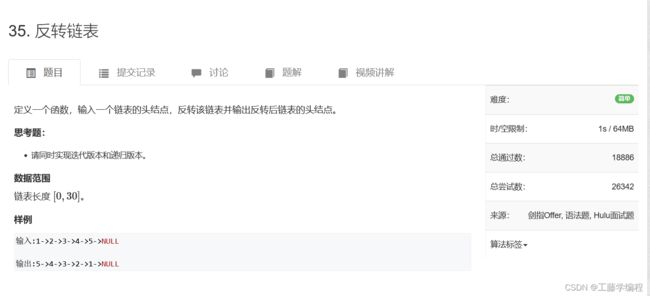
题目4.反转链表
题目5.两个链表的第一个公共结点
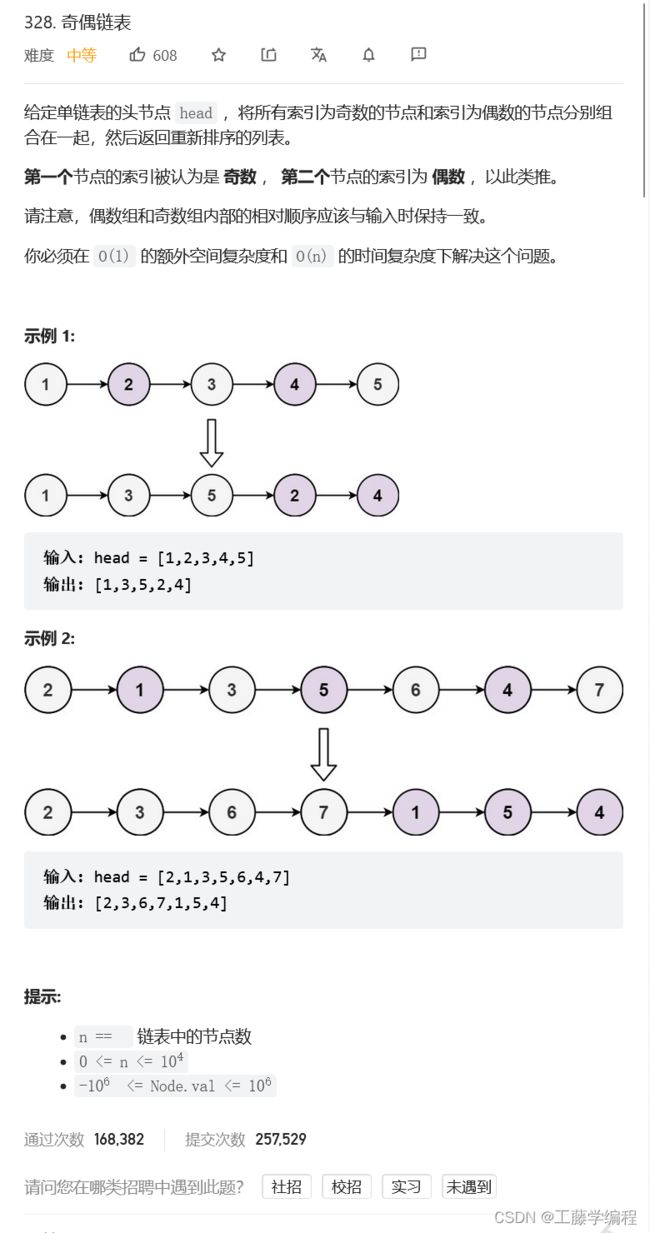
题目6.奇偶链表
题目7.链表随机节点
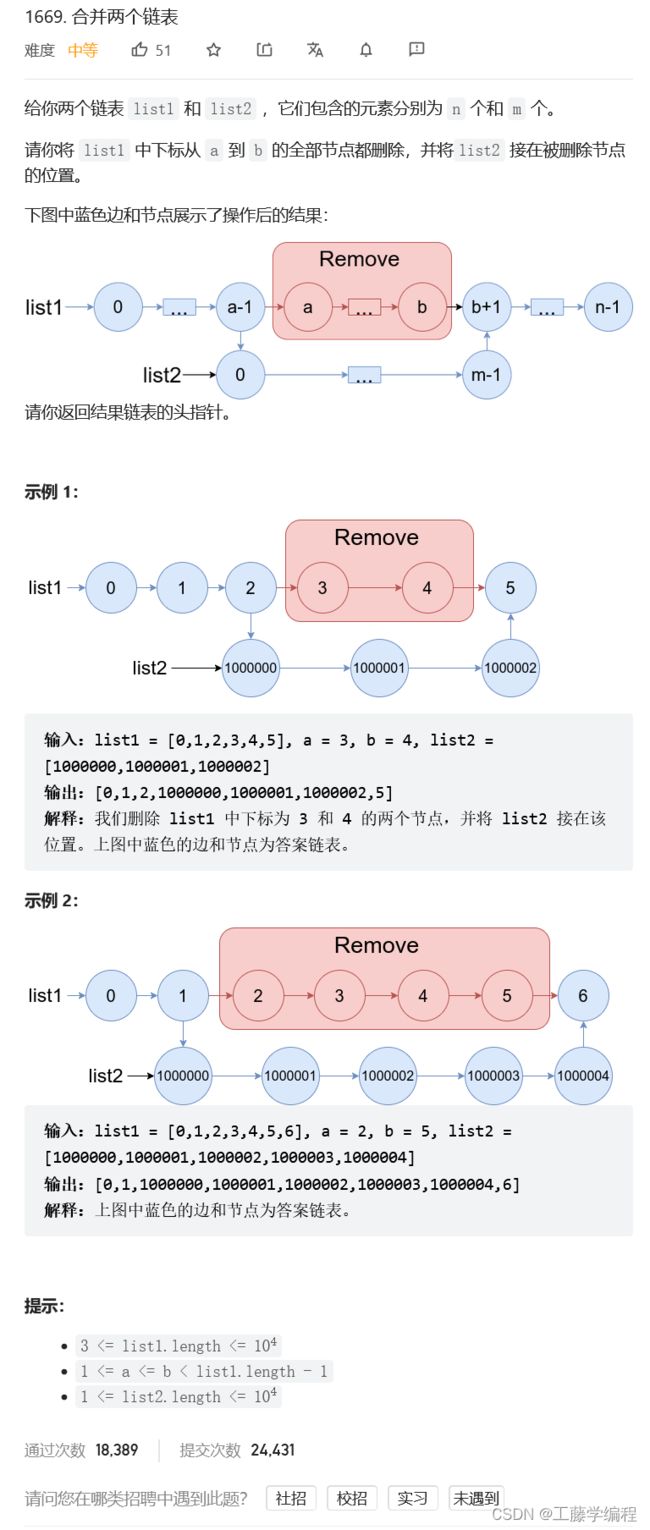
题目8.合并两个链表
题目9.删除链表的倒数第N个元素
题目10.从链表中删去总和值为0的连续节点
由于是单链表,我们不能找到前驱节点,所以我们不能按常规方法将该节点删除。
但是我们可以换一种思路,将下一个节点的值复制到当前节点,然后将下一个节点删除即可(因为题目保证了删除的节点一定不是尾节点)。
参考代码(c++):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next;
}
};
题目2.删除链表中重复的节点
通常可能会删除首元节点的情况,我们都会通过定义一个虚拟头节点 指向链表首元节点。
对于此题,定义好头节点之后,从前往后扫描整个链表,每次扫描元素相同的一段,如果这段中的元素个数多于1个,则将整段元素直接删除即可。
拓展:头指针和头节点的区别
头指针:
(1)头指针是指链表指向第一个结点的指针,若链表有头结点,则是指向头结点的指针
(2)无论链表是否为空,头指针均不为空。头指针是链表的必要元素
头结点:
(1)头结点是为了操作的统一和方便而设立的,放在第一个元素的结点之前,其数据域一般无意义(也可存放链表的长度)
(2)有了头结点,对第一元素结点前插入结点和删除第一结点,其操作与其他结点的操作就统一了
(3)头结点不一定是链表必须要素
参考代码(c++):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto p = dummy;
while (p->next) {
auto q = p->next;
while (q && p->next->val == q->val) q = q->next;
if (p->next->next == q) p = p->next;
else p->next = q;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
题目3.链表中环的入口节点
参考代码(c++)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
if(head==NULL || head->next==NULL) return NULL;
auto first = head,second = head;
while(first && second){
first = first->next;
second=second->next;
if(second) second=second->next;//巧妙
if(first == second){
first = head;
while(first!=second){
first=first->next;
second=second->next;
}
return first;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
翻转即将所有节点的next指针指向前驱节点。
由于是单链表,我们在迭代时不能直接找到前驱节点,所以我们需要一个额外的指针保存前驱节点。同时在改变当前节点的next指针前,不要忘记保存它的后继节点。
参考代码(c++循环版):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
auto per = head,cur = per->next;
while(cur){
auto temp=cur->next;
cur->next=per;
per=cur;
cur=temp;
}
head->next=nullptr;
return per;
}
};
递归版(来自y总):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *tail = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return tail;
}
};
作者:yxc
链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/743/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
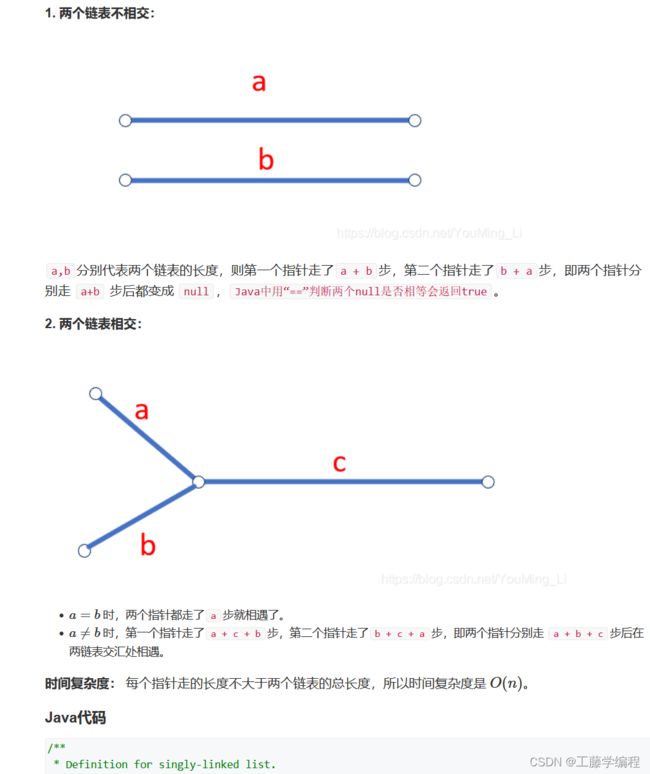
题目5.两个链表的第一个公共结点
参考代码(c++):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto p=headA,q=headB;
while(p!=q)
{
if(p) p=p->next;
else p=headB;
if(q) q=q->next;
else q=headA;
}
return p;
}
};
如果链表为空,则直接返回链表。
对于原始链表,每个节点都是奇数节点或偶数节点。头节点是奇数节点,头节点的后一个节点是偶数节点,相邻节点的奇偶性不同。因此可以将奇数节点和偶数节点分离成奇数链表和偶数链表,然后将偶数链表连接在奇数链表之后,合并后的链表即为结果链表
注意需要有一个链表代替偶数节点去遍历,不然遍历之后你就失去他了
参考代码(c++)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
auto enve = head,unodd1=head->next;
auto unodd=unodd1;
while(enve && enve->next && unodd->next)
{
enve->next=unodd->next;
enve=enve->next;
unodd->next=enve->next;
unodd=unodd->next;
}
enve->next=unodd1;
return head;
}
};
题目7.链表随机节点
方法1:用一个数组记录链表中的所有元素,这样随机选择链表的一个节点,就变成在数组中随机选择一个元素
方法2:蓄水池抽样算法
由于真的不好理解,视频推荐:蓄水池抽样算法
参考代码:
方法1:
class Solution {
vector<int> arr;
public:
Solution(ListNode *head) {
while (head) {
arr.emplace_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
}
int getRandom() {
return arr[rand() % arr.size()];
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-random-node/solution/lian-biao-sui-ji-jie-dian-by-leetcode-so-x6it/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
方法2:
class Solution {
ListNode *head;
public:
Solution(ListNode *head) {
this->head = head;
}
int getRandom() {
int i = 1, ans = 0;
for (auto node = head; node; node = node->next) {
if (rand() % i == 0) { // 1/i 的概率选中(替换为答案)
ans = node->val;
}
++i;
}
return ans;
}
};
不要想着直接返回left,而因返回list1,因为left只是list1的一部分
参考代码(c++):
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeInBetween(ListNode* list1, int a, int b, ListNode* list2) {
auto left=new ListNode(),right=new ListNode(),tail=new ListNode();
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
auto q=dummy;
int i=0;
for(auto p=list1;p;p=p->next)
{
i++;
if(i==a) left=p;
}
i=0;
for(auto p=list1;p;p=p->next)
{
i++;
if(i==b+2) right=p;
}
for(tail=list2;tail->next;tail=tail->next)
{
}
left->next=list2;
tail->next=right;
return list1;
}
};
一边扫描的方法:先让一个指针走n步,然后再用另一个指针,直到第一个指针走到空节点,这时即可走到倒数第N个节点上,为了方变,我们在第二指针上定义一个头节点,这样我们更容易删除倒数第n个节点
参考代码(c++)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto first = head;
auto second = dummy;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
first=first->next;
}
while(first)
{
first=first->next;
second=second->next;
}
second->next=second->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};
题目10.从链表中删去总和值为0的连续节点

参考大佬解法:
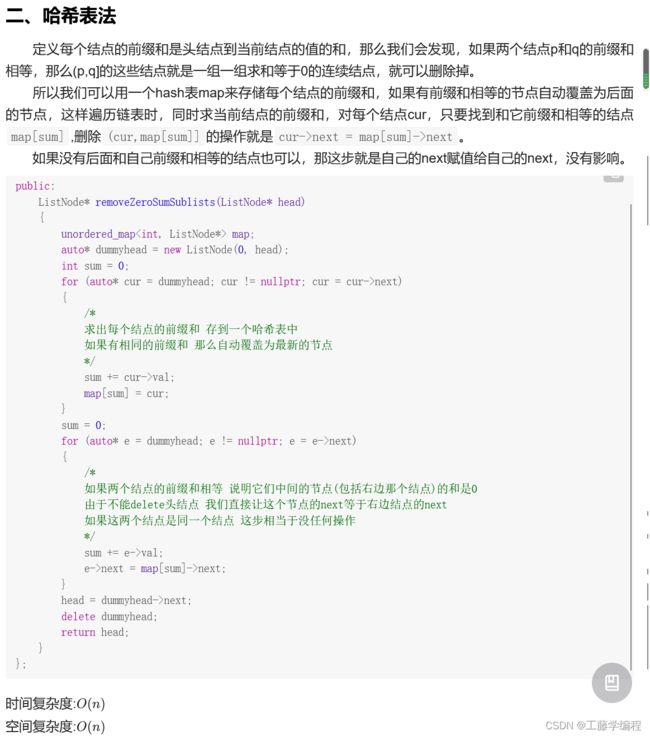
大佬代码:
unordered_map<int, ListNode*> map;
auto* dummyhead = new ListNode(0, head);
int sum = 0;
for (auto* cur = dummyhead; cur != nullptr; cur = cur->next)
{
/*
求出每个结点的前缀和 存到一个哈希表中
如果有相同的前缀和 那么自动覆盖为最新的节点
*/
sum += cur->val;
map[sum] = cur;
}
sum = 0;
for (auto* e = dummyhead; e != nullptr; e = e->next)
{
/*
如果两个结点的前缀和相等 说明它们中间的节点(包括右边那个结点)的和是0
由于不能delete头结点 我们直接让这个节点的next等于右边结点的next
如果这两个结点是同一个结点 这步相当于没任何操作
*/
sum += e->val;
e->next = map[sum]->next;
}
head = dummyhead->next;
delete dummyhead;
return head;
作者:Sleeping-Router
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-zero-sum-consecutive-nodes-from-linked-list/solution/bao-li-jie-fa-he-ha-xi-biao-jie-fa-by-mo-bqb3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。