C++泛型编程和STL(黑马程序员)
模板
函数模板
#includeSTL
容器vector(数组)
#include#include#include#include#include#include#includestring容器
#include#includedeque容器
#includeSTL评委打分
#includestack容器
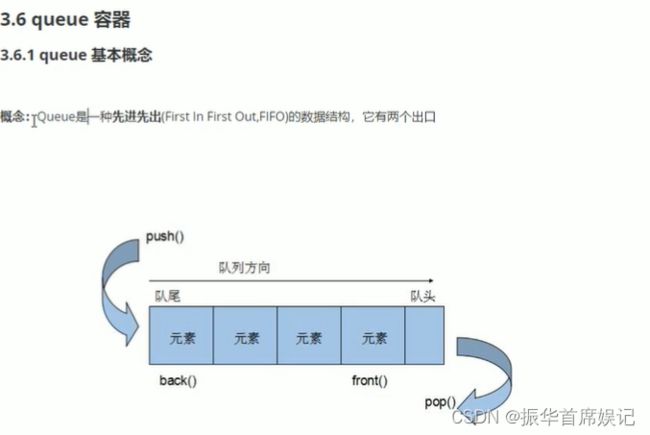
queue容器
list容器(链表)
#include
using namespace std;
//list数据存取
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
cout << "第一个元素" << L1.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素" << L1.back() << endl;
//验证迭代器不支持随机访问
list<int>::iterator it = L1.begin();
it++;
//it=it+1(wrong)
}
int mian()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
#include
#include排序案例
#include
#includeset容器
#include#include#includeset内置数据类型按序输出
#includemap容器
#include案例——员工分组
#include函数对象
#include#include#include