Spring Boot 属性加载原理解析
基于Spring Boot 3.1.0 系列文章
- Spring Boot 源码阅读初始化环境搭建
- Spring Boot 框架整体启动流程详解
- Spring Boot 系统初始化器详解
- Spring Boot 监听器详解
- Spring Boot banner详解
- Spring Boot 属性配置解析
- Spring Boot 属性加载原理解析
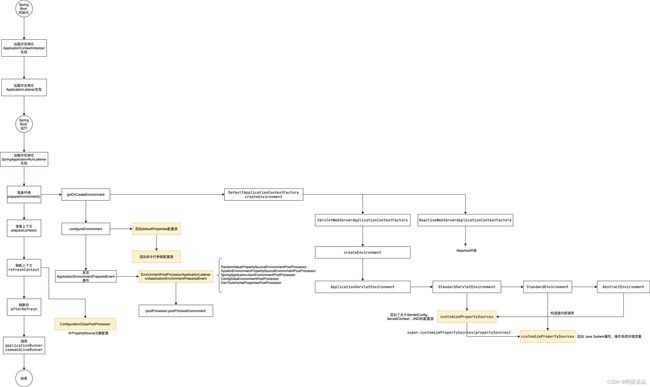
在《Spring Boot 框架整体启动流程详解》中,我们了解到有一步是准备环境prepareEnvironment,属性加载就是在这一步开始的。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//创建并配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境,如果需要转换服务,添加ApplicationConversionService,另外委托给了configurePropertySources(属性源)和configureProfiles(配置文件),子类可以覆盖该方法或分别覆盖两者进行细粒度控制
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//将ConfigurationPropertySource支持附加到指定的环境
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
//调用environmentPrepared方法
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
//将defaultProperties属性源移动到指定配置环境的最后
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
//绑定环境到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//非自定义环境配置,就将其转换为标准类型
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
//重新将ConfigurationPropertySource支持附加到指定的环境
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
进入getOrCreateEnvironment()
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
//判断environment 是否为null,不为null使用environment
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
//根据web应用程序类型,通过applicationContextFactory创建environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.applicationContextFactory.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
//如果environment为null,并且applicationContextFactory不是用的默认ApplicationContextFactory
if (environment == null && this.applicationContextFactory != ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT) {
//使用默认的ApplicationContextFactory创建environment
environment = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
}
//如果不为null返回environment,否则只显示创建一个ApplicationEnvironment
return (environment != null) ? environment : new ApplicationEnvironment();
}
this.applicationContextFactory 由于没有显示设置,使用的是默认的ApplicationContextFactory
private ApplicationContextFactory applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = new DefaultApplicationContextFactory();
进入createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType)中:
public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::createEnvironment, null);
}
进入getFromSpringFactories中:
private <T> T getFromSpringFactories(WebApplicationType webApplicationType,
BiFunction<ApplicationContextFactory, WebApplicationType, T> action, Supplier<T> defaultResult) {
//循环获取ApplicationContextFactory类型的实例
for (ApplicationContextFactory candidate : SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(ApplicationContextFactory.class,
getClass().getClassLoader())) {
//调用实例的createEnvironment方法
T result = action.apply(candidate, webApplicationType);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return (defaultResult != null) ? defaultResult.get() : null;
}
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(ApplicationContextFactory.class, getClass().getClassLoader()) 从META-INF/spring.factories中获取并实例化ApplicationContextFactory实例,Spring Boot定义了ReactiveWebServerApplicationContextFactory 和 ServletWebServerApplicationContextFactory,所以在这里会分别去调用其中的createEnvironment方法,由于这边是web环境,进入ServletWebServerApplicationContextFactory的createEnvironment中。
public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
//不是Web Servlet环境的话返回null,是的话创建一个ApplicationServletEnvironment
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null : new ApplicationServletEnvironment();
}
进入ApplicationServletEnvironment类中,其继承了StandardServletEnvironment,StandardServletEnvironment类继承了StandardEnvironment并实现了ConfigurableWebEnvironment接口,StandardEnvironment继承了AbstractEnvironment
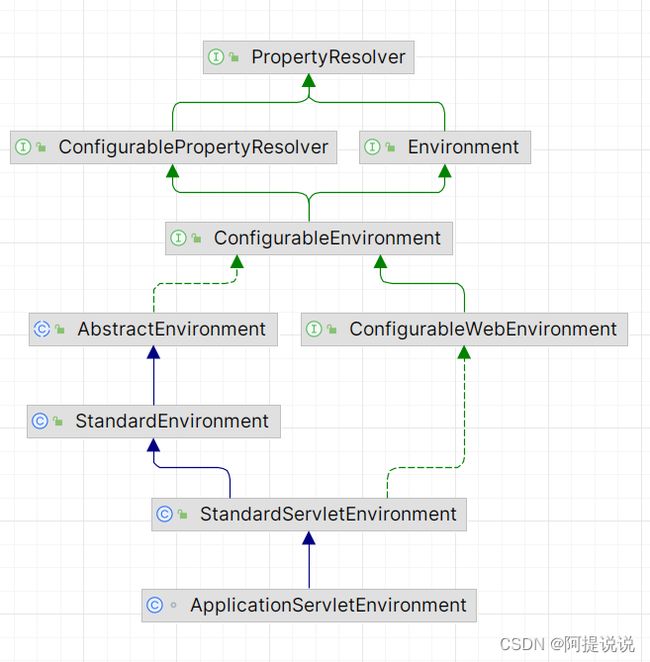
在创建ApplicationServletEnvironment的时候,会先创建父类的构造器,所以会先执行AbstractEnvironment的构造器,AbstractEnvironment是Environment的抽象基类
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources());
}
MutablePropertySources 是PropertySources接口的默认实现,PropertySources是属性配置源接口,描述了如何获取属性值。
这里再调用了当前类的有参构造器。
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
//创建配置解析器
this.propertyResolver = createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
//调用自定义配置源,具体由子类实现
customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}
这里就调用到了StandardServletEnvironment的customizePropertySources中:
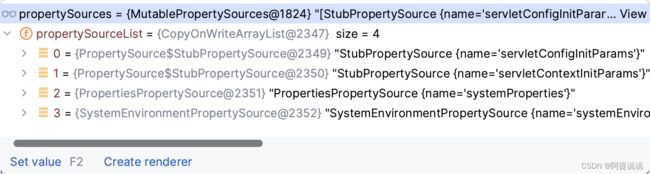
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (jndiPresent && JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
在这里添加了关于ServletConfig、ServletContext、JNDI的配置源

在该方法的最后,又调用到了父类StandardEnvironment的customizePropertySources中:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
在这里添加了Java System属性、操作系统环境变量两个配置源

到此为止已经添加了4个配置源,由于这里不是JNDI环境,没有添加JNDI的配置源,这里执行结束后返回到SpringApplication的getOrCreateEnvironment()处
接着进入configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs())中
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//这里用于添加转换服务
if (this.addConversionService) {
environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());
}
//这里也是设置配置源,后面详解
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
//设置激活的配置文件
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
进入configurePropertySources(environment, args)中
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//获取环境中已有的配置源
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
//默认配置不为空,则添加到配置源中,defaultProperties通过springApplication.setDefaultProperties(properties) 配置
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) {
//addOrMerge会判断已有的配置源中是否已经存在了defaultProperties,来判断是合并还是直接添加
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources);
}
//判断是否有命令行参数,addCommandLineProperties表示是否允许添加命令行配置,默认为true,可通过setAddCommandLineProperties配置
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
//命令行配置源名称
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
//已有配置源中是否包含命令行配置源名称
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
//创建一个具有新名称的组合配置源
composite
.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
//使用新的替换原来的配置源
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
//不包含就添加到已有源的最前面
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 用于解析命令行参数并填充到CommandLineArgs中,解析规则为:
–optName[=optValue]
必须以“–”为前缀,并且可以指定值,也可以不指定值。如果指定了值,则名称和值必须用等号(“=”)分隔,不带空格。该值可以是空字符串(可选)。
有效示例有:
–foo
–foo=
–foo=“”
–foo=bar
–foo=“bar then baz”
–foo=bar,baz,biz
无效示例:
-foo
–foo bar
–foo = bar
–foo=bar --foo=baz --foo=biz
添加完命令行配置源有,进入configureProfiles(environment, args)中,开始设置激活的配置文件:
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
}
这是一个空的protected方法,可见需要子类去实现,这边没有SpringApplication的子类,也就不会在这里处理。
configureEnvironment处理完后,进入ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment):
public static void attach(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources();
PropertySource<?> attached = getAttached(sources);
if (attached == null || !isUsingSources(attached, sources)) {
attached = new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources));
}
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
sources.addFirst(attached);
}
该处代码用于将ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource类型的源添加到已有的配置源中,名称为configurationProperties
这里处理完后,会调用listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment),通过EventPublishingRunListener发送ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,这块前面我们已经多次讲到过,这里不再复述,我们进入EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener,其中的onApplicationEvent在收到ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件后,执行onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event)
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication();
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(),
event.getBootstrapContext())) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application);
}
}
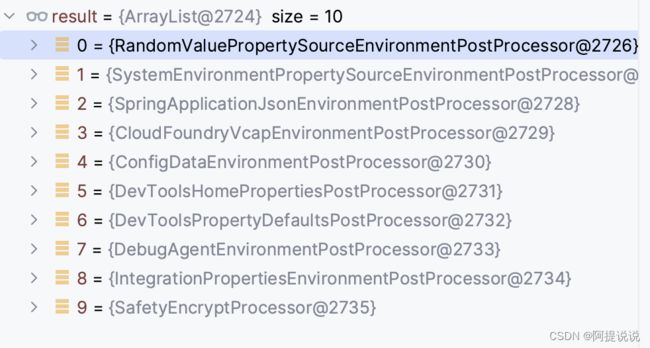
getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(), event.getBootstrapContext()) 会获取所有的EnvironmentPostProcessor实例,如根据本系列文章的Demo获取到的实例有:
-
RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor: 添加RandomValuePropertySource 配置源,用来解析RandomValuePropertySource的随机值属性 -
SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor:将原来的SystemEnvironmentPropertySource替换为OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource,以便能够跟踪每个属性的SystemEnvironmentOrigin -
SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor:添加嵌入在环境变量或系统属性中的SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON 的属性 -
CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor:如果是Cloud Foundry平台,添加Cloud Foundry相关的配置源 -
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor:添加application.yml等配置源 -
DevToolsHomePropertiesPostProcessor:添加Devtools 全局配置的配置源
另外@PropertySource注解配置的加载是在刷新上下文中的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类中处理,具体代码可见ConfigurationClassParser:

17种属性配置的加载基本都在这里了,最后总结一下
总结
作者其他要推荐的文章,欢迎来学习:
Prometheus 系列文章
- Prometheus 的介绍和安装
- 直观感受PromQL及其数据类型
- PromQL之选择器和运算符
- PromQL之函数
- Prometheus 告警机制介绍及命令解读
- Prometheus 告警模块配置深度解析
- Prometheus 配置身份认证
- Prometheus 动态拉取监控服务
- Prometheus 监控云Mysql和自建Mysql
Grafana 系列文章,版本:OOS v9.3.1
- Grafana 的介绍和安装
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(一)
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(二)
- Grafana监控大屏可视化图表
- Grafana 查询数据和转换数据
- Grafana 告警模块介绍
- Grafana 告警接入飞书通知
Spring Boot Admin 系列
- Spring Boot Admin 参考指南
- SpringBoot Admin服务离线、不显示健康信息的问题
- Spring Boot Admin2 @EnableAdminServer的加载
- Spring Boot Admin2 AdminServerAutoConfiguration详解
- Spring Boot Admin2 实例状态监控详解
- Spring Boot Admin2 自定义JVM监控通知
- Spring Boot Admin2 自定义异常监控
- Spring Boot Admin 监控指标接入Grafana可视化