编译原理 实验一 词法分析器设计
一. 实验目的
1. 深入理解有限自动机及其应用
2. 掌握根据语言的词法规则构造识别其单词的有限自动机的方法
3. 基本掌握词法分析程序的开发方法
4. 能够设计词法扫描器程序,对源程序进行词法分析,并输出单词序列
二. 实验内容及要求
编写识别单词的词法分析程序。
已知某语言中各类单词的DFA如下图,编写程序实现:
1、输入:txt文件(存放要分析的源程序)
2、输出:从输入的源程序中,识别出各个具有独立意义的单词,即基本保留字、标识符、常数、运算符、分隔符五大类。并依次输出各个单词的种别码及单词符号自身值。(遇到错误时可显示“Error”,然后跳过错误部分继续显示)。
输出格式:每个单词的表示:(种别码,单词符号自身值)
要求:对识别出的每一单词均单行输出。
源程序中每类单词都要有
三. 实验过程
1、设计的DFA转换图
字母与下划线:letter -> A|B|…|Z|a|b|c|d…|y|z|_
数字:digit1 -> 1~9 digit-> 0~9
标识符定义:id -> letter(letter|digit)*
运算符定义:op -> +-*/%=!&|<>
关键字定义:keyword -> int float const bool void char double struct return if else while do static break for switch case default continue true false
界符定义:delimiter -> ; , ' " * */ ? : ( ) [ ] } { .
整型定义:int -> (+|-)(0 | digit1 digit*)
字符常量:char -> letter|digit|……
字符串常量:string -> char*
实型定义:double-> (0|(+|-)digit1 digit*)(.digit*)
我画的DFA如图
2、采用的数据结构
输出Token流为类型名称+种别码+值(该关键字/变量名/数字/运算符/界符),重载输出流。
struct Token {
int type; // 种别码
string value; // 值 关键字/变量名/数字/运算符/界符
string category; // 种别码对应的类型名称
Token(int type, string value, string category) : type(type), value(value), category(category) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Token& t) {
os << t.category << ", type: " << t.type << ", value: " << t.value;
return os;
}
};
3、头文件声明和全局变量定义
如下,应该非常的一目了然吧。
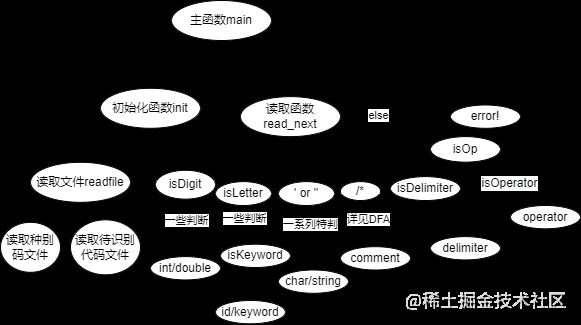
#include 4、函数汇总
(1)函数汇总表
| 函数名称 | 功能简述 |
|---|---|
readFile |
读取文件函数,返回一个string动态数组 |
init |
初始化函数,在该函数中进行读取种别码文件、关键字文件,并进行相应赋值与初始化 |
peek |
探测下一个字符,若存在则返回该字符,否则返回\0即字符串结束符 |
isDigit |
判断字符ch是否为数字0-9 |
isLetter |
判断字符ch是否为字母或下划线(即A-Z a-z _ ) |
isKeyword |
判断字符串s是否为关键字(在关键字表中) |
isOP |
判断字符ch是否为单个运算符(在op中) |
isOperator |
判断字符串s是否为运算符(运算符表中) |
isDelimiter |
判断字符ch是否为界符(在operate中) |
judge |
核心函数,判断并返回当前字符(code[pos])的枚举类型,并对一些特殊的token进行处理后直接放入tokenList(如注释、字符和字符串常量) |
read_next |
核心函数,读取下一个字符,根据返回的枚举类型,将对应的token放入tokenList |
main |
主程序入口,从此进入,调用init函数初始化 |
(2)函数的调用关系
5、实验结果
输入
code.txt
int main() {
char ch = 'ss';
string str = "Hello, World!"
char ch2 = 's';
init();
double x = 10.31;/* some comment */
int m = 0;
int y = 310, m = 0.31;
while(pos < len) {
int flag = read_next();
if(flag == _EOF_) break;
if(flag != _ERROR_) {
Token t(flag, tempToken);
tokenList.push_back(t);
cout << t << endl;
} else cout << "Error!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
四、实验总结
此次实验还是很有意思的,最终跑通的时候也是非常有成就感,个人感觉不用拘泥于用什么算法,只需要捋清楚自己的思路,如何设计才能使这个程序能正确识别?主要有一个优先级的思路,空格和换行符会被跳过,然后先判断是否为数字或者字母,在进行相应处理,然后进行一些特殊界符的判断,如字符串、注释等。我认为代码就足以很好的说清楚这个流程。这个程序暂时只使用常用符号(.)来支持小数,如果需要更多,可以在judge中的isdigit()后进行修改,改起来并不困难。显然,judge函数中的函数还可以拆成更细致的几个函数,但这就等以后再补全了。
五、思考题回答
程序设计中哪些环节影响词法分析的效率?如何提高效率?
答:有待优化的部分还有不少,例如在判断是否为关键字时,目前的方法是把可能为标识符或者关键字的字符串读取完后存放在一个字符数组后再逐个与关键字表进行匹配,可改为在读取的同时判断,这样会提高效率。还有就是界符匹配也是同理。
完整代码
/*
* @Author: cos
* @Date: 2022-04-05 00:10:59
* @LastEditTime: 2022-04-08 02:37:49
* @LastEditors: cos
* @Description: 词法分析器设计实现
* @FilePath: \CS\experiment_1\demo\main.cpp
*/
#include