Spring Boot命令行启动添加参数
一、Spring Boot命令行三种参数形式
通过java -jar启动springboot的jar项目时,可以动态传递参数来进行配置和开发,比如
java -jar xxx.jar --server.port=8081可以通过server.port修改项目启动的端口,通过命令行传递的参数具有更高的优先级,会覆盖同名的其他配置参数。
启动Spring Boot项目时传递参数,有三种参数形式:
1、选项参数
选项参数,上面的示例便是选项参数的使用方法,通过“–-server.port”来设置应用程序的端口。基本格式为“--name=value”(“--”为连续两个减号)。其配置作用等价于在application.properties中配置的server.port=8081。
2、非选项参数
java -jar xxx.jar abc def上述示例中,“abc”和“def”便是非选项参数。
3、系统参数
系统参数,该参数会被设置到系统变量中,使用示例如下
java -jar -Dserver.port=8081 xxx.jar二、参数值得获取
选项参数和非选项参数均可以通过ApplicationArguments接口获取,具体获取方法直接在使用参数的类中注入该接口即可,比如这里通过命令行参数获取数据库连接信息创建数据源
@Component
public class ComponentDB {
@Autowired
private ApplicationArguments applicationArguments;
public final String driverClassName = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
//private final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
@Bean
DataSource dataSource(){
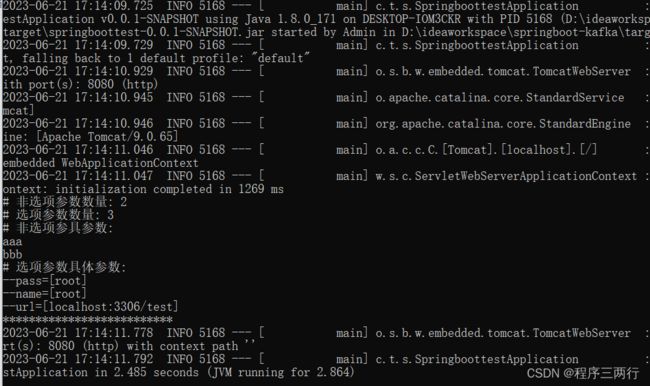
System.out.println("# 非选项参数数量: " + applicationArguments.getNonOptionArgs().size());
System.out.println("# 选项参数数量: " + applicationArguments.getOptionNames().size());
System.out.println("# 非选项参具参数:");
applicationArguments.getNonOptionArgs().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("# 选项参数具体参数:");
applicationArguments.getOptionNames().forEach(optionName ->{
System.out.println("--" + optionName + "=" + applicationArguments.getOptionValues(optionName));
});
System.out.println("**************************");
String dbUrl = applicationArguments.getOptionValues("url").get(0);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://"+dbUrl+"?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String name = applicationArguments.getOptionValues("name").get(0);
String pass = applicationArguments.getOptionValues("pass").get(0);
return DataSourceBuilder.create()
.url(url)
.username(name)
.password(pass)
.driverClassName(driverClassName).build();
}
}启动
java -jar springboottest-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --url=localhost:3306/test --name=root --pass=root aaa bbb结果
选项参数,也可以直接通过@Value在类中获取,如下
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
}系统参数可以通过java.lang.System提供的方法获取:
String systemServerPort = System.getProperty("server.port");注意
- 通过@Value形式可以获得系统参数和选项参数,但通过System.getProperty方法只能获得系统参数
- 通过@Value形式可以获得系统参数和选项参数,但通过System.getProperty方法只能获得系统参数
- 使用选项参数时,参数在命令中是位于xxx.jar之后传递的,而系统参数是紧随java -jar之后。
三、ApplicationArguments源码
ApplicationArguments接口中封装了启动时原始参数的数组、选项参数的列表、非选项参数的列表以及选项参数获得和检验。相关源码如下:
public interface ApplicationArguments {
/** * 原始参数数组(未经过处理的参数) */
String[] getSourceArgs();
/** * 选项参数名称 */
Set getOptionNames();
/** * 根据名称校验是否包含选项参数 */
boolean containsOption(String name);
/** * 根据名称获得选项参数 */
List getOptionValues(String name);
/** * 获取非选项参数列表 */
List getNonOptionArgs();
}
上面直接使用了ApplicationArguments的注入和方法,那么它的对象是何时被创建,何时被注入Spring容器的?
在执行SpringApplication的run方法的过程中会获得传入的参数,并封装为ApplicationArguments对象。相关源代码如下:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // ... prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, // ... } catch (Throwable ex) { // ... } return context;}
在上述代码中,通过创建一个它的实现类DefaultApplicationArguments来完成命令行参数的解析。
DefaultApplicationArguments部分代码如下:
public class DefaultApplicationArguments implements ApplicationArguments {
private final Source source;
private final String[] args;
public DefaultApplicationArguments(String... args) {
Assert.notNull(args, "Args must not be null");
this.source = new Source(args);
this.args = args;
}
public String[] getSourceArgs() {
return this.args;
}
public Set getOptionNames() {
String[] names = this.source.getPropertyNames();
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(new HashSet(Arrays.asList(names)));
}
public boolean containsOption(String name) {
return this.source.containsProperty(name);
}
public List getOptionValues(String name) {
List values = this.source.getOptionValues(name);
return values != null ? Collections.unmodifiableList(values) : null;
}
public List getNonOptionArgs() {
return this.source.getNonOptionArgs();
}
private static class Source extends SimpleCommandLinePropertySource {
Source(String[] args) {
super(args);
}
public List getNonOptionArgs() {
return super.getNonOptionArgs();
}
public List getOptionValues(String name) {
return super.getOptionValues(name);
}
}
} 通过构造方法,将args赋值给成员变量args,其中接口ApplicationArguments中getSourceArgs方法的实现在该类中便是返回args值。
针对成员变量Source(内部类)的设置,在创建Source对象时调用了其父类SimpleCommandLinePropertySource的构造方法,
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {
super(new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}在该方法中创建了真正的解析器SimpleCommandLineArgsParser并调用其parse方法对参数进行解析。
public CommandLineArgs parse(String... args) {
CommandLineArgs commandLineArgs = new CommandLineArgs();
for (String arg : args) {
if (arg.startsWith("--")) {
String optionText = arg.substring(2);
String optionName;
String optionValue = null;
int indexOfEqualsSign = optionText.indexOf('=');
if (indexOfEqualsSign > -1) {
optionName = optionText.substring(0, indexOfEqualsSign);
optionValue = optionText.substring(indexOfEqualsSign + 1);
}
else {
optionName = optionText;
}
if (optionName.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid argument syntax: " + arg);
}
commandLineArgs.addOptionArg(optionName, optionValue);
}
else {
commandLineArgs.addNonOptionArg(arg);
}
}
return commandLineArgs;
}上述解析规则比较简单,就是根据“--”和“=”来区分和解析不同的参数类型。
通过上面的方法创建了ApplicationArguments的实现类的对象,但此刻还并未注入Spring容器,注入Spring容器是依旧是通过上述SpringApplication#run方法中调用的prepareContext方法来完成的。相关代码如下:
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner)
{ // ...
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 通过beanFactory将ApplicationArguments的对象注入Spring容器 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
// ...}
以上就是关于Spring Boot中ApplicationArguments的相关源码解析