mysql 索引和查询优化
mysql 索引和查询优化
关于索引
索引是一种排好序便于快速查找数据的数据结构,一般默认为 B+树 结构组织的索引,由于索引本身也很大,不可能全部存储在内存中,一般存储在磁盘上。
MySQL索引的建立对于MySQL的高效运行是很重要的,索引可以大大提高MySQL的检索速度。
实际上,索引也是一张表,该表保存了主键与索引字段,并指向实体表的记录。
上面都在说使用索引的好处,但过多的使用索引将会造成滥用。因此索引也会有它的缺点:虽然索引大大提高了查询速度,同时却会降低更新表的速度,如对表进行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE。因为更新表时,MySQL不仅要保存数据,还要保存一下索引文件。
因此,创建索引要根据项目业务场景分析进行创建。创建索引时,你需要确保该索引是应用在 SQL 查询语句的条件(一般作为 WHERE 子句的条件)。
同时,当表的数据量十分巨大的时候,索引的效率也有局限性了,则需要进行表的分区。
- 普通索引 : 任何字段都可以创建,一个索引只包含一个列,一个表可以有多个单列索引
- 唯一索引 : 字段的值必须有唯一性(允许空值)才可以创建,效率高于普通索引
- 主键索引 : 主键的值必须有唯一性才可以创建,当一个字段加上 primary key 或者 key,则默认加上主键索引,效率高于前两者
- 全文索引 : 只针对文本类型,不支持中文
索引建立情景
适合建立索引的情况:
- 主键自动建立唯一索引;
- 频繁作为查询条件的字段应该创建索引;
- 查询中与其他表关联的字段,外键关系建立索引;
- 在高并发下倾向于创建组合索引?
- 查询中排序的字段,排序字段若通过索引去访问将大大提高排序速度;
- 查询中 统计或 分组 字段
不适合建立索引的情况:
- Where 条件里用不到的字段不要创建索引;
- 经常需要增删改的表,对表进行 Insert,Update,Delete,需要更新表记录,同时页需要跟新索引文件;
- 表记录太少;
- 某个数据列包含过多的重复内存,则不需要建立,没有太大的实际效果;
优化指标
| 分析项 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| id: | 选择标识符 |
| select_type | 表示查询的类型 |
| table | 输出结果集的表 |
| partitions | 匹配的分区 |
| type | 表示表的连接类型 |
| possible_keys | 表示查询时,可能使用的索引 |
| key | 表示实际使用的索引 |
| key_len | 索引字段的长度 |
| ref | 列与索引的比较 |
| rows | 扫描出的行数(估算的行数) |
| filtered | 按表条件过滤的行百分比 |
| Extra | 执行情况的描述和说明 |
| 主要分析项 | 解释 | 优化常识 |
|---|---|---|
| type | 显示连接使用了哪种类别 从最好到最差的连接类型为const、eq_reg、ref、range、index和ALL |
避免 all |
| possiblyble_keys | 可能使用的索引 | 避免 null |
| key | 使用的索引 | 避免 null |
| rows | 遍历的行数 | 越少越好 |
| extra | 额外的操作 | 避免 using filesort, using temporary |
案例分析
使用测试数据
这里我模拟生成了200W条学生数据,和1000条班级记录进行关联。
- 测试用表:
create table i_class (
id int(11) key auto_increment,
cname varchar(20) default null comment "班级名称"
) engine = innodb default charset=utf8;
create table i_student (
id int(11) key auto_increment,
sname varchar(20) default null comment "学生名称",
sex tinyint(1) default 1 comment "性别",
age tinyint(3) default null comment "年龄",
classid int(11) default null comment "班级id",
idnumber varchar(25) default null comment "身份证",
education varchar(20) default null comment "学历"
) engine = innodb default charset=utf8;
- 数据:
use 库;
source index_test.sql;
- 查看表
可以看到目前只有一个主键索引。
show create table i_student;
#------
i_student | CREATE TABLE `i_student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`sname` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生名称',
`sex` tinyint(1) DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '性别,1为男生,2为女生',
`age` tinyint(3) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`classid` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '班级id',
`idnumber` varchar(25) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '身份证',
`education` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学历',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2000151 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
#-------
###案例1 - 查询 classid 为 5 的人数
sql 语句
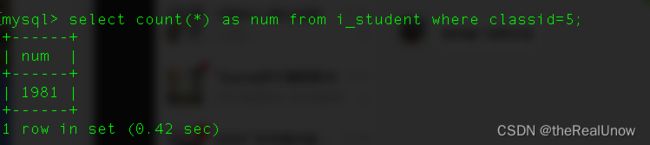
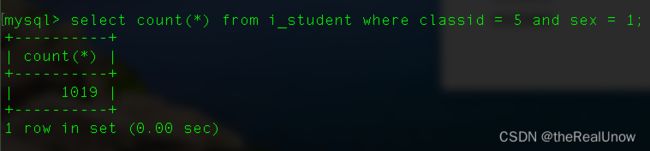
select count(*) from i_student where classid = 5;
结果
分析和优化
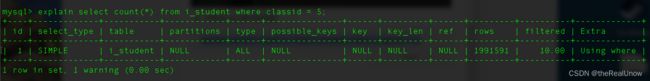
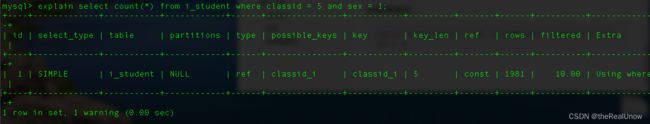
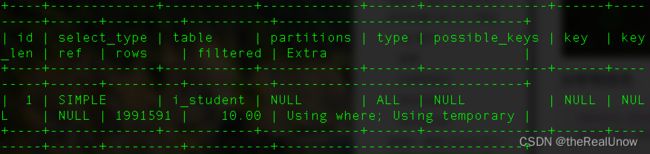
explain select count(*) from i_student where classid = 5;
-
分析:
type: NULL: 查看其第一性能指标 type ,发现它为 ALL ,它的性能是最差的,即全表遍历。之所以造成全表遍历,其原因是条件中 where classid=5 ,classid没有创建索引。
-
优化:
为 classid 设置索引
create index classid_i on i_student(classid);
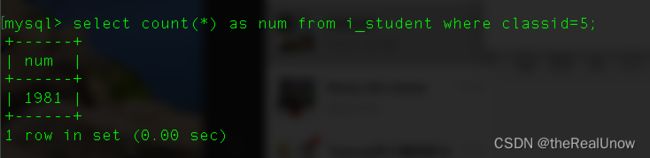
优化后测试
优化后分析
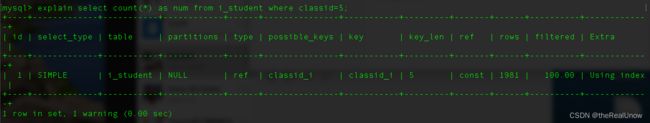
设置索引后,type 由 ALL 变为了 ref,rows 遍历行数也由之前的 199W+ 降低到 1981。
案例2 - 查询 classid 为 5 的男生人数
sql 语句
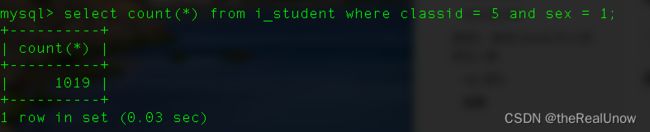
select count(*) from i_student where classid = 5 and sex = 1;
结果
分析和优化
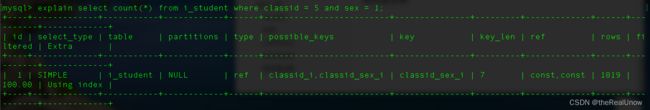
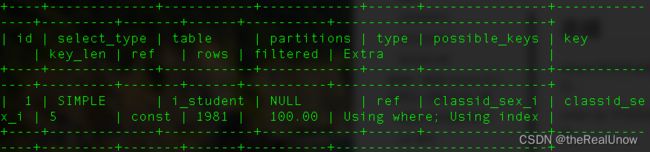
explain select count(*) from i_student where classid = 5 and sex = 1;
-
分析:
发现rows 和 案例-1 优化后的 rows 数目是一样的,所以这条语句是基于案例-1 的优势的,在 classid 索引下,再对 sex 进行条件过滤。
尝试进步一步优化,由于每次 sql 语句查询时,只能使用一个索引,那么我们这里尝试使用 classid 和 sex 的联合索引。
-
优化:
create index classid_sex_i on i_student(classid, sex);
优化后测试
优化后分析
可以发现,rows 较之前也相对减少了,possible_keys 可用索引中有 classid_i 和 classid_sex_i,mysql 自身会选择最优索引,即 key 为 classid_sex_i。
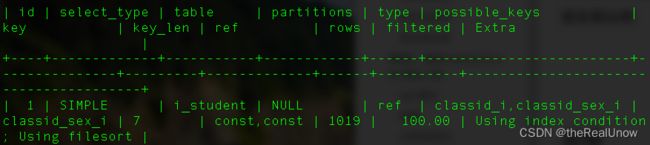
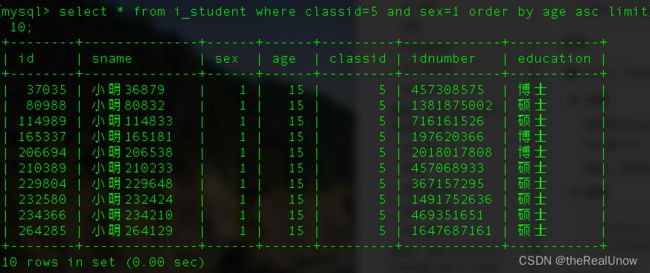
案例3 - 找出 classid 为 5 的年龄最小的 10 个男生
sql 语句
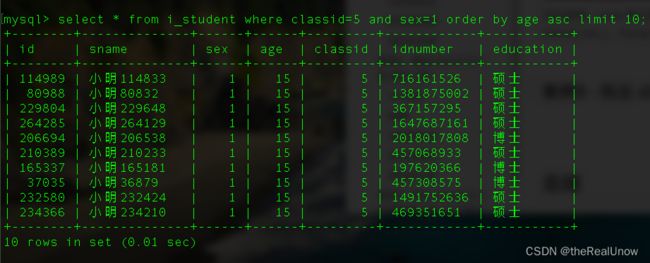
select * from i_student where classid=5 and sex=1 order by age asc limit 10;
结果
分析和优化
explain select * from i_student where classid=5 and sex=1 order by age asc limit 10;
-
分析
发现在 Extra 中,出现了 Using filesort,即表外排序,问题出现在于 order by age asc 。
因此,应该让 order by 的字段设置上索引。
-
优化
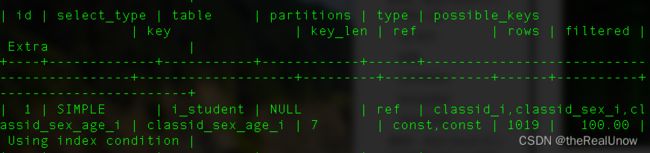
create index classid_sex_age_i on i_student(classid,sex,age);
优化后测试
优化后分析
案例4 - 查询 classid 为 5 的男生人数和女生人数
删除之前设置的索引
drop index classid_i on i_student;
drop index classid_sex_i on i_student;
drop index classid_sex_age_i on i_student;
sql 语句
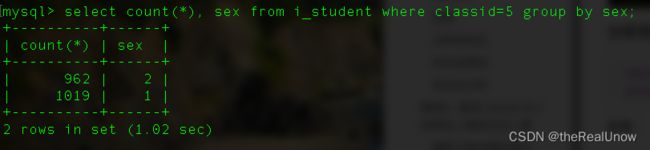
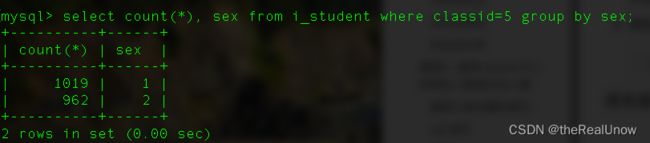
select count(*), sex from i_student where classid=5 group by sex;
结果
分析和优化
explain select count(*), sex from i_student where classid=5 group by sex;
-
分析:
可以发现这条语句非常糟糕,以及出现了新的字眼,在 Extra 中出现了 Using temporary,即生成了一个临时表,将会占用内存空间,查询完毕后再释放。
主要造成 Using temporary,是 group by sex ,由分组造成的,那么必须让分组使用上索引。
-
优化:
create index classid_sex_i on i_student(classid,sex);
优化后测试
优化后分析
优化后不再出现使用临时表的现象,其余项也优化。
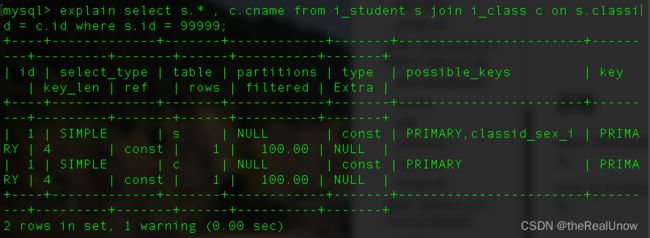
案例5 - 查询学生 id 为 99999 的 班级名称
sql语句
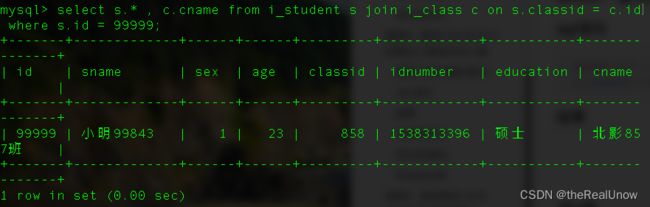
select s.* , c.cname from i_student s join i_class c on s.classid = c.id where s.id = 99999;
结果
分析
explain select s.* , c.cname from i_student s join i_class c on s.classid = c.id where s.id = 99999;
通过分析,发现有 2 条分析记录,因为这里有 2 个表连接查询,在观察,2 条记录都是使用主键索引,这是性能高的原因所在。
在思考一下,为什么 i_student 使用主键索引而不是用包含有 classid 的 classid_sex_i 的索引?
因为 sql 语句中出现 where,mysql 会先针对 where 的子句字段进行选择最优索引,因此表在连接的时候,即 s.classid = c.id ,没有用上索引。
若没有 where 子句,在需要为表的外键,即 classid 创建索引。
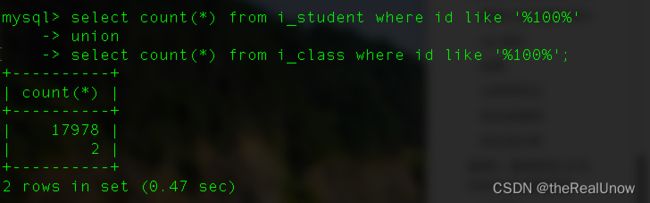
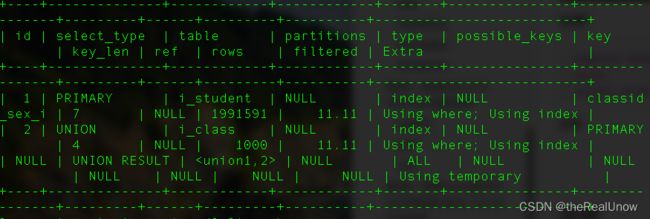
案例6 - 使用union查询学生id和班级id包含 ‘100’ 的记录数量
sql 语句
select count(*) from i_student where id like '%100%'
union
select count(*) from i_class where id like '%100%';
结果
分析
explain select count(*) from i_student where id like '%100%'
union
select count(*) from i_class where id like '%100%';
首先,不去观察 where 的字段有没有用上索引,发现 Extra 出现了 Using temporary,是由于 union 将 2 个结果集连在一起而导致出现的临时表。
查看 where 的字段 id 也没用上索引,是由于使用了 like ‘%关键字%’, like ‘%关键字%’ 会导致字段无法使用索引。
因此 union 尽量避免使用,他会造成临时表且无法优化,
总结
-
where 字句中出现的字段要创建索引,如果根据 and 联合多个字段查询,要创建联合索引,但 or 、in 、like 无法使用索引。
-
order by 子句中出现的字段要创建索引,当子句有多个字段,则要创建联合索引。
-
group by 子句中出现的字段要创建索引,当子句有多个字段,则要创建联合索引。
-
表的外键要创建索引。
-
union 不能使用索引,且会生成临时表。