【服务治理】服务熔断、服务降级、服务限流、流量削峰、错峰
文章目录
-
- 服务熔断、服务降级和服务限流
-
-
- 服务熔断
- 服务降级
- 服务限流
- 实现
-
- 步骤三、Polly在.NetCore项目中封装
- 流量错峰、流量限流、流量削峰
-
- 流量错峰
-
- 服务端错峰策略
- 客户端错峰策略
- 流量限流
- 流量削峰
-
- 设置两次请求最小有效时间间隔
- 概率请求策略
- 公平性策略
服务熔断、服务降级和服务限流
熔断也叫断路器,英文Circuit Breaker,
降级也叫 回退,英文Fallback,
限流 也叫 舱壁隔离,英文Bulkhead。
服务熔断
服务熔断的作用类似于我们家用的保险丝,当某服务出现不可用或响应超时的情况时,为了防止整个系统出现雪崩,暂时停止对该服务的调用。
服务降级
服务降级是当服务器压力剧增的情况下,根据当前业务情况及流量对一些服务和页面有策略的降级,以此释放服务器资源以保证核心任务的正常运行。降级往往会指定不同的级别,面临不同的异常等级执行不同的处理。
根据服务方式:可以拒接服务,可以延迟服务,也有时候可以随机服务。
根据服务范围:可以砍掉某个功能,也可以砍掉某些模块。
总之服务降级需要根据不同的业务需求采用不同的降级策略。主要的目的就是服务虽然有损但是总比没有好。
-
熔断VS降级
-
相同点
目标一致:都是从可用性和可靠性出发,为了防止系统崩溃;
用户体验类似:最终都让用户体验到的是某些功能暂时不可用; -
不同点:
触发原因不同:服务熔断一般是某个服务(下游服务)故障引起,而服务降级一般是从整体负荷考虑;
服务限流
限流可以认为服务降级的一种,限流就是限制系统的输入和输出流量已达到保护系统的目的。一般来说系统的吞吐量是可以被测算的,为了保证系统的稳定运行,一旦达到的需要限制的阈值,就需要限制流量并采取一些措施以完成限制流量的目的。比如:延迟处理,拒绝处理,或者部分拒绝处理等等。
实现
以下为Polly框架,Hystrix 请参考:.NET Core + Spring Cloud:熔断降级
添加Microsoft.Extensions.Http.Polly包
//<1>、降级后的返回值
HttpResponseMessage fallbackResponse = new HttpResponseMessage
{
Content = new StringContent("降级,服务暂时不可用"),
StatusCode = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError,
};
//<2>、降级策略
var FallBackPolicy = Policy<HttpResponseMessage>.Handle<Exception>().FallbackAsync(fallbackResponse, async b =>
{
// 1、降级打印异常
Console.WriteLine($"服务开始降级,异常消息:{b.Exception.Message}");
// 2、降级后的数据
Console.WriteLine($"服务降级内容响应:{await fallbackResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()}");
await Task.CompletedTask;
});
//<3>、熔断策略/断路器策略
var CircuitBreakPolicy = Policy<HttpResponseMessage> // HttpResponseMessage 为HttpClient的返回值
.Handle<Exception>() //捕获Exception异常
.OrResult(res => res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError || res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout)
.CircuitBreakerAsync(
3, // 出现3次异常
TimeSpan.FromSeconds(20), // 断路器的时间(例如:设置为20秒,断路器两秒后自动由开启到关闭)
(ex, ts) =>
{ //熔断器开启事件触发
Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器开启,异常消息:{ex.Result}");
Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器开启的时间:{ts.TotalSeconds}s");
}, //断路器重置事件触发
() => { Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器重置"); }, //断路器半开启事件触发
() => { Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器半开启(一会开,一会关)"); }
);
//<4>、限流策略
var bulk = Policy.BulkheadAsync<HttpResponseMessage>(
maxParallelization: 30,//最大请求并发数
maxQueuingActions: 20,//可以有20个请求在队列里排队
onBulkheadRejectedAsync: context =>//当我们的请求超出了并发数时怎么处理 这里可以定义自己的规则
{
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
);
services.AddHttpClient();
services.AddHttpClient("myhttpclienttest", client =>
{
client.BaseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:9002/");
// client.Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1);
})
//<5>、添加 降级策略
.AddPolicyHandler(FallBackPolicy)
//<6>、添加 熔断策略
.AddPolicyHandler(CircuitBreakPolicy)
//<7>、添加限流策略
.AddPolicyHandler(bulk)
;
先看下注释里带括号<>的大步骤,<1>到<7> ,注释已经写的非常清楚了。
注意: 第一、 <3>熔断的策略里,我们加了 .OrResult(res => res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError || res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout) ,网上的教程一般没有,这句话的意思是说,当请求返回的状态是500服务器异常或者请求超时,都计算在内。若没有这句话,对方的接口必须要抛异常,才计算在内。
第二、这些策略可以组合起来使用;
步骤二:HttpClient调用远程接口服务
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HttpClientDemo.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger;
private readonly IHttpClientFactory _clientFactory;
public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger, IHttpClientFactory clientFactory)
{
_logger = logger;
_clientFactory = clientFactory;
}
/// 这里有个坑,httpClient最后一定要返回的是 HttpResponseMessage ,不然无法返回降级的返回内容。
步骤三、Polly在.NetCore项目中封装
根据步骤一,我们将这些代码封起来。使用配置文件来配置相关参数。
3.1 新建配置文件:pollyconfig.json,并且将该json文件保存的格式为UTF-8,不然会有中文乱码问题。
{
"Polly": [
{
"ServiceName": [ "myhttpclienttest", "myhttpclienttest2" ], //服务名称,可以多个服务使用同一个配置
"TimeoutTime": 5, //超时时间设置,单位为秒
"RetryCount": 2, //失败重试次数
"CircuitBreakerOpenFallCount": 2, //执行多少次异常,开启短路器(例:失败2次,开启断路器)
"CircuitBreakerDownTime": 6, //断路器关闭的时间(例如:设置为2秒,短路器两秒后自动由开启到关闭)
"HttpResponseMessage": "系统繁忙,请稍后再试!", //降级处理提示信息
"HttpResponseStatus": 200 //降级处理响应状态码
},
{
"ServiceName": [ "myhttpclienttest3" ], //假如服务名称存在相同的,则后面的会替换掉前面的
"TimeoutTime": 2,
"RetryCount": 5,
"CircuitBreakerOpenFallCount": 2,
"CircuitBreakerDownTime": 8,
"HttpResponseMessage": "系统繁忙,请稍后再试~!",
"HttpResponseStatus": 503
}
]
}
3.2 创建配置实体类:PollyHttpClientConfig.cs对应配置文件里的节点
public class PollyHttpClientConfig
{
/// 3.3 封装拓展类:PollyHttpClientServiceCollectionExtension.cs
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Polly;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace HttpClientDemo
{
public static class PollyHttpClientServiceCollectionExtension
{
public static void AddPollyHttpClient(this IServiceCollection service)
{
//读取服务配置文件
try
{
var config = new ConfigurationBuilder().AddJsonFile("pollyconfig.json").Build(); //nuget: Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json
List<PollyHttpClientConfig> configList = config.GetSection("Polly").Get<List<PollyHttpClientConfig>>(); // nuget: Microsoft.Extensions.Options.ConfigurationExtensions
if (configList != null && configList.Count > 0)
{
configList.ForEach((pollyHttpClientConfig) =>
{
service.AddPollyHttpClient(pollyHttpClientConfig);
});
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception("请正确配置pollyconfig.json");
}
}
public static void AddPollyHttpClient(this IServiceCollection service, PollyHttpClientConfig pollyHttpClientConfig)
{
if (pollyHttpClientConfig == null)
throw new Exception("请配置:pollyHttpClientConfig");
if (pollyHttpClientConfig.ServiceName == null || pollyHttpClientConfig.ServiceName.Count < 1)
throw new Exception("请配置:pollyHttpClientConfig.Polly.ServiceName");
for (int i = 0; i < pollyHttpClientConfig.ServiceName.Count; i++)
{
var builder = service.AddHttpClient(pollyHttpClientConfig.ServiceName[i]);
builder.BuildFallbackAsync(pollyHttpClientConfig.HttpResponseMessage, pollyHttpClientConfig.HttpResponseStatus);
builder.BuildCircuitBreakerAsync(pollyHttpClientConfig.CircuitBreakerOpenFallCount, pollyHttpClientConfig.CircuitBreakerDownTime);
builder.BuildRetryAsync(pollyHttpClientConfig.RetryCount);
builder.BuildTimeoutAsync(pollyHttpClientConfig.TimeoutTime);
}
}
//降级
private static void BuildFallbackAsync(this IHttpClientBuilder builder, string httpResponseMessage, int httpResponseStatus)
{
if (httpResponseStatus < 1 || string.IsNullOrEmpty(httpResponseMessage))
return;
HttpResponseMessage fallbackResponse = new HttpResponseMessage
{
Content = new StringContent(httpResponseMessage),
StatusCode = (HttpStatusCode)httpResponseStatus
};
builder.AddPolicyHandler(Policy<HttpResponseMessage>.HandleInner<Exception>().FallbackAsync(fallbackResponse, async b =>
{
// 1、降级打印异常
Console.WriteLine($"服务开始降级,异常消息:{b.Exception.Message}");
// 2、降级后的数据
Console.WriteLine($"服务降级内容响应:{await fallbackResponse.Content.ReadAsStringAsync()}");
await Task.CompletedTask;
}));
}
//熔断
private static void BuildCircuitBreakerAsync(this IHttpClientBuilder builder, int circuitBreakerOpenFallCount, int circuitBreakerDownTime)
{
if (circuitBreakerOpenFallCount < 1 || circuitBreakerDownTime < 1)
return;
builder.AddPolicyHandler(
Policy<HttpResponseMessage> // HttpResponseMessage 为HttpClient的返回值
.Handle<Exception>() //捕获Exception异常
.OrResult(res => res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError || res.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout)
.CircuitBreakerAsync(
circuitBreakerOpenFallCount, // 出现3次异常
TimeSpan.FromSeconds(circuitBreakerDownTime), //10秒之内; 结合上面就是:10秒之内出现3次异常就熔断
(res, ts) =>
{ //熔断器开启事件触发
Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器开启,异常消息:{res.Result}");
Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器开启的时间:{ts.TotalSeconds}s");
}, //断路器重置事件触发
() => { Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器重置"); }, //断路器半开启事件触发
() => { Console.WriteLine($"服务断路器半开启(一会开,一会关)"); }
)
);
}
//失败重试
private static void BuildRetryAsync(this IHttpClientBuilder builder, int retryCount)
{
if (retryCount > 0)//失败重试
builder.AddPolicyHandler(Policy<HttpResponseMessage>.Handle<Exception>().RetryAsync(retryCount));
}
//超时
private static void BuildTimeoutAsync(this IHttpClientBuilder builder, int timeoutTime)
{
if (timeoutTime > 0)//超时
builder.AddPolicyHandler(Policy.TimeoutAsync<HttpResponseMessage>(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(timeoutTime)));
}
}
}
3.4 在startup.cs类的ConfigureServices方法中注册,放在所有命名模式的HttpClient客户端注册之后。
services.AddPollyHttpClient();
3.5 HttpClient调用远程接口服务的方法不变。
流量错峰、流量限流、流量削峰
服务端每秒流量处理能力是通过QPS衡量的,最大QPS(峰值)就是对服务端抗压能力的衡量指标,如果来自客户端的流量超过了服务端最大QPS,要么服务端发生宕机,要么将超过能力范围内的请求忽略掉,返回限流错误给客户端,两者都造成用户体验的崩塌和品牌受损。
策略概括起来就三点:错峰、限流、削峰,本质上都是为了降低QPS。

流量错峰
“错峰”,顾名思义就是将请求峰值错开,服务端的QPS峰值可以看做是一系列的小QPS峰值请求的叠加,因此通过一些技术手段来错开这些小峰值,有效降低最大QPS。我们可以从服务端和客户端两个维度来错峰。
服务端错峰策略
如果触发客户端的请求动作是通过服务端主动下发实现的,比如PowerMsg支持服务端主动下发,那么服务端可以分批下发给客户端(假设所有服务端到客户端的时延RT是一样的)。

客户端错峰策略
常用的客户端错峰策略采用的是随机算法,假设所有客户端接收要触发请求动作的时间![]() 是一样的,给定一个时间T,客户端采用随机延迟,t时刻再去触发请求动作,其中t在[0,T]时间段内随机。
是一样的,给定一个时间T,客户端采用随机延迟,t时刻再去触发请求动作,其中t在[0,T]时间段内随机。
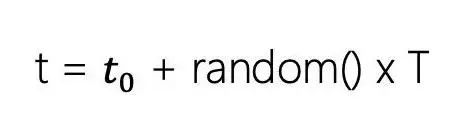
从大量数据来看,这个公式可以保证 t 在区间 [0, T] 之间均匀分布。那么理论上新的最大QPS等于老的最大QPS除以T。


流量限流
服务端基本都会做限流,比如Mtop限流之后返回对应的限流错误码。下面主要介绍客户端限流。客户端限流主要目标是消除频繁或不必要的请求。
- 用户已经到达最大请求次数,就不去请求;
- 用户已经被限流,则延迟再去第二次请求;
- 用户已经拿到所要的返回结果,则不再去请求。
流量削峰
削峰,也就是消除峰值的最大QPS,有几种削峰策略。
设置两次请求最小有效时间间隔
设置两次请求最小有效时间间隔,假设最小时间间隔是t,那么在小于t的时间的请求都视为无效请求,忽略掉。像红包雨这类频繁请求的活动,该策略非常有效。
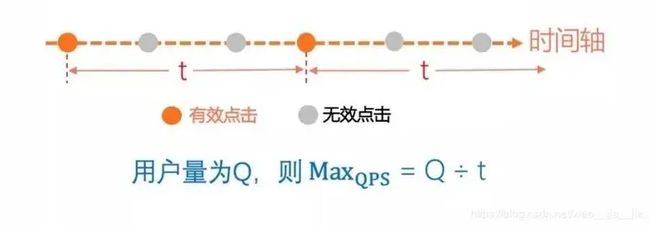
例如上图,红色是有效请求,灰色是无效请求,灰色也就不会向服务端发送请求。假设t秒内只有一次有效请求,那么1秒内,有1/t次有效请求,用户量是Q,那么最大QPS如下(假设所有的用户都是同时开始请求,间隔时间一致):
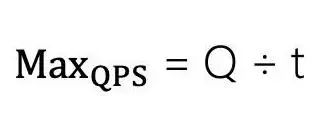
概率请求策略
如果不想每次都让用户去请求,给用户请求的动作加一个概率P,那么每次发送请求的概率就是P,这个时候需要结合3.1的策略去控制用户的每秒请求次数。最大QPS公式如下:

通过控制t和P的值,就可以灵活控制最大QPS范围。这里有一个问题,就是根据概率容易产生极端请求,比如:

大量数据就容易产生大量的极端请求,违反公平性原则,就需要用到公平性策略。
公平性策略
这里提供一种公平性策略的方式,随机算法+插值算法,生成有效请求序列。
每个用户一次活动周期内有效请求概率是P,比如概率0.2,也就是5次中1次请求机会,或者10次中2次请求机会。根据随机算法+插值算法生成请求序列:

根据上述方式就可以得到公平性策略,粒度可以***把控。
通过上述错峰、限流、削峰方式,达到降低QPS的目的。通常,一场大促需要上述几种方案的结合。
使用事件总线框架CAP实现削峰:商城高并发秒杀系统(.NET Core版) 27-性能优化-事件总线的使用(流量削峰)
来源
.NetCore中HttpClient使用Polly实现熔断、降级和限流
如何降低QPS(错峰、限流、削峰)
后端开发术语大全