C++面向对象(黑马程序员)
内存分区模型
#includenew操作
#include引用
#include#include引用的本质:在C++内部实现是一个指针常量
函数重载
#include类和对象
C++面向对象三大特征:封装,继承,多态
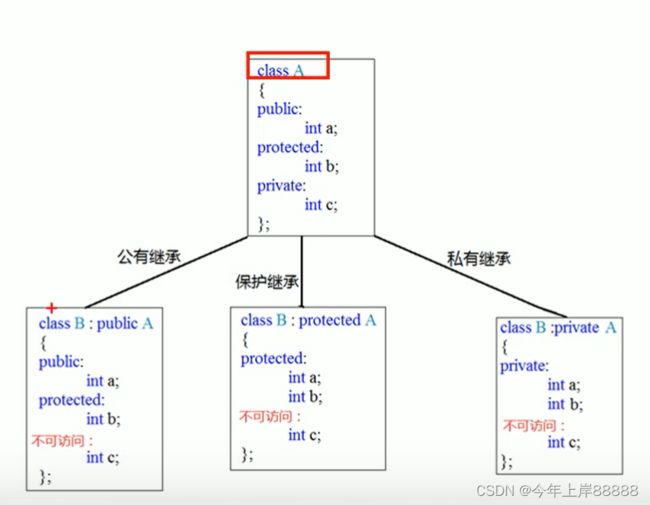
封装
公共权限 public 成员类内可以访问,类外可以访问
保护权限 protected 成员类内可以范文,类外不可以访问
私有权限 private 成员类内可以范文,类外不可以访问
保护权限和私有权限在继承中体现出不同。儿子可以访问父亲中的保护内容,儿子不可以访问父亲的私有内容
struct和class区别
构造函数和析构函数
#include

浅拷贝带来的问题:队取得内存重复释放
解决浅拷贝问题:使用深拷贝
静态成员
#include#includeC++对象模型+this指针
#include#include#includeconst修饰成员函数
友元
#include#include运算符重载
加号重载
#include继承

下级别成员拥有上一级的共性+自己的特性,继承可以减少代码复杂度
#include继承中父类子类构造函数和析构函数调用顺序:先调用父类构造函数,子类构造函数,子类析构函数,父类析构函数

#include菱形继承
#include多态
#include构造函数与析构函数
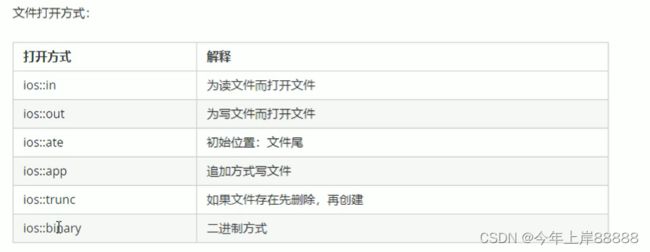
文件操作
文本文件
#include