SpringBoot核心运行原理解析之------@Conditional条件注解
在SpringBoot核心运行原理解析之------@EnableAutoConfiguration文档中我们完成了自动配置类的读取和筛选,在这个过程中已经涉及了像@ConditionalOnClass这样的条件注解。打开每个自动配置类,都会看到@Conditional或其衍生的条件注解,本节我们来认识下@Conditional注解。
认识条件注解
@Conditional注解是由Spring4.0版本引入的新特性,可根据是否满足指定的条件来决定是否进行Bean的实例化装配,比如设定类路径下包含某个jar包的时候才会对注解的类进行实例化操作。总之,是根据一些特定条件来控制Bean实例化行为,@Conditional注解代码如下:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
/**
* All {@link Condition Conditions} that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match}
* in order for the component to be registered.
*/
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
@Conditional注解唯一的元素属性是接口Condition的数组,只有在数组中指定的所有Condition的matches方法都返回true的情况下,被注解的类才会被加载。上一篇文章讲到的OnClassCondition类就是Condition的子类之一,相关代码如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
//决定条件是否匹配
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
matches方法的第一个参数为ConditionContext,可以通过接口提供的方法来获取Spring应用的上下文信息,ConditionContext接口定义如下:
public interface ConditionContext {
//返回BeanDefinitionRegistry注册表,可以检查Bean的定义
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
//ConfigurableListableBeanFactory ,可以检查Bean是否已经存在,进一步检查Bean属性
@Nullable
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory();
//获取Envirment,获取当前环境变量,监测当前环境变量是否存在
Environment getEnvironment();
//ResourceLoader ,用于读取或检查所加载的资源
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
//返回ClassLoader ,用于检查类是否存在
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
matches方法的第二个参数为AnnotatedTypeMetadata ,该接口提供了访问特定类或方法的注解功能,并且不需要加载类,可以用来检查带有@Bean注解的方法上是否还有其他注解,AnnotatedTypeMetadata 接口定义如下:
public interface AnnotatedTypeMetadata {
MergedAnnotations getAnnotations();
default boolean isAnnotated(String annotationName) {
return this.getAnnotations().isPresent(annotationName);
}
@Nullable
default Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName) {
return this.getAnnotationAttributes(annotationName, false);
}
@Nullable
default Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString) {
MergedAnnotation<Annotation> annotation = this.getAnnotations().get(annotationName, (Predicate)null, MergedAnnotationSelectors.firstDirectlyDeclared());
return !annotation.isPresent() ? null : annotation.asAnnotationAttributes(Adapt.values(classValuesAsString, true));
}
@Nullable
default MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName) {
return this.getAllAnnotationAttributes(annotationName, false);
}
@Nullable
default MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString) {
MergedAnnotation.Adapt[] adaptations = Adapt.values(classValuesAsString, true);
return (MultiValueMap)this.getAnnotations().stream(annotationName).filter(MergedAnnotationPredicates.unique(MergedAnnotation::getMetaTypes)).map(MergedAnnotation::withNonMergedAttributes).collect(MergedAnnotationCollectors.toMultiValueMap((map) -> {
return map.isEmpty() ? null : map;
}, adaptations));
}
}
isAnnotated方法能够提供判断带有@Bean注解的方法上是否还有其他注解的功能。其他方法提供不同形式的获取@Bean注解的方法上其他注解的属性信息。
条件注解的衍生注解
在Spring Boot的autoconfigure项目中提供了各类基于@Conditional注解的衍生注解,它们适用于不同的场景并提供了不同的功能。以下相关注解均位于spring-boot-auroconfigure项目的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition包下。
- @ConditionalOnBean:在容器中有指定Bean的条件下。
- @ConditionalOnClass:在classPath类路径下有指定类的条件下。
- @ConditionalOnCloudPlatform:当指定的平台处于active状态时。
- @ConditionalOnExpression:基于SpEL表达式的条件判断。
- @ConditionalOnJava:基于JVM作为判断条件。
- @ConditionalOnJndi:在JNDI存在的条件下查找指定的位置。
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean:当容器中没有指定Bean的条件时。
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass:当类路径下没有指定类的条件时。
- @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication:在项目不是一个Web项目的条件下。
- @ConditionalOnProperty:在指定的属性有指定的值。
- @ConditionalOnResource: 类路径是否有指定的值。
- @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate: 在指定的Bean在容器中只有一个或者多个但是指定了首选的Bean时。
- @ConditionalOnWebApplication: 在项目是一个Web项目的条件下。
如果仔细观察这些注解的源码,会发现他们其实都组合了@Conditional注解,不同之处时他们中指定的条件(Condition)不同。下面以@ConditionalOnWebApplication为例对衍生注解进行简单的分析。
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnWebApplication {
//所需的web类型
Type type() default Type.ANY;
//可选应用枚举类
enum Type {
//任何类型
ANY,
//基于servlet的web应用
SERVLET,
//基于reactive的web应用
REACTIVE
}
}
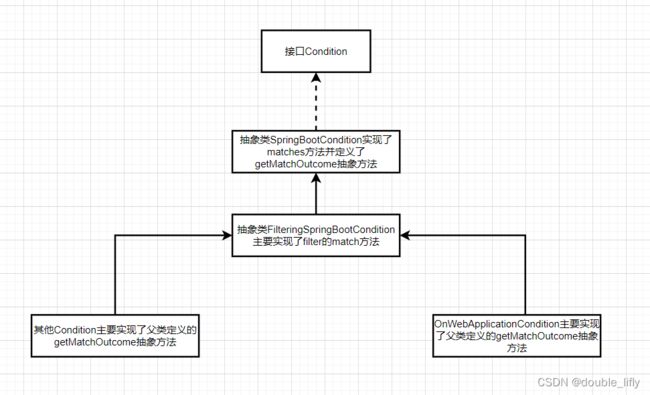
@ConditionalOnWebApplication注解的源码中组合了@Conditional注解,并且指定了对应的Condition为OnWebApplicationCondition。OnWebApplicationCondition类的结构与前面讲到的OnClassCondition一样,都继承自SpringBootCondition并实现了AutoConfigurationImportFilter接口。下图讲述了以OnWebApplicationCondition为例衍生注解的关系结构,重点讲述了Condition的功能和用法。
上面学习了Condition接口的源码,抽象类SpringBootCondition是如何实现该方法的呢?相关源码如下:
public abstract class SpringBootCondition implements Condition {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Override
public final boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String classOrMethodName = getClassOrMethodName(metadata);
try {
ConditionOutcome outcome = getMatchOutcome(context, metadata);
logOutcome(classOrMethodName, outcome);
recordEvaluation(context, classOrMethodName, outcome);
return outcome.isMatch();
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not evaluate condition on " + classOrMethodName + " due to "
+ ex.getMessage() + " not found. Make sure your own configuration does not rely on "
+ "that class. This can also happen if you are "
+ "@ComponentScanning a springframework package (e.g. if you "
+ "put a @ComponentScan in the default package by mistake)", ex);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error processing condition on " + getName(metadata), ex);
}
}
......
/**
* Determine the outcome of the match along with suitable log output.
* @param context the condition context
* @param metadata the annotation metadata
* @return the condition outcome
*/
public abstract ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
......
}
在抽象类SpringBootCondition中实现类matches方法,而该方法中最核心的部分是通过调用新定义的抽象方法getMatchOutcome并交由子类来实现,在matches方法中根据子类返回的结果判断是否匹配。下面来看下OnWebApplicationCondition的源代码。
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20)
class OnWebApplicationCondition extends FilteringSpringBootCondition {
......
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
boolean required = metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnWebApplication.class.getName());
ConditionOutcome outcome = isWebApplication(context, metadata, required);
if (required && !outcome.isMatch()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
if (!required && outcome.isMatch()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
......
}
可以看出,是否匹配是由两个条件决定的:被注解的类或方法是否包含ConditionalOnWebApplication注解,是否为web应用。
- 如果包含ConditionalOnWebApplication注解,并且不是Web应用,那么返回不匹配。
- 如果不包含ConditionalOnWebApplication注解,并且时Web应用,那么返回不匹配。
- 其他情况返回匹配。
下面以SERVLET Web应用为例,看相关源码如何判断是否为web应用的。
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20)
class OnWebApplicationCondition extends FilteringSpringBootCondition {
private static final String SERVLET_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.support.GenericWebApplicationContext";
......
//推断web应用是否匹配
private ConditionOutcome isWebApplication(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata,
boolean required) {
switch (deduceType(metadata)) {
case SERVLET:
return isServletWebApplication(context);
case REACTIVE:
return isReactiveWebApplication(context);
default:
return isAnyWebApplication(context, required);
}
}
......
private ConditionOutcome isServletWebApplication(ConditionContext context) {
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition("");
//判断常量定义是否存在
if (!ClassNameFilter.isPresent(SERVLET_WEB_APPLICATION_CLASS, context.getClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("servlet web application classes").atAll());
}
//判断BeanFactory是否存在
if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) {
String[] scopes = context.getBeanFactory().getRegisteredScopeNames();
if (ObjectUtils.containsElement(scopes, "session")) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("'session' scope"));
}
}
//判断Enviroment的类型是否为ConfigurableWebEnvironment类型
if (context.getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("ConfigurableWebEnvironment"));
}
//判断ResourceLoader的类型是否为WebApplicationContext
if (context.getResourceLoader() instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("WebApplicationContext"));
}
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.because("not a servlet web application"));
}
......
//从AnnotateTypeMeatdata中获取type值
private Type deduceType(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Map<String, Object> attributes = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnWebApplication.class.getName());
if (attributes != null) {
return (Type) attributes.get("type");
}
return Type.ANY;
}
}
首先在isWebApplication方法中进行Web应用类型的推断。这里使用AnnotatedTypeMetadata的getAnnotationAttributes方法获取所有关于@ConditionalOnWebApplication的注解属性。返回值为null说明未配置任何属性,默认为Type.ANY,如果配置属性,会获取type属性对应的值。
如果返回值为Type.SERVLET,调用isServletWebApplication方法来进行判断。该方法的判断有以下条件:
- GenericWebApplicationContext类是否在类路径下
- 容器内是否存在注册名为session的scope
- 容器的Environment是否为ConfigurableWebEnvironment
- 容器的ResourceLoader是否为WebApplicationContext
在完成以上判断以后,得出的最终结果封装为ConditionOutcome对象返回,并在抽象类SpringBootCondition的matches方法中完成判断,返回最终结果。