力扣刷题日志23天
Day 1
// 三数据方法差别
Queue:是collection子类,方法:add、offer、remove、poll、peek、element
Stack:是colleciton子类,方法:push、pop、peek、empty
Deque:继承Queue,方法:poll、push、addFirst
1 709. 转换成小写字母
题目:给你一个字符串 s ,将该字符串中的大写字母转换成相同的小写字母,返回新的字符串。
解析:
(1)可用String自带的.toLowerCase()函数。
(2)使用哈希映射
-
大写字母 A - Z 的 ASCII\text{ASCII}ASCII 码范围为 [65,90];
-
小写字母 a - z 的 ASCII\text{ASCII}ASCII 码范围为[97,122];
class Solution {
public String toLowerCase(String s) {
StringBuilder a=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char b=s.charAt(i);
if(b<=90 && b>=65){
b +=32;
}
a.append(b);
}
return a.toString();
}
}
注意:
全转小写:ch|=32
全转大写:ch&=-33 (原理是32的补码(原码取反+1)再-1)
大小写对换(大写变小写,小写变大)ch^=32
2 742. 二叉树最近的叶节点
给定一个 每个结点的值互不相同 的二叉树,和一个目标整数值 k,返回 树中与目标值 k 最近的叶结点 。
与叶结点最近 表示在二叉树中到达该叶节点需要行进的边数与到达其它叶结点相比最少。而且,当一个结点没有孩子结点时称其为叶结点。
解析:
先使用DFS进行树到图的转换,后通过BFS寻找最近的叶子节点。
class Solution {
public int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode root, int k) {
Map<TreeNode, List<TreeNode>> graph = new HashMap();
dfs(graph, root, null);
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
Set<TreeNode> seen = new HashSet();
for (TreeNode node: graph.keySet()) {
if (node != null && node.val == k) {
queue.add(node);
seen.add(node);
}
}
// BFS寻找叶子节点
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node != null) {
if (graph.get(node).size() <= 1)
return node.val;
for (TreeNode nei: graph.get(node)) {
if (!seen.contains(nei)) {
seen.add(nei);
queue.add(nei);
}
}
}
}
throw null;
}
public void dfs(Map<TreeNode, List<TreeNode>> graph, TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) {
if (node != null) {
if (!graph.containsKey(node)) graph.put(node, new LinkedList<TreeNode>());
if (!graph.containsKey(parent)) graph.put(parent, new LinkedList<TreeNode>());
graph.get(node).add(parent);
graph.get(parent).add(node);
dfs(graph, node.left, node);
dfs(graph, node.right, node);
}
}
}
Day2
1 判定字符是否唯一
实现一个算法,确定一个字符串 s 的所有字符是否全都不同。
题解:
(1)使用Set数据结构
(2)两次循环暴力破解
(3)按位进行运算
class Solution {
public boolean isUnique(String astr) {
long bits=0;
for(int i=0;i<astr.length();i++){
int a=astr.charAt(i)-'a';
if((bits &(1L << a))!=0){
return false;
}else{
bits |=(1L<<a);
}
}
return true;
}
}
2 编写一个 SQL 查询,按产品 id product_id 来统计每个产品的销售总量。
select product_id,sum(quantity) as total_quantity
from sales
group by product_id
3 构造 K 个回文字符串
给你一个字符串 s 和一个整数 k 。请你用 s 字符串中 所有字符 构造 k 个非空 回文串 。
如果你可以用 s 中所有字符构造 k 个回文字符串,那么请你返回 True ,否则返回 False 。
输入:s = "annabelle", k = 2
输出:true
解释:可以用 s 中所有字符构造 2 个回文字符串。
一些可行的构造方案包括:"anna" + "elble","anbna" + "elle","anellena" + "b"
题解:
注意审题。
1.求出字符串最少可以构造的回文串个数left
2.求出字符串最多可以构造的回文串right
3.找出[left,right]范围内满足要求的那些值,并判断k是否在其中
- 对于条件2,单个字符即可构成回文字符串,故right值为字符串长度
- 对于条件1,分析两种出现的回文字符串清况。(1)长度为奇数(2)长度为偶数。
- 如果s中有p个奇数字符,q个偶数字符,则s最少构建p个回文,因为奇数字符需要放在不同的回文串中,特别地,那么最少构造地回文串个数为1.
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String s, int k) {
int max=s.length(); // 最大回文串数量
int[] count=new int[26];
Arrays.fill(count,0);
for(int i=0;i<max;i++){
count[s.charAt(i)-'a'] +=1;
}
int p=0;
int q=0;
int min=0;
for(int j=0;j<count.length;j++){
if(count[j]%2!=0){
p +=1;
}
if(count[j]%2==0 && count[j]!=0){
q +=1;
}
}
if(p==0){
min=1;
}else{
min=p;
}
if(k>=min && k<= max){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
Day 3
1 606. 根据二叉树创建字符串
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,请你采用前序遍历的方式,将二叉树转化为一个由括号和整数组成的字符串,返回构造出的字符串。
空节点使用一对空括号对 “()” 表示,转化后需要省略所有不影响字符串与原始二叉树之间的一对一映射关系的空括号对。

题解:
(1)使用前序递归遍历,在递归函数中增加限制条件
class Solution {
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder result=new StringBuilder();
dfs(result,root);
return result.toString().substring(1,result.length()-1);
}
public void dfs(StringBuilder s,TreeNode root){
s.append("(");
s.append(root.val);
if(root.left !=null){
dfs(s,root.left);
}else if(root.right !=null){
s.append("()");
}
if(root.right!=null){
dfs(s,root.right);
}
s.append(")");
}
}
2 627. 变更性别
(1) update salary set sex=Case sex when 'm' then 'f' else 'm' end;
(2)update salary set sex = IF(sex = 'm','f','m');
3 739. 每日温度
解析:
(1)双重循环暴力破解,比较损耗时间
(2)考虑单调栈(涉及需要在进程中需要考虑到最开始状态的情形)
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int[] result= new int[temperatures.length];
Deque<Integer> deque= new LinkedList<Integer>();
// deque.addFirst(temperatures[0]);
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<temperatures.length;i++){
int temperature=temperatures[i];
while(!deque.isEmpty() && temperature>temperatures[deque.peek()]){
int a=deque.peek();
int pre=deque.pop();
result[pre]=i-pre;
}
deque.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}
Day 4
1 495. 提莫攻击
- 1下一次攻击在中毒时间内:上一次中毒时间为timeseries[i+1]-timeseries[i]
- 2 下一次攻击在中毒时间外:上一次中毒时间为timeSeries[i]+duration
class Solution {
public int findPoisonedDuration(int[] timeSeries, int duration) {
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<timeSeries.length-1;i++){
if(timeSeries[i]+duration<=timeSeries[i+1]){
count +=duration;
}else {
count +=timeSeries[i+1]-timeSeries[i];
}
}
count +=duration;
return count;
}
}
2 1795. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
select product_id,'store1' store,store1 as price
from products where store1 is not null
union
select product_id,'store2' store,store2 price
from products where store2 is not null
union
select product_id,'store3' store,store3 price
from products where store3 is not null
3 1010. 总持续时间可被 60 整除的歌曲

解析:
(1)暴力循环会超时
(2)可以创建一个60大小的辅助数组,我们取每个数时,取60-它与60的余数,去辅助数组寻找是否有,有加上所在大小,并把它的与60的余数位置的辅助数组+1;
class Solution {
public int numPairsDivisibleBy60(int[] time) {
int[] res=new int[60];
int count=0;
for(int t:time){
int a=60-t%60; // 取与之对应可以组成组合的值
count +=res[a%60]; // 查询位置处是否有,有则加之
res[t%60]++; // 关于60余数位置+1;
}
return count;
}
}
4 1587. 银行账户概要 II
select name,sum(amount) as balance
from users
left join transactions on users.account=transactions.account
group by users.account
having balance >10000
4 920. 播放列表的数量
你的音乐播放器里有 N 首不同的歌,在旅途中,你的旅伴想要听 L 首歌(不一定不同,即,允许歌曲重复)。请你为她按如下规则创建一个播放列表:
- 每首歌至少播放一次。
- 一首歌只有在其他 K 首歌播放完之后才能再次播放。
返回可以满足要求的播放列表的数量。由于答案可能非常大,请返回它模 10^9 + 7 的结果。

解析:
使用动态规划进行问题解决
(1)首先考虑题目中情形,设置二维数据进行动态规划
(2)创建大小为int[][] dp=int[L][N]的二维数组
(3)进行假设分析,求dp[i][j],则考虑如何由前一个状态得到后一个状态
- dp[i][j]由两部分构成,第一部分为增条新曲目,则dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]*(n-j+1)
- 第二部分为增条旧曲目,dp[i][j] +=dp[i-1][j]*Math.max(j-k,0);
- 上面写的[n-j+1],[j-k]不同,k是指k+1种,所以dp[i - 1]j从第i - 1个数末尾(含它)往前的k个区间里一定刚好有k个不同的数, 因为我们总共有j个不同的数, 所以就剩下j - k个可以选择的数了,强调一下是j - k而不是j - (k + 1), 因为第i个位置占一个, 前面有k个。
class Solution {
public int numMusicPlaylists(int n, int goal, int k) {
int mod=1_000_000_007;
long [][] dp=new long[goal+1][n+1];
dp[0][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=goal;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
dp[i][j] +=dp[i-1][j-1]*(n-j+1);
dp[i][j] +=dp[i-1][j]*Math.max(j-k,0);
dp[i][j] %=mod;
}
}
return (int)dp[goal][n];
}
}
Day 5
1 1085. 最小元素各数位之和
解析:
可以使用Arrays内置函数sort进行排序,也可以设定Integer.MAX_Values进行大小比较,后可以进行相关相加。
class Solution {
public int sumOfDigits(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int result=nums[0];
int count=0;
while(result>0){
count +=result%10;
result=result/10;
}
return count%2==0?1:0;
}
}
2 1023. 驼峰式匹配

解析:
本题可以使用双指针进行解决
一个指针p进行对应String种char扫描
另一个指针q用于pattern种字符扫描
- 当p进行扫描时,q在pattern大小范围内,扫描的字符等于p对应字符时,p进行增加
- 当扫描的字符是大写字符,标志位flag为false
class Solution {
public List<Boolean> camelMatch(String[] queries, String pattern) {
List<Boolean> result=new ArrayList<Boolean>();
for(String s:queries){
int q=0;
boolean flag=true;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char c=s.charAt(i);
if(q<pattern.length() && c==pattern.charAt(q)){
q++;
}else if(Character.isUpperCase(c)){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(q<pattern.length()){
flag=false;
}
result.add(flag);
}
return result;
}
}
3 872. 叶子相似的树
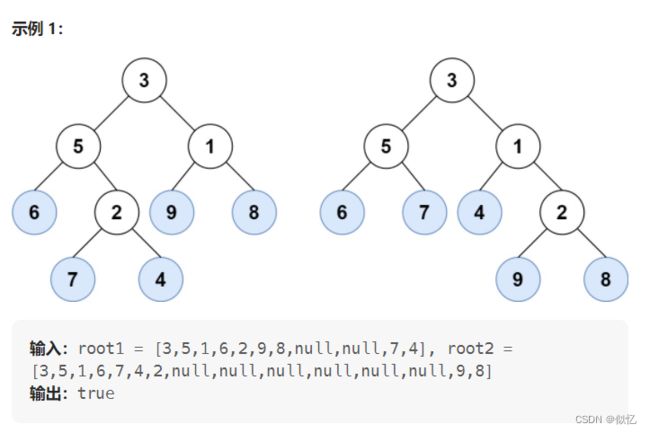
题解:
通过创建一个Deque,进行遍历,当左节点右节点为0时,将对应节点值加入list,最后进行比较,代码如下
class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque1=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Deque<TreeNode> deque2=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer> a=get(deque1,root1);
System.out.print(a);
List<Integer> b= get(deque2,root2);
System.out.print(b);
return a.equals(b);
}
public ArrayList<Integer> get(Deque<TreeNode> deque,TreeNode root){
ArrayList<Integer> list= new ArrayList<Integer>();
deque.push(root);
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
TreeNode a=deque.poll();
if(a.left!=null){
deque.push(a.left);
}
if(a.right!=null){
deque.push(a.right);
}
if(a.left==null && a.right==null) {
list.add(a.val);
}
}
return list;
}
}
4 1638. 统计只差一个字符的子串数目
class Solution {
public int countSubstrings(String s, String t) {
int a=s.length(); // s的长度
int b=t.length(); //t的长度
int[][] dp1=new int[a+1][b+1];
int[][] dp2=new int[a+1][b+1];
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
for(int j=0;j<b;j++){
dp1[i+1][j+1]=s.charAt(i)==t.charAt(j)?dp1[i][j]+1:0;
}
}
for(int i=a-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=b-1;j>=0;j--){
dp2[i][j]=s.charAt(i)==t.charAt(j)?dp2[i+1][j+1]+1:0;
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
for(int j=0;j<b;j++){
if(s.charAt(i)!=t.charAt(j)){
ans +=(dp1[i][j]+1)*(dp2[i+1][j+1]+1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
(2)枚举
class Solution {
public int countSubstrings(String s, String t) {
int m = s.length(), n = t.length();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int diff = 0;
for (int k = 0; i + k < m && j + k < n; k++) {
diff += s.charAt(i + k) == t.charAt(j + k) ? 0 : 1;
if (diff > 1) {
break;
} else if (diff == 1) {
ans++;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Day 6
1042. 不邻接植花
![]()
解析:此类题可以考虑用list中装list进行图的构建,后单独取出对应list,进行颜色分析
class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
List<Integer>[] map= new List[n];
for(int i=0;i<map.length;i++){
map[i]=new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
// 进行图的创建
for(int[] p:paths){
map[p[0]-1].add(p[1]-1);
map[p[1]-1].add(p[0]-1);
}
int[] result =new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<map.length;i++){
// 辅助栈进行颜色分配 5是指 0假想色 和1-4真实色
boolean[] flower=new boolean[5];
for(int d:map[i]){
// 对对应区域颜色进行查询,查询后改变对应位置辅助数组
flower[result[d]]=true;
}
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++){
if(!flower[j]){
result[i]=j;
break;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
Day 7
1 1303. 求团队人数

解析:
返回结果呈现多种,使用over(partition by)窗口函数进行查询
select employee_id, count(team_id) over(partition by team_id)
as team_size
from employee
// 其中count为符合条件的计数
// over 指对符合条件的进行窗口查询
2 1157. 子数组中占绝大多数的元素
解析:
传统的暴力方式会超时,此时应考虑随机化+二分查找
为了减少遍历次数,选择随机查找,查找20次还找不到的概率会很低
class MajorityChecker {
public static final int K = 20;
private int[] arr;
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> loc;
private Random random;
public MajorityChecker(int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
this.loc = new HashMap<Integer, List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i) {
loc.putIfAbsent(arr[i], new ArrayList<Integer>());
loc.get(arr[i]).add(i);
}
this.random = new Random();
}
public int query(int left, int right, int threshold) {
int length = right - left + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
int x = arr[left + random.nextInt(length)];
List<Integer> pos = loc.get(x);
int occ = searchEnd(pos, right) - searchStart(pos, left);
if (occ >= threshold) {
return x;
} else if (occ * 2 >= length) {
return -1;
}
}
return -1;
}
private int searchStart(List<Integer> pos, int target) {
int low = 0, high = pos.size();
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (pos.get(mid) >= target) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private int searchEnd(List<Integer> pos, int target) {
int low = 0, high = pos.size();
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (pos.get(mid) > target) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
}
3 2409. 统计共同度过的日子数

解析:
(1)首先可以进行日期的转化存储,用int[]进行存储
class Solution {
public int countDaysTogether(String arriveAlice, String leaveAlice, String arriveBob, String leaveBob) {
int[] datesOfMonths = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int[] prefixSum = new int[13];
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
prefixSum[i + 1] = prefixSum[i] + datesOfMonths[i];
}
int arriveAliceDay = calculateDayOfYear(arriveAlice, prefixSum);
int leaveAliceDay = calculateDayOfYear(leaveAlice, prefixSum);
int arriveBobDay = calculateDayOfYear(arriveBob, prefixSum);
int leaveBobDay = calculateDayOfYear(leaveBob, prefixSum);
return Math.max(0, Math.min(leaveAliceDay, leaveBobDay) - Math.max(arriveAliceDay, arriveBobDay) + 1);
}
public int calculateDayOfYear(String day, int[] prefixSum) {
int month = Integer.parseInt(day.substring(0, 2));
int date = Integer.parseInt(day.substring(3));
return prefixSum[month - 1] + date;
}
}
Day 8
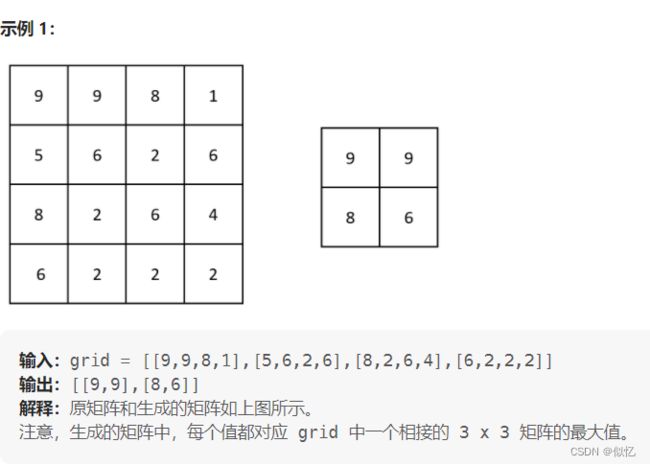
1 2373. 矩阵中的局部最大值
class Solution {
public int[][] largestLocal(int[][] grid) {
int n=grid.length; // 矩阵长度
int[][] result=new int[n-2][n-2];
for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++){
for(int q=0;q<n-2;q++){
int max=0;
for(int j=i;j<i+3;j++){
for(int k=q;k<q+3;k++){
if(grid[j][k]>max){
max=grid[j][k];
}
}
}
result[i][q]=max;
}
}
return result;
}
}
2 1026. 节点与其祖先之间的最大差值

解析:
(1)自己想的用了笨方法,使用DFS将树转化为图进行表述
class Solution {
HashMap<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>> map;
public int maxAncestorDiff(TreeNode root) {
map=new HashMap<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>>();
deal(map,root,null);
int max=0;
for(TreeNode t:map.keySet()){
if(t!=null){
List<TreeNode> list=map.get(t);
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
if(i==0){
int max2=caluate(t,map);
max=Math.max(max2,max);
}
if(list.get(i)!=null){
max=Math.max(max,Math.abs(list.get(i).val-t.val));
}
}
}
}
return max;
}
public void deal(HashMap<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>>map,TreeNode root,TreeNode par){
if(root!=null){
if(!map.containsKey(root)){
map.put(root,new LinkedList<TreeNode>());
}
if(!map.containsKey(par)){
map.put(par,new LinkedList<TreeNode>());
}
map.get(root).add(par);
map.get(par).add(root);
deal(map,root.left,root);
deal(map,root.right,root);
}
}
public int caluate(TreeNode root,HashMap<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>> map){
List<TreeNode> list=map.get(root);
int max=0;
while(list.get(0)!=null ){
TreeNode par=list.get(0);
max=Math.max(Math.abs(par.val-root.val),max);
list=map.get(par);
}
return max;
}
}
(2)也是dfs,只需要在dfs过程中存储住最大最小值即可。
class Solution {
public int maxAncestorDiff(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root,root.val,root.val);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root,int max,int min){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int diff=Math.max(Math.abs(root.val-max),Math.abs(root.val-min));
max=Math.max(root.val,max);
min=Math.min(root.val,min);
diff = Math.max(diff,dfs(root.left,max,min));
diff=Math.max(diff,dfs(root.right,max,min));
return diff;
}
}
3 2566. 替换一个数字后的最大差值

解析:
根据题意,进行贪心算法,最大值为将首先不为9的数字替换为9,最小值为将首先不为0的替换为0
class Solution {
public int minMaxDifference(int num) {
int max=num;
int min=num;
String a=String.valueOf(num);
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++){
if(a.charAt(i)=='0'){
continue;
}else{
min=Integer.valueOf(a.replaceAll(String.valueOf(a.charAt(i)),"0"));
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++){
if(a.charAt(i)=='9'){
continue;
}else{
max=Integer.valueOf(a.replaceAll(String.valueOf(a.charAt(i)),"9"));
break;
}
}
return max-min;
}
}
4 (背包问题)494. 目标和
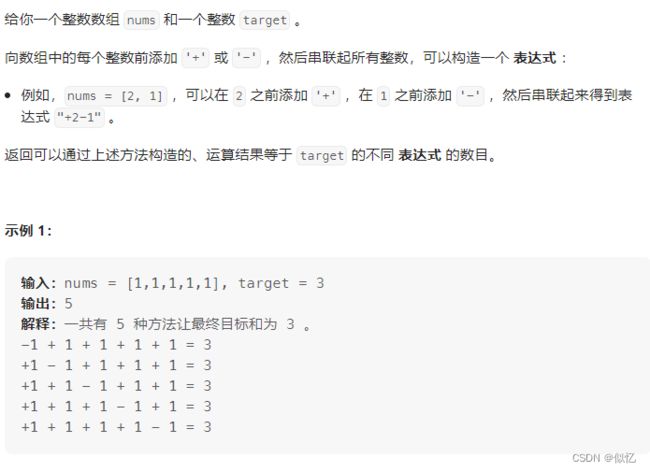
解析:
(1)回溯
遍历所有符合条件的清况,在回溯中每两个数字间考虑两种清况,进行回溯分析,类似于递归
class Solution {
int count = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
backtrack(nums, target, 0, 0);
return count;
}
public void backtrack(int[] nums, int target, int index, int sum) {
if (index == nums.length) {
if (sum == target) {
count++;
}
} else {
backtrack(nums, target, index + 1, sum + nums[index]);
backtrack(nums, target, index + 1, sum - nums[index]);
}
}
}
(2)动态规划
将之转换成动态规划问题,

这里的neg为正整数,故进行动态规划分析,创建dp[i][j]代表第i个值能够组成值为j的组合次数。
后对dp[i][j]进行初始化处理,当i=0,j=0的清况只有一种。
后面对dp[i][j]分情况进行分析:
(1)当j

代码如下
class Solution {
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
}
int diff = sum - target;
if (diff < 0 || diff % 2 != 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = nums.length, neg = diff / 2;
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][neg + 1];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int num = nums[i - 1];
for (int j = 0; j <= neg; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (j >= num) {
dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1][j - num];
}
}
}
return dp[n][neg];
}
}
Day 9
1 474. 一和零

解析:
动态规划,类似于背包问题,此题相比于普通的背包问题多了一个容量,故可以使用三维数组进行动态求解
class Solution {
public int findMaxForm(String[] strs, int m, int n) {
int length = strs.length;
int[][][] dp = new int[length + 1][m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= length; i++) {
int[] zerosOnes = getZerosOnes(strs[i - 1]);
int zeros = zerosOnes[0], ones = zerosOnes[1];
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
dp[i][j][k] = dp[i - 1][j][k];
if (j >= zeros && k >= ones) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j - zeros][k - ones] + 1);
}
}
}
}
return dp[length][m][n];
}
public int[] getZerosOnes(String str) {
int[] zerosOnes = new int[2];
int length = str.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
zerosOnes[str.charAt(i) - '0']++;
}
return zerosOnes;
}
}
2 1043. 分隔数组以得到最大和

解析:
使用动态规划,动态选取最大值在k范围内进行大小比较。
class Solution {
public int maxSumAfterPartitioning(int[] arr, int k) {
int n=arr.length;
int[] dp=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int max=arr[i-1];
for(int j=i-1;j>=0&&j>=i-k;j--){
dp[i]=Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+max*(i-j));
if(j>0){
max=Math.max(max,arr[j-1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
3 31. 下一个排列
- 首先寻找较小值,从数组末尾进行往前查询,查询nums[i]
- 找到较小值后,往后寻找较大值,较大值为数组末端到较小值前第一个比较小值大的值,找到后将较小值与较大值翻转,后将原较小值下标后数进行从小到大排序。
Day 10
1 1413. 逐步求和得到正数的最小值

解析:
(1)以0为起始值,计算每次最小值,寻找1-最小值的值即为所要值
class Solution {
public int minStartValue(int[] nums) {
int[] sum=new int[nums.length];
sum[0]=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+nums[i];
}
int min=1;
for(int a:sum){
if(a<1){
int tem=1-a;
if(tem>min){
min=tem;
}
}
}
return min;
}
}
(2)计算累加过程中最小值
class Solution {
public int minStartValue(int[] nums) {
int sum=0,countMin=0;
for(int a:nums){
sum +=a;
countMin=Math.min(countMin,sum);
}
return Math.abs(1-countMin);
}
}
2 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int m = s.length();
if(m==0) {
return 0;
}
int num =1; //初始值表示以s的第一个字符为结束的不重复的最长子串
int max =1;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
int index = s.indexOf(s.charAt(i),i-num);
if(index<i) { //num更新,表示以s的第i+1个字符为结束的不重复的最长子串
num = i-index;
} else {
num = num+1;
}
max = Math.max(max,num);
}
return max;
}
}
(2)滑动窗口
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
// 哈希集合,记录每个字符是否出现过
Set<Character> occ = new HashSet<Character>();
int n = s.length();
// 右指针,初始值为 -1,相当于我们在字符串的左边界的左侧,还没有开始移动
int rk = -1, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i != 0) {
// 左指针向右移动一格,移除一个字符
occ.remove(s.charAt(i - 1));
}
while (rk + 1 < n && !occ.contains(s.charAt(rk + 1))) {
// 不断地移动右指针
occ.add(s.charAt(rk + 1));
++rk;
}
// 第 i 到 rk 个字符是一个极长的无重复字符子串
ans = Math.max(ans, rk - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
Day 11
1 529. 扫雷游戏

解析:
根据题意,可使用DFS和BFS两种方法,首先要进行扫雷得条件判定,分别针对不同情况进行搜索分析
(1)
class Solution {
int[] dirX = {0, 1, 0, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1};
int[] dirY = {1, 0, -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1};
public char[][] updateBoard(char[][] board, int[] click) {
int x = click[0], y = click[1];
if (board[x][y] == 'M') {
// 规则 1
board[x][y] = 'X';
} else{
dfs(board, x, y);
}
return board;
}
public void dfs(char[][] board, int x, int y) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + dirX[i];
int ty = y + dirY[i];
if (tx < 0 || tx >= board.length || ty < 0 || ty >= board[0].length) {
continue;
}
// 不用判断 M,因为如果有 M 的话游戏已经结束了
if (board[tx][ty] == 'M') {
++cnt;
}
}
if (cnt > 0) {
// 规则 3
board[x][y] = (char) (cnt + '0');
} else {
// 规则 2
board[x][y] = 'B';
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + dirX[i];
int ty = y + dirY[i];
// 这里不需要在存在 B 的时候继续扩展,因为 B 之前被点击的时候已经被扩展过了
if (tx < 0 || tx >= board.length || ty < 0 || ty >= board[0].length || board[tx][ty] != 'E') {
continue;
}
dfs(board, tx, ty);
}
}
}
}
(2)BFS
class Solution {
int[] dirX = {0, 1, 0, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1};
int[] dirY = {1, 0, -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1};
public char[][] updateBoard(char[][] board, int[] click) {
int x = click[0], y = click[1];
if (board[x][y] == 'M') {
// 规则 1
board[x][y] = 'X';
} else{
bfs(board, x, y);
}
return board;
}
public void bfs(char[][] board, int sx, int sy) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[board.length][board[0].length];
queue.offer(new int[]{sx, sy});
vis[sx][sy] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = queue.poll();
int cnt = 0, x = pos[0], y = pos[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + dirX[i];
int ty = y + dirY[i];
if (tx < 0 || tx >= board.length || ty < 0 || ty >= board[0].length) {
continue;
}
// 不用判断 M,因为如果有 M 的话游戏已经结束了
if (board[tx][ty] == 'M') {
++cnt;
}
}
if (cnt > 0) {
// 规则 3
board[x][y] = (char) (cnt + '0');
} else {
// 规则 2
board[x][y] = 'B';
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + dirX[i];
int ty = y + dirY[i];
// 这里不需要在存在 B 的时候继续扩展,因为 B 之前被点击的时候已经被扩展过了
if (tx < 0 || tx >= board.length || ty < 0 || ty >= board[0].length || board[tx][ty] != 'E' || vis[tx][ty]) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{tx, ty});
vis[tx][ty] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
Day 12
1 1027. 最长等差数列
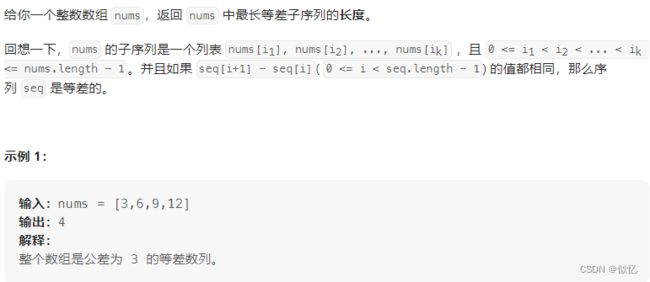
解析:使用动态规划解决问题
(1)创建一个大小为【数组长度】【所有可能差大小】得集合
(2)后动态规划,分别遍历不同差得数组,在基础上+1
class Solution {
public int longestArithSeqLength(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int[][] dp=new int[n][1001];
int max=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int num=nums[i];
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
int diff=num-nums[j]+500;
dp[i][diff]=dp[j][diff]+1;
max=Math.max(dp[i][diff],max);
}
}
return max+1;
}
}
2 1105. 填充书架

解析:
跟上一题类似,注意审题,是按顺序进行摆放。
首先创建dp[i]作为前i本书所用得最小高度。因为最多1000本书,设高度最大为1000000;初始dp[0]=0;
后进行转移方程构建。
class Solution {
public int minHeightShelves(int[][] books, int shelfWidth) {
int n=books.length;
int[] dp=new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dp,1000000);
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int maxheight=0,curwidth=0;
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){ //倒过来循环判断
curwidth +=books[j][0];
if(curwidth>shelfWidth){
break;
}
maxheight=Math.max(books[j][1],maxheight);
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i],dp[j]+maxheight);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
3 1163. 按字典序排在最后的子串
class Solution {
public String lastSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int i = 0;
for (int j = 1, k = 0; j + k < n;) {
int d = s.charAt(i + k) - s.charAt(j + k);
if (d == 0) {
++k;
} else if (d < 0) {
i += k + 1;
k = 0;
if (i >= j) {
j = i + 1;
}
} else {
j += k + 1;
k = 0;
}
}
return s.substring(i);
}
}
4 2551. 将珠子放入背包中
class Solution {
public long putMarbles(int[] weights, int k) {
if(k==1){
return 0;
}
int n=weights.length;
long[] value =new long[n-1];
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
value[i]=weights[i]+weights[i+1];
}
Arrays.sort(value);
long a=0;
for(int i=0;i<k-1;i++){
a +=value[n-2-i]-value[i];
}
return a;
}
}
Day 13
1 2418. 按身高排序

解析
(1)Arrays.sort进行排序,后进行对应查询,使用二分查找
class Solution {
public String[] sortPeople(String[] names, int[] heights) {
int n =names.length;
int[] id=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
id[i]=heights[i];
}
String[] result=new String[n];
Arrays.sort(heights);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int pos=select(heights,id[i]);
result[n-1-pos]=names[i];
}
return result;
}
public int select(int[] a,int target){
int i=0;
int j=a.length-1;
while(i<=j){
int mid=i+(j-i)/2;
if(a[mid]>target){
j=mid;
}else if(a[mid]<target){
i=mid+1;
}else if(a[mid]==target){
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
(2)使用Arrays.sort加lambda表达式进行排序
class Solution {
public String[] sortPeople(String[] names, int[] heights) {
int n = names.length;
Integer[] indices = new Integer[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
indices[i] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(indices, (a, b) -> heights[b] - heights[a]);
String[] res = new String[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = names[indices[i]];
}
return res;
}
}
2 986 区间列表的交集
class Solution {
public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] firstList, int[][] secondList) {
List<int[]> list=new ArrayList<int[]>();
int m=firstList.length;
int n=secondList.length;
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<m &&j<n){
int low=Math.max(firstList[i][0],secondList[j][0]);
int hihh=Math.min(firstList[i][1],secondList[j][1]);
if(low<=hihh){
list.add(new int[]{low,hihh});
}
if(firstList[i][1]<secondList[j][1]){
i++;
}else{
j++;
}
}
int[][] result=new int[list.size()][2];
for(int k=0;k<list.size();k++){
result[k]=list.get(k);
}
return list.toArray(new int[list.size()][]);
}
}
3 1561. 你可以获得的最大硬币数目

解析:
按题解说就是贪心
如:一共只有三堆,最大就是取中值那堆
若有六堆,从小到大排序,最小的那一堆和最大的会取掉首尾,而我们可以取剩余最大的,后面依次。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public int maxCoins(int[] piles) {
Arrays.sort(piles);
int count=0;
int n=piles.length/3;
int k=1;
for(int i=piles.length-2;i>=0 &&k<=n;i=i-2,k++){
count +=piles[i];
}
return count;
}
}
Day14
1 1048. 最长字符串链

解析:
动态规划,可以知道wordb任意删除去除一个字母,其其他保持不变则为wordb前身。
首先将数组进行按大小由小到大排序,后对该字符串进行循环去除,得到一个新字符串,再去寻找前一个的串最大值,最后返回可能的最大值
class Solution {
public int longestStrChain(String[] words) {
Map<String, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
Arrays.sort(words, (a, b) -> a.length() - b.length());
int res = 0;
for (String word : words) {
cnt.put(word, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
String prev = word.substring(0, i) + word.substring(i + 1);
if (cnt.containsKey(prev)) {
cnt.put(word, Math.max(cnt.get(word), cnt.get(prev) + 1));
}
}
res = Math.max(res, cnt.get(word));
}
return res;
}
}
2 923. 三数之和的多种可能

解析:
两种方法:
(1)三指针
循环遍历arr,后用双指针进行两数智慧为targer-arr[i]的查询,最终得到结果
class Solution {
public int threeSumMulti(int[] arr, int target) {
int[] map= new int[101];
int mod=1_000_000_007;
long ans=0;
Arrays.sort(arr);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
int T=target-arr[i];
int j=i+1,k=arr.length-1;
while(j<k){
if(arr[j]+arr[k]>T){
k--;
}else if(arr[j]+arr[k]<T){
j++;
}else if(arr[j]!=arr[k]){
int left=1,right=1;
while(j+1<k && arr[j]==arr[j+1]){
left++;
j++;
}
while(k-1>j &&arr[k]==arr[k-1]){
right++;
k--;
}
ans +=left*right;
ans %=mod;
j++;
k--;
}else{
ans+=(k-j+1)*(k-j)/2;
ans %=mod;
break;
}
}
}
return (int)ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public int threeSumMulti(int[] A, int target) {
int MOD = 1_000_000_007;
long[] count = new long[101];
for (int x: A)
count[x]++;
long ans = 0;
// All different
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; ++x)
for (int y = x+1; y <= 100; ++y) {
int z = target - x - y;
if (y < z && z <= 100) {
ans += count[x] * count[y] * count[z];
ans %= MOD;
}
}
// x == y != z
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; ++x) {
int z = target - 2*x;
if (x < z && z <= 100) {
ans += count[x] * (count[x] - 1) / 2 * count[z];
ans %= MOD;
}
}
// x != y == z
for (int x = 0; x <= 100; ++x) {
if (target % 2 == x % 2) { //判断x和target的奇偶性
int y = (target - x) / 2;
if (x < y && y <= 100) {
ans += count[x] * count[y] * (count[y] - 1) / 2;
ans %= MOD;
}
}
}
// x == y == z
if (target % 3 == 0) {
int x = target / 3;
if (0 <= x && x <= 100) {
ans += count[x] * (count[x] - 1) * (count[x] - 2) / 6;
ans %= MOD;
}
}
return (int) ans;
}
}
Day 15
1 1172. 餐盘栈

解析:正常思维即可,但防止时间超时,需要用额外空间换取时间
TreeSet 或者PriorityQueue 可以进行空餐盘的存储。
class DinnerPlates {
ArrayList<Stack<Integer>> plates;
Integer cap;
TreeSet<Integer> res;
public DinnerPlates(int capacity) {
cap=capacity;
plates=new ArrayList<Stack<Integer>>();
res=new TreeSet<Integer>();
}
public void push(int val) {
int size=plates.size();
if(size==0){
Stack<Integer> one=new Stack<Integer>();
one.push(val);
plates.add(one);
if(cap>1){
res.add(0);
}
}else{
if(res.size()==0){
Stack<Integer> two=new Stack<Integer>();
two.add(val);
plates.add(two);
if(cap>1){
res.add(size);
}
}else{
int index=res.first();
plates.get(index).add(val);
if(plates.get(index).size()==cap){
res.pollFirst();
}
}
}
}
public int pop() {
return popAtStack(plates.size() - 1);
}
public int popAtStack(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= plates.size() || plates.get(index).isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int val = plates.get(index).pop();
if (index == plates.size() - 1 && plates.get(plates.size() - 1).isEmpty()) {
while (!plates.isEmpty() && plates.get(plates.size() - 1).isEmpty()) {
res.remove(plates.size() - 1);
plates.remove(plates.size() - 1);
}
} else {
res.add(index);
}
return val;
}
}
/**
* Your DinnerPlates object will be instantiated and called as such:
* DinnerPlates obj = new DinnerPlates(capacity);
* obj.push(val);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.popAtStack(index);
*/
Day 16
1 2423. 删除字符使频率相同
class Solution {
public boolean equalFrequency(String word) {
int[] charCount = new int[26];
int n = word.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
charCount[word.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (charCount[i] == 0) {
continue;
}
charCount[i]--;
HashSet<Integer> frequency = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int f : charCount) {
if (f > 0) {
frequency.add(f);
}
}
if (frequency.size() == 1) {
return true;
}
charCount[i]++;
}
return false;
}
}
2 62. 不同路径
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int count=dfs(0,0,m-1,n-1);
return count;
}
public int dfs(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2){
if(x1<0||x1>x2 ||y1<0 ||y1>y2){
return 0;
}
if(x1==x2 &&y1==y2){
return 1;
}
int xr=x1+1;
int yr=y1+1;
int a=dfs(xr,y1,x2,y2);
int b=dfs(x1,yr,x2,y2);
int c=a+b;
return c;
}
}
(2)动态规划
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] dp= new int[m][n];
dp[0][0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
dp[i][0]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[0][i]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
3 63. 不同路径 II
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m=obstacleGrid.length;
int n=obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[][] dp=new int[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][0]==1){
break;
}else{
dp[i][0]=1;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(obstacleGrid[0][i]==1){
break;
}else{
dp[0][i]=1;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][j]==1){
continue;
}else{
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m=obstacleGrid.length;
int n=obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[] dp=new int[n];
dp[0]=obstacleGrid[0][0]==1?0:1;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][j]==1){
dp[j]=0;
continue;
}
if(j-1>=0 ){
dp[j] +=dp[j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
Day 17
1 1033. 移动石子直到连续
class Solution {
public int[] numMovesStones(int a, int b, int c) {
int x = Math.min(Math.min(a, b), c);
int z = Math.max(Math.max(a, b), c);
int y = a + b + c - x - z;
int[] res = new int[2];
res[0] = 2;
if (z - y == 1 && y - x == 1) {
res[0] = 0;
} else if (z - y <= 2 || y - x <= 2) {
res[0] = 1;
}
res[1] = z - x - 2;
return res;
}
}
2 113. 路径总和 II
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> path= new ArrayList<>();
Deque<Integer> a=new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root,targetSum);
return path;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int targetSum){
if(root==null){
return;
}
a.addLast(root.val);
targetSum -=root.val;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(targetSum==0){
path.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(a));
}
}
dfs(root.left,targetSum);
dfs(root.right,targetSum);
a.pollLast();
}
}
(2)BFS
用map记录父节点,找到路径最后一点时,返回寻找父节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> list=new LinkedList<>();
Map<TreeNode,TreeNode> map=new HashMap<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null){
return list;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque1= new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Deque<Integer> deque2= new LinkedList<Integer>();
deque1.push(root);
deque2.push(root.val);
while(!deque1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode re=deque1.poll();
Integer ie=deque2.poll();
if(re.left==null&&re.right==null){
if(ie==targetSum){
getMap(re);
}
}
if(re.left!=null){
deque1.push(re.left);
deque2.push(re.left.val+ie);
map.put(re.left,re);
}
if(re.right!=null){
deque1.push(re.right);
deque2.push(re.right.val+ie);
map.put(re.right,re);
}
}
return list;
}
public void getMap(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> a= new ArrayList<>();
while(root!=null){
a.add(root.val);
root=map.get(root);
}
Collections.reverse(a);
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(a));
}
}
3 980. 不同路径 III
解析:
回溯DFS
class Solution {
int endX;
int endY;
int[] xr=new int[]{0,1,0,-1};
int[] yr=new int[]{1,0,-1,0};
int count;
int m;
int n;
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
count=0;
int go=0;
m=grid.length;
n=grid[0].length;
int x=0;
int y=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]!=-1){
go++;
}
if(grid[i][j]==2){
endX=i;
endY=j;
}
if(grid[i][j]==1){
x=i;
y=j;
}
}
}
dfs(grid,x,y,go);
return count;
}
public void dfs(int[][] grid,int x,int y,int go){
go--;
if(go<0){
return;
}
if(x==endX&&y==endY){
if(go==0){
count++;
}
return;
}
grid[x][y]=3;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x1=x+xr[k];
int y1=y+yr[k];
if(x1>=0 && x1<m&&y1>=0&&y1<n){
if(grid[x1][y1]%2==0){
dfs(grid,x1,y1,go);
}
}
}
grid[x][y]=0;
}
}
4 437. 路径总和 III
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> map=new HashMap<>();
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
int count=0;
dfs(root,null);
for(TreeNode a:map.keySet()){
long sum=0;
while(a!=null){
sum +=a.val;
if(sum==targetSum){
count++;
}
a=map.get(a);
}
}
return count;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,TreeNode parent){
if(root==null){
return;
}
map.put(root,parent);
dfs(root.left,root);
dfs(root.right,root);
}
}
(2)另一种深度优先搜索法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, long targetSum) {
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int ret=dfs(root,targetSum);
ret +=pathSum(root.left,targetSum);
ret +=pathSum(root.right,targetSum);
return ret;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root,long targetSum){
int ret=0;
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
if(root.val==targetSum){
ret++;
}
ret +=dfs(root.left,targetSum-root.val);
ret +=dfs(root.right,targetSum-root.val);
return ret;
}
}
5 1730. 获取食物的最短路径

解析:这种有多解求最优的路线建议用BFS,BFS可以实现最快找到所要的点
class Solution {
int M,N;
char[][] grid;
int[] xr=new int[]{1,-1,0,0};
int[] yr=new int[]{0,0,1,-1};
Deque<int[]> deque=new LinkedList<int[]>();
public int getFood(char[][] grid){
this.grid=grid;
M=grid.length;
N=grid[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
for(int j=0;j<N;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='#'){
deque.push(new int[]{i,j});
}
}
}
return bfs();
}
public int bfs(){
int res=0;
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
int size=deque.size();
res++;
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
int[] re=deque.pop();
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
int x2=re[0]+xr[j];
int y2=re[1]+yr[j];
if(isVaild(x2,y2)){
return res;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public boolean isVaild(int x,int y){
if(x<0 ||x>=M ||y<0 ||y>=N){
return false;
}
if(grid[x][y]=='X'){
return false;
}
if(grid[x][y]=='O'){
deque.add(new int[]{x,y});
grid[x][y]='X';
return false;
}
return grid[x][y]=='*';
}
}
Day 18
1 1376. 通知所有员工所需的时间
class Solution {
int[] informTime;
public int numOfMinutes(int n, int headID, int[] manager, int[] informTime) {
this.informTime=informTime;
Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map= new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
map.putIfAbsent(manager[i],new ArrayList<Integer>());
map.get(manager[i]).add(i);
}
return dfs(map,headID);
}
public int dfs(Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map,Integer headID){
int res=0;
for(Integer i:map.getOrDefault(headID,new ArrayList<Integer>())){
res =Math.max(res,dfs(map,i));
}
return informTime[headID]+res;
}
}
(2)BFS
class Solution {
int[] informTime;
public int numOfMinutes(int n, int headID, int[] manager, int[] informTime) {
this.informTime=informTime;
Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map= new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
map.putIfAbsent(manager[i],new ArrayList<Integer>());
map.get(manager[i]).add(i);
}
return dfs(map,headID);
}
public int dfs(Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map,Integer headID){
int res=0;
for(Integer i:map.getOrDefault(headID,new ArrayList<Integer>())){
res =Math.max(res,dfs(map,i));
}
return informTime[headID]+res;
}
}
2 1041. 困于环中的机器人
class Solution {
public boolean isRobotBounded(String instructions) {
int[][] direc = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int direcIndex = 0;
int x = 0, y = 0;
int n = instructions.length();
for (int idx = 0; idx < n; idx++) {
char instruction = instructions.charAt(idx);
if (instruction == 'G') {
x += direc[direcIndex][0];
y += direc[direcIndex][1];
} else if (instruction == 'L') {
direcIndex += 3;
direcIndex %= 4;
} else {
direcIndex++;
direcIndex %= 4;
}
}
return direcIndex != 0 || (x == 0 && y == 0);
}
}
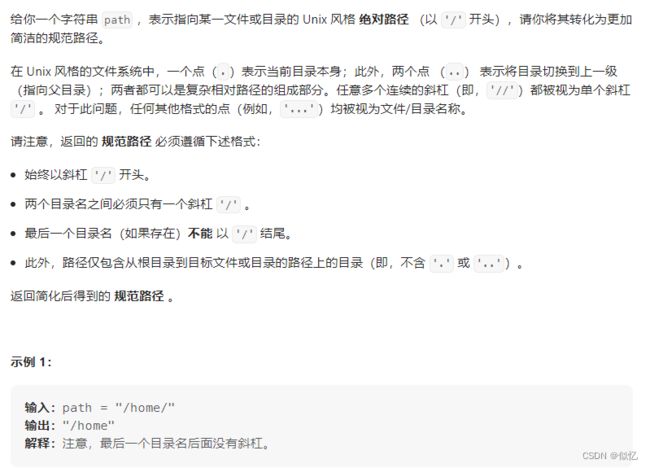
3 71. 简化路径
class Solution {
public String simplifyPath(String path) {
String[] names=path.split("/");
Deque<String> deque=new LinkedList<String>();
for(String name:names){
if("..".equals(name)){
if(!deque.isEmpty()){
deque.pollLast();
}
}else if(name.length()>0 && !".".equals(name)){
deque.offerLast(name);
}
}
StringBuilder ans=new StringBuilder();
if(deque.isEmpty()){
ans.append('/');
}else{
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
ans.append('/');
ans.append(deque.pollFirst());
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
4 55. 跳跃游戏

解析:
(1)自己的方法
查询所有可能为0的点,然后倒序进行查询,如果查询是否有点能通过0,有则为true,没有为false
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==1){
return true;
}
boolean res=true;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]==0 && i!=nums.length-1){
res=false;
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
if(nums[j]>i-j){
res=true;
break;
}
}
}
if(res==false){
break;
}
}
return res;
}
}
(2)官方解
public class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int rightmost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i <= rightmost) {
rightmost = Math.max(rightmost, i + nums[i]);
if (rightmost >= n - 1) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
5 45. 跳跃游戏 II
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int position = nums.length - 1;
int steps = 0;
while (position > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i + nums[i] >= position) {
position = i;
steps++;
break;
}
}
}
return steps;
}
}
(2) 正向查找可到达的最大位置
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int length = nums.length;
int end = 0;
int maxPosition = 0;
int steps = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
if (i == end) {
end = maxPosition;
steps++;
}
}
return steps;
}
}
Day 19
1 1306. 跳跃游戏 III

解析:
(1)自己的就是进行DFS,加上一个辅助数组防止循环
class Solution {
boolean[] map;
boolean a;
List<Integer> G;
public boolean canReach(int[] arr, int start) {
G=new ArrayList<Integer>();
a=false;
int n=arr.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(arr[i]==0){
G.add(i);
}
}
map=new boolean[n];
bfs(arr,start);
return a;
}
public void bfs(int[] arr,int start){
int n=arr.length;
for(int i=0;i<G.size();i++){
if(start==G.get(i)){
a=true;
}
}
map[start]=true;
if(start+arr[start]<n && map[start+arr[start]]==false){
bfs(arr,start+arr[start]);
}
if(start-arr[start]>=0&& map[start-arr[start]]==false){
bfs(arr,start-arr[start]);
}
// map[start]=false;
}
}
Day 20
1 1003. 检查替换后的词是否有效
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
StringBuilder stk = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
stk.append(c);
if (stk.length() >= 3 && stk.substring(stk.length() - 3).equals("abc")) {
stk.delete(stk.length() - 3, stk.length());
}
}
return stk.isEmpty();
}
}
(2)自己
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n=s.length();
Deque<Character> deque= new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
char re=s.charAt(i);
if(deque.size()==0){
if(re!='a'){
return false;
}
deque.addFirst(re);
}else{
if(re=='b' &&deque.peekLast()=='b' && deque.peek()=='c'){
return false;
}
if(re=='c' && deque.peekLast()=='a'){
return false;
}
deque.addLast(re);
if(re=='c'){
if(deque.size()<3){
return false;
}else{
deque.pollLast();
deque.pollLast();
if(deque.pollLast()!='a'){
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
return deque.size()==0?true:false;
}
}
(3) 新思路
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] cs = new char[s.length()];
int point = -1;
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
if (ch == 'c') {
if (point < 1 || cs[point--] != 'b' || cs[point--] != 'a') return false;
}
else cs[++point] = ch;
}
return point == -1;
}
}
2 294. 翻转游戏 II
private Map<String,Boolean> hmap = new HashMap<>();;
public boolean canWin(String s) {
if(hmap.containsKey(s)) return hmap.get(s);
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '+' && s.charAt(i-1) == '+'){
String ss = s.substring(0, i - 1) + "--" + s.substring(i + 1);
if(!canWin(ss)) {
hmap.put(ss,false);
return true;
}
hmap.put(ss,true);
}
}
return false;
}
3 589. N 叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
List<Integer> list;
public List<Integer> preorder(Node root) {
list=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root);
return list;
}
public void dfs(Node root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
List<Node> res=root.children;
list.add(root.val);
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
dfs(res.get(i));
}
}
}
Day 21
1 2106. 摘水果
class Solution {
public int maxTotalFruits(int[][] fruits, int startPos, int k) {
int m=fruits.length;
int[] id=new int[m];
int[] sum=new int[m+1];
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
id[i]=fruits[i][0];
sum[i+1] =sum[i]+fruits[i][1];
}
for(int x=0;x<=k/2;x++){
int y=k-2*x;
int left=startPos-x;
int right=startPos+y;
int start=low(id,0,m-1,left);
int end=high(id,0,m-1,right);
count =Math.max(count,sum[end]-sum[start]);
y=y=k-2*x;
left=startPos-y;
right=startPos+x;
start=low(id,0,m-1,left);
end=high(id,0,m-1,right);
count =Math.max(count,sum[end]-sum[start]);
}
return count;
}
public int low(int[] arr,int left,int right,int val){
int res = right + 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] >= val) {
res = mid;
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
public int high(int[] arr,int left,int right,int val){
int res = right + 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] > val) {
res = mid;
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxTotalFruits(int[][] fruits, int startPos, int k) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int n = fruits.length;
int sum = 0;
int ans = 0;
// 每次固定住窗口右边界
while (right < n) {
sum += fruits[right][1];
// 移动左边界
while (left <= right && step(fruits, startPos, left, right) > k) {
sum -= fruits[left][1];
left++;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, sum);
right++;
}
return ans;
}
public int step(int[][] fruits, int startPos, int left, int right) {
return Math.min(Math.abs(startPos - fruits[right][0]), Math.abs(startPos - fruits[left][0])) + fruits[right][0] - fruits[left][0];
}
}
2 1749. 任意子数组和的绝对值的最大值
class Solution {
public int maxAbsoluteSum(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int[] dp=new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
dp[i+1]=nums[i]+dp[i];
min=Math.min(dp[i+1],min);
max=Math.max(dp[i+1],max);
}
return Math.max(Math.abs(max-min),Math.max(Math.abs(max),Math.abs(min)));
}
}
Day 22
1 135. 分发糖果
class Solution {
public int candy(int[] ratings) {
int n = ratings.length;
int ret = 1;
int inc = 1, dec = 0, pre = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (ratings[i] >= ratings[i - 1]) {
dec = 0;
pre = ratings[i] == ratings[i - 1] ? 1 : pre + 1;
ret += pre;
inc = pre;
} else {
dec++;
if (dec == inc) {
dec++;
}
ret += dec;
pre = 1;
}
}
return ret;
}
}
2 490. 迷宫
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[maze.length][maze[0].length];
return dfs(maze, start, destination, visited);
}
public boolean dfs(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination, boolean[][] visited) {
if (visited[start[0]][start[1]])
return false;
if (start[0] == destination[0] && start[1] == destination[1])
return true;
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true;
int r = start[1] + 1, l = start[1] - 1, u = start[0] - 1, d = start[0] + 1;
while (r < maze[0].length && maze[start[0]][r] == 0) // right
r++;
if (dfs(maze, new int[] {start[0], r - 1}, destination, visited))
return true;
while (l >= 0 && maze[start[0]][l] == 0) //left
l--;
if (dfs(maze, new int[] {start[0], l + 1}, destination, visited))
return true;
while (u >= 0 && maze[u][start[1]] == 0) //up
u--;
if (dfs(maze, new int[] {u + 1, start[1]}, destination, visited))
return true;
while (d < maze.length && maze[d][start[1]] == 0) //down
d++;
if (dfs(maze, new int[] {d - 1, start[1]}, destination, visited))
return true;
return false;
}
}
(2)BFS
class Solution {
public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int[] xr=new int[]{0,1,0,-1};
int[] yr=new int[]{1,0,-1,0};
int m=maze.length;
int n=maze[0].length;
boolean[][] vis=new boolean[m][n];
Deque<int[]> deque=new LinkedList<>();
deque.push(start);
vis[start[0]][start[1]]=true;
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
int[] res=deque.poll();
int x=res[0];
int y=res[1];
if(x==destination[0] && y==destination[1]){
return true;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int xre=x+xr[i];
int yre=y+yr[i];
while(xre>=0&&xre<m && yre>=0 && yre<n && maze[xre][yre]==0){
xre +=xr[i];
yre +=yr[i];
}
if(!vis[xre-xr[i]][yre-yr[i]]){
deque.push(new int[]{xre-xr[i],yre-yr[i]});
vis[xre-xr[i]][yre-yr[i]]=true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
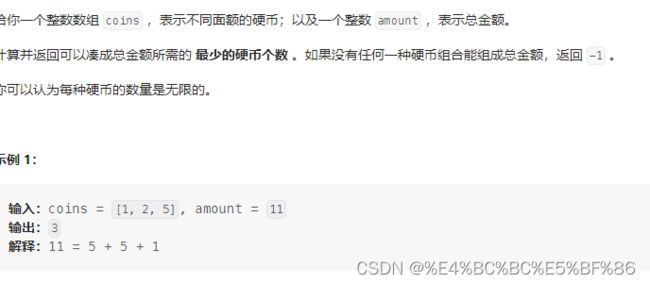
3 322. 零钱兑换
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if (amount < 1) {
return 0;
}
return coinChange(coins, amount, new int[amount]);
}
private int coinChange(int[] coins, int rem, int[] count) {
if (rem < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (rem == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (count[rem - 1] != 0) {
return count[rem - 1];
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int coin : coins) {
int res = coinChange(coins, rem - coin, count);
if (res >= 0 && res < min) {
min = 1 + res;
}
}
count[rem - 1] = (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? -1 : min;
return count[rem - 1];
}
}
(2)动态规划
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int n=coins.length;
int[] dp=new int[amount+1];
Arrays.fill(dp,amount+1);
dp[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<amount+1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(coins[j]<=i){
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i],dp[i-coins[j]]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount]>amount?-1:dp[amount];
}
}
4 518. 零钱兑换 II
class Solution {
public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int coin : coins) {
for (int i = coin; i <= amount; i++) {
dp[i] += dp[i - coin];
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
}
Day 23
1 1419. 数青蛙
class Solution {
public int minNumberOfFrogs(String croakOfFrogs) {
if (croakOfFrogs.length() % 5 != 0) {
return -1;
}
int res = 0, frogNum = 0;
int[] cnt = new int[4];
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>() {{
put('c', 0);
put('r', 1);
put('o', 2);
put('a', 3);
put('k', 4);
}};
for (int i = 0; i < croakOfFrogs.length(); i++) {
char c = croakOfFrogs.charAt(i);
int t = map.get(c);
if (t == 0) {
cnt[t]++;
frogNum++;
if (frogNum > res) {
res = frogNum;
}
} else {
if (cnt[t - 1] == 0) {
return -1;
}
cnt[t - 1]--;
if (t == 4) {
frogNum--;
} else {
cnt[t]++;
}
}
}
if (frogNum > 0) {
return -1;
}
return res;
}
}
2 198. 打家劫舍
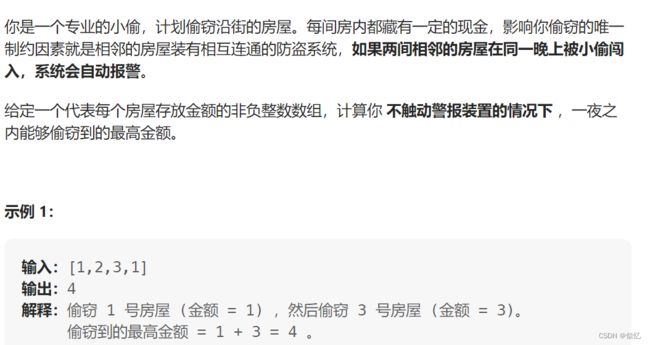
解析:
动态规划问题
首先确认状态转移方程,到当前房子,可以选择不打劫,也可以打劫,故

public int rob(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 子问题:
// f(k) = 偷 [0..k) 房间中的最大金额
// f(0) = 0
// f(1) = nums[0]
// f(k) = max{ rob(k-1), nums[k-1] + rob(k-2) }
int N = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[N+1];
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = nums[0];
for (int k = 2; k <= N; k++) {
dp[k] = Math.max(dp[k-1], nums[k-1] + dp[k-2]);
}
return dp[N];
}
3 213. 打家劫舍 II
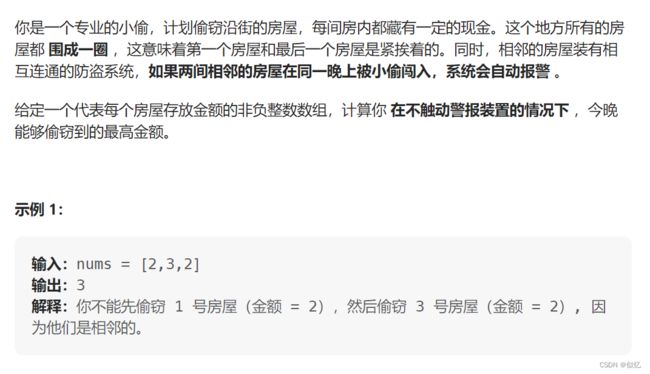
解析:
类似于上题的思路,不同是首尾连环了,我们可以分别去掉头和尾再分别按上题思路计算结果,最后返回最大值。
class Solution {
public int rob(int[] nums) {
int length = nums.length;
if (length == 1) {
return nums[0];
} else if (length == 2) {
return Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
}
return Math.max(robRange(nums, 0, length - 2), robRange(nums, 1, length - 1));
}
public int robRange(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
int first = nums[start], second = Math.max(nums[start], nums[start + 1]);
for (int i = start + 2; i <= end; i++) {
int temp = second;
second = Math.max(first + nums[i], second);
first = temp;
}
return second;
}
}
4 1631. 最小体力消耗路径
class Solution {
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
int left = 0, right = 999999, ans = 0;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
boolean[] seen = new boolean[m * n];
seen[0] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int x = cell[0], y = cell[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int nx = x + dirs[i][0];
int ny = y + dirs[i][1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !seen[nx * n + ny] && Math.abs(heights[x][y] - heights[nx][ny]) <= mid) {
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
seen[nx * n + ny] = true;
}
}
}
if (seen[m * n - 1]) {
ans = mid;
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-with-minimum-effort/solutions/581109/zui-xiao-ti-li-xiao-hao-lu-jing-by-leetc-3q2j/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。