利用JDBC实现图书管理系统------数据库
目录
1.利用JDBC实现图书管理系统
2.通过对象封装关键数据——面向对象思想
3.java日期相关的类和方法
(1).首先把建表语句在workbench中输入如下
CREATE TABLE `books` ( `bid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(45) NOT NULL COMMENT '书籍名称', `count` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '存量', `total` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '总量', PRIMARY KEY (`bid`), UNIQUE KEY `name_UNIQUE` (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='书籍信息'; CREATE TABLE `readers` ( `rid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`rid`), UNIQUE KEY `name_UNIQUE` (`name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='借阅者信息'; CREATE TABLE `records` ( `reid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `rid` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '谁借的', `bid` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '借的哪本书', `borrowed_at` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '借阅时间', PRIMARY KEY (`reid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='借阅记录';(2).在idea中创建项目(代码如下所示)
需要注意的是,包的package声明与文件所在的目录保持一致
同一个package下是不需要导入的
如果害怕出错就多输出也就是写日志(DEBUG)
1.1管理员(不考虑登陆问题)
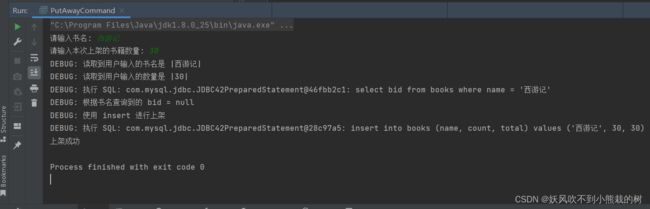
上架操作
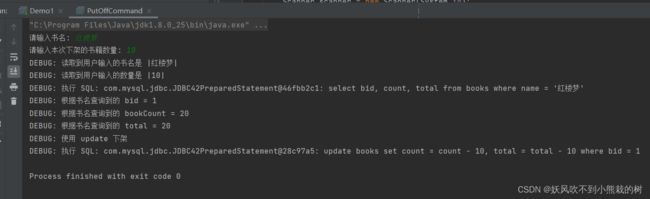
package com.wangqi.lib; import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; // utilize public class DBUtil { // 由于 MysqlDataSource 对象只需要一份,所以,一个 static 就够了 private static final DataSource dataSource; static { MysqlDataSource db = new MysqlDataSource(); db.setServerName("localhost"); db.setPort(3306); db.setUser("root"); db.setPassword("123456"); db.setDatabaseName("test2"); db.setUseSSL(false); db.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); db.setServerTimezone("Asia/Shanghai"); dataSource = db; } public static Connection connection() throws SQLException { return dataSource.getConnection(); } }package com.wangqi.lib; import com.wangqi.lib.DBUtil; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Scanner; // 书籍上架命令 // 1. 属于管理员角色 -> 在我们当下的设计中,不考虑登录问题 // 2. 需要用户输入:1、书名 2. 本次上架的书籍数量 // 3. 实际要执行的 SQL: // select * from books where name = ?; 行数: 0 or 1 // insert into books (...) // update books set ... where bid = ?; public class PutAwayCommand { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { // 1. 不存在登录 // 2. 提示用户输入本次操作的基本信息 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入书名: "); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("请输入本次上架的书籍数量: "); int count = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("DEBUG: 读取到用户输入的书名是 |" + name + "|"); System.out.println("DEBUG: 读取到用户输入的数量是 |" + count + "|"); // 3. 开始执行 SQL // 3.1 先去执行 select Integer bid = null; try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "select bid from books where name = ?"; //bid是书籍id try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setString(1, name); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) { if (rs.next()) { // 说明这里返回 1 行了 bid = rs.getInt("bid"); } } } } System.out.println("DEBUG: 根据书名查询到的 bid = " + bid); // 根据 bid 是否为 null if (bid == null) { // 通过 insert 进行上架 System.out.println("DEBUG: 使用 insert 进行上架"); try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "insert into books (name, count, total) values (?, ?, ?)"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setString(1, name); ps.setInt(2, count); ps.setInt(3, count); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); ps.executeUpdate(); } } } else { // 通过 update 进行上架 System.out.println("DEBUG: 使用 update 进行上架"); try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "update books set count = count + ?, total = total + ? where bid = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setInt(1, count); ps.setInt(2, count); ps.setInt(3, bid); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); ps.executeUpdate(); } } } System.out.println("上架成功"); } }下架操作(和上架操作基本类似)
package com.wangqi.lib; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.print.event.PrintJobEvent; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Scanner; // 下架 public class PutOffCommand { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { // 1. 不需要的登录 // 2. 读取用户输入 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入书名: "); String name = scanner.nextLine(); System.out.print("请输入本次下架的书籍数量: "); int count = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("DEBUG: 读取到用户输入的书名是 |" + name + "|"); System.out.println("DEBUG: 读取到用户输入的数量是 |" + count + "|"); // 3. sql // 3.1 select // 根据用户输入 和 总量的关系,决定是 delete 还是 update Integer bid = null; Integer bookCount = null; Integer total = null; try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "select bid, count, total from books where name = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setString(1, name); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) { if (rs.next()) { bid = rs.getInt("bid"); bookCount = rs.getInt("count"); total = rs.getInt("total"); } } } } System.out.println("DEBUG: 根据书名查询到的 bid = " + bid); System.out.println("DEBUG: 根据书名查询到的 bookCount = " + bookCount); System.out.println("DEBUG: 根据书名查询到的 total = " + total); if (bid == null) { System.out.println("没有此书"); return; } if (count >= total) { // delete System.out.println("DEBUG: 使用 delete 下架"); try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "delete from books where bid = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setInt(1, bid); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); ps.executeUpdate(); // } } } else { // update System.out.println("DEBUG: 使用 update 下架"); try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "update books set count = count - ?, total = total - ? where bid = ?"; // TODO: 存在一个 BUG,书籍的存量可能会出现负数 try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setInt(1, count); ps.setInt(2, count); ps.setInt(3, bid); System.out.println("DEBUG: 执行 SQL: " + ps); ps.executeUpdate(); } } } } }
1.2用户(考虑登录问题)
这里要先在workbench表中插入几行数据哦!!!
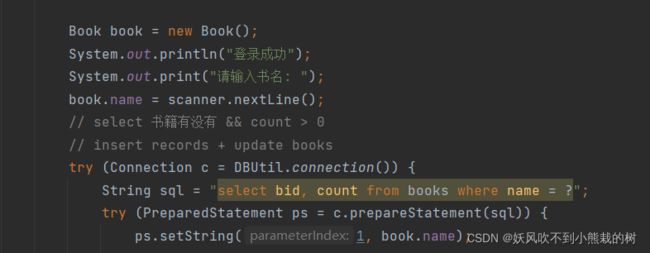
package com.wangqi.lib; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Scanner; // 借书命令 public class BorrowBookCommand { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { // 1. 登录 // 1.1 证明你是你 // 1.2 权限(角色) Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入用户名: "); String username = scanner.nextLine(); // select * from readers where name = ? int currentUserRid;//当前读者的读书号 try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "select rid from readers where name = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setString(1, username); try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) { if (!rs.next()) { System.out.println("登录失败"); return; } currentUserRid = rs.getInt("rid");//记录当前读者的读书号 } } } System.out.println("登录成功"); System.out.print("请输入书名: "); String bookName = scanner.nextLine(); // select 书籍有没有 && count > 0 // insert records + update books int bid;//Interger 原因是没有null这一情况,错误就直接返回 ,书号 int count; //数量 try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "select bid, count from books where name = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setString(1, bookName); try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) { if (!rs.next()) { System.out.println("查无此书"); return; } bid = rs.getInt("bid"); //同样也是记录 count = rs.getInt("count"); if (count == 0) { System.out.println("书被借空了"); return; } } } System.out.println("借书成功"); } // 借书操作 try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "update books set count = count - 1 where bid = ?"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setInt(1, bid); ps.executeUpdate(); } } try (Connection c = DBUtil.connection()) { String sql = "insert into records (rid, bid) values (?, ?)"; try (PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql)) { ps.setInt(1, currentUserRid); ps.setInt(2, bid); ps.executeUpdate(); } } } }
通过对象封装关键数据——面向对象思想
把book、reader、record的类封装成三个类,在操作的时候生成对象调用即可
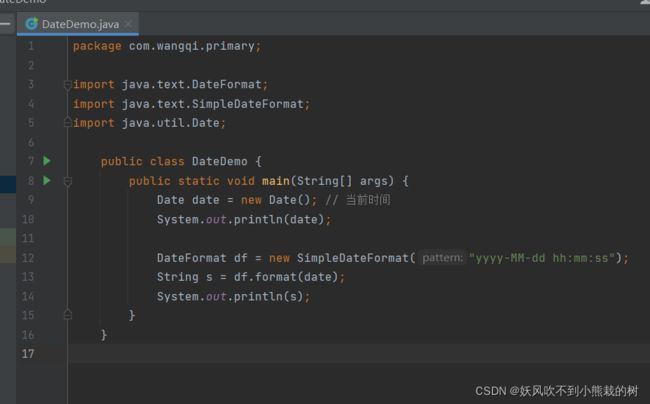
java日期相关的类和方法 (固定格式,记住即可)
Date date = new Date(); // 当前时间 System.out.println(date); DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"); String s = df.format(date); System.out.println(s);