ShardingSphere——分片及策略
SpringBoot配置文件
pom文件
<!-- shardingsphere 4.1.0配置 -->
<!-- 基本配置 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-core-common</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-common</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-core-api</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>encrypt-core-common</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-core</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 事务配置(需要时增加) -->
<!-- XA事务模块 -->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-transaction-core</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-transaction-xa-core</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>-->
<!-- BASE事务(Seata)模块 -->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-transaction-base-seata-at</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>-->
<!-- 数据编排治理(需要时增加) -->
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-orchestration-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>-->
<!-- 使用Zookeeper作为编排治理组件 -->
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-orchestration-center-zookeeper-curator</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>-->
项目配置文件
ShardingSphere项目配置文件支持application.properties、application.yml、Spring XML、JavaBean等多种方式。配置文件需包含的配置如下:
- 指定Datasource名字
- 每个具体的Datasource的连接数据库的信息
- 分库的策略
- 分表的策略(单个表或者多个表分表策略、主键策略)
- 读写分离配置(如果需要的话)
- 数据治理配置(如果需要的话)
# 数据源配置
# 指定多个database的名字,逗号隔开(必要项)
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=
# 可以配置多个DataSource,和names等号后的对应
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=
# 分库配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=
# 如果有绑定表的话
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables=
# 分表配置(一个或多个)
# 指定真实表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=
# 分片键设置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=
# 分片键设置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=
# 广播表设置(逗号分隔指定多个)
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=
# 打印SQL
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
JavaBean配置方式示例
public class MasterSlaveConfiguration {
public DataSource getDataSource() throws SQLException {
// 配置读写分离规则
MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration masterSlaveRuleConfig = new MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration(
"ds_master_slave", "ds_master",
Arrays.asList("ds_slave0", "ds_slave1"));
// 获取数据源对象
DataSource dataSource = MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(
createDataSourceMap(),
masterSlaveRuleConfig, new Properties());
return dataSource;
}
private Map<String, DataSource> createDataSourceMap() {
// 配置真实数据源
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
// 配置主库
DruidDataSource masterDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
masterDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
masterDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_master");
masterDataSource.setUsername("root");
masterDataSource.setPassword("123456");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_master", masterDataSource);
// 配置第一个从库
DruidDataSource slaveDataSource1 = new DruidDataSource();
slaveDataSource1.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
slaveDataSource1.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_slave0");
slaveDataSource1.setUsername("root");
slaveDataSource1.setPassword("123456");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_slave0", slaveDataSource1);
// 配置第二个从库
DruidDataSource slaveDataSource2 = new DruidDataSource();
slaveDataSource2.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
slaveDataSource2.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_slave1");
slaveDataSource2.setUsername("root");
slaveDataSource2.setPassword("123456");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_slave1", slaveDataSource2);
return dataSourceMap;
}
}
分片及策略
分片键
用于分片的数据库字段,是将数据库(或者表)拆分的关键字段。
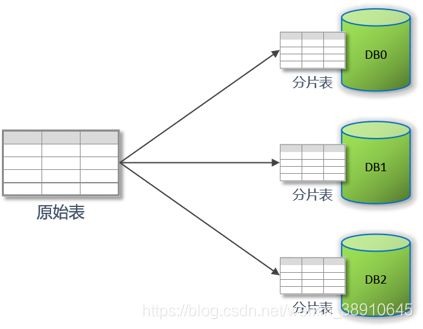
例如:将订单表中的订单主键的尾数取模分片,则订单主键为分片字段。
分片策略
ShardingSphere通过分片算法将数据分片。真正可用于分片操作的是分片键和分片算法,也就是分片策略则包含分片键和算法。
// 分片策略接口
public interface ShardingStrategy {
// 分片键
Collection<String> getShardingColumns();
// 分片算法
Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, Collection<RouteValue> shardingValues, ConfigurationProperties properties);
}
行表达策略(Inline)
对应InlineShardingStrategy。提供对SQL语句中的=和IN的分片操作支持,只支持单分片键。在繁琐的数据分片规则配置中,随着数据节点的增多,大量的重复配置使得配置本身不易被维护。通过行表达式可以有效的简化数据节点配置工作量。
行表达式的内容使用的是Groovy的语法,Groovy能够支持的所有操作,行表达式均能够支持。ShardingSphere提供了2种Groovy方式:
- 枚举型:${begin…end}
// 语法示例
db0.t_order${0..1},db1.t_order${2..4}
// 解析后
db0.t_order0 db0.t_order1
db1.t_order2 db1.t_order3 db1.t_order4
- 范围型:${[n0,n1,n2,nx]}
// 语法示例
${['t1', 't2']}_table${1..3}
// 解析后
t1_table1, t1_table2, t1_table3, t2_table1, t2_table2, t2_table3
使用示例
application.properties配置文件
# 数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
# 分库配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables=t_order,t_order_item
# t_order分表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}
# 分片键设置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order$->{order_id % 2}
#sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator-class-name=io.shardingsphere.core.keygen.DefaultKeyGenerator
#sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator-column-name=id
# t_order_item分表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_item$->{0..1}
# 分片键设置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order_item$->{order_id % 2}
# 广播表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_province
# sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_province
# 打印SQL
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
标准策略(Standard)
StandardShardingStrategy只支持单分片键,提供PreciseShardingAlgorithm和RangeShardingAlgorithm两个分片算法。
PreciseShardingAlgorithm是必选的,用于处理=和IN的分片。RangeShardingAlgorithm是可选的,用于处理BETWEEN AND, >, <, >=, <=分片,如果不配置RangeShardingAlgorithm,SQL中的BETWEEN AND将按照全库路由处理。
复合策略(Complex)
ComplexShardingStrategy支持多分片键,由于多分片键之间的关系复杂,因此并未进行过多的封装,而是直接将分片键值组合以及分片操作符透传至分片算法,完全由应用开发者实现,提供最大的灵活度。
使用示例
自定义算法接口
public interface ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<T extends Comparable<?>> extends ShardingAlgorithm {
// 实现该函数的主要目的:根据shardingValue的值,最终计算出数据应该落在
// 哪个分片上(确定数据存放位置)
// availableTargetNames 从配置文件中读取出来的Database或者Table
// shardingValues 是sql中包含的分片键的值
Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<T> shardingValue);
}
自定义Complex分片算法
public class ComplexShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames,
ComplexKeysShardingValue<Integer> shardingValues) {
{
System.out.println("collection:" + availableTargetNames + ",shardingValues:" + shardingValues);
Collection<Integer> orderIdValues = getShardingValue(shardingValues, "order_id");
Collection<Integer> userIdValues = getShardingValue(shardingValues, "user_id");
List<String> shardingSuffix = new ArrayList<>();
// user_id,order_id分片键进行分表
for (Integer userId : userIdValues) {
for (Integer orderId : orderIdValues) {
String suffix = userId % 2 + "_" + orderId % 2;
for (String s : availableTargetNames) {
if (s.endsWith(suffix)) {
shardingSuffix.add(s);
}
}
}
}
return shardingSuffix;
}
}
private Collection<Integer> getShardingValue(ComplexKeysShardingValue<Integer> shardingValues,
final String key) {
Map<String, Collection<Integer>> map = shardingValues.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap();
return map.get(key);
}
}
application.properties配置文件
# 数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
# 分库配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables=t_order,t_order_item
# t_order分表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=user_id,order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=ai.yunxi.sharding.config.ComplexShardingAlgorithm
# t_order_item分表配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_item$->{0..1}_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=user_id,order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order_item.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=ai.yunxi.sharding.config.ComplexShardingAlgorithm
# 打印SQL
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
Hint强制路由(Hint)
有些SQL语句比较复杂比如说有 INSERT INTO … SELECT … FROM,这个时候sqlparser并不支持的时候。这种情况下,可以通过sharding-jdbc的Hint分片策略来实现各种sharding-jdbc不支持的语法的限制。
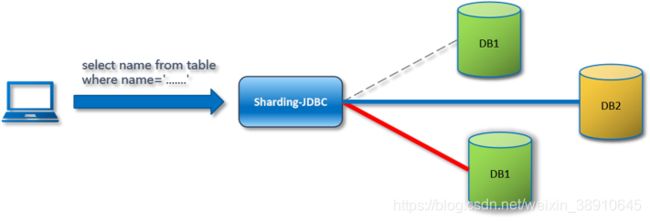
因为Hint分片策略是绕过SQL解析的,所以对于这些比较复杂的需要分片的查询,采用Hint分片策略性能可能会更好。
hint策略需要实现org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingAlgorithm接口。
不支持的SQL
- 不支持CASE WHEN、HAVING、UNION (ALL)
- 有限支持子查询。无论嵌套多少层,ShardingSphere都可以解析至第一个包含数据表的子查询,一旦在下层嵌套中再次找到包含数据表的子查询将直接抛出解析异常。
- 运算表达式和函数中的分片键会导致全路由。
-- 不支持UNION
SELECT * FROM t_order1 UNION SELECT * FROM t_order2
INSERT INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT col1, col2, … FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ?
-- 不支持多层子查询
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM (SELECT * FROM t_order o WHERE o.id IN (SELECT id FROM t_order WHERE status = ?))
-- 不支持函数计算。ShardingSphere只能通过SQL字面提取用于分片的值
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE to_date(create_time, 'yyyy-mm-dd') = '2019-01-01';
使用示例
自定义Hint分片算法
public class HintShardingKeyAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames,
HintShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
System.out.println("shardingValue=" + shardingValue);
System.out.println("availableTargetNames=" + availableTargetNames);
List<String> shardingResult = new ArrayList<>();
for (String targetName : availableTargetNames) {
String suffix = targetName.substring(targetName.length() - 1);
if (StringUtils.isNumber(suffix)) {
Collection<Integer> tmpSharding = shardingValue.getValues();
for (Integer value : tmpSharding) {
// ds0, ds1
if (value % 2 == Integer.parseInt(suffix)) {
shardingResult.add(targetName);
}
}
}
}
return shardingResult;
}
}
application.properties配置文件
# 数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
# 分库配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
# t_order强制分片配置
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=ai.yunxi.sharding.config.HintShardingKeyAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=ai.yunxi.sharding.config.HintShardingKeyAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
读写分离
对于读多写少的场景,如果读操作成为数据库访问的瓶颈,这时如果希望能够提升数据库的读性能,那么就可以使用读写分离架构。

ShardingSphere对于主库写操作,目前仅支持单主库。查询数据操作所使用的数据库,支持多从库,并支持通过负载均衡策略将查询请求发送到不同的从库。
使用示例
# 主从读写分离
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1,ds2
# 主数据源(负责写)
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds0.password=123456
# 从数据源(负责读)
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds2
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456
# 读写分离配置
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.name=dataSource
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.load-balance-algorithm-type=round_robin
# 负责写
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.master-data-source-name=ds0
# 负责读
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.slave-data-source-names=ds1,ds2
# 打印SQL
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
深入核心
ShardingSphere的数据分片核心流程由以下几个重要流程组成:
SQL解析 => 执行器优化 => SQL路由 => SQL改写 => SQL执行 => 结果归并
- SQL解析:通过词法解析器将SQL拆分为一个个不可再分的单词。再使用语法解析器对SQL进行理解,并解析出上下文
- 查询优化:合并和优化分片条件,如OR等
- SQL路由:根据解析上下文匹配用户配置的分片策略,并生成路由路径
- SQL改写:将SQL改写为在真实数据库中可以正确执行的语句
- SQL执行:通过多线程执行器异步执行
- 结果归并:将多个执行结果集归并以便于通过统一的JDBC接口输出。结果归并包括流式归并、内存归并和使用装饰者模式的追加归并
MetaData加载
SQL解析
Antlr
ANTLR是一款强大的语法分析器生成工具,可用于读取、处理、执行和翻译结构化的文本或二进制文件。它被广泛应用于学术领域和工业生产实践,是众多语言、工具和框架的基石。Twitter搜索使用ANTLR进行语法分析,每天处理超过20亿次查询;Hadoop生态系统中的Hive、Pig、数据仓库和分析系统所使用的语言都用到了ANTLR;Oracle公司在SQL开发者IDE和迁移工具中使用了ANTLR;Hibernate ORM映射框架使用ANTLR来处理HQL语言。
Antlr语法规则文件:https://github.com/antlr/grammars-v4
应用领域
- 定制特定领域语言(DSL):类似hibernate中的HQL,用DSL来定义要执行操作的高层语法,这种语法接近人可理解的语言,由DSL到计算机语言的翻译则通过ANTLR来做,可在ANTLR的结构语言中定义DSL命令具体要执行何种操作
- 文本解析:可利用ANTLR解析JSON,HTML,XML,EDIFACT,或自定义的报文格式。解析出来的信息需要做什么处理也可以在结构文件中定义
- 数学计算:加减乘除,线性方程,几何运算,微积分等等
ANTLR 语法识别一般分为二个阶段:
1、词法分析 (lexical analysis):对应的分析程序叫做 Lexer ,负责将符号(Token)分组成符号类(Token Class or Token Type)
2、语法解析:根据词法,构建出一棵分析树或叫抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)
ShardingSphere在解析SQL过程同样分为词法解析和语法解析。词法解析读取字符流,将SQL语句分组为单词或者符号(Token),并标记每一个符号的类别。而后根据不同数据库方言所提供的字典,将其归类为关键字,表达式,字面量和操作符。 再使用语法解析器将SQL转换为抽象语法树。
SELECT id, name FROM t_user WHERE status = ‘ACTIVE’ AND age > 18
解析之后的为抽象语法树见下图:

抽象语法树中的关键字的Token用绿色表示,变量的Token用红色表示,灰色表示需要进一步拆分。
通过对抽象语法树的遍历去提炼分片所需的上下文,并标记有可能需要改写的位置。供分片使用的解析上下文包含:
- 查询选择项(Select Items)
- 表信息(Table)
- 分片条件(Sharding Condition)
- 自增主键信息(Auto increment Primary Key)
- 排序信息(Order By)
- 分组信息(Group By)
- 分页信息(Limit、Rownum、Top)
SQL 解析引擎在 parsing 包下,通常包含两大组件:
- Lexer:词法解析器
- Parser:SQL解析器
两者都是解析器,区别在于 Lexer 只做词法的解析,不关注上下文,将字符串拆解成 N 个词法。而 Parser 在 Lexer 的基础上,还需要理解 SQL。
Lexer
Lexer 能把相关的记号组成记号类型,例如INT(整数)、ID(标志符)、FLOAT(浮点数)等。记号至少包含两块信息:记号类型(确定词法结构)和匹配记号的文本。

Parser
词法解析器Lexer是如何解析SQL里的词法。而SQL解析引擎是如何解析与理解SQL的是建立在词法解析之上。区别于 Lexer,Parser 理解SQL:
- 提炼分片上下文
- 标记需要SQL改写的部分
- SQLParserEngine :SQL 解析引擎(调用 StatementParser 解析 SQL)
- SQLParser :SQL 解析器(调用 SQLParserExecutor 执行SQL )
- Parser :SQL语句解析器(调用 具体的Lexer 解析 SQL 词法)
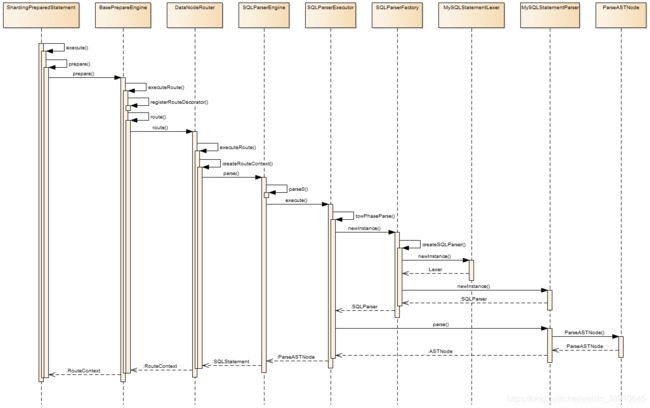
源码解析
SQL路由
根据解析上下文匹配数据库和表的分片策略,并生成路由路径。 对于携带分片键的SQL,根据分片键的不同可以划分为单片路由(分片键的操作符是等号)、多片路由(分片键的操作符是IN)和范围路由(分片键的操作符是BETWEEN)。不携带分片键的SQL则采用广播路由。

分片路由
根据分片键进行路由。具体又可以划分为3种类型:
- 直接路由
- 标准路由
- 笛卡尔路由
广播路由
对于不携带分片键的SQL,则采取广播路由的方式。具体又可以划分为5种类型:
SQL改写
在包含分表的场景中,需要将分表配置中的逻辑表名称改写为路由之后所获取的真实表名称。仅分库则不需要对表名称进行改写。除此之外,还包括补列和分页信息修正等内容。
源码解析
结果归并
将从各个数据节点获取的多数据结果集,组合成为一个结果集并正确的返回至请求客户端,称为结果归并。
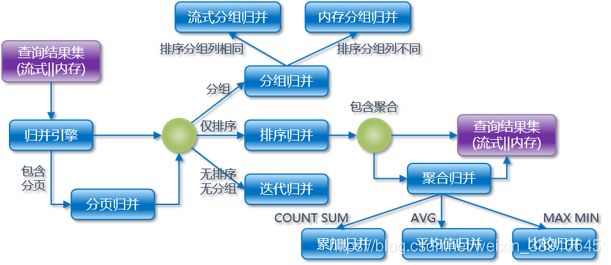
ShardingSphere支持的结果归并从功能上分为以下5种类型:
- 遍历归并
- 排序归并
- 分组归并
- 聚合归并
- 分页归并
它们是组合而非互斥的关系。 从结构划分,可分为流式归并、内存归并和装饰者归并。流式归并和内存归并是互斥的,装饰者归并可以在流式归并和内存归并之上做进一步的处理。