Ansible之playbooks剧本
目录
- 一、playbooks
-
- 1、playbooks简述
- 2、playbooks剧本格式
- 3、playbooks组成部分
- 4、playbooks启动
- 二、playbook编写 apache 的yum安装部署剧本
- 三、playbook编写 nginx 的yum安装并且能修改其监听端口的剧本
- 四、 playbook的定义、引用变量
-
- 1、基础变量的定义与引用
- 2、引用fact信息中的变量
- 五、playbook中的when条件判断和变量循环使用
-
- 1、when条件判断
- 2、变量循环
- 3、四种迭代循环方式的总结
- 六、Templates 模块
- 七、Tags
-
- 1、单标签的使用
- 2、多标签的运用
- 3、通用标签always的运用
- 八、roles
- 九、集中式lamp的简单role编写过程
一、playbooks
1、playbooks简述
playbooks是ansible用于配置,部署,和管理被控节点的剧本。通过playbooks的详细描述,执行其中的tasks,可以让远端主机达到预期的状态。playbooks是由一个或多个”play”组成的列表。 当对一台机器做环境初始化的时候往往需要不止做一件事情,这时使用playbooks会更加适合。通过playbooks你可以一次在多台机器执行多个指令。通过这种预先设计的配置保持了机器的配置统一,并很简单的执行日常任务。
ansible通过不同的模块实现相应的管理,管理的方式通过定义的清单文件(hosts)所管理的主机包括认证的方式连接的端口等。所有的功能都是通过调用不同的模块(modules)来完成不同的功能的。不管是执行单条命令还是play-book都是基于清单文件。
2、playbooks剧本格式
playbooks由YMAL语言编写,YMAL格式是类似于JSON的文件格式,一个文件中有多个play,一个play中只能有一个tasks,一个tasks中可以有多个name任务。
注意事项:
①大小写明个
②通过缩进表示层级关系
③不支持制表符tab键缩进,只能使用空格缩进
④缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级左右对齐,通常开头缩进2个空格
⑤#号注释
⑥符号字符后缩进1个空格,如冒号:逗号,横杠-后面空一个格
⑦如果包含特殊字符用单引号和双引号引起来会作为字符串处理,单引号不识别变量,双引号识别变量。
3、playbooks组成部分
| 模块名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| tasks | 任务,即通过task调用ansible的模块将多个操作组织在一个playbooks中运行 |
| variables | 变量,使用{{}}调用,可简写vars |
| templates | 模板 |
| handlers | 处理器,当changed状态条带满足时,notify触发执行的操作,不会立即执行notify,要等playbooks中的所有任务完成才会执行notify,好处是可以多次触发notify单最后只执行一次对应的handlers。 |
| roles | 角色 |
| ignore_errors | 如果执行命令的返回值不为0则报错tasks停止默认,如果需要忽略报错则设置为false |
| notify | 如果上面的条件成立则执行handlers模块的内容 |
| whit_item | 定义循环的内容即列表,使用{{item}}调用每一次的值,即名称为item。遍历内容直到结束 |
| when | 条件判断,提供唯一通用的条件判断,true时执行,否则不执行 |
| become | 2.6版本以后的参数,之前是sudo,意思为切换用户运行 |
| tags | 为某个或某些任务定义标签,playbooks执行时可以指定只执行某个标签,若标签为always则无论执行此playbooks的那个标签都会将有always标签的name一起执行 |
4、playbooks启动
ansible-playbook 文件名.yaml
ansible-playbook 文件.yaml --start-at-task='任务名/标签' #从某个task开始执行或只执行某个标签的name
#启动此文件
补充参数:-k(-ask-pass):用来交互式输入ssh密码
-K(-ask-become-pass):用来交互式输入sudo密码
-U:指定用户
二、playbook编写 apache 的yum安装部署剧本
vim test1.yaml
#新建编辑yaml文件,内容如下
---
- name: apache yum apply
gather_facts: false
hosts: webservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
- name: stop firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=stopped
- name: stop selinux
command: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'
ignore_errors: true
- name: yum install apache service
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: start apache service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
运行剧本的方法:
#运行playbook
ansible-playbook apache.yaml
补充参数:
-k(–ask-pass):用来交互输入ssh密码
-K(-ask-become-pass):用来交互输入sudo密码
-u:指定用户
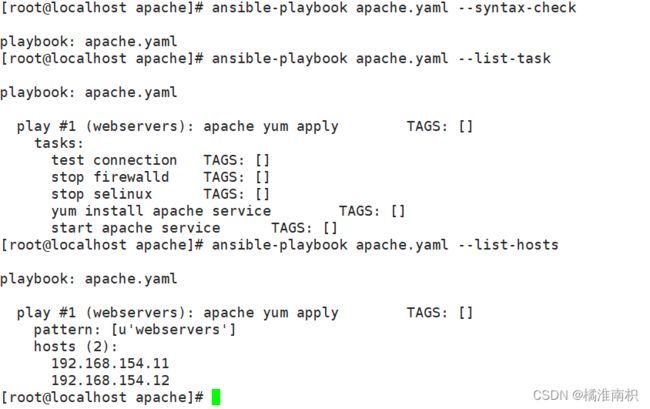
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --syntax-check #检查yaml文件的语法是否正确
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-task #检查tasks任务
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --list-hosts #检查生效的主机
ansible-playbook apache.yaml --start-at-task='install httpd' #指定从某个task开始运行
三、playbook编写 nginx 的yum安装并且能修改其监听端口的剧本
通过yum安装nginx服务,并且能够控制被管理的主机的服务的开启,按照预设的配置在运行时的端口。
在编写剧本前,需要准备相应的两个文件,一个为nginx的yum源。一个为相对应的主配置文件,在主配置文件中修改其端口,在将该配置移至被管理主机中,作为运行启动时的默认配置
mkdir /etc/ansible/nginx
vim nginx.yaml
---
- name: nginx script
gather_facts: false
hosts: webservers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
- name: stop firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=stopped enabled=no
- name: stop selinux
command: '/usr/sbin/setenforce 0'
ignore_errors: true
- name: prepare nginx repo
copy: src=/etc/ansible/nginx/nginx.repo dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: change port
copy: src=/opt/default.conf dest=/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
notify: "restart nginx"
- name: start nginx
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
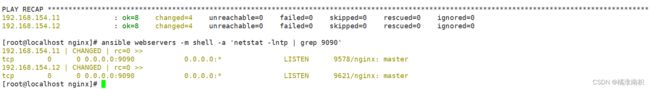
ansible webservers -m shell -a 'netstat -lntp | grep 9090'
cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/
cp default.conf /opt/
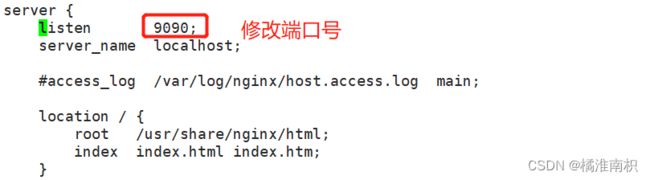
vim /opt/default.conf
server {
listen 9090;
server_name localhost;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
...
四、 playbook的定义、引用变量
1、基础变量的定义与引用
在yaml文件中,我们可以在初始配置的模块中用var去定义变量的存在,变量的格式为key:value,以此来确定该变量在剧本中的存在
vim test1.yaml
---
- name: this is a play for testing variables
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
vars:
filename: abc.txt
tasks:
- name: touch a test file
file: path=/opt/{{filename}} state=touch
ansible-playbook test1.yaml
ansible dbservers -a 'ls /opt'
2、引用fact信息中的变量
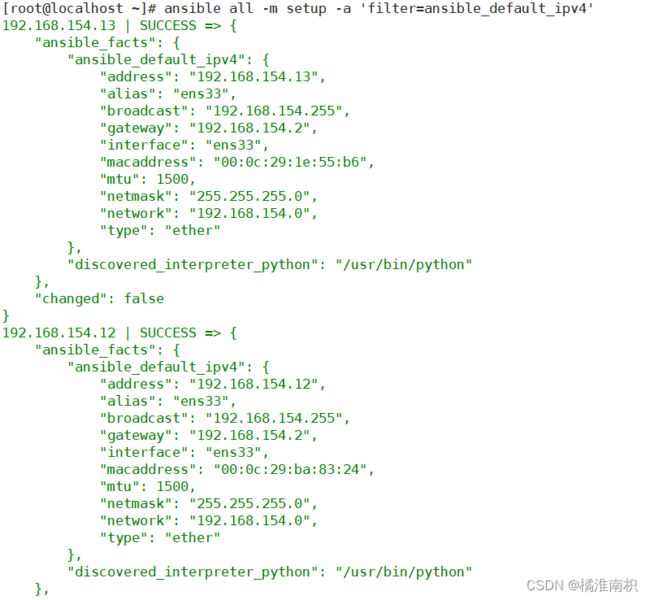
首先我们知道 使用 ansible 组 -m setup 可以收集该组中所有的节点信息 ,
所以setup中fact’信息,有时候会剧本编写中需要,而fact的信息也是可以通过变量的方式进行调用
ansible dbservers -m setup
五、playbook中的when条件判断和变量循环使用
1、when条件判断
#选用filter=ansible_default_ipv4中的address作为when条件进行测试
ansible all -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_default_ipv4'
vim test3.yaml
---
- name: this is when test playbook
hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: test when
debug: msg='判断位置'
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "192.168.154.12"
ansible-playbook test3.yaml
2、变量循环
(1)with_item 单循环输出
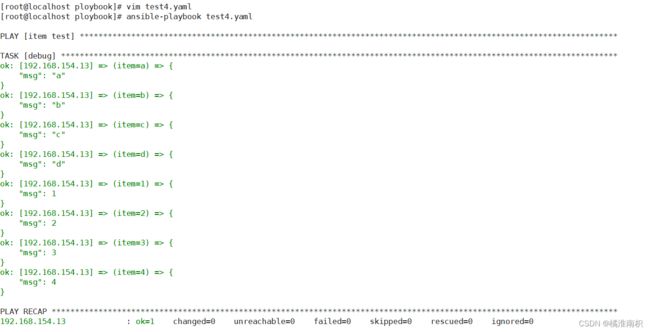
vim test4.yaml
---
- name: item test
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{item}}"
with_items: [a, b, c, d]
ansible-playbook test4.yaml


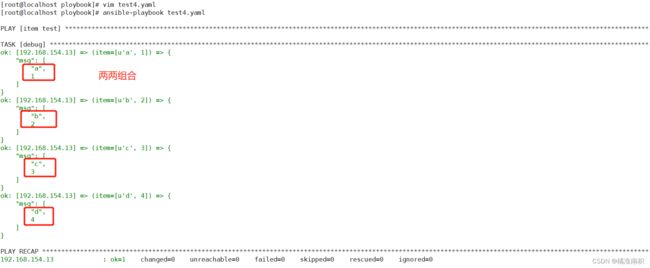
当列表为两个时。with_item的输出方式:
(3) with_together 同一列表位置数据组合输出的循环
vim test4.yaml
---
- name: item test
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{item}}"
with_together:
- [a, b, c, d]
- [1 ,2, 3, 4]
ansible-playbook test4.yaml
vim test4.yaml
---
- name: item test
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{item}}"
with_together:
- [a, b, c, d]
- [1 ,2, 3, 4]
- [A, B, C]
ansible-playbook test4.yaml

(4) with_nested 列表数据循环匹配的循环(根据列表个数定义有多少层的循环)
vim test4.yaml
---
- name: item test
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{item}}"
with_nested:
- [a, b, c, d]
- [1 ,2, 3, 4]
ansible-playbook test4.yaml
3、四种迭代循环方式的总结
whith_items: {{item}}会把所有的列表展开进行遍历输出,with_flattened也可以替代with_items
with_list: {{item}}会把每个列表当作一个整体输出。如果每个列表中只有一个值,则效果与with items一致。loop也可以替代ith
with_together: {{item}}引用时会把每个列表相同位置的值对齐合并后输出
with nested:{ {item}}引用时会把每个列表的值两两组合循环输出
六、Templates 模块
Jinja是基于Python的模板引擎。Template类是Jinja的一个重要组件,可以看作是一个编译过的模板文件,用来产生目标文本,传递Python的变量给模板去替换模板中的标记。
本次我们以改变apche的配置文件为例,来展现Templates模块的运用
(1)先准备一个以 .j2 为后缀的 template 模板文件,设置引用的变量
#如果没有相关的httpd的配置文件,可以先yum按住一个httpd的服务,取其主配置文件
cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /opt/httpd.conf.j2
vim /opt/httpd.conf.j2
Listen {{http_port}} #42行,修改
ServerName {{server_name}} #95行,修改
DocumentRoot "{{root_dir}}" #119行,修改
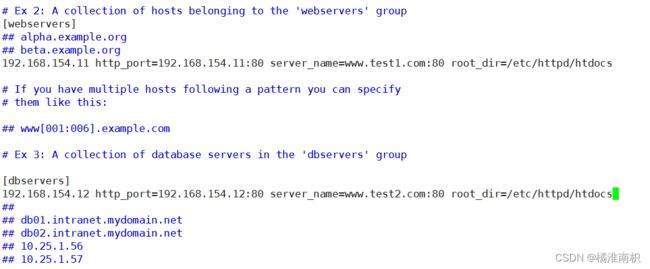
(2) 修改主机清单文件,使用主机变量定义一个变量名相同,而值不同的变量
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
192.168.154.11 http_port=192.168.154.11:80 server_name=www.test1.com:80 root_dir=/etc/httpd/htdocs
[dbservers]
192.168.154.12 http_port=192.168.154.12:80 server_name=www.test2.com:80 root_dir=/etc/httpd/htdocs
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.154.11 www.test1.com
192.168.154.12 www.test2.com
(3) 编写 playbook
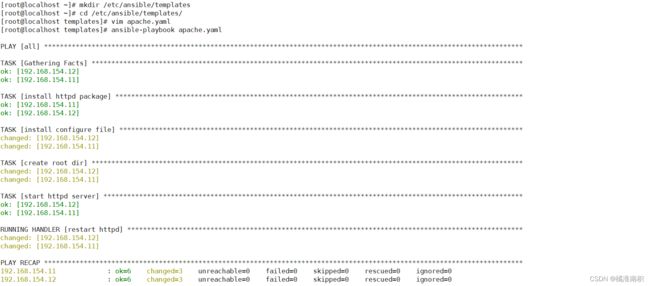
mkdir /etc/ansible/templates
cd /etc/ansible/templates/
vim apache.yaml
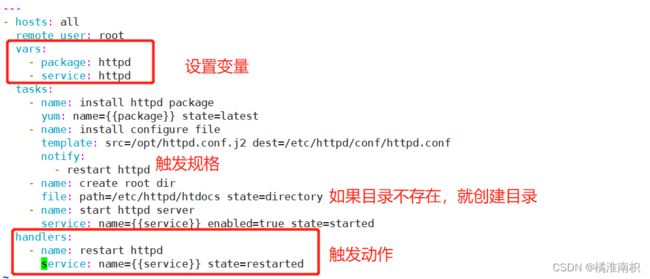
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
- package: httpd
- service: httpd
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name={{package}} state=latest
- name: install configure file
template: src=/opt/httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart httpd
- name: create root dir
file: path=/etc/httpd/htdocs state=directory
- name: start httpd server
service: name={{service}} enabled=true state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name={{service}} state=restarted
ansiable-playbook apache.yaml
七、Tags
可以在一个playbook中为某个或某些任务定义“标签”,在执行此playbook时通过ansible-playbook命令使用–tags选项能实现仅运行指定的tasks。
playbook还提供了一个特殊的tags为always。作用就是当使用always作为tags的task时,无论执行哪一个tags时,定义有always的tags都会执行。
1、单标签的使用
mkdir /etc/ansible/tag
cd /etc/ansible/tag/
vim test1.yaml
---
- name: this is a play for testing variables
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
vars:
filename: abc.txt
tasks:
- name: position 1
debug:
msg: 'ls /opt'
tags:
- only
- name: position 2
debug:
msg: 'ls /mnt'
ansible-playbook test1.yaml --tags="only"
2、多标签的运用
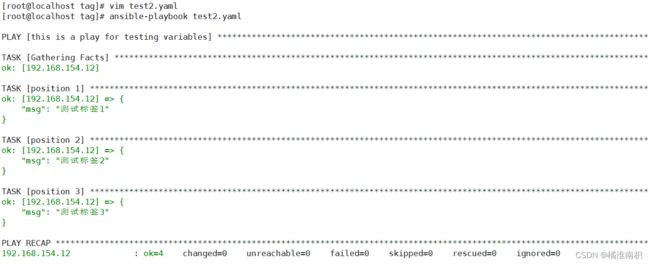
vim test2.yaml
---
- name: this is a play for testing variables
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
vars:
filename: abc.txt
tasks:
- name: position 1
debug:
msg: '测试标签1'
tags:
- one
- name: position 2
debug:
msg: '测试标签2'
tags:
- two
- name: position 3
debug:
msg: '测试标签3'
tags:
- one
ansible-playbook test2.yaml
3、通用标签always的运用
vim test2.yaml
---
- name: this is a play for testing variables
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
vars:
filename: abc.txt
tasks:
- name: position 1
debug:
msg: '测试标签1'
tags:
- one
- name: position 2
debug:
msg: '测试通用标签always'
tags:
- always
- name: position 3
debug:
msg: '测试标签3'
tags:
- one
ansible-playbook test2.yaml
八、roles
Roles又称为角色,playbook被称为剧本。Roles角色是自1.2版本之后引入的新特性,用于层次性、结构化的组织剧本
roles能够根据层次型结构自动装载变量文件、任务集、以及触发的动作等,要使用roles只需要在剧本中使用include命令引入即可
简单的来说,roles就是分别将变量、文件、任务、模板以及处理器放置于不同的单独的目录,并且可以便捷的通过include引入
角色一般用于基于主机构建的服务的场景中,但是也可以是用于构建守护进程等场景中,主要是使用在代码复用度较高的场景下
● files
用来存放由 copy 模块或 script 模块调用的文件。
● templates
用来存放 jinjia2 模板,template 模块会自动在此目录中寻找 jinjia2 模板文件。
● tasks
此目录应当包含一个 main.yml 文件,用于定义此角色的任务列表,此文件可以使用 include 包含其它的位于此目录的 task 文件。
● handlers
此目录应当包含一个 main.yml 文件,用于定义此角色中触发条件时执行的动作。
● vars
此目录应当包含一个 main.yml 文件,用于定义此角色用到的变量。
● defaults
此目录应当包含一个 main.yml 文件,用于为当前角色设定默认变量。
● meta
此目录应当包含一个 main.yml 文件,用于定义此角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系。
九、集中式lamp的简单role编写过程
#在一个 playbook 中使用 roles 的步骤:
(1)创建以 roles 命名的目录
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/ -p #yum装完默认就有
(2)创建全局变量目录(可选)
mkdir /etc/ansible/group_vars/ -p
touch /etc/ansible/group_vars/all #文件名自己定义,引用的时候注意
(3)在 roles 目录中分别创建以各角色名称命名的目录,如 httpd、mysql
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql
(4)在每个角色命名的目录中分别创建files、handlers、tasks、templates、meta、defaults和vars目录,用不到的目录可以创建为空目录,也可以不创建
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta}
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta}
(5)在每个角色的 handlers、tasks、meta、defaults、vars 目录下创建 main.yml 文件,千万不能自定义文件名
touch /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
(6)修改 site.yml 文件,针对不同主机去调用不同的角色
vim /etc/ansible/site.yml
---
- hosts: webservers
remote_user: root
roles:
- httpd
- hosts: dbservers
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
(7)运行 ansible-playbook
cd /etc/ansible
ansible-playbook site.yml
示例:
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
mkdir /etc/ansible/roles/php/{files,templates,tasks,handlers,vars,defaults,meta} -p
touch /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
touch /etc/ansible/roles/php/{defaults,vars,tasks,meta,handlers}/main.yml
------编写httpd模块------
写一个简单的tasks/main.yml
vim /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/tasks/main.yml
- name: install apache
yum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start apache
service: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started
#定义变量:可以定义在全局变量中,也可以定义在roles角色变量中,一般定义在角色变量中
vim /etc/ansible/roles/httpd/vars/main.yml
pkg: httpd
svc: httpd
-------编写mysql模块-------
vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml
- name: install mysql
yum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start mysql
service: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started
vim /etc/ansible/roles/mysql/vars/main.yml
pkg:
- mariadb
- mariadb-server
svc: mariadb
-------编写php模块-----
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/tasks/main.yml
- name: install php
yum: name={{pkg}} state=latest
- name: start php-fpm
service: enabled=true name={{svc}} state=started
vim /etc/ansible/roles/php/vars/main.yml
pkg:
- php
- php-fpm
svc: php-fpm
-----编写roles示例-----
vim /etc/ansible/site.yml
---
- hosts: webservers
remote_user: root
roles:
- httpd
- mysql
- php
cd /etc/ansible
ansible-playbook site.yml