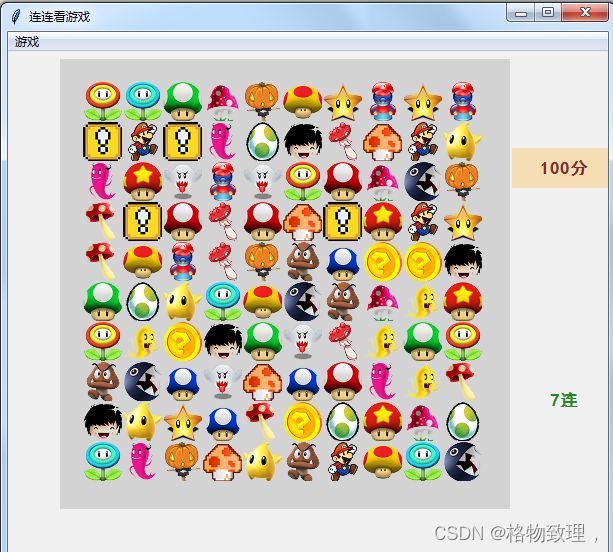
python开发的连连看小游戏
说明:
1.在网上找了一个基础版本改进而来,大概增加了200行代码,相对原版要复杂了一些;
2.界面采用tkinter开发,比较简单;
3.新增了连接连功能;
4.新增了积分功能;
5.新增了陷入死局时,重新打散功能;
6.新增了关卡功能,目前设置了5关;
7.新增了计算当前地图有多少可连通图标功能。
陷入死局时,效果如下:
打散后,重新排列,然后聚在一起:
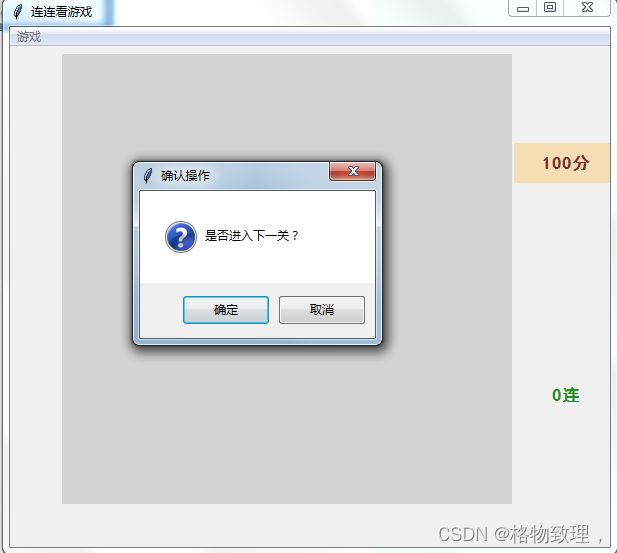
进入下一关界面:
进入第二关效果如下:
后面的关卡与上面类似。
源代码只有一个文件,用到的库比较少、比较小,安装起来很容易。代码如下:
from tkinter import BOTH,FIRST,LAST,GROOVE,FLAT
import os, random
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.messagebox
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import time
from playsound import playsound
class MainWindow():
__gameTitle = "连连看游戏"
__windowWidth = 600
__windowHeigth = 500
__gameSize = 10 # 游戏尺寸
__iconKind = __gameSize * __gameSize / 4 # 小图片种类数量
__iconWidth = 40
__iconHeight = 40
__map = [] # 游戏地图
__delta = 25
__isFirst = True
__isGameStart = False
__formerPoint = None
EMPTY = -1
NONE_LINK = 0
STRAIGHT_LINK = 1
ONE_CORNER_LINK = 2
TWO_CORNER_LINK = 3
__images = []#蒙板阴影图像
__level = 1#游戏关卡
__point_position = {}
__score = 0
def __init__(self):
self.__root = tk.Tk()
self.__root.title(self.__gameTitle)
self.centerWindow(self.__windowWidth, self.__windowHeigth)
self.__root.minsize(460, 460)
self.__addComponets()
self.new_game()
self.__root.mainloop()
#菜单栏中添加一个叫“游戏”的菜单项
def __addComponets(self):
#菜单栏
self.menubar = tk.Menu(self.__root, bg="lightgrey", fg="black")
#子菜单
self.file_menu = tk.Menu(self.menubar, tearoff=0, bg="lightgrey", fg="black")
self.file_menu.add_command(label="新游戏", command=self.new_game, accelerator="Ctrl+N")
self.menubar.add_cascade(label="游戏", menu=self.file_menu)
self.__root.configure(menu=self.menubar)
self.__root.bind('',self.new_game)#实现快捷键功能ctrl+N
#
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self.__root, bg = '#D3D3D3', width = 450, height = 450,cursor="hand2")
self.canvas.grid(row=0,column=0,sticky='N',pady = 5,rowspan=2,padx=(50,0))
self.canvas.bind('', self.clickCanvas)
#分数面板
self.label_score = tkinter.Label(self.__root,width=10,height=2,font=('黑体',13,'bold'),fg="#802A2A",bg="#F5DEB3")
self.label_score.grid(row=0,column=1)
#显示当前可连接数
self.label_linknums = tkinter.Label(self.__root,width=10,height=2,font=('黑体',13,'bold'),fg="#228B22")
self.label_linknums.grid(row=1,column=1)
'''
判断两个接点之间是否能连通
'''
def __isLink(self,fromPoint,point):
return self.isStraightLink(fromPoint,point) or self.isOneCornerLink(fromPoint,point) or self.isTwoCornerLink(fromPoint,point)
'''
获取提示,逻辑有点复杂,主要解决以下问题:
1.获取当前地图上所有的图标;
2.然后遍历,计算有多少对可连通的图标;
3.如果有三个或者四个相同的图标可以相互连通,要进行判断,以勉出现重复计算。
'''
def getPromptPoint(self):
_link_point = []
_icons_arr = self.__map.flatten()#先转化为一维数组,便于操作
for i in set(_icons_arr):
if i == self.EMPTY: continue #忽略为空的坐标
_arr = np.where(_icons_arr==i)[0]#元组的第一个元素,是由i元素的索引组成的数组
if _arr.size == 4:#剩下4个相同图标
_point1 = Point(int(_arr[0]%10),int(_arr[0]/10))# 计算x,y坐标
_point2 = Point(int(_arr[1]%10),int(_arr[1]/10))
_point3 = Point(int(_arr[2]%10),int(_arr[2]/10))
_point4 = Point(int(_arr[3]%10),int(_arr[3]/10))
#4个接点6条线,但最多只能计算2条线,再多就会出现重复计数
if self.__isLink(_point1,_point2):
_link_point.append((_point1,_point2))
if self.__isLink(_point3,_point4):
_link_point.append((_point3,_point4))
elif self.__isLink(_point1,_point3):
_link_point.append((_point1,_point3))
if self.__isLink(_point2,_point4):
_link_point.append((_point2,_point4))
elif self.__isLink(_point1,_point4):
_link_point.append((_point1,_point4))
if self.__isLink(_point2,_point3):
_link_point.append((_point2,_point3))
elif self.__isLink(_point2,_point3):
_link_point.append((_point2,_point3))
elif self.__isLink(_point2,_point4):
_link_point.append((_point2,_point4))
elif self.__isLink(_point3,_point4):
_link_point.append((_point3,_point4))
elif _arr.size == 2:#剩下2个相同图标
_point1 = Point(int(_arr[0]%10),int(_arr[0]/10))# 计算x,y坐标
_point2 = Point(int(_arr[1]%10),int(_arr[1]/10))
if self.__isLink(_point1,_point2):
_link_point.append((_point1,_point2))
self.label_linknums['text'] = f"{len(_link_point)}连"
print("_link_point",_link_point)
return _link_point
def centerWindow(self, width, height):#700 500
screenwidth = self.__root.winfo_screenwidth()#窗口距离屏幕左边的宽
screenheight = self.__root.winfo_screenheight()#窗口距离屏幕顶部的高
size = '%dx%d+%d+%d' % (width, height, (screenwidth - width)/2, (screenheight - height)/2)
self.__root.geometry(size)
def add_score(self):
self.__score += 2 #消除一对图标,分数加2
self.set_label_text()
def set_label_text(self):
self.label_score['text'] = f"{self.__score}分"
'''
这个方法需要注意的积分问题:
1.开始新游戏时,将积分清零;
2.开始下一关时,将前一关的积分累积起来。
'''
def new_game(self, event=None,level=1,score = 0):
self.__score = score
self.set_label_text()
self.__level = level
self.extractSmallIconList()
self.iniMap()
self.drawMap()
self.getPromptPoint()
self.__isGameStart = True
def clickCanvas(self, event):
if not self.__isGameStart:
return
# 确认有效点击坐标
point = self.getInnerPoint(Point(event.x, event.y))
if not point.isUserful() or self.isEmptyInMap(point):
return
#__isFirst在三种情况下为True,1.游戏开始的时候;2.同一个图标点击了两次;3.成功消除一组图标。
if self.__isFirst:
self.drawSelectedArea(point)
self.__isFirst= False
self.__formerPoint = point
else:
if self.__formerPoint.isEqual(point):#两次点击的是同一个图标
self.__isFirst = True
self.canvas.delete("rectRedOne")
self.canvas.delete('image_mask')
else:
linkType = self.getLinkType(self.__formerPoint, point)
if linkType['type'] != self.NONE_LINK:
#画连接线
self.draw_link_line(self.__formerPoint,point,linkType)
playsound("music2.mp3")
time.sleep(.5)# 显示画线的延迟
self.ClearLinkedBlocks(self.__formerPoint, point)
self.canvas.delete("rectRedOne")
self.canvas.delete("linkline")
self.canvas.delete('image_mask')
#增加分数
self.add_score()
_link_point = self.getPromptPoint()
self.__isFirst = True
if len(_link_point) == 0:
if self.isGameEnd():
if tk.messagebox.askokcancel('确认操作', '是否进入下一关?'):
self.__level = self.__level+1
self.new_game(level = self.__level,score = self.__score)
else:
self.__isGameStart = False
else: #没有可连通图标,且当前地图上还有图标存在,游戏未结束时,打散当前地图
tk.messagebox.showinfo("提示", "已没有可连通图标,需重新打散!")
self.shuffleMap()
self.drawMap()
self.getPromptPoint()
else:
self.__formerPoint = point
self.canvas.delete("rectRedOne")
self.drawSelectedArea(point)
# 判断游戏是否结束
def isGameEnd(self):
for y in range(0, self.__gameSize):
for x in range(0, self.__gameSize):
if self.__map[y][x] != self.EMPTY:
return False
return True
'''
消除图像前,把两个图像之间的连接线画出来。
'''
def draw_link_line(self,formerPoint,point,linkType):
if linkType['type'] == self.STRAIGHT_LINK:
p1 = self.getOuterCenterPoint(formerPoint)
p2 = self.getOuterCenterPoint(point)
#arrow表示线的箭头样式,默认不带箭头,参数值 FIRST表示添加箭头带线段开始位置,LAST表示到末尾占位置,BOTH表示两端均添加
self.canvas.create_line((p1.x, p1.y),(p2.x, p2.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3, arrow=LAST)
if linkType['type'] == self.ONE_CORNER_LINK:
corner1 = self.getOuterCenterPoint(linkType["p1"])
p1 = self.getOuterFitCenterPoint(formerPoint,corner1)
p2 = self.getOuterFitCenterPoint(point,corner1)
self.canvas.create_line((p1.x, p1.y),(corner1.x, corner1.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3)
self.canvas.create_line((p2.x, p2.y),(corner1.x, corner1.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3, arrow=FIRST)
elif linkType['type'] == self.TWO_CORNER_LINK:
corner1 = self.getOuterCenterPoint(linkType["p1"])
corner2 = self.getOuterCenterPoint(linkType["p2"])
p1 = self.getOuterFitCenterPoint(formerPoint,corner1)
p2 = self.getOuterFitCenterPoint(point,corner2)
self.canvas.create_line((p1.x, p1.y),(corner1.x, corner1.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3)
self.canvas.create_line((p2.x, p2.y),(corner2.x, corner2.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3, arrow=FIRST)
self.canvas.create_line((corner1.x, corner1.y),(corner2.x, corner2.y),fill = 'red',tags = 'linkline',width=3)
self.canvas.update()
'''
提取小头像数组
'''
def extractSmallIconList(self):
self.__icons = []
imageSouce = Image.open(f"图片/new{self.__level}.png")
for index in range(0, int(self.__iconKind)):#0-24
region = imageSouce.crop((self.__iconWidth * index, 0,
self.__iconWidth * index + self.__iconWidth - 1, self.__iconHeight - 1))
self.__icons.append(ImageTk.PhotoImage(region))
'''
初始化地图 存值为0-24
'''
def iniMap(self):
self.__map = [] # 重置地图
_tmpRecords = []
# 0-24,一共25个图标,每个图标出现4次,总共出现100次
_total = self.__gameSize * self.__gameSize
_tmpRecords = np.linspace(0, self.__iconKind, _total, endpoint = False,dtype=int)
np.random.shuffle(_tmpRecords)#重新打散洗牌
self.__map = _tmpRecords.reshape((10,10))#将一维数组100,转化为二维10*10
'''
初始化地图 存值为0-24,当前地图中,如果没有可连通路线、进入死局时,将现有的图标进行打散重新洗牌。
'''
def shuffleMap(self):
_icons_arr = self.__map.flatten()#先转化为一维数组,便于操作
self.__map = []#重置地图
for i in set(_icons_arr):
if i == self.EMPTY: continue
_tuple = np.where(_icons_arr==i)[0]#元组的第一个元素,是由i元素的索引组成的数组
self.__map.extend([i]* _tuple.size)#第i个图标出现的次数
np.random.shuffle(self.__map)#洗牌
_len = len(self.__map)
_total = self.__gameSize * self.__gameSize
self.__map[_len:_total] = [self.EMPTY]*(_total-_len)#剩余元素置为空(-1),填满至整个地图0-99
self.__map = np.array(self.__map).reshape((self.__gameSize,self.__gameSize))#转化为二维数组10*10
'''
根据地图绘制图像
1.在使用create_image()函数时,需要先通过Pillow库(或其他图片处理库)读取图片文件并生成图片对象,然后再将这个图片对象传递给create_image()函数,在指定的坐标位置将图片添加到画布上。
2.canvas.create_image(x, y, image=图像对象, anchor=定位点),x和y表示图像锚点在画布上的位置,即图像在画布上的左上角坐标。image参数是一个tkinter中的PhotoImage()对象,它可以指定要加载的图像文件。anchor参数是一个字符串,用于指定图像锚点的位置,可以是"nw"(左上角)、"n"(上)、"ne"(右上角)、"w"(左)、"center"(中心)、"e"(右)、"sw"(左下角)或"s"(下)。如果不指定anchor参数,则默认为“center”。
'''
def drawMap(self):
self.canvas.delete("all")#字符串"all""是代表画布上所有项目的特殊标记
for y in range(0, self.__gameSize):
for x in range(0, self.__gameSize):
point = self.getOuterLeftTopPoint(Point(x, y))
if self.__map[y][x] != self.EMPTY:#打散重绘时,不再置空的图标
self.canvas.create_image((point.x, point.y),image=self.__icons[self.__map[y][x]], anchor='nw', tags = 'im%d%d' % (x, y))
'''
根据两点不同的位置,获取对应边的中心连接点。例如目标图标在左边,就取靠左的一边的中点。如果连接目标在右边,就取靠右一边的中点坐标。
'''
def getOuterFitCenterPoint(self, formerPoint, corner):
_formerPoint = self.getOuterCenterPoint(formerPoint)
if _formerPoint.y>corner.y:
fitCenterPoint = Point(self.getX(formerPoint.x) + int(self.__iconWidth / 2),self.getY(formerPoint.y))#顶边
elif _formerPoint.y corner.x:
fitCenterPoint = Point(self.getX(formerPoint.x),self.getY(formerPoint.y)+int(self.__iconHeight / 2))#左边
elif _formerPoint.x < corner.x:
fitCenterPoint = Point(self.getX(formerPoint.x) + int(self.__iconWidth),self.getY(formerPoint.y)+int(self.__iconHeight / 2))#右边
return fitCenterPoint
'''
获取内部坐标对应矩形左上角顶点坐标
'''
def getOuterLeftTopPoint(self, point):
return Point(self.getX(point.x), self.getY(point.y))
'''
获取内部坐标对应矩形中心坐标
'''
def getOuterCenterPoint(self, point):
return Point(self.getX(point.x) + int(self.__iconWidth / 2),
self.getY(point.y) + int(self.__iconHeight / 2))
def getX(self, x):# x * 40 + 25
return x * self.__iconWidth + self.__delta
def getY(self, y):
return y * self.__iconHeight + self.__delta
'''
获取内部坐标
'''
def getInnerPoint(self, point):
x = -1
y = -1
for i in range(0, self.__gameSize):
x1 = self.getX(i)
x2 = self.getX(i + 1)
if point.x >= x1 and point.x < x2:
x = i
for j in range(0, self.__gameSize):
j1 = self.getY(j)
j2 = self.getY(j + 1)
if point.y >= j1 and point.y < j2:
y = j
return Point(x, y)
'''
创建一块蒙板,覆盖到选中的图形上
'''
def create_mask(self,x1, y1, x2, y2, **kwargs):
#(0,0,0)代表黑色的RGB,127代表alpha透明度,(x2-x1, y2-y1)指长宽
image = Image.new('RGBA', (x2-x1, y2-y1), (0,0,0,127))
self.__images = [ImageTk.PhotoImage(image)]#这里一定要用一个实例变量存储,局部变量没有效果,原因不清楚
self.canvas.create_image(x1, y1, image=self.__images[0], anchor='nw',tags = "image_mask")
'''
选择的区域变红,point为内部坐标
'''
def drawSelectedArea(self, point):
pointLT = self.getOuterLeftTopPoint(point)
pointRB = self.getOuterLeftTopPoint(Point(point.x + 1, point.y + 1))
self.canvas.create_rectangle(pointLT.x, pointLT.y, pointRB.x - 1, pointRB.y - 1, outline = 'red', tags = "rectRedOne", width=2)
#蒙板
self.create_mask(pointLT.x, pointLT.y, pointRB.x - 1, pointRB.y - 1, fill='skyblue', alpha=.5,width=0)
'''
消除连通的两个块
'''
def ClearLinkedBlocks(self, p1, p2):
self.__map[p1.y][p1.x] = self.EMPTY
self.__map[p2.y][p2.x] = self.EMPTY
self.canvas.delete('im%d%d' % (p1.x, p1.y))
self.canvas.delete('im%d%d' % (p2.x, p2.y))
'''
地图上该点是否为空
'''
def isEmptyInMap(self, point):
if self.__map[point.y][point.x] == self.EMPTY:
return True
else:
return False
'''
获取两个点连通类型
'''
def getLinkType(self, p1, p2):
# 首先判断两个方块中图片是否相同
if self.__map[p1.y][p1.x] != self.__map[p2.y][p2.x]:
return { 'type': self.NONE_LINK }
if self.isStraightLink(p1, p2):
return {
'type': self.STRAIGHT_LINK
}
res = self.isOneCornerLink(p1, p2)
if res:
return {
'type': self.ONE_CORNER_LINK,
'p1': res
}
res = self.isTwoCornerLink(p1, p2)
if res:
return {
'type': self.TWO_CORNER_LINK,
'p1': res['p1'],
'p2': res['p2']
}
return {
'type': self.NONE_LINK
}
'''
直连
'''
def isStraightLink(self, p1, p2):
start = -1
end = -1
# 水平
if p1.y == p2.y:
# 大小判断
if p2.x < p1.x:
start = p2.x
end = p1.x
else:
start = p1.x
end = p2.x
for x in range(start + 1, end):
if self.__map[p1.y][x] != self.EMPTY:
return False
return True
elif p1.x == p2.x:
if p1.y > p2.y:
start = p2.y
end = p1.y
else:
start = p1.y
end = p2.y
for y in range(start + 1, end):
if self.__map[y][p1.x] != self.EMPTY:
return False
return True
return False
def isOneCornerLink(self, p1, p2):
pointCorner = Point(p1.x, p2.y)
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner, p2) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner):
return pointCorner
pointCorner = Point(p2.x, p1.y)
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner, p2) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner):
return pointCorner
def isTwoCornerLink(self, p1, p2):
for y in range(-1, self.__gameSize + 1):
pointCorner1 = Point(p1.x, y)
pointCorner2 = Point(p2.x, y)
if y == p1.y or y == p2.y:
continue
if y == -1 or y == self.__gameSize:
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner1) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner2, p2):
return {'p1': pointCorner1, 'p2': pointCorner2}
else:
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner1) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner1, pointCorner2) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner2, p2) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner1) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner2):
return {'p1': pointCorner1, 'p2': pointCorner2}
# 横向判断
for x in range(-1, self.__gameSize + 1):
pointCorner1 = Point(x, p1.y)
pointCorner2 = Point(x, p2.y)
if x == p1.x or x == p2.x:
continue
if x == -1 or x == self.__gameSize:
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner1) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner2, p2):
return {'p1': pointCorner1, 'p2': pointCorner2}
else:
if self.isStraightLink(p1, pointCorner1) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner1, pointCorner2) and self.isStraightLink(pointCorner2, p2) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner1) and self.isEmptyInMap(pointCorner2):
return {'p1': pointCorner1, 'p2': pointCorner2}
class Point():
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def isUserful(self):
if self.x >= 0 and self.y >= 0:
return True
else:
return False
'''
判断两个点是否相同
'''
def isEqual(self, point):
if self.x == point.x and self.y == point.y:
return True
else:
return False
'''
克隆一份对象
'''
def clone(self):
return Point(self.x, self.y)
'''
改为另一个对象
'''
def changeTo(self, point):
self.x = point.x
self.y = point.y
'''
显示坐标
'''
def __repr__(self):
return f"x={self.x},y={self.y}"
MainWindow()
再提一点,就是游戏地图的制作,原理就是找25张图片,把它们压缩成40*40像素的图标,然后横排合成一张图。在网上找了很久,也没发现靠谱的软件,其实用python程序就能实现这个功能。
代码来源:
使用Python批量拼接图片_python多图合并成一张图_谢欣桁的博客-CSDN博客
稍微改了下:
import os
import math
from PIL import Image
def merge_images(image_folder, output_file, n, m):
# 获取所有图像文件的列表
image_files = [os.path.join(image_folder, f) for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith('.png')]
# 计算每个小图像的大小和大图像的大小
image_count = len(image_files)
if image_count == 0:
print('No image files found in the directory:', image_folder)
return
# 计算小图像的大小以及大图像的大小
img = Image.open(image_files[0])
# img_size0 = img.size[0]
# img_size1 = img.size[1]
img_size0 = 40
img_size1 = 40
new_img_size0 = img_size0 * n
new_img_size1 = img_size1 * m
# 创建一个新的大图像
new_img = Image.new('RGB', (new_img_size0, new_img_size1), 'white')
# 将所有小图像粘贴到新图像的正确位置
for i, f in enumerate(image_files):
row = int(i / n)
col = i % n
img = Image.open(f)
img = img.resize((img_size0, img_size1))
new_img.paste(img, (col * img_size0, row * img_size1))
# 保存大图像
new_img.save(output_file)
# 用法示例
image_folder = 'C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/图标/卡通' #目录下放25张png图片
output_file = 'C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/图标/卡通/new5.png'#运行程序合成一张图
n = 25 # 每行显示的图像数
m = 1 # 每列显示的图像数
merge_images(image_folder, output_file, n, m)改进版尽管功能更加强大,但有点复杂,如果初学,可以先看基础版。
增强版代码包(含图片、音效文件):
https://download.csdn.net/download/qiuqiuit/87895753
基础版代码包(包含图片):
https://download.csdn.net/download/qiuqiuit/87895720