select 函数实现 三种拓扑结构 n个客户端的异步通信 (完全图+线性链表+无环图)
一、这里只介绍简单的三个客户端异步通信(完全图拓扑结构)
1 1 //建立管道 2 2 mkfifo 12 13 21 23 31 32
open顺序:
cl1 读 , cl2 cl3 向 cl1写
cl2 读 , cl1 cl3 向 cl2写
cl3 读 , cl1 cl2 向 cl3写
顺序的规律就是 第i个 客户端读 其他各个客户端 ,其他的各个客户端 向 i 写 ,i 从 1 到 3.
cl1 代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<sys/stat.h> 6 #include<sys/types.h> 7 #include<fcntl.h> 8 #include <sys/time.h> 9 #include<sys/select.h> 10 #include <sys/select.h> 11 12 /* According to earlier standards */ 13 #include <sys/time.h> 14 #include <sys/types.h> 15 #include <unistd.h> 16 17 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//21 18 { 19 20 int fd21, fd31,fd12,fd13 ; 21 fd21 = open("21", O_RDONLY); 22 fd31 = open("31", O_RDONLY); 23 24 fd12 = open("12",O_WRONLY); 25 26 fd13 = open("13",O_WRONLY); 27 printf("OK!\n"); 28 29 30 printf("OK!\n"); 31 fd_set read_sets ; 32 fd_set write_sets ; 33 int iret,iwrt ; 34 char buf[1024] ; 35 struct timeval tm ; 36 while(1) 37 { 38 39 tm.tv_sec = 1 ; 40 tm.tv_usec = 0 ; 41 FD_ZERO(&read_sets); 42 FD_ZERO(&write_sets); 43 44 FD_SET(fd21, &read_sets); 45 FD_SET(fd31, &read_sets); 46 FD_SET( 0, &write_sets); 47 //FD_SET(fd12, &write_sets); 48 //FD_SET(fd13, &write_sets); 49 50 iret = select(10, &read_sets, NULL, NULL, &tm); 51 iwrt = select(10,&write_sets,NULL,NULL,&tm); 52 53 //读 54 if(iret != 0) 55 { 56 printf("active: %d\n", iret); 57 58 if(FD_ISSET(fd21, &read_sets)) 59 { 60 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 61 read(fd21, buf, 1023); 62 printf("from 2: %s\n", buf); 63 } 64 if(FD_ISSET(fd31, &read_sets)) 65 { 66 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 67 read(fd31, buf, 1023); 68 printf("from 3: %s\n", buf); 69 } 70 } 71 72 73 // write 74 if(iwrt != 0) 75 { 76 printf("active: %d\n", iwrt); 77 if(FD_ISSET( 0 /*fd12*/, &write_sets)) 78 { 79 memset(buf, 0, 128); 80 read(0, buf, 127) ; 81 write(fd12, buf, strlen(buf)); 82 write(fd13, buf, strlen(buf)); 83 } 84 /*if(FD_ISSET(fd13, &write_sets)) 85 { 86 memset(buf, 0, 128); 87 read(0, buf, 127) ; 88 write(fd13, buf, strlen(buf)); 89 }*/ 90 } 91 92 } 93 return 0 ; 94 }
cl2 代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<sys/stat.h> 6 #include<sys/types.h> 7 #include<fcntl.h> 8 #include<sys/select.h> 9 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//21 10 { 11 int fd12, fd32,fd21,fd23 ; 12 fd21 = open("21",O_WRONLY); 13 14 fd12 = open("12", O_RDONLY); 15 fd32 = open("32", O_RDONLY); 16 17 fd23 = open("23",O_WRONLY); 18 19 20 fd_set read_sets ,write_sets ; 21 int iret ,iwrt; 22 char buf[1024] ; 23 struct timeval tm ; 24 while(1) 25 { 26 27 tm.tv_sec = 1 ; 28 tm.tv_usec = 0 ; 29 FD_ZERO(&read_sets); 30 FD_ZERO(&write_sets); 31 FD_SET(fd12, &read_sets); 32 FD_SET(fd32, &read_sets); 33 FD_SET( 0, &write_sets); 34 //FD_SET(fd21,&write_sets); 35 //FD_SET(fd23,&write_sets); 36 37 iret = select(10, &read_sets, NULL, NULL, &tm); 38 iwrt = select(10,&write_sets,NULL,NULL,&tm); 39 40 if(iret != 0) 41 { 42 printf("active: %d\n", iret); 43 44 if(FD_ISSET(fd12, &read_sets)) 45 { 46 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 47 read(fd12, buf, 1023); 48 printf("from 1: %s\n", buf); 49 } 50 if(FD_ISSET(fd32, &read_sets)) 51 { 52 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 53 read(fd32, buf, 1023); 54 printf("from 3: %s\n", buf); 55 } 56 } 57 58 59 // write 60 if(iwrt != 0) 61 { 62 printf("active: %d\n", iwrt); 63 if(FD_ISSET( 0 , &write_sets)) 64 { 65 memset(buf, 0, 128); 66 read(0, buf, 127) ; 67 write(fd21, buf, strlen(buf)); 68 write(fd23, buf, strlen(buf)); 69 } 70 /* if(FD_ISSET(fd23, &write_sets)) 71 { 72 memset(buf, 0, 128); 73 read(0, buf, 127) ; 74 write(fd23, buf, strlen(buf)); 75 }*/ 76 } 77 78 } 79 return 0 ; 80 }
cl3 代码:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<sys/stat.h> 6 #include<sys/types.h> 7 #include<fcntl.h> 8 #include<sys/select.h> 9 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//31 10 { 11 int fd13, fd23,fd31,fd32 ; 12 fd31 = open("31",O_WRONLY); 13 14 fd32 = open("32",O_WRONLY); 15 16 fd13 = open("13", O_RDONLY); 17 fd23 = open("23", O_RDONLY); 18 19 printf("OK!\n"); 20 fd_set read_sets ,write_sets ; 21 int iret,iwrt ; 22 char buf[1024] ; 23 struct timeval tm ; 24 while(1) 25 { 26 27 tm.tv_sec = 1 ; 28 tm.tv_usec = 0 ; 29 FD_ZERO(&read_sets); 30 FD_ZERO(&write_sets); 31 FD_SET(fd13, &read_sets); 32 FD_SET(fd23, &read_sets); 33 //FD_SET(fd31,&write_sets); 34 //FD_SET(fd32,&write_sets); 35 FD_SET( 0, &write_sets); 36 37 iret = select(10, &read_sets, NULL, NULL, &tm); 38 iwrt = select(10,&write_sets,NULL,NULL,&tm); 39 40 //读 41 if(iret != 0) 42 { 43 printf("active: %d\n", iret); 44 45 if(FD_ISSET(fd13, &read_sets)) 46 { 47 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 48 read(fd13, buf, 1023); 49 printf("from 1: %s\n", buf); 50 } 51 if(FD_ISSET(fd23, &read_sets)) 52 { 53 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 54 read(fd23, buf, 1023); 55 printf("from 2: %s\n", buf); 56 } 57 } 58 59 60 // write 61 if(iwrt != 0) 62 { 63 printf("active: %d\n", iwrt); 64 if(FD_ISSET( 0 , &write_sets)) 65 { 66 memset(buf, 0, 128); 67 read(0, buf, 127) ; 68 write(fd31, buf, strlen(buf)); 69 write(fd32, buf, strlen(buf)); 70 } 71 /*if(FD_ISSET(fd32, &write_sets)) 72 { 73 memset(buf, 0, 128); 74 read(0, buf, 127) ; 75 write(fd32, buf, strlen(buf)); 76 }*/ 77 } 78 } 79 80 return 0 ; 81 }
二 、n个客户端异步通信 (线性链表的拓扑结构)
很显然的,如果用上述的方法需要每个客户端和其他客户端都直接相邻,即完全图。
建立n个客户端通信,需要 2*((n-1)+(n-2)+(n-3)+……3+2+1) = 2*(n-1 + 1)*(n -1)/2 =n * (n-1) 根管道,
这么多的管道连接会使得代码实现变得非常冗杂、而且系统浪费资源管道。
这里,用线性链表的拓扑结构,可以解决这个问题:
1、 客户端以线性存储
2、 当 pre 发来数据时, 打印出来,并且转发给next(若next存在)。
3、 当 next 发来数据时, 打印出来,并且转发给pre(若pre存在)。
4、 当键盘发来数据时,转发给next(若next存在),转发给pre(若pre存在)。
例子:
1、客户端拓扑结构为 1——3——2——4
在文件存储如下:

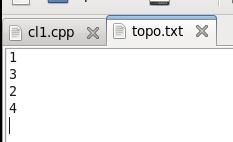
2、我还编写一个读取topo.txt 文件 ,自动生成管道的代码:
BuildFIFO.cpp 如下:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<unistd.h> 6 #include<sys/stat.h> 7 #include<sys/types.h> 8 #include<fcntl.h> 9 #include <sys/time.h> 10 #include<sys/select.h> 11 using namespace std; 12 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//21 13 { 14 15 FILE* topu = fopen("topo.txt","r"); 16 int fir = 1; 17 char dir[5],DIR[11]; 18 string str1,str2,str ; 19 while(!feof(topu)) 20 { 21 fscanf(topu ,"%s\n",dir); 22 str1 = dir; 23 if(fir) 24 { 25 fir =0 ; 26 str2=str1; 27 continue; 28 } 29 str=str1+"T"+str2; 30 strcpy(DIR,str.c_str()); 31 mkfifo(DIR,0777); 32 33 str=str2+"T"+str1; 34 strcpy(DIR,str.c_str()); 35 mkfifo(DIR,0777); 36 str2 = str1; 37 } 38 39 fclose(topu); 40 41 return 0; 42 }
3、从客户端3键盘输入数据后,发送到各个客户端:

4、这里也有个 open 的 顺序的问题,但其实这种拓扑结构很好解决这个问题:
只需要每个相邻的客户端 读写顺序相反就能解决了
如下:
1 if(count & 1== 1) //判断节点的位置是奇数 还是 偶数 ,如果是 奇数 就 先读后写 2 { 3 if(strcmp("-1",pre->val)!=0) 4 { 5 6 fdReadFromPre = My_Open(pre->val,p->val,0); 7 fdWriteToPre = My_Open(p->val,pre->val,1); 8 } 9 10 if(p->next!=NULL) 11 { 12 fdReadFromNext = My_Open(p->next->val,p->val,0); 13 fdWriteToNext = My_Open(p->val,p->next->val,1); 14 } 15 } 16 else //如果是偶数,先写后读 17 { 18 if(strcmp("-1",pre->val)!=0) 19 { 20 fdWriteToPre = My_Open(p->val,pre->val,1); 21 fdReadFromPre = My_Open(pre->val,p->val,0); 22 } 23 24 if(p->next!=NULL) 25 { 26 fdWriteToNext = My_Open(p->val,p->next->val,1); 27 fdReadFromNext = My_Open(p->next->val,p->val,0); 28 } 29 30 }
5、各客户端代码:
这里只发 cl1.cpp
(
其他客户端就是
1 while( strcmp("1",p->val)!=0)
1 char tembuf[1024] = "Form1 :";
这两句代码不一样而已
)
如下:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<sys/stat.h> 6 #include<sys/types.h> 7 #include<fcntl.h> 8 #include <sys/time.h> 9 #include<sys/select.h> 10 11 12 #define fdNULL -9999 13 14 struct node 15 { 16 char val[5]; 17 node* next; 18 }; 19 20 int My_Open(char A[],char B[],int type) 21 { 22 char Cstr[11]; 23 memset( Cstr, '\0', sizeof(Cstr) ); 24 strcat(Cstr,A); 25 strcat(Cstr,"T"); 26 strcat(Cstr,B); 27 if(type == 0) return open(Cstr, O_RDONLY); 28 else return open(Cstr, O_WRONLY); 29 } 30 31 32 int main(int argc, char* argv[])//21 33 { 34 35 FILE* topu = fopen("/home/soso/Desktop/1-30/LineSelect/topo.txt","r"); 36 char a[5]; 37 38 node* L = (node*)calloc(1, sizeof(node)); //save topo 39 strcpy(L->val,"-1"); 40 L->next = NULL; 41 node* tem , *p ,*pre; 42 p=L; 43 while(!feof(topu)) 44 { 45 fscanf(topu ,"%s\n",a); 46 tem= (node*)calloc(1, sizeof(node)); 47 strcpy(tem->val,a); 48 tem->next = NULL; 49 p->next=tem; 50 p=p->next; 51 } 52 fclose(topu); 53 54 pre=L; 55 p= L->next; 56 int count = 1; 57 while( strcmp("1",p->val)!=0) 58 { 59 p=p->next; 60 pre=pre->next; 61 ++count; 62 } 63 64 int fdReadFromPre,fdReadFromNext,fdWriteToPre,fdWriteToNext ; 65 fdReadFromPre=fdReadFromNext=fdWriteToPre=fdWriteToNext=fdNULL; 66 if(count & 1== 1) //判断节点的位置是奇数 还是 偶数 ,如果是 奇数 就 先读后写 67 { 68 if(strcmp("-1",pre->val)!=0) 69 { 70 71 fdReadFromPre = My_Open(pre->val,p->val,0); 72 fdWriteToPre = My_Open(p->val,pre->val,1); 73 } 74 75 if(p->next!=NULL) 76 { 77 fdReadFromNext = My_Open(p->next->val,p->val,0); 78 fdWriteToNext = My_Open(p->val,p->next->val,1); 79 } 80 } 81 else //如果是偶数,先写后读 82 { 83 if(strcmp("-1",pre->val)!=0) 84 { 85 fdWriteToPre = My_Open(p->val,pre->val,1); 86 fdReadFromPre = My_Open(pre->val,p->val,0); 87 } 88 89 if(p->next!=NULL) 90 { 91 fdWriteToNext = My_Open(p->val,p->next->val,1); 92 fdReadFromNext = My_Open(p->next->val,p->val,0); 93 } 94 95 } 96 97 printf("OK!\n"); 98 99 fd_set read_sets ; 100 fd_set write_sets ; 101 int iret,iwrt ; 102 char buf[1024] ; 103 struct timeval tm ; 104 while(1) 105 { 106 107 tm.tv_sec = 1 ; 108 tm.tv_usec = 0 ; 109 FD_ZERO(&read_sets); 110 FD_ZERO(&write_sets); 111 if(fdReadFromPre != fdNULL) 112 FD_SET(fdReadFromPre, &read_sets); 113 if(fdReadFromNext != fdNULL) 114 FD_SET(fdReadFromNext, &read_sets); 115 FD_SET( 0, &write_sets); 116 117 118 iret = select(10, &read_sets, NULL, NULL, &tm); 119 iwrt = select(10,&write_sets,NULL,NULL,&tm); 120 121 //读 122 if(iret != 0) 123 { 124 125 if(FD_ISSET(fdReadFromPre, &read_sets)) 126 { 127 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 128 read(fdReadFromPre, buf, 1023); 129 if(fdWriteToNext!=fdNULL) //把从pre读过来的数据转发到next去 130 write(fdWriteToNext, buf, strlen(buf)); 131 printf("%s\n" ,buf); 132 } 133 if(FD_ISSET(fdReadFromNext, &read_sets)) 134 { 135 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 136 read(fdReadFromNext, buf, 1023); 137 if(fdWriteToPre!=fdNULL) //把从next读过来的数据转发到pre去 138 write(fdWriteToPre, buf, strlen(buf)); 139 printf("%s\n", buf); 140 } 141 } 142 143 144 // write 145 if(iwrt != 0) 146 { 147 148 if(FD_ISSET( 0 , &write_sets)) 149 { 150 memset(buf, 0, 128); 151 read(0, buf, 127) ; 152 char tembuf[1024] = "Form1 :"; 153 strcat(tembuf,buf); 154 if(fdWriteToNext!=fdNULL) //把从键盘输入的数据向next、pre 转发 155 write(fdWriteToNext, tembuf, strlen(tembuf)); 156 if(fdWriteToPre!=fdNULL) 157 write(fdWriteToPre, tembuf, strlen(tembuf)); 158 } 159 } 160 161 } 162 return 0; 163 }
6、添加的客户端
1、在topo.txt 添加 客户名 再 换行
2、再按一下 已经生成的 BuildFIFO 可执行文件,及自动生成所需的管道
3、vim 出客户端,代码只需 改动两处(见5) 便可以完成客户端的添加。
三 、n个客户端异步通信 (无环图的拓扑结构)
线性拓扑结构有个很大的缺陷
如图:

客户端1 发送消息,要经过 3、2 的转发才能到达 4。当客户端数量很大时,链表前部和后部之间的通信的延迟会很大。
如果改进,用树形拓扑机构就会很大的缓解这个问题。
1、 《计算机网络》的OSPF路由算法里面提到的泛洪法+无环图拓扑结构
如图 为Zhu客户端键盘输入数据:

2、存储结构
在文件topo.txt 中以类似于邻接的方式存储:
topo文件格式为:
顶点 节点个数 节点1 节点2 ……
如图:


客户端读取文件后的邻接表存储代码:
1 map<string,bool> visit; 2 3 struct TreeLine 4 { 5 vector<string> TreeNode; 6 int level; //层号 7 }; 8 9 10 map<string,TreeLine> Tree;
1 FILE* topu = fopen("topo.txt","r"); 2 int fir = 1; 3 int i,j; 4 char strtem[5],strtem2[5],tem,Lval[5]; 5 int num; 6 while(!feof(topu)) 7 { 8 fscanf(topu ,"%s %d",strtem,&num); 9 if(fir) //记录第一个客户端的名称 10 { 11 fir = 0; 12 strcpy(Lval,strtem); 13 } 14 15 16 TreeLine TemLine; 17 for(int i =0 ;i< num;i++) 18 { 19 fscanf(topu," %s",strtem2); 20 TemLine.TreeNode.push_back(strtem2); 21 } 22 fgetc(topu); 23 24 Tree[strtem]=TemLine; 25 visit[strtem] = false; //初始化访问位 26 } 27 fclose(topu);
3、DFS来标注奇偶层号,判断open顺序(只要奇偶层顺序相反)

1 void DFS(string val,int level) 2 { 3 visit[val] = true ; 4 Tree[val].level = level; 5 //cout<<val<<":"<<level<<" "<<Tree[val].TreeNode.size()<<endl; 6 int i; 7 for(i = 0;i<Tree[val].TreeNode.size();++i) 8 { 9 if(visit[Tree[val].TreeNode[i]] == false) 10 DFS(Tree[val].TreeNode[i],level+1); 11 } 12 }
1 int level = 1; 2 DFS(Lval,level); 3 4 vector<int> fdReadOpen,fdWriteOpen; 5 6 7 string TemString; 8 if(Tree[UserName].level & 1 == 1) //判断层号 奇数先读后写 9 { 10 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 11 { 12 TemString=Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]+"TO"+UserName; 13 fdReadOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(), O_RDONLY)); 14 } 15 16 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 17 { 18 TemString = UserName; 19 TemString+="TO"+Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]; 20 fdWriteOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(),O_WRONLY)); 21 } 22 23 } 24 else //判断层号 偶数数先写后读 25 { 26 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 27 { 28 TemString = UserName; 29 TemString+="TO"+Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]; 30 fdWriteOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(),O_WRONLY)); 31 } 32 33 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 34 { 35 TemString=Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]+"TO"+UserName; 36 fdReadOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(), O_RDONLY)); 37 } 38 }
3、各客户端代码:
这次用了宏定义,每个客户端只需修改:
1 #define UserName "Ye"
其他代码都相同。
这里分析客户端 Ye 的代码:
1 #include <vector> 2 #include<map> 3 #include<string> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<stdio.h> 6 #include<stdlib.h> 7 #include<string.h> 8 #include<unistd.h> 9 #include<sys/stat.h> 10 #include<sys/types.h> 11 #include<fcntl.h> 12 #include <sys/time.h> 13 #include<sys/select.h> 14 using namespace std; 15 16 #define MaxSize 10000 17 18 #define UserName "Ye" 19 20 map<string,bool> visit; 21 22 struct TreeLine 23 { 24 vector<string> TreeNode; 25 int level; //层号 26 }; 27 28 29 map<string,TreeLine> Tree; 30 31 void DFS(string val,int level) 32 { 33 visit[val] = true ; 34 Tree[val].level = level; 35 //cout<<val<<":"<<level<<" "<<Tree[val].TreeNode.size()<<endl; 36 int i; 37 for(i = 0;i<Tree[val].TreeNode.size();++i) 38 { 39 if(visit[Tree[val].TreeNode[i]] == false) 40 DFS(Tree[val].TreeNode[i],level+1); 41 } 42 } 43 44 45 46 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 47 { 48 49 FILE* topu = fopen("topo.txt","r"); 50 int fir = 1; 51 int i,j; 52 char strtem[5],strtem2[5],tem,Lval[5]; 53 int num; 54 while(!feof(topu)) 55 { 56 fscanf(topu ,"%s %d",strtem,&num); 57 if(fir) //记录第一个客户端的名称 58 { 59 fir = 0; 60 strcpy(Lval,strtem); 61 } 62 63 64 TreeLine TemLine; 65 for(int i =0 ;i< num;i++) 66 { 67 fscanf(topu," %s",strtem2); 68 TemLine.TreeNode.push_back(strtem2); 69 } 70 fgetc(topu); 71 72 Tree[strtem]=TemLine; 73 visit[strtem] = false; //初始化访问位 74 } 75 fclose(topu); 76 77 int level = 1; 78 DFS(Lval,level); 79 80 vector<int> fdReadOpen,fdWriteOpen; 81 82 83 string TemString; 84 if(Tree[UserName].level & 1 == 1) //判断层号 奇数先读后写 85 { 86 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 87 { 88 TemString=Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]+"TO"+UserName; 89 fdReadOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(), O_RDONLY)); 90 } 91 92 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 93 { 94 TemString = UserName; 95 TemString+="TO"+Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]; 96 fdWriteOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(),O_WRONLY)); 97 } 98 99 } 100 else //判断层号 偶数数先写后读 101 { 102 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 103 { 104 TemString = UserName; 105 TemString+="TO"+Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]; 106 fdWriteOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(),O_WRONLY)); 107 } 108 109 for(i= 0 ;i<Tree[UserName].TreeNode.size();++i) 110 { 111 TemString=Tree[UserName].TreeNode[i]+"TO"+UserName; 112 fdReadOpen.push_back(open(TemString.c_str(), O_RDONLY)); 113 } 114 } 115 116 117 118 119 printf("OK!\n"); 120 121 fd_set read_sets ; 122 fd_set write_sets ; 123 int iret,iwrt ; 124 char buf[1024] ; 125 struct timeval tm ; 126 while(1) 127 { 128 129 tm.tv_sec = 1 ; 130 tm.tv_usec = 0 ; 131 FD_ZERO(&read_sets); 132 FD_ZERO(&write_sets); 133 for(i=0;i<fdReadOpen.size();i++) 134 FD_SET(fdReadOpen[i], &read_sets); 135 FD_SET( 0, &write_sets); 136 137 iret = select(1023, &read_sets, NULL, NULL, &tm); 138 iwrt = select(1023,&write_sets,NULL,NULL,&tm); 139 140 //读 141 if(iret != 0) 142 { 143 144 for(i=0;i<fdReadOpen.size();i++) //遍历ReadOpen 145 { 146 if(FD_ISSET(fdReadOpen[i], &read_sets)) //当收到ReadOpen[i]时 147 { 148 memset(buf, 0, 1024); 149 read(fdReadOpen[i], buf, 1023); 150 printf("%s\n" ,buf); //打印出来 151 for(j=0;j<fdWriteOpen.size();j++) //向其他客户端转发 152 { 153 if(j != i) //AtoB 和 BtoA 的fdOpen存储位置是对应的 154 write(fdWriteOpen[j], buf, strlen(buf)); 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 } 159 160 161 // write 162 if(iwrt != 0) 163 { 164 if(FD_ISSET( 0 , &write_sets)) 165 { 166 memset(buf, 0, 128); 167 read(0, buf, 127) ; 168 char tembuf[1024] = UserName; 169 strcat(tembuf," :"); 170 strcat(tembuf,buf); 171 for(i =0 ;i< fdWriteOpen.size();i++) 172 write(fdWriteOpen[i], tembuf, strlen(tembuf)); 173 } 174 } 175 176 } 177 178 179 return 0; 180 }
4、添加的客户端
1、按照输入格式在topo.txt 添加
2、再按一下 已经生成的 BuildFIFO 可执行文件,及自动生成所需的管道
3、vim 出客户端,代码只需 改动一处(见3) 便可以完成客户端的添加。