VRRP协议个人理解(RFC5798)+典型配置+RFC2338/RFC3768文档翻译
本文档源地址位于RFC 2338: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol,在此仅为个人学习加深理解使用。转载等操作请保留源文档版权声明。
RFC2338存在更新RFC3768,由于并未有较大改动,此处不对RFC3768做详细介绍仅在正文翻译前作相关说明。
RFC3768存在更新RFC5798。由于涉及VRRPv3版本但相应协议逻辑并未改动,此处直接将其内容于第0章节就报文格式、流量行为和配置差别(华为)进行比对。RFC5798个人翻译可见
【无标题】VRRP协议RFC5798文档翻译_fengxingzhe008的博客-CSDN博客
RFC2338仅涉及IPv4网络,个人感觉RFC2338的重点在于第6章协议状态机制,重点介绍了VRRP的三种状态机制(Initialize、Master和Backup),以及在状态改变时的两种定时器(Master_Down_Timer定时器和Adver_Timer)的赋值操作。
默认情况下Master_Down_Timer=3*Adver_Timer+Skew_time;
Adver_Timer默认1s,Skew_time=(256-Priority)/256。
之后会对VRRP协议状态机及其进行详细描述,并增加RFC3768改变内容。同时也将对本文档进行修改校对。
RFC3768源文档位于
RFC 3768: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
RFC3768相比于RFC2338未作过多改动,此处不再进行详细翻译介绍。只在下文进行说明。
RFC5798源文档位于
RFC 5798: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) Version 3 for IPv4 and IPv6
version2.2 进行排版调整(简单介绍VRRP和M-LAG)
version2.1 详细介绍vrrpv2和vrrpv3流量行为差异
version2.0 添加0.5章节关于vrrp与动态协议的小联系。
version1.3-2022.10.10
编辑校对第0章节错误描述。
Note:由于篇幅及APP排版问题,关于RFC翻译内容推荐使用PC端进行查看。后续也将安排内容进行优化。有一定功底读者,可直接从第5章节开始阅读。
目录
0 个人VRRP协议理解
0.1 VRRP相关参数
0.2 VRRP状态机
0.3流量行为
0.4VRRPv3和VRRPv2对比介绍
0.4.1报文内容介绍
0.4.2流量行为差异
0.4.3VRRPv2和VRRPv3的兼容性
0.4.4VRRP的典型配置
0.5其他有待理解记录的内容
0.5.1VRRP与动态路由协议
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol-RFC2338(RFC2338已被RFC3768/5798更新替代)
1.Introduction
1.1范围
1.2定义
2.所需功能
2.2偏好路径指示
2.3最小化非必要服务的干扰
2.4扩展安全
3.VRRP概述
4.简易配置
4.1简易配置1
4.2简易配置2
5.协议
5.1 VRRP数据包格式
5.2IP段描述
5.3VRRP字段描述
6.协议状态机制
6.1参数
6.1.1接口参数
6.1.2虚拟路由器参数
6.2定时器
6.3状态转变图
6.4状态描述
6.4.1Initialize
6.4.2Backup
6.4.3Master
7.发送和接受VRRP报文
7.1接收VRRP报文
7.2传输VRRP数据包
7.3虚拟路由器MAC地址
8.使用问题
8.1ICMP重定向
8.2 主机ARP请求
8.3ARP代理
9.在FDDI和Token Ring上的使用
9.1在FDDI上的使用
9.2在Token Ring上的使用
10.安全性考虑
10.1无认证
10.2简单文本密码
10.3IP头认证
11.致谢
12.参考文献。
13.作者地址
14.完整的版权声明
VRRP协议相关理解:
0 个人VRRP协议理解
接下来本人将就VRRP协议相关内容浅谈下个人理解。想要详细了解VRRP协议,可直接阅读相关文档
0.1 VRRP相关参数
为了便于后续介绍,在此首先进行VRRP(2)相关参数的介绍
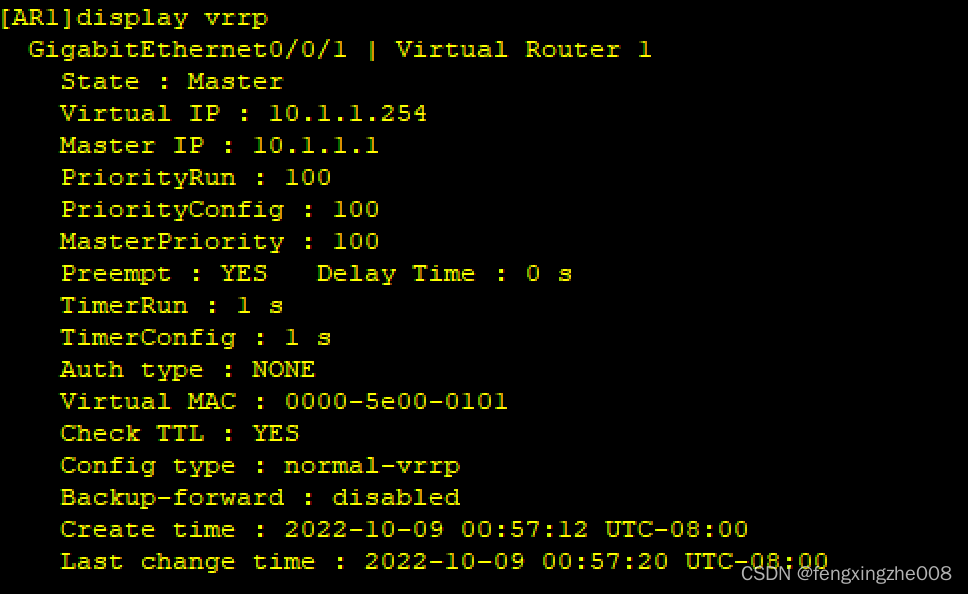
1@VRID: Virtual Router id==虚拟路由器ID用于标识及区分接口上所使用的vrrp。是VRRP进行协商的参数之一。
2@Priority:==优先级。用于选举VRRP的主备状态(Master、Backup)。手动可配置取值范围1-254:0用于Master主动表明退出建立VRRP,255用于IP拥有者发送Advertisement通告报文时主动标识。
3@IP地址:通常指的是人为定义的VRRP的虚拟IP地址。该地址进行虚地址相关数据包的处理。
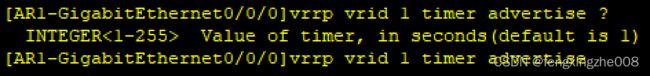
4@通告间隔:VRRP的Master路由器主动发送Advertisement通告报文的间隔时间。默认为1s。(VRRPv2版本取值1-255,VRRPv3版本取值1-40)
5@偏移时间(Shew_Time):Backup路由器转变为Master路由器的偏移时间。计算公式=
(256 - Priority) / 256
之后内容将对其介绍
6@Master中断间隔(Master_Down_Interval):网络中Master设备失效时间。可以理解为允许网络中不存在Master的最大时间,或者可以理解为Backup设备转变为Master的等待时间。计算公式=
3*通告时间+偏移时间(3*Advertisement+Skew_Time)
7@定时器。VRRP协议定义了两个定时器,分别用于Master和Backup设备进行状态改变计时使用。
通告定时器(Adver_Timer):Master设备上用于判断是否发送Advertisement报文。默认从1s倒数计时,为0s时触发发送通告报文。
Master中断时间定时器(Master_Down_Timer):Backup设备上用于向Master状态转变的计时器,一般从Master中断间隔(Master_Down_Interval)开始,为0时触发发送通告报文表明自己的Master身份
接下来的介绍将使用到这两个定时器
0.2 VRRP状态机
VRRP的状态机比较简单,只有三种:Initial、Master和Backup。
而VRRP的状态切换简单来说,可以用一句话进行概括:通过比对通告报文优先级从而一次完成主备选举并周期进行报文通告。(一次指的是无需类似OSPF的LSR和LSAck或TCP的确认回应机制)。而实际操作也只稍微增加了些判断条件,使该过程更精细和周密。
Initial:协议的初始状态,通告可以理解为开始运行VRRP协议。这一状态不是一个稳定状态,会向Master和Backup状态进行过渡。这个过渡通常在秒级内切换完成。
有一个特殊情况是运行VRRP协议端口的实IP地址和VRRP虚拟IP地址相同时,将直接过渡到Master状态。并触发Master的相关动作:
1@通告VRRP报文。此时VRRP报文优先级直接设置为255。
2@广播免费ARP报文,用于刷新下行局域网内设备的MAC表便于流量正常转发。ARP的相关将在后文说明。
3@启动通告定时器,将其设置为通告间隔。当通告定时器=0s,重新发送Advertisement通告报文并重置通告定时器
Backup:具有Backup状态的VRRP路由器将时时监测Master的相关动作。这里仅指监听Master所通告的Advertisement通告报文。
当具有Initial状态的VRRP路由器收到高优先级或者优先级相同但Advertisement报文源地址<自身运行VRRP接口的实地址时会过渡到该状态。
也即Master的选举为:
1@优先级越大越优先;
2@优先级相同,接口IP地址越大越优先
具有Backup状态路由器的动作:
1@丢弃目的MAC=虚拟MAC的ARP请求;
2@不响应目的IP=虚拟IP的数据包
3@不接受目的IP=虚拟IP的数据包
Backup路由器程序动作:
if1@判断触发shutdown事件,将
转变为Initial状态。这一行为可以理解为运行VRRP端口down。
endif1
if2@Master中断时间定时器(Master_Down_Timer)=0,将
转变为Master状态。执行相应行为。也即在未收到通告报文的3*1s+偏移时间(3*Advertisement+Skew_Time)后转变为Master。该定时器由通告报文进行刷新
endif2
if3@收到Advertisement报文,将继续判断
if3.1@Advertisement报文优先级=0,该报文为Master路由器主动通告退出VRRP协议,将自身的Master中断时间定时器(Master_Down_Timer)设置为偏移时间(Shew_Time),在该时间结束后状态转变为Master。
else,也即Advertisement报文优先级=!0,将
if3.2@不设置抢占或者有通告报文优先级比自身更大或优先级相同但通告报文源IP大于自身接口地址,将
重置Master中断时间定时器(Master_Down_Timer)
else,也即自己收到的通告报文更优
丢弃Advertisement报文
endif3.2
endif3.1
endif3
Master:处于Master状态的设备具有相应虚拟IP地址,可以在相应接口处理虚拟IP地址的报文。
具有Master状态路由器的动作:
1@回应具有虚拟路由器IP地址的ARP请求
2@转发目的MAC地址为虚拟路由器MAC的数据包
3@处理发往虚拟IP 地址的数据包
Master路由器程序动作:
if1@判断触发shutdown事件,将
清除通告间隔定时器;发送通告报文优先级=0的Advertisement报文;过渡到Initinal状态
endif1
if2@通告间隔定时器倒计为0,将
发送一个通告报文;并将通告间隔定时器置为通告间隔
endif2
if3@收到一个通告报文,将
if3.1通告报文优先级=0,将
发送一个通告报文;并将通告间隔定时器置为通告间隔
else,也即收到报文优先级=!0,将
if3.1.1通告报文优先级>自身或者通告报文优先级=自身但报文源地址大于=自身,将
清除通告间隔定时器;建立Master中断间隔定时器并置为Master中断间隔;过渡到Backup状态
else,
丢弃通告报文
endif3.1.1
endif3.1
endif3
0.3流量行为
VRRP的流量行为主要通过免费ARP报文来实现。为了加快收敛过程,VRRP的Master状态建立时会通告一次免费的ARP报文用于刷新下行设备的MAC地址表。同时在Backup转变为Master状态时也通告一次免费的ARP报文,防止下行设备保存了错误的MAC地址表导致流量的中断。
并且Master设备也会定期进行免费ARP的通告进行MAC地址表的保活。(VRRPv3 IPv6则主动进行ND协议的NA通告)
[AR1]vrrp gratuitous-arp timeout 120
华为默认120s,暂不支持单vrid设置。
其他友商命令,CISIO
vrrp
interface vlan10
vrrp 1 periodic-arp-na interval 30
$
$
0.4VRRPv3和VRRPv2对比介绍
0.4.1报文内容介绍
VRRPv2和VRRPv3报文格式上并无明显差别,只需注意相关字段即可。
VRRPv2报文
VRRPv3报文格式
接下来对报文字段进行相应比较
1@链路层(Link-layer):
VRRPv2使用虚拟MAC作为报文源MAC=00-00-5e-00-01-[VRID]。00-00-5e由IANA固定分配,00-01表明地址族为VRRP协议。[VRID]随人为定义的VRRP虚拟路由器ID决定,取值1个字节1-255。目的MAC=01-00-5e-00-00-12,该MAC为组播MAC由组播IP转换而来。转换规则可查阅相关规定。
VRRPv3使用虚拟MAC作为报文源MAC=00-00-5e-00-02-[VRID]。00-00-5e由IANA固定分配,00-02表明地址族为VRRPv6协议。[VRID]随人为定义的VRRP虚拟路由器ID决定,取值1个字节1-255。目的MAC=33-33-00-00-00-12,该MAC为组播MAC由组播IPv6(请求节点组播地址)转换而来。转换规则可查阅相关规定。
2@网络层:
VRRPv2为网络层协议,主要用于IPv4(Type=0x8000)使用,标识协议号112。数据包源IP地址为运行VRRP协议接口实地址IP,该地址可在多个VRRP路由器优先级配置相同情况下用于选举VRRP的Master和Backup状态。越大越优先。目的IP地址为IANA分配的组播IP=224.0.0.18。
VRRPv3为网络层协议,主要用于IPv6(Type=0x86dd)使用,标识协议号112。IP包源地址为运行VRRPv3协议接口IP的链路本地地址(Link-local),该地址可在多个VRRP路由器优先级配置相同情况下用于选举VRRP的Master和Backup状态。越大越优先。需要注意的是VRRPv3虚拟IP也有链路本地地址,与此地址不同。目的IP地址为IANA分配的组播IP(请求节点组播地址)=ff02::12。
Note:VRRPv2和VRRPv3协议都规定了TTL/Hop limit=255。VRRP路由器将会丢弃非255的通告报文。255设置主要是考虑远程伪造通告报文的可能。255将攻击报文限制在了局域网范围内。
3@VRRP字段比对:
Version字段(4 bits)、Type字段(4 bits)、VRID字段(1字节)、Priority字段(1字节)和Addr count字段(1字节)。除VRRPv2使用0010表示(二进制)而VRRPv3字段使用0011表示(二进制),其他完全相同。
VRRPv2之后为认证字段(1字节)+Adv Int通告间隔(1字节),RFC2338中规定了3种认证方式:无认证、简单认证和IP头认证,而在后续的RFC3768中将相应规定取消设置为保留字段。目前华为仍然支持认证,详细内容可查阅相关内容。
VRRPv3之后为保留字段(4bits)+Adv Int通告间隔(12bits)。
因此VRRP的通告间隔略有不同,VRRPv2通告间隔默认1s取值1-255单位秒/s;VRRPv3通告间隔默认100cs(cs厘秒,100厘秒=1s)取值100-4095cs。(VRRPv3对IPv4的支持情况,Huawei=1-40s)。
两种协议之后为Checksum(2字节)保持一致,用于校验VRRP报文。
Checksum之后为VRRP的虚拟IP地址,不同之处在于VRRPv2该字段为32bits,VRRPv3该字段为128bits。另有一个值得注意的是VRRPv3的第一个IPv6地址必须为虚拟路由器的Link-local链路本地地址(人为定义的虚拟IPv6的Link-local,注意与接口的Link-local区别)。因此VRRPv3在使用IPv6时,Addr count字段最小为2。
VRRPv2如果配置了认证信息,则之后还存在相应的认证信息。
0.4.2流量行为差异
由于IPv6有独特的ND协议和DAD协议,并且不存在广播报文。因此VRRPv2和VRRPv3的流量行为存在一定差异。
VRRPv2周期使用免费ARP报文方式主动通告防止流量中断。
路由器在使能vrrpv2功能时,master设备主动通告一次免费arp用于局域网记录虚拟ip的mac地址。同时周期性发送免费arp持续进行mac老化更新。如果存在backup向master的转化,在backup成为master时会主动通告一次免费arp,此后周期性进行通告免费arp。
VRRPv3主要依靠ND协议来实现该功能。vrrpv3和vrrpv2的流量逻辑基本相同,只是免费arp功能的实现由ND协议来完成。
在此首先简单介绍下ND协议的NA报文。
ND协议的NA(Neighbor Advertisement,邻居通告)报文使用ICMPv6的136号协议号。通常与 NS(Neighbor Solicitation,邻居请求。ICMPv6协议号135)报文共同使用,NA也可单独使用。
NA报文的Flags位有三个标志位用于VRRPv3的流量通告过程。
R标志位(Router):路由器标识,用于标识路由器。也即置为1时向外通告自己为非终端设备
S标志位(Solicited):请求标识,通常用于标识本报文是否为NS的回应报文。也即置为0时可用于主动向外发送。
O标志位(Overside):重写标识,通常用于重写相应地址信息。也即置为1时表明收到该报文的设备需要根据本报文携带信息进行相应表项/流表的刷新。
值得注意的是ICMPv6使用了TLV方式(Type、Length和Value)构建报文,可以方便进行报文格式修改大大提高了协议的扩展性。相似使用TLV方式的协议有ISIS、BGP和LDP等协议。这里携带了ICMPv6 Option TLV对数据进行了描述。
通信过程:
Master状态建立时主动进行ICMPv6 ND协议NA报文通告。(类似VRRPv2的免费ARP)
NA报文:
源MAC=VRRP组播MAC(也即00-00-5e-00-02-[VRID]),目的MAC=请求节点组播MAC(也即33-33-00-00-00-01)
源IP=虚拟路由器IP的链路本地地址(非实接口链路本地地址),目的IP=请求节点IP(也即ff02::1)
携带Flags字段其中R=1,S=0,O=1。指定Target Address=虚拟路由器链路本地地址。(该地址也在通告报文中出现)。并添加ICMPv6 Option(T=2,L=1。T=2表示目的链路层地址),该Option携带链路层地址(Link-layer)为虚拟路由器的MAC(也即00-00-5e-00-02-[VRID])。
当主机通信时:
VRRP虚拟路由首先发送NS请求报文@@源MAC=Master设备实接口MAC,目的MAC=IPv6组播MAC(该组播地址由目的IP转化而来,并非请求节点组播MAC);源IP=Master设备链路本地地址Link-Local地址,目的IP=主机链路本地地址Link-local
发送ICMPv6 ND协议NS报文。报文中Target Address字段填充主机IPv6地址。添加ICMPv6 Option(T=1,L=1。T=1表示源链路层地址),该Option携带链路层地址(Link-layer)为Master设备实接口的MAC。
主机进行NA回应@@源MAC=设备自身MAC,目的MAC=Master设备实接口MAC;源IP=主机IPv6地址,目的IP=Master设备的实接口链路本地地址(Link-local)
回应ICMPv6 ND协议ND报文。该ND报文Flags字段R=0,S=1,O=1,并添加ICMPv6 Option(T=2,L=1。T=2表示目的链路层地址),该Option携带链路层地址(Link-layer)为主机设备的MAC。此时虚拟路由器获取到主机的MAC。
这一过程可以近似理解为Master设备主动发起了一次ARP请求(NS/NA交互)。
详细的ND协议,可查阅相关文档
0.4.3VRRPv2和VRRPv3的兼容性
RFC5798的8.4章节介绍了VRRP之间的兼容性问题,协议介绍VRRPv2可与VRRPv3兼容。但要求VRRPv2和VRRPv3共用场景不可作为永久操作使用。
考虑到RFC2338和RFC3768规定了不同的VRRPv2报文格式(RFC3768取消了认证字段),实际的兼容情况需根据实际情况判断。
例如(Huawei)VRRPv2 对IPv4认证间隔取1-255s,VRRPv3对IPv4认证间隔取1-40s。
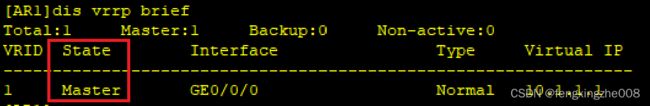
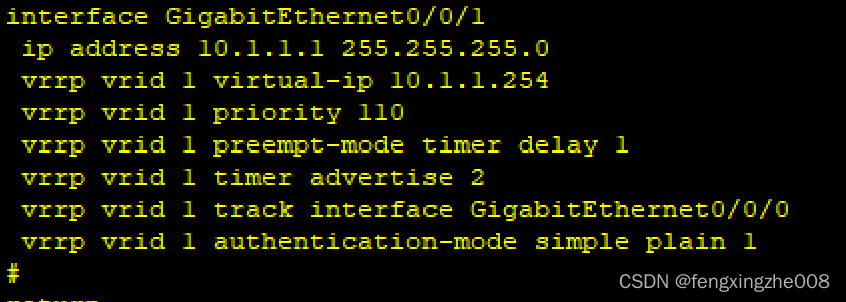
0.4.4VRRP的典型配置
VRRPv2
vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 10.1.1.254
//定义VRID1的虚拟路由器地址
vrrp vrid 1 priority 110
//定义VRID1的优先级,默认100
vrrp vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 1
//定义VRID1抢占延时1s。默认抢占,默认延时0立即抢占
vrrp vrid 1 timer advertise 2
//定义VRID1的通告间隔2s。默认1s。取值1-255s。(VRRPv2取值1-255,VRRPv3的IPv4取值1-40s)
vrrp vrid 1 track interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
//定义VRID1联动端口。如果端口状态改变可修改相应优先级
vrrp vrid 1 authentication-mode simple plain 1
//定义VRID1认证信息,VRRPv2(RFC2338定义,RFC3768定义的VRRPv2取消了认证字段)
#
VRRPv3
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ipv6 enable
ipv6 address 2001::1/64
ipv6 address FE80::11 link-local
vrrp6 vrid 1 virtual-ip FE80:1::254 link-local
//定义VRID1的虚拟路由器Link-local地址
vrrp6 vrid 1 virtual-ip 2001::254
//定义VRID1的虚拟路由器IPv6地址
vrrp6 vrid 1 priority 110
//定义VRID1优先级,默认100
vrrp6 vrid 1 preempt-mode timer delay 1
//定义VRID1抢占延时1s,默认抢占0s,立即抢占。
vrrp6 vrid 1 timer advertise 200
//定义VRID1通告间隔200厘秒(2s),默认100厘秒,100-4095。
vrrp6 vrid 1 track interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
//定义VRID1联动端口。如果端口状态改变可修改相应优先级
#
兼容性设置
信息查看
0.5.其他有待理解记录的内容
例如:vrrp组 负载分担等细节问题。之后将对其进行介绍
0.5.1.VRRP与动态路由协议
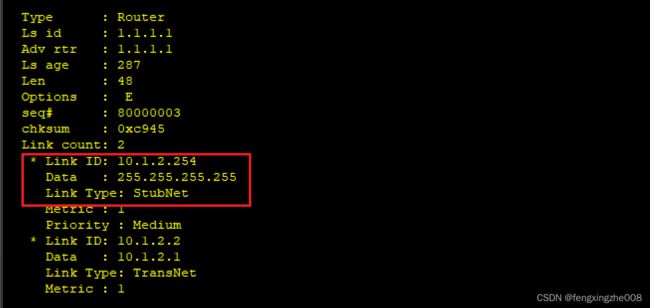
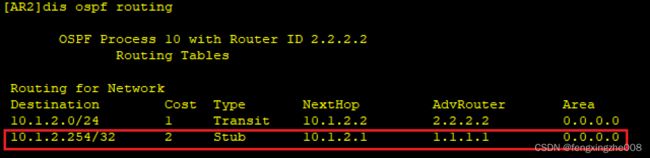
将虚拟IP作为一条主机路由进行通告,作为协议叶子路由存在。但引入额外的cost。
OSPF
ISIS
只有network才生成相应的主机路由。
0.5.2.VRRP与其他冗余协议
在M-LAG场景下启用VRRP时会展现双主状态。
version1.1-2022.10.06
RFC3768相比于RFC2338更新内容:
RFC3768未作过多改动,只删除了认证类型和认证字段的相关定义。并为了兼容RFC2338,将相应字段置0处理。并新增8.4章节 对潜在的环路进行分析。
详情请查看源文档。
此处简单说明,在配置了认证信息后。由于认证信息不匹配,有可能出现双主状态。
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol-RFC2338
(RFC2338已被RFC3768/5798更新替代)
备忘录声明:
本文档为网络交流指定了一种网络标准协议并处于改善协议的角度对其进行了讨论和给出建议。请参考"Internet Official Protocol Standards" (STD 1)了解该协议的标准化状态。该备忘录的转发不受限制。
Status of this Memo
This document specifies an Internet standards track protocol for the
Internet community, and requests discussion and suggestions for
improvements. Please refer to the current edition of the "Internet
Official Protocol Standards" (STD 1) for the standardization state
and status of this protocol. Distribution of this memo is unlimited.
版权声明
版权为网络协会(1998)所有,并保留所有权。
Copyright Notice
Copyright (C) The Internet Society (1998). All Rights Reserved.
摘要
本文档定义了一种虚拟路由冗余协议(VRRP)。VRRP为局域网定义了一个选举协议可在VRRP路由器中动态选举一个可靠的虚拟路由器。控制着与虚拟路由器相关IP地址的VRRP路由器被称为Master,并转发发往该IP地址的数据包。当Master不可用,将重新动态可靠的进行选举。这一行为使得在局域网上的任何一个虚拟路由器IP地址都可作为终端数据第一条路由器节点。这一优势使得VRRP具有高可用性而无需在每个终端上进行动态路由或路由发现协议的配置。
Abstract
This memo defines the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
VRRP specifies an election protocol that dynamically assigns
responsibility for a virtual router to one of the VRRP routers on a
LAN. The VRRP router controlling the IP address(es) associated with
a virtual router is called the Master, and forwards packets sent to
these IP addresses. The election process provides dynamic fail over
in the forwarding responsibility should the Master become
unavailable. This allows any of the virtual router IP addresses on
the LAN to be used as the default first hop router by end-hosts. The
advantage gained from using VRRP is a higher availability default
path without requiring configuration of dynamic routing or router
discovery protocols on every end-host.
1. Introduction...............................................Page 2
2. Required Features..........................................Page 5
3. VRRP Overview..............................................Page 6
4. Sample Configurations......................................Page 8
5. Protocol...................................................Page 9
5.1 VRRP Packet Format....................................Page 10
5.2 IP Field Descriptions.................................Page 10
5.3 VRRP Field Descriptions................................Page 11
6. Protocol State Machine.....................................Page 13
6.1 Parameters.............................................Page 13
6.2 Timers.................................................Page 15
6.3 State Transition Diagram...............................Page 15
6.4 State Descriptions.....................................Page 15
7. Sending and Receiving VRRP Packets.........................Page 18
7.1 Receiving VRRP Packets.................................Page 18
7.2 Transmitting Packets...................................Page 19
7.3 Virtual MAC Address....................................Page 19
8. Operational Issues.........................................Page 20
8.1 ICMP Redirects.........................................Page 20
8.2 Host ARP Requests......................................Page 20
8.3 Proxy ARP..............................................Page 20
9. Operation over FDDI and Token Ring.........................Page 21
9.1 Operation over FDDI....................................Page 21
9.2 Operation over Token Ring..............................Page 21
10. Security Considerations....................................Page 23
10.1 No Authentication.....................................Page 23
10.2 Simple Text Password..................................Page 23
10.3 IP Authentication Header..............................Page 24
11. Acknowledgments............................................Page 24
12. References.................................................Page 24
13. Authors' Addresses.........................................Page 25
14. Full Copyright Statement...................................Page 27
1.Introduction
实际上由很多方式可以为终端确定指向确切目的地址第一个路由节点。例如,运行动态路由协议,路由信息协议RIP,OSPFv2,运行ICMP路由器发现客户端或者配置静态路由。
There are a number of methods that an end-host can use to determine
its first hop router towards a particular IP destination. These
include running (or snooping) a dynamic routing protocol such as
Routing Information Protocol [RIP] or OSPF version 2 [OSPF], running
an ICMP router discovery client [DISC] or using a statically
configured default route.
在终端上运行动态路由协议是不切实际的,例如管理开销、进程开销、安全问题以及缺少协议实现的平台。邻居路由发现协议可能需要大量的活动终端参与网络,这将导致需要数倍的运算值进行大量终端接入导致的降低协议开销。这将导致在探测邻居过程中产生不可估量的延迟,不可接受的长时间的黑洞周期。
Running a dynamic routing protocol on every end-host may be infeasible for a number of reasons, including administrative overhead, processing overhead, security issues, or lack of a protocol implementation for some platforms. Neighbor or router discovery protocols may require active participation by all hosts on a network, leading to large timer values to reduce protocol overhead in the face of large numbers of hosts. This can result in a significant delay in the detection of a lost (i.e., dead) neighbor, which may introduce unacceptably long "black hole" periods.
静态路由的使用将会相当便捷,只需在终端上进行最小化的配置和进程开销。终端只需支持每个实现虚拟IP的配置。这种方式与DHCP的配置要求相近,DHCP只需在终端上配置IP和网关即可。然而,如果产生单点故障,默认路由消失将会造成灾难性后果。所有终端主机将无法检测到任何可用备用路径的。
The use of a statically configured default route is quite popular; it minimizes configuration and processing overhead on the end-host and is supported by virtually every IP implementation. This mode of operation is likely to persist as dynamic host configuration protocols [DHCP] are deployed, which typically provide configuration for an end-host IP address and default gateway. However, this creates a single point of failure. Loss of the default router results in a catastrophic event, isolating all end-hosts that are unable to detect any alternate path that may be available.
VRRP协议的问世用于消除在静态路由故障场景下单点故障导致的网络异常。VRRP提供了一种选举协议用于在局域网上为VRRP路由器动态指定一个靠靠可靠的虚拟路由器。具有虚拟路由器IP地址的VRRP路由器称为Master,并转发发向这些IP地址的数据包。当Master不可用,将重新动态可靠的进行选举。局域网上的任何一个虚拟路由器IP都可作为终端的第一跳路由器节点。这一优势使得VRRP具有高可用性而无需在每个终端上进行动态路由或路由发现协议的配置。
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is designed to eliminate the single point of failure inherent in the static default routed environment. VRRP specifies an election protocol that
dynamically assigns responsibility for a virtual router to one of the VRRP routers on a LAN. The VRRP router controlling the IP address(es) associated with a virtual router is called the Master, and forwards packets sent to these IP addresses. The election process provides dynamic fail-over in the forwarding responsibility should the Master become unavailable. Any of the virtual router's IP addresses on a LAN can then be used as the default first hop router by end-hosts. The advantage gained from using VRRP is a higher availability default path without requiring configuration of dynamic routing or router discovery protocols on every end-host.
VRRP提供了一个与CISIO系统相似的功能。这一功能相近的协议由路由热备协议HSRP。与Digital Equipment Corporation公司相近的协议IP备份协议IPSTB。
VRRP provides a function similar to a Cisco Systems, Inc. proprietary protocol named Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) [HSRP] and to a Digital Equipment Corporation, Inc. proprietary protocol named IP Standby Protocol [IPSTB].
本文档对下列关键词的定义可在RFC 2119中找到。必须、必须不、需要、应当、应当不、应该、应该不、推荐、可能、可能不、自选。
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this document are to be interpreted as described in [RFC 2119].
IESG/IETF对可能声称与技术的实施或使用有关的任何知识产权或其他权利的有效性或范围,或此类权利下的任何许可可能或可能不可用的程度不采取任何立场。 有关其他信息,请参阅 http://www.ietf.org/ipr.html IETF 知识产权网页。
The IESG/IETF take no position regarding the validity or scope of any intellectual property right or other rights that might be claimed to pertain to the implementation or use of the technology, or the extent to which any license under such rights might or might not be available. See the IETF IPR web page at http://www.ietf.org/ipr.html for additional information.
1.1范围
本文档的其余部分将介绍 VRRP 的功能、设计目标和操作理论。 介绍了消息格式、协议处理规则和状态机,以确保与单个虚拟路由器主服务器会聚。 最后,解决了与 MAC 地址映射、ARP 请求的处理、ICMP 重定向消息的生成以及安全问题相关的操作问题。
本协议只用于IPv4路由器。IPv6环境相应功能的实现将生成单独规范。
The remainder of this document describes the features, design goals, and theory of operation of VRRP. The message formats, protocol processing rules and state machine that guarantee convergence to a single Virtual Router Master are presented. Finally, operational issues related to MAC address mapping, handling of ARP requests, generation of ICMP redirect messages, and security issues are addressed.
This protocol is intended for use with IPv4 routers only. A separate specification will be produced if it is decided that similar functionality is desirable in an IPv6 environment.
1.2定义
VRRP 路由器:运行了VRRP协议的路由器。其可能包含1个或多个虚拟路由器
虚拟路由器:一个由VRRP产生的抽象对象,作为一个共享局域网上终端的默认网关。由一个虚拟路由器ID和一系列横跨公共局域网的IP地址相关联。一个VRRP路由器有可能成为1个或多个虚拟路由器的备份。
IP地址具有者:将虚拟路由器IP地址作为真接口地址的VRRP路由器。IP地址拥有者在UP状态下响应发向该地址的ICMP、TCP连接等的数据包。
主IP地址:被选举出具有真接口IP地址的IP地址。一个可能选举算法是总是选举第一个地址。VRRP通告报文总是将主IP地址作为IP包的源地址。
虚拟路由器Master:VRRP路由器选举出用于处理转发给具有虚拟路由器IP地址的报文。如ARP请求等。注意的是如果IP地址拥有者可能,则其总是Master
虚拟路由器Backup:选举虚拟路由器Master失败的路由器。
VRRP Router
A router running the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol. It may participate in one or more virtual routers.
Virtual Router
An abstract object managed by VRRP that acts as a default router for hosts on a shared LAN. It consists of a Virtual Router Identifier and a set of associated IP address(es) across a common LAN. A VRRP Router may backup one or more virtual routers.
IP Address Owner
The VRRP router that has the virtual router's IP address(es) as real interface address(es). This is the router that, when up, will respond to packets addressed to one of these IP addresses for ICMP pings, TCP connections, etc.
Primary IP Address
An IP address selected from the set of real interface addresses. One possible selection algorithm is to always select the first address. VRRP advertisements are always sent using the primary IP address as the source of the IP packet.
Virtual Router Master
The VRRP router that is assuming the responsibility of forwarding packets sent to the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router, and answering ARP requests for these IP addresses. Note that if the IP address owner is available, then it will always become the Master.
Virtual Router Backup
The set of VRRP routers available to assume forwarding responsibility for a virtual router should the current Master fail.
2.所需功能
本节概述了被认为是强制性的并指导VRRP设计的一组功能。
This section outlines the set of features that were considered mandatory and that guided the design of VRRP.
2.1IP地址备份
IP地址备份说VRRP协议的首要功能。虚拟路由器Master选举及其额外功能描述如下,协议应该努力:
-最小的黑洞周期
-最小的带宽载荷和过程复杂度
-支持 IP 流量的各种多路访问 LAN 技术。
-提供在网络上选择多个虚拟路由器以实现负载平衡
-支持在单个局域网段上存在多个逻辑IP子网
Backup of IP addresses is the primary function of the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol. While providing election of a Virtual Router Master and the additional functionality described below, the protocol should strive to:
- Minimize the duration of black holes.
- Minimize the steady state bandwidth overhead and processing complexity.
- Function over a wide variety of multiaccess LAN technologies capable of supporting IP traffic.
- Provide for election of multiple virtual routers on a network for load balancing
- Support of multiple logical IP subnets on a single LAN segment.
2.2偏好路径指示
一个在大量路由器间的Master的简易选举应该把每个路由器都看作具有同等优先级,并可以成功收敛出Master。但是,在很多环境中,冗余路由器集之间可能存在明显的偏好(或偏好范围)。 例如,此首选项可能基于接入链路的成本或速度、路由器性能或可靠性,或其它策略注意事项。 该协议应允许以直观的方式表达此相对路径首选项,并保证主路由器收敛到当前可用的最优先路由器。
A simple model of Master election among a set of redundant routers is to treat each router with equal preference and claim victory after converging to any router as Master. However, there are likely to be many environments where there is a distinct preference (or range of preferences) among the set of redundant routers. For example, this preference may be based upon access link cost or speed, router performance or reliability, or other policy considerations. The protocol should allow the expression of this relative path preference in an intuitive manner, and guarantee Master convergence to the most preferential router currently available.
2.3最小化非必要服务的干扰
一旦Master选举完成,Master和Backup之间的任何不必要的转换都可能导致服务中断。 该协议应确保在主路由器选择后,只要主路由器继续正常运行,任何具有相同或较低优先级的备份路由器都不会触发任何状态转换。
Once Master election has been performed then any unnecessary transitions between Master and Backup routers can result in a disruption in service. The protocol should ensure after Master election that no state transition is triggered by any Backup router of equal or lower preference as long as the Master continues to function properly
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 5]
某些环境可能会发现,避免在路由器可用时比当前Master更优先导致的状态转换是有益的。 支持覆盖直接收敛到首选路径可能很有用。
Some environments may find it beneficial to avoid the state transition triggered when a router becomes available that is more preferential than the current Master. It may be useful to support an override of the immediate convergence to the preferred path.
2.4扩展安全
虚拟路由器功能适用于可能采用不同安全策略的各种互联环境。 该协议应该在不安全的操作中需要最少的配置和开销,在需要提高安全性时提供强身份验证,并允许在不破坏向后兼容操作的情况下集成新的安全机制。
The virtual router functionality is applicable to a wide range of internetworking environments that may employ different security policies. The protocol should require minimal configuration and overhead in the insecure operation, provide for strong authentication when increased security is required, and allow integration of new security mechanisms without breaking backwards compatible operation.
2.5在扩展局域网上高效工作
在多路访问局域网上发送IP包需要IP和Mac之间的映射。在使用学习网桥的扩展 LAN 中使用虚拟路由器 MAC 地址可能会对发送到虚拟路由器的数据包的带宽开销产生重大影响。 如果虚拟路由器 MAC 地址从未用作链路级帧中的源地址,则永远不会知道工作站位置,从而导致所有数据包泛洪虚拟路由器。 为了提高这种环境下的效率,协议应该:1)使用虚拟路由器MAC作为Master发送的数据包中的源来触发站学习;2)转换到Master后立即触发消息,更新站学习;3)Master周期性触发消息,以维护站学习缓存。
Sending IP packets on a multiaccess LAN requires mapping from an IP address to a MAC address. The use of the virtual router MAC address in an extended LAN employing learning bridges can have a significant effect on the bandwidth overhead of packets sent to the virtual router. If the virtual router MAC address is never used as the source address in a link level frame then the station location is never learned, resulting in flooding of all packets sent to the virtual router. To improve the efficiency in this environment the protocol should: 1) use the virtual router MAC as the source in a packet sent by the Master to trigger station learning; 2) trigger a message immediately after transitioning to Master to update the station learning; and 3) trigger periodic messages from the Master to maintain the station learning cache.
Note:免费ARP?
3.VRRP概述
VRRP 指定一个选择协议来提供前面描述的虚拟路由器功能。 所有协议消息传递都使用IP组播数据报执行,因此该协议可以在支持IP组播的各种多路访问LAN技术上运行。 每个 VRRP 虚拟路由器都有一个分配给它的已知 MAC 地址。 虚拟路由器 MAC 地址用作Master所有定期发送VRRP 消息的源地址,以便在扩展 LAN中进行网桥学习。
VRRP specifies an election protocol to provide the virtual router function described earlier. All protocol messaging is performed using IP multicast datagrams, thus the protocol can operate over a variety of multiaccess LAN technologies supporting IP multicast. Each VRRP virtual router has a single well-known MAC address allocated to it. This document currently only details the mapping to networks using the IEEE 802 48-bit MAC address. The virtual router MAC address is used as the source in all periodic VRRP messages sent by the Master router to enable bridge learning in an extended LAN.
一个虚拟路由器由其虚拟路由I和一系列IP地址所定义。一个VRRP路由器应该与虚拟路由器及其在接口上的实际地址相关联,还可以为其Backup的虚拟路由器配置其他虚拟路由器映射和优先级。 VRID 和地址之间的映射必须在局域网上的所有 VRRP 路由器之间协商一致。
A virtual router is defined by its virtual router identifier (VRID) and a set of IP addresses. A VRRP router may associate a virtual router with its real addresses on an interface, and may also be configured with additional virtual router mappings and priority for virtual routers it is willing to backup. The mapping between VRID and addresses must be coordinated among all VRRP routers on a LAN.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 6]
但是,对于在不同的 LAN 上重用具有不同地址映射的 VRID 没有限制。 每个虚拟路由器的作用域仅限于单个 LAN。
However, there is no restriction against reusing a VRID with a different address mapping on different LANs. The scope of each virtual router is restricted to a single LAN.
为了最小化网络负载,只有每个虚拟路由器的Master周期发送VRRP通告报文,一个备份路由器将不会试图尝试成为Master除非其具有更高优先级。在没有更好路径条件下这将最小化服务中断的影响。也可以人为禁止所有抢占式尝试。 唯一的例外是 VRRP 路由器将始终成为与其拥有的地址关联的任何虚拟路由器的Master。 如果Master变得不可用,则最高优先级的备份将在短暂延迟后转换为Master,从而以最小的服务中断提供虚拟路由器责任的受控转换。
To minimize network traffic, only the Master for each virtual router sends periodic VRRP Advertisement messages. A Backup router will not attempt to pre-empt the Master unless it has higher priority. This eliminates service disruption unless a more preferred path becomes available. It's also possible to administratively prohibit all pre-emption attempts. The only exception is that a VRRP router will always become Master of any virtual router associated with addresses it owns. If the Master becomes unavailable then the highest priority Backup will transition to Master after a short delay, providing a controlled transition of the virtual router responsibility with minimal service interruption.
VRRP 定义了三种类型的身份验证,可在不安全的环境中提供简单部署,增加对配置错误的保护,以及在安全意识环境中提供强身份验证。对提供保护的分析,以及每个机制的漏洞都推迟到第 10.0 节“安全注意事项”。考虑到未来可能定义新的认证类型和数据而不影响到协议数据包的格式修补,从而保持向后兼容的操作。
VRRP defines three types of authentication providing simple deployment in insecure environments, added protection against misconfiguration, and strong sender authentication in security conscious environments. Analysis of the protection provided and vulnerability of each mechanism is deferred to Section 10.0 Security Considerations. In addition new authentication types and data can be defined in the future without affecting the format of the fixed portion of the protocol packet, thus preserving backward compatible operation.
VRRP 协议设计提供了从Backup到Master的快速转换,以最大限度地减少服务中断,并结合了可降低协议复杂性的优化,同时保证了典型操作场景的受控Master转换。优化会产生具有最小运行时状态要求、最小活动协议状态以及单个消息类型和发送方的选举协议。 典型的操作方案定义为两个冗余路由器和/或每个路由器之间的不同路径优先级。当违反这些假设(即,两条以上的冗余路径都具有相同的优先级)时,一个副作用是重复的数据包可能会在主选举期间短暂转发。 但是,典型的场景假设很可能覆盖绝大多数部署,Maseter的丢失并不常见,并且主选举收敛的预期持续时间相当小(<<1秒)。因此,VRRP优化代表了协议设计中的显着简化,同时产生了短暂的网络降级的微小概率。
The VRRP protocol design provides rapid transition from Backup to Master to minimize service interruption, and incorporates optimizations that reduce protocol complexity while guaranteeing controlled Master transition for typical operational scenarios. The optimizations result in an election protocol with minimal runtime state requirements, minimal active protocol states, and a single message type and sender. The typical operational scenarios are defined to be two redundant routers and/or distinct path preferences among each router. A side effect when these assumptions are violated (i.e., more than two redundant paths all with equal preference) is that duplicate packets may be forwarded for a brief period during Master election. However, the typical scenario assumptions are likely to cover the vast majority of deployments, loss of the Master router is infrequent, and the expected duration in Master election convergence is quite small ( << 1 second ). Thus the VRRP optimizations represent significant simplifications in the protocol design while incurring an insignificant probability of brief network degradation.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 6]
4.简易配置
4.1简易配置1
下图展示了一个具有两个VRRP路由器产生一个虚拟路由器的简单网络。值得注意的时这个例子可供理解VRRP协议,但是并不一定出现于实际环境中
The following figure shows a simple network with two VRRP routers implementing one virtual router. Note that this example is provided to help understand the protocol, but is not expected to occur in actual practice.
上面的配置显示了一个非常简单的VRRP场景。在该场景中中断配置了一个走向IP A的缺省路由,两台路由器都运行VRRP协议。左边路由器成为虚拟路由器的Master(VRID=1),右边路由器成为虚拟路由器的Backup。如果左边路由器失效,其他路由器将会接替虚拟路由器#1及其IP地址并为主机提供不中断服务。
The above configuration shows a very simple VRRP scenario. In this configuration, the end-hosts install a default route to the IP address of virtual router #1 (IP A) and both routers run VRRP. The router on the left becomes the Master for virtual router #1 (VRID=1) and the router on the right is the Backup for virtual router #1. If the router on the left should fail, the other router will take over virtual router #1 and its IP addresses, and provide uninterrupted service for the hosts.
请注意,在此示例中,左侧的路由器未备份 IP B。 IP B仅由右侧的路由器用作其接口地址。 为了备份 IP B,必须配置第二个虚拟路由器。 这将在下一节中显示。
Note that in this example, IP B is not backed up by the router on the left. IP B is only used by the router on the right as its interface address. In order to backup IP B, a second virtual router would have to be configured. This is shown in the next section.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 8]
4.2简易配置2
下图展示了一个具有两个VRRP路由器的简单网络,主机将在其中进行流量分担。这个例子在实际环境中预期比较常见。
The following figure shows a configuration with two virtual routers with the hosts spitting their traffic between them. This example is expected to be very common in actual practice.
在上面的配置中,一半的主机安装到虚拟路由器 #1 的 IP 地址 (IP A) 的默认路由,另一半的主机安装到虚拟路由器 #2 的 IP 地址 (IP B) 的默认路由。 这具有对传出流量进行负载平衡的效果,同时还提供完全冗余。
In the above configuration, half of the hosts install a default route to virtual router #1's IP address (IP A), and the other half of the hosts install a default route to virtual router #2's IP address (IP B). This has the effect of load balancing the outgoing traffic, while also providing full redundancy.
5.协议
VRRP 数据包的目的是向所有 VRRP 路由器传达与虚拟路由器ID关联的主路由器的优先级和状态。
VRRP 数据包以 IP 数据包封装的方式发送。它们被发送到分配给VRRP的 IPv4 组播地址。
The purpose of the VRRP packet is to communicate to all VRRP routers the priority and the state of the Master router associated with the Virtual Router ID.
VRRP packets are sent encapsulated in IP packets. They are sent to the IPv4 multicast address assigned to VRRP.
5.1 VRRP数据包格式
本节定义 VRRP 数据包的格式以及 IP 报头中的相关字段。
This section defines the format of the VRRP packet and the relevant fields in the IP header.
5.2IP段描述
5.2.1源地址
从中发送数据包的接口的主 IP 地址。
The primary IP address of the interface the packet is being sent from.
5.2.2目的地址
由IANA为VRRP指定的IP组播地址为:224.0.0.18
这是一个链路本地组播地址。路由器无视TTL一定不会转发目的地址为该地址的数据包。
The IP multicast address as assigned by the IANA for VRRP is:
224.0.0.18
This is a link local scope multicast address. Routers MUST NOT forward a datagram with this destination address regardless of its TTL.
5.2.3 TTL
TTL一定被设置为255。一个VRRP路由器收到一个非TTL=255的包将会丢弃该报文。
The TTL MUST be set to 255. A VRRP router receiving a packet with the TTL not equal to 255 MUST discard the packet.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 10]
5.2.4协议
IANA为VRRP指定IP协议号为112。(十进制)
The IP protocol number assigned by the IANA for VRRP is 112 (decimal).
5.3VRRP字段描述
5.3.1 Version
Version字段定义了VRRP协议报文包的版本号。本文档定义为Version2。
The version field specifies the VRRP protocol version of this packet. This document defines version 2.
5.3.2类型
type字段定义了该VRRP数据包的类型。在本版本只定义了一种数据包
1 Advertise
未知类型数据包将会被丢弃
The type field specifies the type of this VRRP packet. The only packet type defined in this version of the protocol is:
1 ADVERTISEMENT
A packet with unknown type MUST be discarded.
5.3.3虚拟路由器ID(VRID)
虚拟路由器ID字段定义了此数据包报告其状态的虚拟路由器。
The Virtual Router Identifier (VRID) field identifies the virtual router this packet is reporting status for.
5.3.4优先级
优先级字段指定发送 VRRP 路由器对虚拟路由器的优先级。值越高,优先级越高。 此字段是一个 8 位无符号整数字段。
拥有与虚拟路由器关联的 IP 地址的 VRRP 路由器的优先级值必须为 255(十进制)。
备份虚拟路由器的 VRRP 路由器必须使用介于 1-254(十进制)之间的优先级值。 备份虚拟路由器的 VRRP 路由器的默认优先级值为 100(十进制)。
优先级值零(0)具有特殊含义,表示当前主服务器已停止参与 VRRP。 这用于触发备份路由器快速转换为主路由器,而不必等待当前主路由器超时。
The priority field specifies the sending VRRP router's priority for the virtual router. Higher values equal higher priority. This field is an 8 bit unsigned integer field.
The priority value for the VRRP router that owns the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router MUST be 255 (decimal).
VRRP routers backing up a virtual router MUST use priority values between 1-254 (decimal). The default priority value for VRRP routers backing up a virtual router is 100 (decimal).
The priority value zero (0) has special meaning indicating that the current Master has stopped participating in VRRP. This is used to trigger Backup routers to quickly transition to Master without having to wait for the current Master to timeout.
5.3.5IP地址数量
VRRP通告报文中的IP地址数目
The number of IP addresses contained in this VRRP advertisement.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 11]
5.3.6认证类型
认证类型字段标识正在使用的身份验证方法。身份验证类型在每个接口上都是唯一的。认证类型字段是 8 位无符号整数。必须丢弃具有未知身份验证类型或与本地配置的身份验证方法不匹配的数据包。
当前定义的认证方式有:
0-无认证
1-简易认证
2-IP头认证
The authentication type field identifies the authentication method being utilized. Authentication type is unique on a per interface basis. The authentication type field is an 8 bit unsigned integer. A packet with unknown authentication type or that does not match the locally configured authentication method MUST be discarded.
The authentication methods currently defined are:
0 - No Authentication
1 - Simple Text Password
2 - IP Authentication Header
5.3.6.1无认证
使用此身份验证类型意味着不对 VRRP 协议交换进行身份验证。“身份验证数据”字段的内容在传输时应设置为零,在接收时应忽略。
The use of this authentication type means that VRRP protocol exchanges are not authenticated. The contents of the Authentication Data field should be set to zero on transmission and ignored on reception.
5.3.6.2简易文字认证
使用此身份验证类型意味着 VRRP 协议交换通过明文密码进行身份验证。 “身份验证数据”字段的内容应设置为传输时本地配置的密码。没有默认密码。接收方必须检查数据包中的身份验证数据是否与其配置的身份验证字符串匹配。必须丢弃不匹配的数据包。
请注意,使用简单文本密码身份验证存在安全隐患,应参阅本文档的安全注意事项部分。
The use of this authentication type means that VRRP protocol exchanges are authenticated by a clear text password. The contents of the Authentication Data field should be set to the locally configured password on transmission. There is no default password. The receiver MUST check that the Authentication Data in the packet matches its configured authentication string. Packets that do not match MUST be discarded.
Note that there are security implications to using Simple Text password authentication, and one should see the Security Consideration section of this document.
5.3.6.3IP头认证
使用此身份验证类型意味着 VRRP 协议交换使用 IP 身份验证标头 [AUTH] 定义的机制进行身份验证,该机制使用“在 ESP 和 AH 中使用 HMAC-MD5-96”[HMAC]。 密钥可以手动配置,也可以通过密钥分发协议进行配置。
如果收到的数据包由于缺少身份验证标头或消息摘要不正确而未通过身份验证检查,则必须丢弃该数据包。 “身份验证数据”字段的内容在传输时应设置为零,在接收时应忽略。
The use of this authentication type means the VRRP protocol exchanges are authenticated using the mechanisms defined by the IP Authentication Header [AUTH] using "The Use of HMAC-MD5-96 within ESP and AH" [HMAC]. Keys may be either configured manually or via a key distribution protocol.
If a packet is received that does not pass the authentication check due to a missing authentication header or incorrect message digest, then the packet MUST be discarded. The contents of the Authentication Data field should be set to zero on transmission and ignored on reception.
5.3.7通告报文间隔
“播发间隔”指示播发之间的时间间隔(以秒为单位)。默认值为 1秒。 此字段用于对配置错误的路由器进行故障排除。
The Advertisement interval indicates the time interval (in seconds) between ADVERTISEMENTS. The default is 1 second. This field is used for troubleshooting misconfigured routers.
5.3.8校验和
校验和字段用于对VRRP报文检验。
校验和是从版本字段开始的整个 VRRP 消息的补码和的16位补码。 为了计算校验和,校验和字段设置为零。
The checksum field is used to detect data corruption in the VRRP message.
The checksum is the 16-bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of the entire VRRP message starting with the version field. For computing the checksum, the checksum field is set to zero.
5.3.9IP地址
与虚拟路由器关联的一个或多个 IP 地址。包含的地址数在“计算 IP 地址数”字段中指定。 这些字段用于对配置错误的路由器进行故障排除。
One or more IP addresses that are associated with the virtual router. The number of addresses included is specified in the "Count IP Addrs" field. These fields are used for troubleshooting misconfigured routers.
5.3.10认证数据
认证字符串目前仅用于简单文本身份验证,类似于在开放最短路径优先路由协议 [OSPF] 中找到的简单文本身份验证。它最多包含8个字符的纯文本。 如果配置的身份验证字符串短于 8 个字节,则剩余空间必须为零填充。必须丢弃接收到的任何具有与本地配置的身份验证字符串不匹配的身份验证字符串的 VRRP 数据包。认证字符串在每个接口上具有唯一性。
该字段无默认值。
The authentication string is currently only utilized for simple text authentication, similar to the simple text authentication found in the Open Shortest Path First routing protocol [OSPF]. It is up to 8 characters of plain text. If the configured authentication string is shorter than 8 bytes, the remaining space MUST be zero-filled. Any VRRP packet received with an authentication string that does not match the locally configured authentication string MUST be discarded. The authentication string is unique on a per interface basis.
There is no default value for this field.
6.协议状态机制
6.1参数
6.1.1接口参数
认证类型-所使用的认证类型。相应值被定义于章节5.3.6
认证数据-认证数据对应于所使用的认证类型
Authentication_Type Type of authentication being used. Values are defined in section 5.3.6.
Authentication_Data Authentication data specific to the Authentication_Type being used.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 13]
6.1.2虚拟路由器参数
VRID-虚拟路由器ID。配置范围1-255(十进制)。无默认值。
优先级-此 VRRP 路由器在此虚拟路由器的主选项中使用的优先级值。 值为拥有与虚拟路由器关联的 IP 地址的路由器保留 255(十进制)。 值为 0(零)是为主路由器保留的,以指示它正在释放对虚拟路由器的责任。 范围 1-254(十进制)可用于备份虚拟路由器的 VRRP 路由器。默认值100(十进制)。
IP地址-与虚拟路由相关的一个或多个IP地址。无默认值。
通告间隔-通告时间间隔。默认值1s。
偏移时间-Master_Down_Interval偏移时间。计算公式为:
(256-Priority)/256
Master_Down_Interval-Backup等待转变为Master的时间。计算公式为:
3*Advertisement_Interval+偏移时间
抢占模式-控制高优先级Backup抢占低优先级Master。True表示允许抢占,False表示禁止抢占。默认为True。
注意:例外情况是,拥有与虚拟路由器关联的 IP 地址的路由器始终独立于此标志的设置而抢占。
VRID
Virtual Router Identifier. Configured item in the range 1-255 (decimal). There is no default.
Priority
Priority value to be used by this VRRP router in Master election for this virtual router. The value of 255 (decimal) is reserved for the router that owns the IP addresses associated with the virtual router. The value of 0 (zero) is reserved for Master router to indicate it is releasing responsibility for the virtual router. The range 1-254 (decimal) is available for VRRP routers backing up the virtual router. The default value is 100 (decimal).
IP_Addresses
One or more IP addresses associated with this virtual router. Configured item. No default.
Advertisement_Interval
Time interval between ADVERTISEMENTS (seconds). Default is 1 second.
Skew_Time
Time to skew Master_Down_Interval in seconds. Calculated as:
( (256 - Priority) / 256 )
Master_Down_Interval
Time interval for Backup to declare Master down (seconds). Calculated as:
(3 * Advertisement_Interval) + Skew_time
Preempt_Mode
Controls whether a higher priority Backup router preempts a lower priority Master. Values are True to allow preemption and False to not prohibit preemption. Default is True.
Note: Exception is that the router that owns the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router always pre-empts independent of the setting of this flag.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 14]
6.2定时器
Master down定时器-在 Master_Down_Interval 未听到通告时触发的定时器。
通告时间定时器-基于通告间隔触发通告报文的定时器
Master_Down_Timer
Timer that fires when ADVERTISEMENT has not been heard for Master_Down_Interval.
Adver_Timer
Timer that fires to trigger sending of ADVERTISEMENT based on Advertisement_Interval.
6.3状态转变图
6.4状态描述
在下面的状态描述中,状态名称由 {state-name} 标识,数据包由所有大写字符标识。
VRRP 路由器为其参与的每个虚拟路由器选举实现状态机的实例。
In the state descriptions below, the state names are identified by {state-name}, and the packets are identified by all upper case characters.
A VRRP router implements an instance of the state machine for each virtual router election it is participating in.
6.4.1Initialize
这一状态为事件变化的起始状态。如果起始状态触发,则:
如果优先级=255(该情况为路由器具有虚拟路由器IP)
-发送通告报文
-广播免费ARP通告每个具有虚拟路由器IP一一对应的虚拟路由mac地址
-设置通告定时器为通告报文间隔
-过渡到Master状态
The purpose of this state is to wait for a Startup event. If a Startup event is received, then:
- If the Priority = 255 (i.e., the router owns the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router)
o Send an ADVERTISEMENT
o Broadcast a gratuitous ARP request containing the virtual router MAC address for each IP address associated with the virtual router.
o Set the Adver_Timer to Advertisement_Interval
o Transition to the {Master} state
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 14]
或者
-设置Master_Down_Timer定时器等于Master_Down_Interval
-过渡到Backup状态
else
o Set the Master_Down_Timer to Master_Down_Interval
o Transition to the {Backup} state
6.4.2Backup
Backup状态用于监控可用的Master 路由器状态
The purpose of the {Backup} state is to monitor the availability and state of the Master Router.
while进入此状态的VRRP路由必须进行如下操作:
-必须不响应具有虚拟路由器IP的ARP请求
-必须丢弃目的地址为链路层MAC等于虚拟路由器MAC的包
-必须不接受等于虚拟路由器IP的包
if收到shutdown事件,将:
-取消Master_Down_Timer
-转变为Initialize状态
endif
if Master_Down_Timer定时器清零,将
-发送通告报文
-广播免费ARP通告每个具有虚拟路由器IP一一对应的虚拟路由mac地址
-设置通告定时器为通告报文间隔
-过渡到Master状态
endif
if收到通告报文,将
if通告报文优先级为0,将
-Master_Down_Timer设置为Skew_Time。
else
if不设置抢占或者有通告报文优先级比自身更大,将
-重置Master_Down_Timer为Master_Down_Interval
else
-丢弃通告报文
endif
endif
endif
While in this state, a VRRP router MUST do the following:
- MUST NOT respond to ARP requests for the IP address(s) associated
with the virtual router.
- MUST discard packets with a destination link layer MAC address
equal to the virtual router MAC address.
- MUST NOT accept packets addressed to the IP address(es) associated
with the virtual router.
- If a Shutdown event is received, then:
o Cancel the Master_Down_Timer
o Transition to the {Initialize} state
endif
- If the Master_Down_Timer fires, then:
o Send an ADVERTISEMENT
o Broadcast a gratuitous ARP request containing the virtual
router MAC address for each IP address associated with the
virtual router
o Set the Adver_Timer to Advertisement_Interval
o Transition to the {Master} state
endif
- If an ADVERTISEMENT is received, then:
If the Priority in the ADVERTISEMENT is Zero, then:
o Set the Master_Down_Timer to Skew_Time
else:
If Preempt_Mode is False, or If the Priority in the
ADVERTISEMENT is greater than or equal to the local
Priority, then:
o Reset the Master_Down_Timer to Master_Down_Interval
else:
o Discard the ADVERTISEMENT
endif
endif
endif
6.4.3Master
处于Master状态的路由器为具有虚拟路由器IP地址的路由器
While in the {Master} state the router functions as the forwarding router for the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router.
while在该状态,一个VRRP路由器必须:
-必须回应具有虚拟路由器IP地址的ARP请求
-必须转发链路层MAC目的地址为虚拟路由器MAC的数据包
-如果虚拟路由器不是 IP 地址所有者,则不得接受发往与虚拟路由器关联的 IP 地址的数据包。
-必须接受发往与虚拟路由器关联的 IP 地址的数据包
-if一个shutdown时间触发,则
-取消Adver_Timer定时器
-发送通告报文优先级=0的报文
-过渡到Initialize状态
endif
if Adver_Timer定时器清零,则
-发发送一个通告报文
-重置Adver_Timer定时器=Advertisement_Interval
endif
if收到一个通告报文,则
if通告报文优先级=0,则
-发送通告报文
-重置Adver_Timer定时器=Advertisement_Interval
else
if通告报文优先级>自身
或者
if通告报文优先级=自身,但发送者的IP地址大于本地,则
-取消Adver_Timer
-设置Master_Down_Timer=Master_Down_Interval
-过渡到Backup状态
else
-丢弃通告报文
endif
endif
endif
While in this state, a VRRP router MUST do the following:
- MUST respond to ARP requests for the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router.
- MUST forward packets with a destination link layer MAC address equal to the virtual router MAC address.
- MUST NOT accept packets addressed to the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router if it is not the IP address owner.
- MUST accept packets addressed to the IP address(es) associated with the virtual router if it is the IP address owner.
- If a Shutdown event is received, then:
o Cancel the Adver_Timer
o Send an ADVERTISEMENT with Priority = 0
o Transition to the {Initialize} state
endif
- If the Adver_Timer fires, then:
o Send an ADVERTISEMENT
o Reset the Adver_Timer to Advertisement_Interval
endif
- If an ADVERTISEMENT is received, then:
If the Priority in the ADVERTISEMENT is Zero, then:
o Send an ADVERTISEMENT
o Reset the Adver_Timer to Advertisement_Interval
else:
If the Priority in the ADVERTISEMENT is greater than the local Priority,
or
If the Priority in the ADVERTISEMENT is equal to the local Priority and the primary IP Address of the sender is greater than the local primary IP Address, then:
o Cancel Adver_Timer
o Set Master_Down_Timer to Master_Down_Interval
o Transition to the {Backup} state
else:
o Discard ADVERTISEMENT
endif
endif
endif
7.发送和接受VRRP报文
7.1接收VRRP报文
接收VRRP报文时进行如下功能
-必须验证IP TTL=255
-必须验证VRRP 版本
-必须验证接收包的长度>=VRRP头
-必须验证VRRP的校验和
-必须展示认证类型相关的认证数据
如果上述任何一个检查失败,接收者将丢弃报文,应当记录日志并可以通过网管上报错误发生。
Performed the following functions when a VRRP packet is received:
- MUST verify that the IP TTL is 255.
- MUST verify the VRRP version
- MUST verify that the received packet length is greater than or equal to the VRRP header
- MUST verify the VRRP checksum
- MUST perform authentication specified by Auth Type
If any one of the above checks fails, the receiver MUST discard the packet, SHOULD log the event and MAY indicate via network management that an error occurred.
-必须检查VRID在接受端口的可用性
如果上述任何一个检查失败,接收者将丢弃报文
- MUST verify that the VRID is valid on the receiving interface If the above check fails, the receiver MUST discard the packet.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 18]
可以检查与IP地址相关联的VRID的可用性
如果上述项检查失败,接收者应当应当记录日志并可以通过网管上报检测到错误配置。如果数据包非IP地址拥有者发送,接收者必须丢弃报文。随后继续该过程
- MAY verify that the IP address(es) associated with the VRID are valid
If the above check fails, the receiver SHOULD log the event and MAY indicate via network management that a misconfiguration was detected. If the packet was not generated by the address owner (Priority does not equal 255 (decimal)), the receiver MUST drop the packet, otherwise continue processing.
必须验证报文中数据间隔与本地虚拟路由器配置是否相同
如果上述项检查失败,接收者必须丢弃报文,应当记录日志并可以通过网管上报检测到错误配置。
- MUST verify that the Adver Interval in the packet is the same as the locally configured for this virtual router If the above check fails, the receiver MUST discard the packet, SHOULD log the event and MAY indicate via network management that a misconfiguration was detected.
7.2传输VRRP数据包
传输VRRP数据包必须执行以下操作:
- 使用适当的虚拟路由器配置状态填写 VRRP 数据包字段
- 计算 VRRP 校验和
- 将源 MAC 地址设置为虚拟路由器MAC地址
- 将源 IP 地址设置为接口主IP地址
- 将 IP 协议设置为 VRRP
- 将 VRRP 数据包发送到 VRRP 网络多播组
注意:VRRP数据包使用虚拟路由器MAC地址作为源地址确保学习网桥能正确探测到使用的虚拟路由器局域网段
The following operations MUST be performed when transmitting a VRRP
packet.
- Fill in the VRRP packet fields with the appropriate virtual
router configuration state
- Compute the VRRP checksum
- Set the source MAC address to Virtual Router MAC Address
- Set the source IP address to interface primary IP address
- Set the IP protocol to VRRP
- Send the VRRP packet to the VRRP IP multicast group
Note: VRRP packets are transmitted with the virtual router MAC address as the source MAC address to ensure that learning bridges correctly determine the LAN segment the virtual router is attached to.
7.3虚拟路由器MAC地址
虚拟路由器MAC地址采用如下格式:
00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID} (网络标准位序中的十六进制)
前三个字节由IANA的OUI分配,紧接着的00-01表明地址族为VRRP协议。VRID表示VRRP虚拟路由器ID。
此映射在网络上最多可提供255个VRRP 路由器。
The virtual router MAC address associated with a virtual router is an IEEE 802 MAC Address in the following format:
00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID} (in hex in internet standard bit-order)
The first three octets are derived from the IANA's OUI. The next two octets (00-01) indicate the address block assigned to the VRRP protocol. {VRID} is the VRRP Virtual Router Identifier. This
mapping provides for up to 255 VRRP routers on a network.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 19]
8.使用问题
8.1ICMP重定向
当VRRP在一组路由器之间运行时,可以正常使用ICMP重定向。这允许在拓扑不对称的环境中使用 VRRP。
ICMP重定向的IP源地址应是最终主机在做出下一跃点路由决策时使用的地址。如果 VRRP路由器充当包含其不拥有的地址的虚拟路由器的Master,则在选择重定向源地址时,它必须确定数据包发送到哪个虚拟路由器。推断所使用的虚拟路由器的一种方法是检查触发重定向的数据包中的目标MAC地址。
对于使用 VRRP 在对称拓扑中的多个路由器之间加载共享流量的特定情况,禁用重定向可能很有用。
ICMP Redirects may be used normally when VRRP is running between a group of routers. This allows VRRP to be used in environments where the topology is not symmetric.
The IP source address of an ICMP redirect should be the address the end host used when making its next hop routing decision. If a VRRP router is acting as Master for virtual router(s) containing addresses it does not own, then it must determine which virtual router the packet was sent to when selecting the redirect source address. One method to deduce the virtual router used is to examine the destination MAC address in the packet that triggered the redirect.
It may be useful to disable Redirects for specific cases where VRRP is being used to load share traffic between a number of routers in a symmetric topology.
8.2 主机ARP请求
当主机为其中一个虚拟路由器IP地址发送 ARP 请求时,主虚拟路由器必须使用虚拟路由器的虚拟MAC地址响应 ARP 请求。 主虚拟路由器不得使用其物理MAC地址进行响应。 这允许客户端始终使用相同的MAC地址,而不管当前的主路由器如何。
当 VRRP 路由器重新启动或启动时,它不应发送任何 ARP 消息及其拥有 IP 地址的物理 MAC 地址,它只应发送包含虚拟 MAC 地址的 ARP 消息。 这可能需要:
-配置接口时,VRRP 路由器应广播免费ARP请求,其中包含该接口上每个 IP 地址的虚拟路由器 MAC 地址
-在系统启动时,初始化VRRP操作的接口时;延迟免费ARP请求和ARP响应,直到同时配置了 IP地址和虚拟路由器 MAC 地址。
When a host sends an ARP request for one of the virtual router IP addresses, the Master virtual router MUST respond to the ARP request with the virtual MAC address for the virtual router. The Master virtual router MUST NOT respond with its physical MAC address. This allows the client to always use the same MAC address regardless of the current Master router.
When a VRRP router restarts or boots, it SHOULD not send any ARP messages with its physical MAC address for the IP address it owns, it should only send ARP messages that include Virtual MAC addresses.
This may entail:
- When configuring an interface, VRRP routers should broadcast a gratuitous ARP request containing the virtual router MAC address for each IP address on that interface.
- At system boot, when initializing interfaces for VRRP operation; delay gratuitous ARP requests and ARP responses until both the IP address and the virtual router MAC address are configured.
8.3ARP代理
如果要在 VRRP 路由器上使用代理 ARP,则VRRP路由器必须在代理 ARP 消息中通告虚拟路由器MAC地址。 否则可能会导致主机了解VRRP路由器的真实MAC地址。
If Proxy ARP is to be used on a VRRP router, then the VRRP router must advertise the Virtual Router MAC address in the Proxy ARP message. Doing otherwise could cause hosts to learn the real MAC address of the VRRP router.
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 20]
9.在FDDI和Token Ring上的使用
9.1在FDDI上的使用
FDDI 接口从具有与设备硬件地址匹配的源 MAC 地址的 FDDI 环帧中删除。在某些情况下,例如路由器隔离,环形故障,协议转换等,VRRP可能会导致存在多个主路由器。如果主路由器将虚拟路由器MAC地址作为硬件地址安装在 FDDI 设备上,则在主路由器收敛期间,其他主路由器的通告将从环中删除,并且收敛将会失败。
FDDI interfaces remove from the FDDI ring frames that have a source
MAC address matching the device's hardware address. Under some
conditions, such as router isolations, ring failures, protocol
transitions, etc., VRRP may cause there to be more than one Master
router. If a Master router installs the virtual router MAC address
as the hardware address on a FDDI device, then other Masters'
ADVERTISEMENTS will be removed from the ring during the Master
convergence, and convergence will fail.
为避免这种情况,实现应通过在FDDI设备中添加单播MAC筛选器来配置虚拟路由器 MAC地址,而不是更改其硬件MAC地址。这将阻止Master删除它不是源自的任何通告。
To avoid this an implementation SHOULD configure the virtual router
MAC address by adding a unicast MAC filter in the FDDI device, rather
than changing its hardware MAC address. This will prevent a Master
router from removing any ADVERTISEMENTS it did not originate.
9.2在Token Ring上的使用
令牌环有几个特征使得其运行VRRP存在困难。他们包括;
-为了在使用源路由桥时切换到位于与先前Master不同的网桥令牌环段上的新Master,需要更新缓存的源路由信息。
-新旧令牌环适配器实现不支持任何通用多播机制。虽然许多较新的令牌环适配器支持组地址,但令牌环功能地址支持是唯一普遍可用的多播机制。由于令牌环功能地址的数量有限,这些地址可能会与相同令牌环功能地址的其他用法发生冲突。
Token ring has several characteristics which make running VRRP
difficult. These include:
- In order to switch to a new master located on a different bridge
token ring segment from the previous master when using source
route bridges, a mechanism is required to update cached source
route information.
- No general multicast mechanism supported across old and new token
ring adapter implementations. While many newer token ring adapters
support group addresses, token ring functional address support is
the only generally available multicast mechanism. Due to the
limited number of token ring functional addresses these may
collide with other usage of the same token ring functional
addresses.
剩下的也没看懂,不想看了。。。有意愿可参考原文。RFC 2338: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
10.安全性考虑
VRRP 专为可能采用不同安全策略的一系列互联环境而设计。 该协议包括多种身份验证方法,从无身份验证,简单的明文密码到使用MD5 HMAC的IP身份验证的强身份验证。 下面详细介绍了每种方法,包括可能的攻击和建议的环境。
独立于任何身份验证类型的 VRRP 包括一种机制(设置 TTL=255,在收到时检查),该机制可防止从另一个远程网络注入 VRRP 数据包。 这会将大多数漏洞限制为本地攻击。
VRRP is designed for a range of internetworking environments that may
employ different security policies. The protocol includes several
authentication methods ranging from no authentication, simple clear
text passwords, and strong authentication using IP Authentication
with MD5 HMAC. The details on each approach including possible
attacks and recommended environments follows.
Independent of any authentication type VRRP includes a mechanism
(setting TTL=255, checking on receipt) that protects against VRRP
packets being injected from another remote network. This limits most
vulnerabilities to local attacks.
10.1无认证
使用此身份验证类型意味着不对 VRRP 协议交换进行身份验证。 这种类型的身份验证应该只在安全风险最小且配置错误机会很小的环境中使用(例如,LAN上的两个VRRP路由器)。
The use of this authentication type means that VRRP protocol
exchanges are not authenticated. This type of authentication SHOULD
only be used in environments were there is minimal security risk and
little chance for configuration errors (e.g., two VRRP routers on a
LAN).
10.2简单文本密码
使用此身份验证类型意味着 VRRP 协议交换通过简单的明文密码进行身份验证。
The use of this authentication type means that VRRP protocol
exchanges are authenticated by a simple clear text password。
--------------------------------------------------------------------[Page 20]
这种类型的身份验证对于防止 LAN 上的路由器意外配置错误非常有用。 它可以防止路由器无意中备份另一个路由器。 新路由器必须先使用正确的密码进行配置,然后才能使用另一个路由器运行 VRRP。 这种类型的身份验证不能防止恶意攻击,其中密码可以被窥探 LAN 上的 VRRP 数据包的节点得知。 简单文本身份验证与 TTL 检查相结合,使得从另一个 LAN 发送的 VRRP 数据包难以中断 VRRP 操作。
This type of authentication is useful to protect against accidental
misconfiguration of routers on a LAN. It protects against routers
inadvertently backing up another router. A new router must first be
configured with the correct password before it can run VRRP with
another router. This type of authentication does not protect against
hostile attacks where the password can be learned by a node snooping
VRRP packets on the LAN. The Simple Text Authentication combined
with the TTL check makes it difficult for a VRRP packet to be sent
from another LAN to disrupt VRRP operation.
当 LAN 上的节点主动中断 VRRP 操作的风险最小时,建议使用这种类型的身份验证。 如果使用这种类型的身份验证,则用户应知道此明文密码经常发送,因此不应与任何安全重要密码相同。
This type of authentication is RECOMMENDED when there is minimal risk
of nodes on a LAN actively disrupting VRRP operation. If this type
of authentication is used the user should be aware that this clear
text password is sent frequently, and therefore should not be the
same as any security significant password.
10.3IP头认证
使用此身份验证类型意味着 VRRP 协议交换使用 IP 身份验证标头 [AUTH] 定义的机制进行身份验证,该机制使用“在 ESP 中使用 HMAC-MD5-96
AH“,[HMAC] 这提供了针对配置错误、重放攻击和数据包损坏/修改的强大保护。
当对 LAN 上节点的管理控制有限时,建议使用这种类型的身份验证。 虽然这种类型的身份验证确实可以保护VRRP的操作,但还有其他类型的攻击可能用于共享媒体链接(例如,生成伪造的ARP回复),这些攻击独立于VRRP并且不受保护。
The use of this authentication type means the VRRP protocol exchanges
are authenticated using the mechanisms defined by the IP
Authentication Header [AUTH] using "The Use of HMAC-MD5-96 within ESP
and AH", [HMAC]. This provides strong protection against
configuration errors, replay attacks, and packet
corruption/modification.
This type of authentication is RECOMMENDED when there is limited
control over the administration of nodes on a LAN. While this type
of authentication does protect the operation of VRRP, there are other
types of attacks that may be employed on shared media links (e.g.,
generation of bogus ARP replies) which are independent from VRRP and
are not protected.
11.致谢
作者要感谢格伦·佐恩、迈克尔·莱恩、克拉克·布雷默、哈尔·彼得森、托尼·李、芭芭拉·丹尼、乔尔·哈尔彭、史蒂夫·贝洛文和托马斯·纳滕的评论和建议。
The authors would like to thank Glen Zorn, and Michael Lane, Clark
Bremer, Hal Peterson, Tony Li, Barbara Denny, Joel Halpern, Steve
Bellovin, and Thomas Narten for their comments and suggestions.
12.参考文献。
参考原文
13.作者地址
参考原文
14.完整的版权声明
The Internet Society (1998)版权所有。保留所有权利。
本文档及其翻译版本可以复制并提供给他人,并且可以全部或部分准备,复制,出版和分发评论或以其他方式解释或协助其实施的衍生作品,不受任何形式的限制,前提是上述版权声明和本段包含在所有此类副本和衍生作品中。但是,本文档本身不得以任何方式进行修改,例如删除版权声明或对互联网协会或其他互联网组织的引用,除非出于制定互联网标准的目的,在这种情况下,必须遵循互联网标准流程中定义的版权程序,或根据需要将其翻译成英语以外的语言。
上述授予的有限权限是永久性的,互联网协会或其继承人或受让人不会撤销。
本文档和此处包含的信息是按“原样”提供的,互联网协会和互联网工程任务组不承担任何明示或暗示的保证,包括但不限于任何保证,即使用此处的信息不会侵犯任何权利或任何暗示的适销性或适用于特定用途的保证。
Copyright (C) The Internet Society (1998). All Rights Reserved.
This document and translations of it may be copied and furnished to
others, and derivative works that comment on or otherwise explain it
or assist in its implementation may be prepared, copied, published
and distributed, in whole or in part, without restriction of any
kind, provided that the above copyright notice and this paragraph are
included on all such copies and derivative works. However, this
document itself may not be modified in any way, such as by removing
the copyright notice or references to the Internet Society or other
Internet organizations, except as needed for the purpose of
developing Internet standards in which case the procedures for
copyrights defined in the Internet Standards process must be
followed, or as required to translate it into languages other than
English.
The limited permissions granted above are perpetual and will not be
revoked by the Internet Society or its successors or assigns.
This document and the information contained herein is provided on an
"AS IS" basis and THE INTERNET SOCIETY AND THE INTERNET ENGINEERING
TASK FORCE DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY THAT THE USE OF THE INFORMATION
HEREIN WILL NOT INFRINGE ANY RIGHTS OR ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.