TRUNCATE 语句到底因何而慢?
作者通过源码分析 truncate 语句形成慢 SQL 的原因和解决方案,并与 MySQL 5.7就相关实现逻辑进行对比。
问题现象
收到反馈某测试环境执行批量操作时,有 truncate 语句存在于慢查询日志中。担心上线后可能影响数据库,请求 DBA 配合分析。
关键配置
| 配置项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 数据库版本 | MySQL 5.7 |
参数 long_query_time 慢查询阈值,单位为秒 |
0.1(100 毫秒) |
参数 innodb_adaptive_hash_index |
ON |
问题分析总结
总结下来主要有如何几个问题:
Q1: TRUNCATE 语句是如何执行的?fd 句柄不变化?为什么执行时间长?
TRUNCATE 语句如何执行?
关键堆栈:
关键操作 debug:
为什么执行时间长?
从以上堆栈可以看到,耗时过程主要是 row_drop_table_for_mysql、os_file_delete_func。
其中:row_drop_table_for_mysql 主要是调用 btr_drop_ahi_for_table 执行 AHI 的 page 页的删除。os_file_delete_func 主要调用 unlink 执行文件的清理。
句柄为什么不变化?
假如需要 truncate 的表分配的 fd 为 43,truncate 过程中,会先将表 rename。这个时候这个 fd 会被关闭,43 就被释放了。然后执行 create table 操作。一般这个间隙过程很短,因此新建立的表可以使用被释放的 43 了,所以会看到 fd 没有变化。
如果 rename 之后,在内部执行 create table 之前,又打开了新文件,那这时候 fd 43 就会被其它打开的文件持有,truncate 之后表的 fd 也就会发生变化。
注意:MySQL 8.0 是真正使用
rename+create+drop实现的truncate,但 MySQL 5.7 是通过文件的truncate实现的。
Q2: 如何分析 TRUNCATE 慢的问题?
方式一:慢日志?
只能看到慢的结果,无法确认原因。
方式二:执行计划?
不支持 truncate 语句。
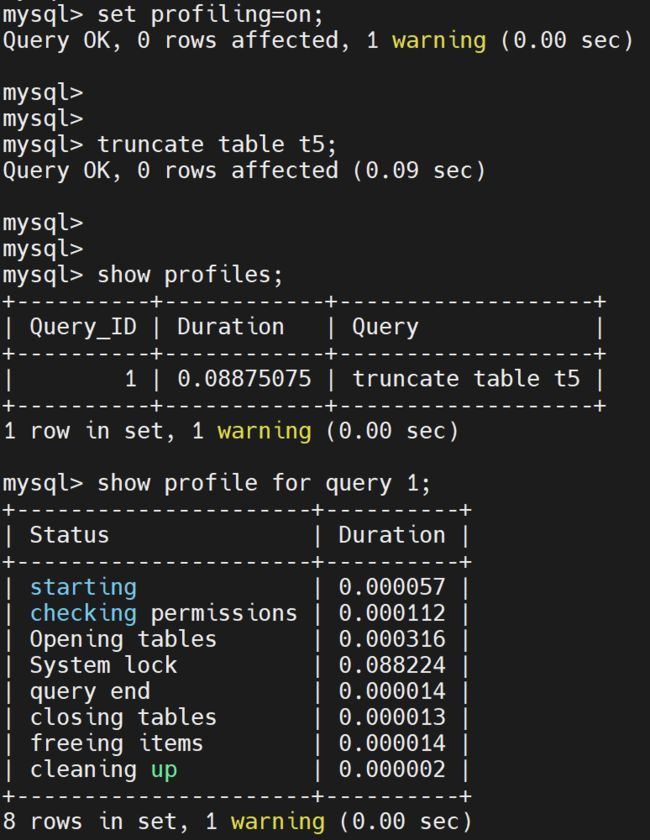
方式三:profile
从 profile 结果来看,对于 truncate 语句,只能看到耗时过程都在System lock 上,无法看到更近一步的原因。
方式四:DEBUG
// 推荐设置
// 其中 T 其实是 MySQL 支持(在 trace 中打印时间)的,但官方文档中缺少了说明。已提交bug说明:Bug #111174
set global debug='d:t:T:i:n:N:o,/tmp/debug_3306.trace.f';
set global debug='';- ① 表示
show processlist的线程 ID - ② 执行时间
- ③ 函数调用层级
- ④ 函数名称
MySQL 8.0 切换对比
// TRUNCATE
// 默认规范配置
// innodb_flush_method = on & innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 08:44:46 15> truncate table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.98 sec)
// 设置 innodb_adaptive_hash_index = off
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 08:52:03 5> truncate table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
// 设置 innodb_flush_method = fsync
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 09:03:34 28> truncate table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.04 sec)
// 设置 innodb_adaptive_hash_index = off & innodb_flush_method = fsync
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 09:20:24 5> truncate table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.22 sec)
// DROP
// 默认规范配置
// innodb_flush_method = on & innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 10:05:41 9> drop table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.94 sec)
// 设置 innodb_adaptive_hash_index = off & innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 09:44:24 5> drop table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
// 设置 innodb_flush_method = on & innodb_flush_method = fsync
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 09:32:15 13> drop table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.13 sec)
// 设置 innodb_adaptive_hash_index = off & innodb_flush_method = fsync
([email protected]) [eolbimsdb] 09:25:10 14> drop table t5;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.19 sec)Q3: 能否优化?慢在哪里?post_ddl 如何调用?
从 Q1 的结果中可以看出,执行的主要耗时在 row_drop_table_for_mysql、os_file_delete_func:
MySQL 8.0 的优化措施
row_drop_table_for_mysql慢的问题,可以通过设置innodb_adaptive_hash_index = off进行优化;os_file_delete_func慢的问题,可以设置innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT或者配置表的 HARD LINK 进行优化。
MySQL 5.7 的优化措施
详见后面 3-Q1、3-Q4 部分。
post_ddl 如何调用?
MySQL 8.0 引入了 scope guard 功能:当定义了 scope guard 之后,会创建 Scope_guard 对象。正常情况下,当执行 return 操作前,会执行 scope guard 定义的逻辑。除非在函数结束前执行 Scope_guard 对象的 commit 操作。文件的删除功能实在 scope guard 的 cleanup_base 阶段调用是现的。
Q4: 生产执行 TRUNCATE 是否存在隐患?
从实现机制来看,主要有以下风险:
IO 压力
当触发 truncate 操作后,需要在短时间由数据库线程将文件 unlink 或 truncate,如果被处理的文件很大,服务器的 IO 压力可能会影响正常的数据库请求。
内存并发
在执行 truncate、drop 的过程中,由于需要对内存的数据进行清理,特别是对 LRU 和 flush_LRU 进行扫描,并释放对应的数据块。这个过程是需要逐个根据 buffer pool instance 获取 mutex 资源的。如果在业务高峰期,特别是 buffer pool 较大时,可能会影响正常的业务情况。
同时,执行 create drop table 操作时需要 dict_operation_lock 的 X 锁(RW_X_LATCH),而一些其他后台线程,比如 Main Thread 检查 dict cache 时,也需要获取 dict_operation_lock 的 X 锁,因此被阻塞。然后用户线程可能由于获取不到锁而处于挂起状态,当无法立刻获得锁时。更多参考:《Drop Table 对 MySQL 的性能影响分析》。
Q5: 不同版本对于 TRUNCATE 的实现是否存在差异?
通过对比 2-Q1 与 3-Q4:
MySQL 8.0 的 truncate 实现方式基本和 drop 实现方式相同,包括主要的耗时位置(都在 row_drop_table_for_mysql、os_file_delete_func)都是相同的。
MySQL 5.7 的 truncate 和 drop 实现差异较大,整个实现过程几乎是完全独立的代码。truncate 使用 row_truncate_table_for_mysql,drop 使用 row_drop_table_for_mysql;truncate 操作的主要的耗时有 dict_drop_index_tree、os_file_truncate。
DROP TABLE 优化失败分析
下面来看一个 MySQL 5.7 测试环境上线 DROP TABLE 优化方案失败问题。
Q1:上线为什么会失败?HARD LINK 为什么不生效?AHI 为什么不生效?
- 当 MySQL 5.7 使用规范配置启动时,从
debug-trace过程来看,在row_drop_single_table_tablespace、row_drop_table_from_cache函数执行期间根本没有耗时,所以实施优化方案后,没有效果; - 耗时的过程在
que_eval_sql: query: PROCEDURE DROP_TABLE_PROC ---> dict_drop_index_tree; row_drop_single_table_tablespace的耗时被 MySQL 5.7 配置innodb_flush_method=O_DIRECT优化了。
Q2:该优化是否适用于 MySQL 8.0?
设置 innodb_flush_method=O_DIRECT 的优化操作,同样适用于 MySQL 8.0。
Q3:MySQL 8.0 如何解决 DROP TABLE 时执行 DROP_TABLE_PROC 慢的问题?
- WL#9536: InnoDB_New_DD: Support crash-safe DDL;
- 依赖于自 Version 8.0.3 的 NEW DD;
- 整个
drop慢的que_eval_sql、DROP_TABLE_PROC被整体砍掉; - 包括
dict_drop_index_tree在内的整个函数,都被砍了; - 具体实现机制,参考分析 NEW DD 实现方法。
Q4:MySQL 5.7 DROP TABLE 和 TRUNCATE 在实现机制、优化措施有何区别呢?
- 执行
truncate操作的耗时,仍然是在dict_drop_index_tree、os_file_truncate这两个阶段; os_file_truncate的耗时:可以通过设置innodb_flush_method=O_DIRECT时间进行优化(不可以通过hard link进行优化);dict_drop_index_tree的耗时,暂时没有优化思路。了解更多:InnoDB 文件系统之文件物理结构。
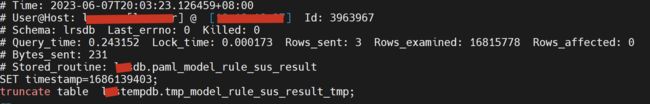
Q5:5.7 慢查询为什么有时记录 TRUNCATE 执行慢,有时不记录?
根据源码,MySQL 是否记录慢查询判断时,主要有两个维度:一个是执行时间(不包括 utime_alter_lock);一个是执行扫描的行数,并对特殊的语句(如 call)进行了忽略。对于 truncate 操作而言,无论执行时间是多少,扫描行数都是 0。当配置了 min_examined_row_limit 大于 0 之后,一般 truncate 操作由于不满足该条件,都不会被记录到慢查询。
但是当 truncate 操作位于存储过程中时,在 truncate 操作之前有其它 DML 操作(如 insert selecct),这时候由于位于同一个 THD 下,在 MySQL 5.7 版本里面 thd->get_examined_row_count() 返回的结果其实是上一个 DML 语句的(这里应该是缺陷)。如果此时 truncate 操作的执行时间又超过了 long_query_time,那么此时这个 truncate 语句就会被记录慢查询。
同时,在 MySQL 8.0 针对 call 的语句,将不在单独记录记录的语句。而是记录为统一的 call 语句里面。需要看存储过程里面的语句执行情况,可以用 show profiles 查看。
慢查询记录堆栈
测试存储过程
DROP PROCEDURE truncate_test;
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE truncate_test()
BEGIN
insert into t1 select * from t1_bak;
truncate table t1;
END
//
DELIMITER ;
call truncate_test();
mysql> call truncate_test();
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 59.58 sec)
# Time: 2023-06-08T00:28:30.969993+08:00
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 2
# Schema: db2 Last_errno: 0 Killed: 0
# Query_time: 119.177518 Lock_time: 0.000233 Rows_sent: 0 Rows_examined: 131072 Rows_affected: 131072
# Bytes_sent: 0
# Stored_routine: db2.truncate_test
use db2;
SET timestamp=1686155310;
insert into t1 select * from t1_bak;
# Time: 2023-06-08T00:28:31.375873+08:00
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 2
# Schema: db2 Last_errno: 0 Killed: 0
# Query_time: 0.405734 Lock_time: 0.003310 Rows_sent: 0 Rows_examined: 131072 Rows_affected: 0
# Bytes_sent: 0
# Stored_routine: db2.truncate_test
SET timestamp=1686155311;
truncate table t1;与 MySQL 8.0 对比
mysql> call truncate_test();
Query OK, 0 rows affected (2 min 28.51 sec)
# Time: 2023-06-07T17:18:39.215632Z
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 8
# Query_time: 148.516478 Lock_time: 0.000372 Rows_sent: 0 Rows_examined: 172032
use testdb;
SET timestamp=1686158318;
call truncate_test();MySQL 8.0 如何跟踪?
mysql> call truncate_test();
Query OK, 0 rows affected (2 min 24.84 sec)
mysql>
mysql>
mysql> show profiles;
+----------+--------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Query_ID | Duration | Query |
+----------+--------------+-----------------------------------------+
| 1 | 144.55113600 | insert into ltb2 select * from ltb3_bak |
| 2 | 0.29312375 | truncate table ltb2 |
+----------+--------------+-----------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)以上包括 truncate 执行慢的分析,如针对细节有任何疑问和建议,欢迎留言交流。
关于 SQLE
爱可生开源社区的 SQLE 是一款面向数据库使用者和管理者,支持多场景审核,支持标准化上线流程,原生支持 MySQL 审核且数据库类型可扩展的 SQL 审核工具。
SQLE 获取
| 类型 | 地址 |
|---|---|
| 版本库 | https://github.com/actiontech/sqle |
| 文档 | https://actiontech.github.io/sqle-docs/ |
| 发布信息 | https://github.com/actiontech/sqle/releases |
| 数据审核插件开发文档 | https://actiontech.github.io/sqle-docs-cn/3.modules/3.7_auditplugin/auditplugin_development.html |