Java 中使用 protobuf :复杂深入篇,看这篇就够了!
上篇文章我们遗留了几个问题
1、protobuf 有没有数据类型?protobuf 怎么与 Java 数据类型对应?
2、protobuf 怎么运用到我们的项目当中?复杂的 List、Map、内嵌对象等等怎么实现?
3、protobuf 怎么和 JSON 互相转换?
4、protobuf 与 Java 对象互转
别急,我们现在继续深入,学习就是要不断深入了解,只有更深入,你才能体会到快乐和成就感
继续接着上一个项目来写
一、protobuf 与 Java 数据类型对应
1、字段规则
required : 字段只能也必须出现 1 次,多用于必填项,必须赋值的字符
例如:
required int32 id = 1 [default = 123]
optional : 字段可出现 0 次或多次,可有可无的字段,可以使用[default = xxx]配置默认值
例如:
optional string name = 1 [default = "张三"]
repeated : 字段可出现任意多次(包括 0),多用于 Java List 属性
例如:
//list String
repeated string strList = 5;
//list 对象
repeated Role roleList = 6;
2、字段编号(标识符):
1 ~ 536870911(除去 19000 到 19999 之间的标识号, Protobuf 协议实现中对这些进行了预留。如果非要在.proto 文件中使用这些预留标识号,编译时就会报警)
在消息定义中,每个字段都有唯一的一个标识符。这些标识符是用来在消息的二进制格式中识别各个字段的,一旦开始使用就不能够再改 变。注:[1,15]之内的标识号在编码的时候会占用一个字节。[16,2047]之内的标识号则占用2个字节。所以应该尽可能为那些频繁出现的消息元素保留 [1,15]之内的标识号
3、字段类型
3.1、基本常用类型
| protobuf 类型 | java 类型 |
|---|---|
| double | double |
| float | float |
| int32 | int |
| int64 | long |
| bool | boolean |
| string | String |
系统默认值:
string默认为空字符串
bool默认为false
数值默认为0
enum默认为第一个元素
3.2、复杂类型
3.2.1、Java String、Integer List 在 protobuf 的定义
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
//list Int
repeated int32 intList = 1;
//list String
repeated string strList = 5;
}
3.2.2、Java 对象 List 在 protobuf 的定义
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
//list 对象
repeated Role roleList = 6;
}
3.2.3、Java String、Integer Map 在 protobuf 的定义
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
// 定义简单的 Map string
map<string, int32> intMap = 7;
// 定义复杂的 Map 对象
map<string, string> stringMap = 8;
}
3.2.4、Java 对象 Map 在 protobuf 的定义
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
// 定义复杂的 Map 对象
map<string, MapVauleObject> mapObject = 8;
}
// 定义 Map 的 value 对象
message MapVauleObject {
string code = 1;
string name = 2;
}
3.2.5、Java 实体类中嵌套实体 在 protobuf 的定义
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
// 对象
NickName nickName = 4;
}
// 定义一个新的Name对象
message NickName {
string nickName = 1;
}
4、定义 proto 的一个属性
看完上面的,你应该明白要怎么定义一个 proto 对象的属性
格式如下
字段规则(可选) 字段类型 字段名称 字段标识符 字段默认值(可选)
例如:
4.1、一个相当于 Java 中的 String类型
Java 实体类写法
private String name;
proto 写法
string name = 1;
4.2、一个相当于 Java 中的 list 类型
Java 实体类写法
private List list;
proto 写法
repeated string list = 1;
二、实现 Java 中 复杂的对象嵌套
看这个之前,应该耐心把上面的数据类型对应先了解清楚
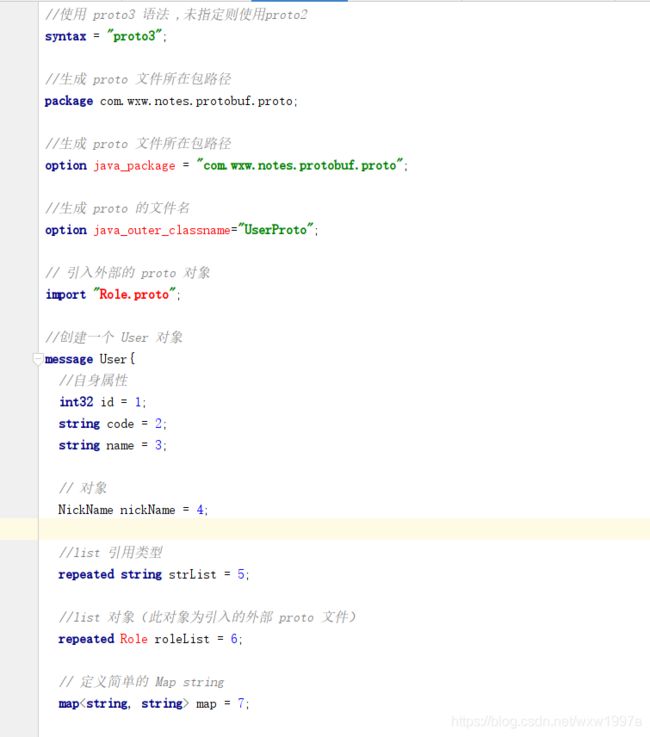
1、直接上一个成品 .proto 文件
这个文件包含了我们平常 Java 实体类属性的基本用法
比如,int、String、内置对象、内置List、内置 Map
//使用 proto3 语法 ,未指定则使用proto2
syntax = "proto3";
// proto 文件包名
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto;
//生成 proto 文件所在包路径,一般来说是和文件包名一致就可以
option java_package = "com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto";
//生成 proto 的文件名
option java_outer_classname="UserProto";
// 引入外部的 proto 对象
import "Role.proto";
//创建一个 User 对象
message User{
//自身属性
int32 id = 1;
string code = 2;
string name = 3;
// 对象
NickName nickName = 4;
//list 引用类型
repeated string strList = 5;
//list 对象(此对象为引入的外部 proto 文件)
repeated Role roleList = 6;
// 定义简单的 Map string
map<string, string> map = 7;
// 定义复杂的 Map 对象
map<string, MapVauleObject> mapObject = 8;
}
// 定义一个新的Name对象
message NickName {
string nickName = 1;
}
// 定义 Map 的 value 对象
message MapVauleObject {
string code = 1;
string name = 2;
}
同样的,代码拿过去之后,有报错不要认为自己有问题,语法高亮罢了
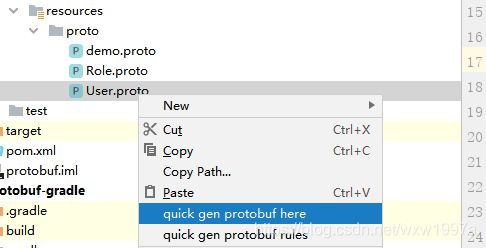
2、生成 proto 对象
3、编写测试类
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.test;
import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException;
import com.google.protobuf.MessageOrBuilder;
import com.google.protobuf.TextFormat;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.RoleProto;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.UserProto;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ComplexTestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化数据
UserProto.User.Builder user = UserProto.User.newBuilder();
user.setId(1)
.setCode("001")
.setName("张三")
.build();
//内部对象
UserProto.NickName.Builder nickName = UserProto.NickName.newBuilder();
user.setNickName(nickName.setNickName("昵称").build());
//简单 list
user.addStrList("01");
user.addStrList("02");
//object list
RoleProto.Role.Builder role1 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role1.setCode("001");
role1.setName("管理员");
RoleProto.Role.Builder role2 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role2.setCode("002");
role2.setName("操作员");
user.addRoleList(role1);
user.addRoleList(role2);
//简单 map
user.putMap("key1", "value1");
user.putMap("key2", "value2");
//object map
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap1 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap1", objectMap1.setCode("code1").setName("name1").build());
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap2 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap2", objectMap2.setCode("code2").setName("name2").build());
//序列化
UserProto.User build = user.build();
//转换成字节数组
byte[] s = build.toByteArray();
System.out.println("protobuf数据bytes[]:" + Arrays.toString(s));
System.out.println("protobuf序列化大小: " + s.length);
UserProto.User user1 = null;
String jsonObject = null;
try {
//反序列化
user1 = UserProto.User.parseFrom(s);
System.out.println("反序列化:\n" + user1.toString());
System.out.println("中文反序列化:\n" + printToUnicodeString(user1));
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// System.out.println("***********************************************");
// //中文反序列化时会转成八进制,可采用 TextFormat.printToUnicodeString 进行转换
// System.out.println("直接反序列化:\n" + printToUnicodeString(user1));
}
/**
* 处理反序列化时中文出现的八进制问题(属性值为中文时可能会出现这样的八进制\346\223\215\344\275\234\345\221\230)
* 可直接使用 protobuf 自带的 TextFormat.printToUnicodeString(message) 方法,但是这个方法过时了,直接从这个方法内部拿出来使用就可以了
*
* @param message 转换的 protobuf 对象
* @return string
*/
public static String printToUnicodeString(MessageOrBuilder message) {
return TextFormat.printer().escapingNonAscii(false).printToString(message);
}
}
4、测试截图
可以看到我们中文会乱码,不过问题不大,项目当中我们肯定也不是这样去使用
三、protobuf 和 JSON 互相转换
使用这个转换必须要使用 protobuf 的 java util jar 包
<!-- proto 与 Json 互转会用到-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java-util</artifactId>
<version>3.15.3</version>
</dependency>
1、protobuf 转 Json
String json = JsonFormat.printer().print(sourceMessage);
2、Json 转 protobuf
//ignoringUnknownFields 如果 json 串中存在的属性 proto 对象中不存在,则进行忽略,否则会抛出异常
JsonFormat.parser().ignoringUnknownFields().merge(json, targetBuilder);
return targetBuilder.build();
3、protobuf 和 JSON 互转工具类
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.util;
import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException;
import com.google.protobuf.Message;
import com.google.protobuf.util.JsonFormat;
/**
* 注意:
* - 该实现无法处理含有Any类型字段的Message
* - enum类型数据会转化为enum的字符串名
* - bytes会转化为utf8编码的字符串
*
以上这段暂未进行测试
*
* @author wuxiongwei
* @date 2021/5/13 16:04
* @Description proto 与 Json 转换工具类
*/
public class ProtoJsonUtil {
/**
* proto 对象转 JSON
* 使用方法: //反序列化之后
* UserProto.User user1 = UserProto.User.parseFrom(user);
* //转 json
* String jsonObject = ProtoJsonUtil.toJson(user1);
* @param sourceMessage proto 对象
* @return 返回 JSON 数据
* @throws InvalidProtocolBufferException
*/
public static String toJson(Message sourceMessage) throws InvalidProtocolBufferException {
if (sourceMessage != null) {
String json = JsonFormat.printer().includingDefaultValueFields().print(sourceMessage);
return json;
}
return null;
}
/**
* JSON 转 proto 对象
* 使用方法:Message message = ProtoJsonUtil.toObject(UserProto.User.newBuilder(), jsonObject);
* @param targetBuilder proto 对象 bulider
* @param json json 数据
* @return 返回转换后的 proto 对象
* @throws InvalidProtocolBufferException
*/
public static Message toObject(Message.Builder targetBuilder, String json) throws InvalidProtocolBufferException {
if (json != null) {
//ignoringUnknownFields 如果 json 串中存在的属性 proto 对象中不存在,则进行忽略,否则会抛出异常
JsonFormat.parser().ignoringUnknownFields().merge(json, targetBuilder);
return targetBuilder.build();
}
return null;
}
}
4、改造测试类
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.test;
import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException;
import com.google.protobuf.Message;
import com.google.protobuf.MessageOrBuilder;
import com.google.protobuf.TextFormat;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.RoleProto;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.UserProto;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.util.ProtoJsonUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JsonTestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化数据
UserProto.User.Builder user = UserProto.User.newBuilder();
user.setId(1)
.setCode("001")
.setName("张三")
.build();
//内部对象
UserProto.NickName.Builder nickName = UserProto.NickName.newBuilder();
user.setNickName(nickName.setNickName("昵称").build());
//简单 list
user.addStrList("01");
user.addStrList("02");
//object list
RoleProto.Role.Builder role1 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role1.setCode("001");
role1.setName("管理员");
RoleProto.Role.Builder role2 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role2.setCode("002");
role2.setName("操作员");
user.addRoleList(role1);
user.addRoleList(role2);
//简单 map
user.putMap("key1", "value1");
user.putMap("key2", "value2");
//object map
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap1 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap1", objectMap1.setCode("code1").setName("name1").build());
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap2 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap2", objectMap2.setCode("code2").setName("name2").build());
//序列化
UserProto.User build = user.build();
//转换成字节数组
byte[] s = build.toByteArray();
System.out.println("protobuf数据bytes[]:" + Arrays.toString(s));
System.out.println("protobuf序列化大小: " + s.length);
UserProto.User user1 = null;
String jsonObject = null;
try {
//反序列化
user1 = UserProto.User.parseFrom(s);
//proto 转 json
jsonObject = ProtoJsonUtil.toJson(user1);
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Json格式化结果:\n" + jsonObject);
System.out.println("Json格式化数据大小: " + jsonObject.getBytes().length);
//将 Json 数据转 proto 对象
try {
Message message = ProtoJsonUtil.toObject(UserProto.User.newBuilder(), jsonObject);
System.out.println("json 转 protobuf 对象:\n " + printToUnicodeString(message));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 处理反序列化时中文出现的八进制问题(属性值为中文时可能会出现这样的八进制\346\223\215\344\275\234\345\221\230)
* 可直接使用 protobuf 自带的 TextFormat.printToUnicodeString(message) 方法,但是这个方法过时了,直接从这个方法内部拿出来使用就可以了
*
* @param message 转换的 protobuf 对象
* @return string
*/
public static String printToUnicodeString(MessageOrBuilder message) {
return TextFormat.printer().escapingNonAscii(false).printToString(message);
}
}
5、测试截图
四、protobuf 与 Java 对象互转
本处使用了 lombok 和 Gson ,记得下载 lombok 插件和导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.6</version>
</dependency>
1、创建对应 Java 实体类
1.1、User
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author wuxiongwei
* @date 2021/5/13 14:55
* @Description
*/
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String code;
private String name;
private NickName nickName;
private List<String> strList;
private List<Role> roleList;
private Map<String,String> map;
private Map<String,MapVauleObject> mapObject;
}
1.2、Role
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.entity;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author wuxiongwei
* @date 2021/5/13 14:55
* @Description
*/
@Data
public class Role {
private String code;
private String name;
}
1.3、NickName
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.entity;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author wuxiongwei
* @date 2021/5/13 14:58
* @Description
*/
@Data
public class NickName {
private String NickName;
}
1.4、MapVauleObject
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.entity;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author wuxiongwei
* @date 2021/5/13 14:59
* @Description
*/
@Data
public class MapVauleObject {
private String code;
private String name;
}
2、改造测试类
package com.wxw.notes.protobuf.test;
import com.google.protobuf.InvalidProtocolBufferException;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.entity.User;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.RoleProto;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.proto.UserProto;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.util.JsonUtil;
import com.wxw.notes.protobuf.util.ProtoJsonUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JavaTestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化数据
UserProto.User.Builder user = UserProto.User.newBuilder();
user.setId(1)
.setCode("001")
.setName("张三")
.build();
//内部对象
UserProto.NickName.Builder nickName = UserProto.NickName.newBuilder();
user.setNickName(nickName.setNickName("昵称").build());
//简单 list
user.addStrList("01");
user.addStrList("02");
//object list
RoleProto.Role.Builder role1 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role1.setCode("001");
role1.setName("管理员");
RoleProto.Role.Builder role2 = RoleProto.Role.newBuilder();
role2.setCode("002");
role2.setName("操作员");
user.addRoleList(role1);
user.addRoleList(role2);
//简单 map
user.putMap("key1", "value1");
user.putMap("key2", "value2");
//object map
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap1 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap1", objectMap1.setCode("code1").setName("name1").build());
UserProto.MapVauleObject.Builder objectMap2 = UserProto.MapVauleObject.newBuilder();
user.putMapObject("objectMap2", objectMap2.setCode("code2").setName("name2").build());
//序列化
UserProto.User build = user.build();
//转换成字节数组
byte[] s = build.toByteArray();
System.out.println("protobuf数据bytes[]:" + Arrays.toString(s));
System.out.println("protobuf序列化大小: " + s.length);
UserProto.User user1 = null;
String jsonObject = null;
try {
//反序列化
user1 = UserProto.User.parseFrom(s);
//proto 转 json
jsonObject = ProtoJsonUtil.toJson(user1);
} catch (InvalidProtocolBufferException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Json格式化结果:\n" + jsonObject);
System.out.println("Json格式化数据大小: " + jsonObject.getBytes().length);
// 复制 proto 对象到 Java 对象 测试,测试下来只能复制基础的属性,内部对象等不可以复制,也就是只有浅拷贝
User user2 = new User();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(user1, user2);
System.out.println("复制后对象:\n " + user2.toString());
//通过 proto Json 数据转 Java 对象
Gson GSON = new GsonBuilder().serializeNulls().create();
User user3 = GSON.fromJson(jsonObject, User.class);
System.out.println("json 转换之后对象:\n " + user3.toString());
}
3、测试截图
五、小总结
至此,我们遗留的四个问题已经全部解决,学会基础入门篇和深入复杂篇之后,我们能够基本满足了日常开发
项目源码地址:https://github.com/wxwhowever/springboot-notes/tree/main/protobuf