【HashMap集合】存储学生对象并遍历
HashMap集合存储学生对象并遍历
1.键是String,值是Student
需求:创建一个HashMap集合,键是学号(String),值是学生对象(Student)。存储三个键值对元素,并遍历
思路:
定义学生类
创建HashMap集合对象
创建学生对象
把学生添加到集合
遍历集合
方式1:键找值
方式2:键值对对象找键和值
学生类:
package com.gather.map.example;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
package com.gather.map.example;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建HashMap集合对象
HashMap<String, Student> hm = new HashMap<String, Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("郝佳乐", 20);
Student s2 = new Student("张三", 18);
Student s3 = new Student("李四", 22);
//把学生添加到集合
hm.put("student001", s1);
hm.put("student002", s2);
hm.put("student003", s3);
//遍历集合
//方式1:键找值
//获取所有键的集合
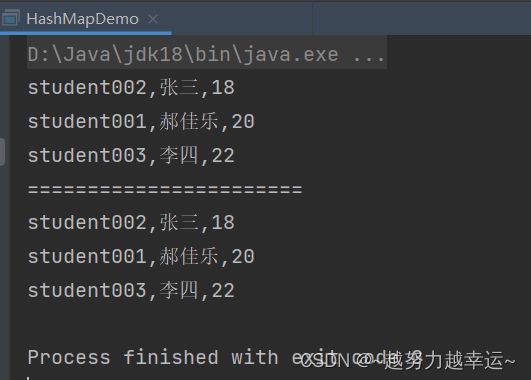
Set<String> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (String key : keySet) {
Student value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "," + value.getName() + "," + value.getAge());
}
System.out.println("=======================");
//方式2:键值对对象找键和值
Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> entrySet = hm.entrySet();
//获取所有的键值对对象
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> me : entrySet) {
String key = me.getKey();
Student value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "," + value.getName() + "," + value.getAge());
}
}
}
2.键是学生对象,值是居住地
需求:创建一个HashMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是居住地(String)。存储多个键值对元素,并遍历
要求保证键的唯一性:如果学生对象的成员变量值相同,我们就认为是同一个对象
思路:
定义学生类
创建HashMap集合对象
创建学生对象
把学生添加到集合
遍历集合
在学生类中重写两个方法
hashCode()
equals()
学生类:
package com.gather.map.example;
public class Student1 {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student1() {
}
public Student1(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student1 student1 = (Student1) o;
if (age != student1.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student1.name) : student1.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0;
result = 31 * result + age;
return result;
}
}
测试类:
package com.gather.map.example;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student1, String> hm = new HashMap<Student1, String>();
Student1 s1 = new Student1("郝佳乐", 20);
Student1 s2 = new Student1("张三", 18);
Student1 s3 = new Student1("李四", 22);
Student1 s4 = new Student1("李四", 22);
hm.put(s1, "西安");
hm.put(s2, "武汉");
hm.put(s3, "郑州");
hm.put(s4, "北京");
//遍历集合
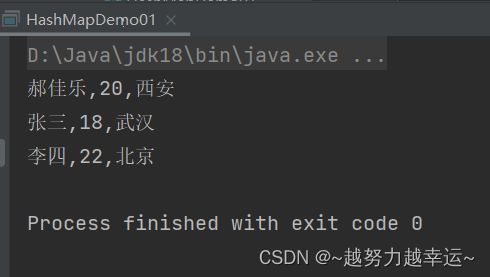
Set<Student1> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (Student1 key : keySet) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key.getName() + "," + key.getAge() + "," + value);
}
}
}
s3和s4的成员变量值相同,将其添加到HashMap集合时,居住地的信息就会进行修改,最终的输出结果时“北京”。