【LeetCode热题100】打卡第33天:环形链表&LRU缓存
文章目录
- 【LeetCode热题100】打卡第33天:环形链表&LRU缓存
-
- ⛅前言
- 环形链表
-
- 题目
- 题解
- LRU缓存
-
- 题目
- 题解
【LeetCode热题100】打卡第33天:环形链表&LRU缓存
⛅前言
大家好,我是知识汲取者,欢迎来到我的LeetCode热题100刷题专栏!
精选 100 道力扣(LeetCode)上最热门的题目,适合初识算法与数据结构的新手和想要在短时间内高效提升的人,熟练掌握这 100 道题,你就已经具备了在代码世界通行的基本能力。在此专栏中,我们将会涵盖各种类型的算法题目,包括但不限于数组、链表、树、字典树、图、排序、搜索、动态规划等等,并会提供详细的解题思路以及Java代码实现。如果你也想刷题,不断提升自己,就请加入我们吧!QQ群号:827302436。我们共同监督打卡,一起学习,一起进步。
博客主页:知识汲取者的博客
LeetCode热题100专栏:LeetCode热题100
Gitee地址:知识汲取者 (aghp) - Gitee.com
Github地址:Chinafrfq · GitHub
题目来源:LeetCode 热题 100 - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
PS:作者水平有限,如有错误或描述不当的地方,恳请及时告诉作者,作者将不胜感激
环形链表
题目
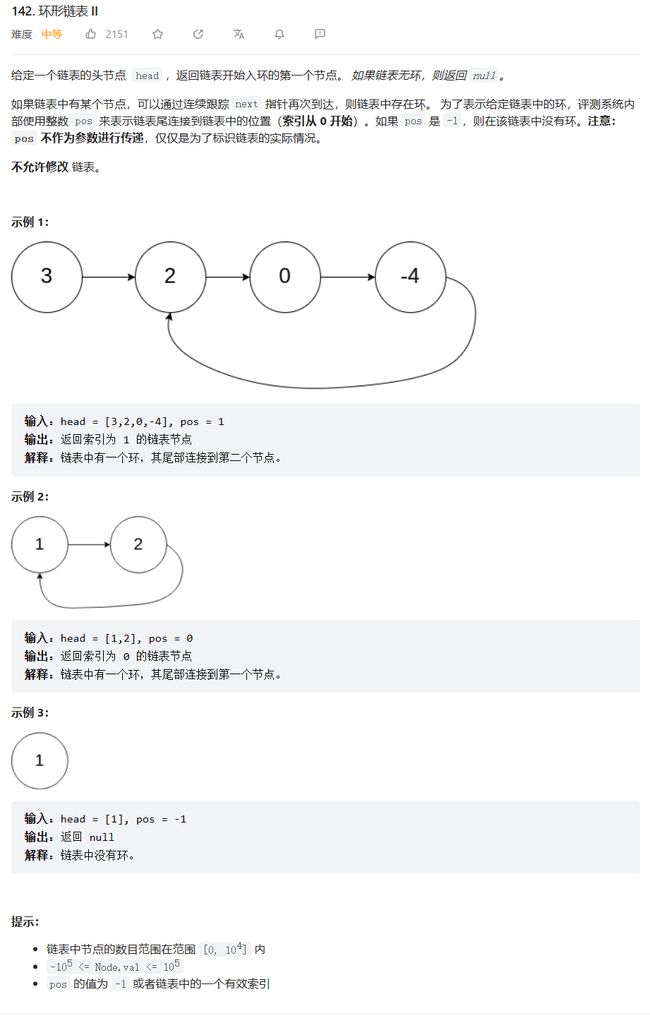
原题链接:142.环形链表II
题解
-
解法一:Set集合
昨天刚写完【LeetCode热题100】打卡第32天的题目,其中就遇到 环形链表I,也是使用这种方式解决的O(∩_∩)O
public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); while (head != null) { if (!set.add(head)) { return head; } head = head.next; } return null; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
-
解法二:快慢指针
这个快慢指针用起来就要比【LeetCode热题100】打卡第32天的题目 的那道环形链表I 要难的多了
详解参考 K神,真的是强,佩服b( ̄▽ ̄)d,这里我给出一些我的理解
假设head到环入口出要走
a步,环的节点数为b,则:-
fast于slow相遇,fast一定是比slow多走
nb步s , f = 2 s = s + n b → s = n b s,f=2s=s+nb → s=nb s,f=2s=s+nb→s=nb
-
a+nb一定是在环入口出 -
第一次相遇后,我们将fast重置到head处,这样就能保障fast和slow相遇一定是是
a+nb,此时两者在环入口相遇f = 0 , s = n b → f = a , s = a + n b f=0,s=nb→f=a,s=a+nb f=0,s=nb→f=a,s=a+nb
这里面具有很严密的数据逻辑推理在里面!
public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if (fast!=null){ fast = fast.next; } if (fast == slow){ break; } } if (fast==null){ return null; } fast = head; while (fast!=slow){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return fast; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为数组中元素的个数
-
LRU缓存
题目
原题链接:146.LRU缓存
题解
-
解法一:Map标记法(超时,22个示例数据过了20个)
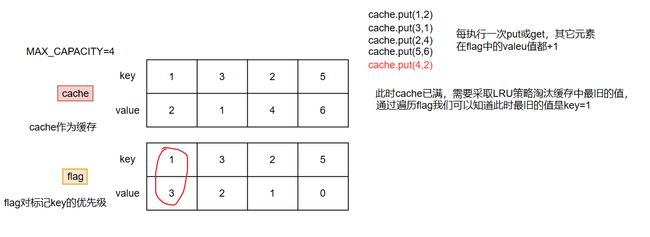
这是最开始的思路,直接使用双Map,一个Map作为缓存,一个Map用于记录key的淘汰优先级,每次进行get或put操作时,未操作的key的淘汰优先级都自增1,如果缓存已满,则根据淘汰优先级进行淘汰。总的来说这个思路还是挺简单的,但是这代码看着就像“屎山代码”w(゚Д゚)w,感觉可以进行优化
class LRUCache { // 缓存 private Map<Integer, Integer> cache; // 用于标记,值越大越优先淘汰 private Map<Integer, Integer> flag; // 最大容量 private int MAX_CAPACITY; public LRUCache(int capacity) { MAX_CAPACITY = capacity; cache = new HashMap<>(capacity); flag = new HashMap<>(capacity); } /** * 从缓存中获取值 */ public int get(int key) { if (cache.containsKey(key)){ // 当前元素置0,其它元素值+1 flag.put(key, 0); increment(key); return cache.get(key); } return -1; } /** * 除key以外的都自增 */ private void increment(int key) { for (Integer i : flag.keySet()) { if (i != key){ flag.put(i, flag.get(i)+1); } } } /** * 往缓存中添加元素 */ public void put(int key, int value) { if (cache.size() < MAX_CAPACITY){ // 缓存容量足够,直接添加,并将新加入元素标记值置为初值0 cache.put(key, value); flag.put(key, 0); increment(key); return; } if (cache.containsKey(key)){ // 缓存容量不够,但是当前添加的key已在缓存中存在,直接更新即可 cache.put(key, value); flag.put(key, 0); increment(key); return; } // 缓存容量不够且key不在缓存中,使用 LRU 策略淘汰缓存中的数据 int i = getDieOutKey(); cache.remove(i); cache.put(key, value); flag.put(key, 0); increment(key); } /** * 获取淘汰元素的索引 */ private int getDieOutKey() { int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int key = 0; for (Integer i : flag.keySet()) { if (flag.get(i)>max){ max = flag.get(i); key = i; } } flag.remove(key); return key; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),每次put和get都需要调用increment方法,increment方法需要遍历整个map,getDieOutKey方法也需要遍历整个map,时间复杂度也是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),但两者没有嵌套,所以总的时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为缓存的大小
代码优化:使用队列代替Map标记(时间优化)
上面我们是利用Map集合对存入缓存中的元素进行一个标记,每次往缓存中存入和获取,都需要遍历一遍 flag ,并且删除时也需要遍历一遍 flag,这就导致虽然看着时间复杂度是 ( n ) (n) (n),但是对于频繁的操作耗时是非常多的。
上面的map标记法,我们可以知道最大耗时在于定位 flag 中最大的value,为了解决定位问题,我们可以采用队列,而不是map,队列具有先进先出的特点(队尾进,对头出),这就意味着我们可以将最旧的元素放到对头,最新的元素放到队尾。
class LRUCache { // 缓存 private Map<Integer, Integer> map; // 用于LRU淘汰 private Queue<Integer> queue; // 最大容量 private int MAX_CAPACITY; public LRUCache(int capacity) { MAX_CAPACITY = capacity; map = new HashMap<>(capacity); queue = new LinkedList<>(); } public int get(int key) { if (map.containsKey(key)){ queue.remove(key); queue.offer(key); return map.get(key); } return -1; } public void put(int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)){ // 缓存中存在该key,直接更新 queue.remove(key); queue.offer(key); map.put(key, value); return; } if (map.size() < MAX_CAPACITY){ // 缓存不存在该key,但当前缓存容量足够,直接添加 queue.offer(key); map.put(key, value); return; } // 缓存容量不足,移除最先进入队列的元素 int first = queue.poll(); queue.add(key); map.remove(first); map.put(key, value); } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),
queue.remove()方法需要遍历链表,时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) - 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
n为缓存中最大能存储元素的个数
PS:显然这段代码比上上面那段代码就要好的多了,但是提交只能够击败5%的 Java选手,这说明还有更好的方法
-
解法二:利用LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap底层是使用一个 Map+双向链表,LinkedHashMap有一个最大容量
class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer>{ // 最大容量 private int capacity; public LRUCache(int capacity) { // 调用构造方法,第三个参数设置为true时,当LinkedHashMap达到最大容量时 // 底层回采用LRU策略,移除最旧的元素 super(capacity, 0.75F, true); this.capacity = capacity; } public int get(int key) { return super.getOrDefault(key, -1); } public void put(int key, int value) { super.put(key, value); } /** * 设置淘汰时机,当超过最大容量时按照LRU策略淘汰最旧的值 */ @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) { return size() > capacity; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为缓存中元素的最大个数
参照LinkedHashMap源码手写一个简易版的LinkedHashMap:
前面我们使用队列进行移除操作,时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),因为队列底层是采用了单链表,单链表删除中间节点需要先遍历链表定位到要删除的节点的前驱节点,而现在我们使用一个双链表数据结构,我们直接可以通过 前驱指针pre 定位到要删除的节点前驱节点,进行删除操作,这就大大提高了删除的效率,从而提高了时间,但是提高了额外的内存开销(典型的空间换时间)
class LRUCache { /** * 定义一个双链表 */ private class DLinkedList { int key; int value; // 前驱指针,用于维护当前节点与前驱节点的关系 DLinkedList pre; // 后继指针,用于维护当前节点与后继节点的关系 DLinkedList next; public DLinkedList() {} public DLinkedList(int key, int value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; } } /** * 缓存最大容量 */ private int capacity; /** * 缓存中的元素的个数(空间换时间) */ private int size; /** * 双链表的头节点指针 */ DLinkedList head; /** * 双链表的尾节点指针 */ DLinkedList tail; /** * 缓存 */ private Map<Integer, DLinkedList> cache = new HashMap<>(); public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; this.size = 0; this.head = new DLinkedList(); this.tail = new DLinkedList(); this.head.next = this.tail; this.tail.pre = this.head; } /** * 从缓存中取值 */ public int get(int key) { DLinkedList node = cache.get(key); if (node == null) { // 缓存未命中,直接返回-1 return -1; } // 缓存命中,则更新双链表(将命中节点更新为双链表的头节点) moveToHead(node); return node.value; } /** * 往缓存中存值 */ public void put(int key, int value) { DLinkedList node = cache.get(key); if (node != null) { // 缓存命中,则更新双链表并直接返回命中的值 node.value = value; moveToHead(node); return; } // 缓存未命中,需要判断当前缓存的容量是否充足 if (size == capacity) { // 缓存容量已满,需要采用LRU策略移除最旧的值(也就是双链表的尾节点) DLinkedList tailNode = remove(tail.pre); cache.remove(tailNode.key); size--; } // 将新增的节点添加到链表头部,并存入缓存 DLinkedList newNode = new DLinkedList(key, value); add(newNode); cache.put(key, newNode); size++; } /** * 将节点更新为双链表的头节点 */ public void moveToHead(DLinkedList node) { // 先移除,后添加,即可将节点更新为头节点 remove(node); add(node); } /** * 移除节点(并返回被移除的节点) */ private DLinkedList remove(DLinkedList node) { if (node.next == tail) { // 要移除的节点是尾节点 node.pre.next = tail; tail.pre = node.pre; } else { // 要移除的节点是中间节点 node.pre.next = node.next; node.next.pre = node.pre; } return node; } /** * 添加节点(从双链表的头部添加) */ private void add(DLinkedList node) { node.pre = head; node.next = head.next; head.next.pre = node; head.next = node; } }复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
其中 n n n 为缓存中元素的最大个数