【BeautifulSoup上】——05全栈开发——如桃花来
目录索引
- ==介绍:==
-
解析库:
-
安装:-
- pip install BeautifulSoup4
- pip install lxml
- ==标签选择器:==
-
1.string属性:.name属性:获取标签中的属性值:
- ==实用——标准选择器:==
-
get_text()方法:使用find_all()根据标签名查找:使用find_all()根据属性查找:text()根据文本值进行选择:find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs):
介绍:
大家都说人生苦短,我用python。而在这里我要说人生苦短,用BeautifulSoup。还在为正则表达式而烦恼么?不用担心,我们用高科技。利用BeautifulSoup就足够解决我们百分之90的问题了。
- 是一个高效的网页解析库,可以从HTML或XML(一种存储数据的文档)文件中提取数据
- 支持不同的解析器,比如,对HTML解析,对XML解析,对HTML5解析
- 就是一个非常强大的工具,爬虫利器
- 一个灵感又方便的网页解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析器
- 利用它就不用编写正则表达式也能方便的实现网页信息的抓取
心动了么?那就让我们来详细看看吧。
解析库:
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”) | Python的内置标准库、执行速度适中 、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 or 3.2.2)前的版本中文容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “lxml”) | 速度快、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”) | 速度快、唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html5lib”) | 最好的容错性、以浏览器的方式解析文档、生成HTML5格式的文档 | 速度慢、不依赖外部扩展 |
这里我们推荐使用的是lxml解析器,为什么?因为它牛蛙牛蛙!又快容错率又高。
安装:
BeautifulSoup和lxml都是第三方库,所以需要自行下载。
pip install BeautifulSoup4
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库
pip install lxml
lxml 是一种使用 Python 编写的解析库,可以迅速、灵活地处理 XML 和 HTML
pip install lxml -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
标签选择器:
通过标签来进行选择。
1.string属性:
不可跨级别,在当前标签下获取文本内容
#举个例子:
h = """
The Dormouse's story
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
#上面就是个注释,模拟html中返回的数据,不需要纠结。
#1. 导包
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#2. 实例化对象,参数1:要解析的内容,参数2:解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(h,"lxml")
#3. 通过标签名选取,会返回包含标签本身及其里面的所有内容
print(soup.head)#返回包含head标签在内的所有内容。
print(soup.p)#返回匹配的第一个结果
print(soup.title.string)#.string是属性,作用是获取字符串文本
当然我们也可以把这串代码放入文件中,通过打开文件的方式来获取数据,效果是一样的:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
with open("try.html","r") as f:#try文件中包含了这些数据
h = f.read()
#上面就是个注释,模拟html中返回的数据,不需要纠结。
#1. 导包
#2. 实例化对象,参数1:要解析的内容,参数2:解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(h,"lxml")
#3. 通过标签名选取,会返回包含标签本身及其里面的所有内容
print(soup.head)#返回包含head标签在内的所有内容。
print(soup.p)#返回匹配的第一个结果
print(soup.title.string)
- 这里BeautifulSoup的导包记得是从bs4里面导入的,而不是直接导入。
.name属性:
获取标签本身的名称
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
The Dormouse's story
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
print(soup.title.name)#返回的是标签本身的名字
print(soup.p.name)
获取标签中的属性值:
我们可以通过.attrs[]来获取属性值,但一般来说这个也可以忽略不写。获取到的标签是符合条件的第一个标签。
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
The Dormouse's story
The Dormouse's story
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
...
|
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
print(soup.p.attrs["name"])#获取p标签name属性的属性值
print(soup.a.attrs["href"])#获取a标签href属性的属性值
print(soup.p.attrs["class"])
#推荐写法:更简单
print(soup.p["id"])
print(soup.a["href"])#只返回第一个值
print(soup.p["class"])#因为有两个类名,所以采用列表的形式返回
实用——标准选择器:
语法:
find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs)
根据标签名、属性、内容查找文档。可以把符合条件的内容都查找出来。
get_text()方法:
该方法非常重要:
- 可以跨级别获取文本内容
- 依旧是单个获取
for ul in soup.find_all('ul'):
# print(ul)
print(ul.get_text())
使用find_all()根据标签名查找:
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html='''
Hello
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo-2
- Bar-2
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all("ul"))#查找到所有ul标签包括在内的内容
print("-"*50)
print(soup.find_all("ul")[0])
我们可以发现,find_all是以列表形式返回的数据,且一个查找标签占一项。这里共两个ul标签,一个ul标签占一项。我们可以通过下标取出。
使用find_all()根据属性查找:
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html='''
Hello
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
#特殊属性查找:
#print(soup.find_all(class="element"))#注意:错误案例
print(soup.find_all(class_="element"))#class属于Python关键字,做特殊处理_(加个下划线)
print("-"*50)
#推荐的查找方式!————指定标签和属性
print(soup.find_all("li",{"class":"element","id":"only"}))
print("-"*50)
print(soup.find_all("li",{"class":"element ele2"}))
通过标签名锁定标签,再通过进行属性的锁定和筛选。特别注意:属性值是字符串也要添加引号。
text()根据文本值进行选择:
语法:
text="要查找的文本内容"
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html='''
Hello
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
# 语法格式:text='要查找的文本内容'
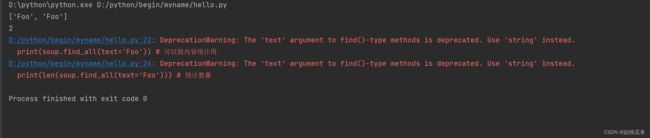
print(soup.find_all(text='Foo')) # 可以做内容统计用
print(len(soup.find_all(text='Foo'))) # 统计数量
text返回的数据是一个列表,一般这种数据用于统计数量。这里的报红不用管,数据是正常获取的
find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs):
find_all是返回所有元素,而find返回的是单个元素
#举个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html='''
Hello
- Foo
- Bar
- Jay
- Foo
- Bar
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find('ul')) # 只返回匹配到的第一个,并把里面的内容全部获取到
# print('---------'*5)
print(soup.find('page')) # 如果标签不存在返回None