STL——stack容器、queue容器、list容器
初识STL
- **stack容器**
-
- **stack容器——基本概念**
- **stack容器——常用接口**
- **queue容器**
-
- **queue容器——基本概念**
- **queue容器——常用接口**
- **list容器**
-
- **list容器基本概念**
- **list容器——构造函数**
- **list容器——赋值和交换**
- **List容器——大小操作**
- **list容器——插入和删除**
- **list容器——数据存取**
- **list容器——反转和排序**
- **list容器——排序案例**
stack容器
stack容器——基本概念
stack容器——常用接口
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include queue容器
queue容器——基本概念
是先进先出的数据结构

**队列容器允许从一端新增元素,从另一端移除元素
队列中只有队头和队尾才可以被外界使用,因此队列不允许有遍历行为
队列中进数据称为—入队push
队列中出数据称为—出队pop
**

queue容器——常用接口
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include list容器
list容器基本概念
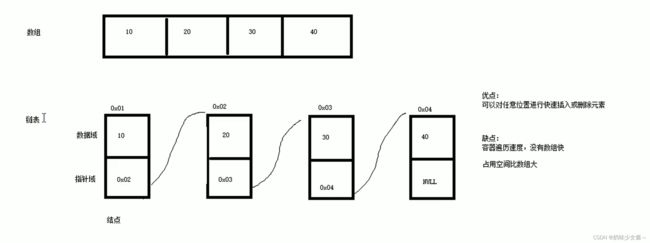
在STL中这个链表是双向链表
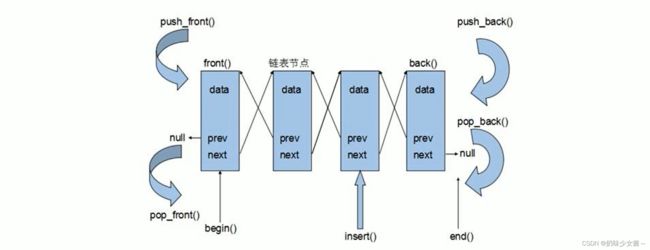
由于链表的存储方式并不是连续的内存空间,因此链表list中的迭代器只支持前移和后移,属于双向迭代器
list的优点∶
采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
list的缺点:
链表灵活,但是空间(指针域)和时间(遍历)额外耗费较大
List有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有list迭代器的失效,这在vector是不成立的。
list和vector是经常被使用的容器
list容器——构造函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&d)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
//加上const防止修改代码
//容器中的数据不可以修改了
//*it = 100; err
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//创建list容器
list<int>L1;//默认构造
//添加数据
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//遍历容器
printList(L1);
//区间方式构造
list<int>L2(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
//拷贝构造
list<int>L3(10, 1000);
printList(L3);
//n个elem
list<int>L4(L3);
printList(L4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
list容器——赋值和交换
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&d)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
list<int>L2;
L2 = L1;
printList(L2);
list<int>L3;
L3.assign(L2.begin(), L2.end());
printList(L3);
list<int>L4;
L4.assign(10, 100);
printList(L4);
}
//交换
void test02()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
list<int>L2;
L2.assign(10, 100);
cout << "交换前: " << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
L1.swap(L2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
}
int main()
{
//test01();
test02();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
List容器——大小操作
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&d)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
//判断容器是否为空
if (L1.empty())
{
cout << "L1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "L1不为空" << endl;
cout << "L1的元素个数为:" << L1.size() << endl;
}
//重新指定大小
L1.resize(10,10000);
printList(L1);
L1.resize(2);
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
list容器——插入和删除
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&d)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L;
//尾插
L.push_back(10);
L.push_back(20);
L.push_back(30);
//头插
L.push_front(100);
L.push_front(200);
L.push_front(300);
printList(L);
//尾删
L.pop_back();
printList(L);
//头删
L.pop_front();
printList(L);
//insert插入
list<int>::iterator it = L.begin();
L.insert(++it, 1000);
printList(L);
//list容器是双向迭代器 不能跳跃移动
//L.insert(L.begin() + 1, 100000);//err
//printList(L);
//删除
it = L.begin();
L.erase(++it);
printList(L);
//移除
L.push_back(10000);
L.push_back(10000);
L.push_back(10000);
L.push_back(10000);
printList(L);
L.remove(10000);//按值删除 删除所有的10000
printList(L);
//清空
L.clear();
printList(L);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
list容器——数据存取
list容器底层是链表 存储的不是连续的空间 不支持随机访问 不能用[]或者at直接进行访问
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
using namespace std;
//list容器赋值和交换
void printList(const list<int>&d)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//L1[0]不可以用 []访问list容器中的元素
//L1[0];err
//L1.at(0);err
//原因是list本质是链表,不是用连续的线性空间存储的,迭代器也是不支持随机访问的
cout << "第一个元素为: " << L1.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素为:" << L1.back() << endl;
//验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的
list<int>::iterator it = L1.begin();
it++;//right 支持双向++ --
it--;//right
//it = it + 1;//err
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
list容器——反转和排序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include list容器——排序案例
案例描述:将Person自定义数据类型进行排序,Person中属性有姓名、年龄、身高排序
规则:按照年龄进行升序,如果年龄相同按照身高进行降序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include 















