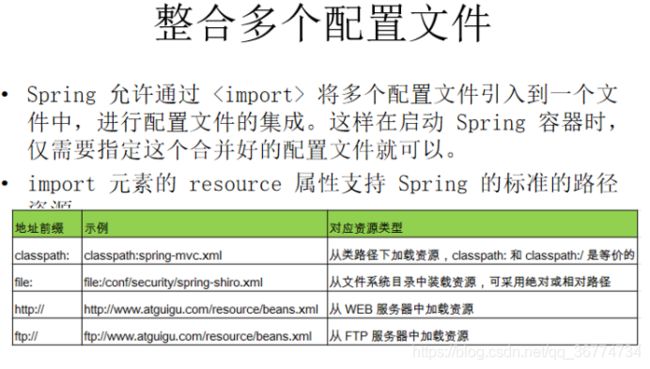
Spring 是什么
Spring 是什么
Spring 是一个开源框架.
Spring 为简化企业级应用开发而生. 使用 Spring 可以使简单的 JavaBean 实现以前只有 EJB 才能实现的功能.
Spring 是一个 IOC(DI) 和 AOP 容器框架
具体描述 Spring:
轻量级:Spring 是非侵入性的 - 基于 Spring 开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于 Spring 的 API
依赖注入(DI --- dependency injection、IOC)
面向切面编程(AOP --- aspect oriented programming)
容器: Spring 是一个容器, 因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
框架: Spring 实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用. 在 Spring 中可以使用 XML 和 Java 注解组合这些对象
一站式:在 IOC 和 AOP 的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库 (实际上 Spring 自身也提供了展现层的 SpringMVC 和 持久层的 Spring JDBC)
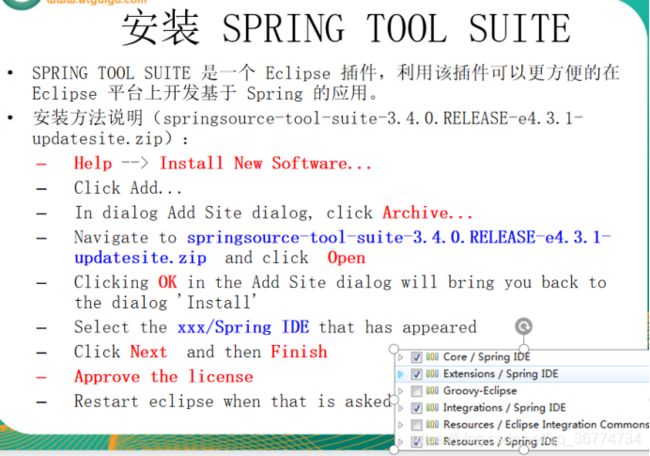
搭建 Spring 开发环境
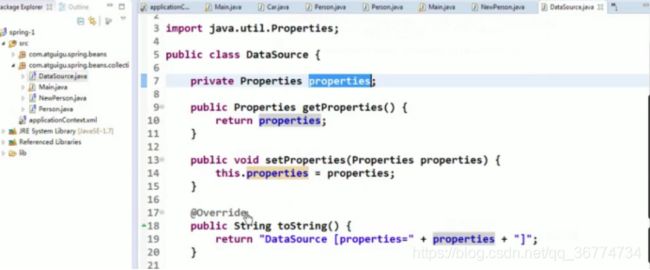
创建对象,为属性赋值可以交给spring完成。
建立 Spring 项目
创建User.java 类
Src/applicationContext.xml
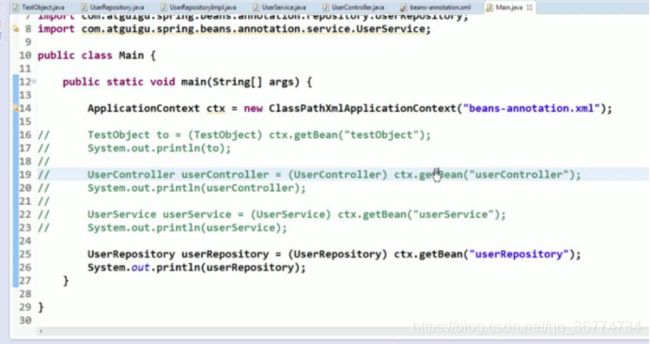
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建 Spring 的 IOC 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2. 从 IOC 容器中获取 bean 的实例
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld3");
//根据类型来获取 bean 的实例: 要求在 IOC 容器中只有一个与之类型匹配的 bean, 若有多个则会抛出异常.
//一般情况下, 该方法可用, 因为一般情况下, 在一个 IOC 容器中一个类型对应的 bean 也只有一个.
// HelloWorld helloWorld1 = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
//3. 使用 bean
helloWorld.hello();
}
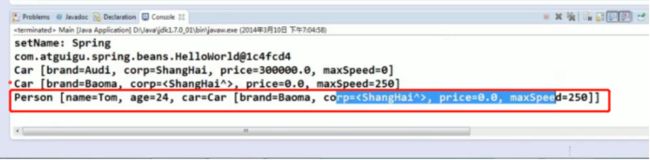
}在 Spring 的 IOC 容器里配置 Bean
Src/applicationContext.xml
Main.java
//1. 创建 Spring 的 IOC 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//2. 从 IOC 容器中获取 bean 的实例
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) ctx.getBean("helloWorld3");
//根据类型来获取 bean 的实例: 要求在 IOC 容器中只有一个与之类型匹配的 bean, 若有多个则会抛出异常.
//一般情况下, 该方法可用, 因为一般情况下, 在一个 IOC 容器中一个类型对应的 bean 也只有一个.
// HelloWorld helloWorld1 = ctx.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
//3. 使用 bean
helloWorld.hello();Spring 支持 3 种依赖注入的方式
属性注入
构造器注入
工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
属性注入
属性注入即通过 setter 方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象
属性注入使用
属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式
构造方法注入
通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了 Bean 实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入在
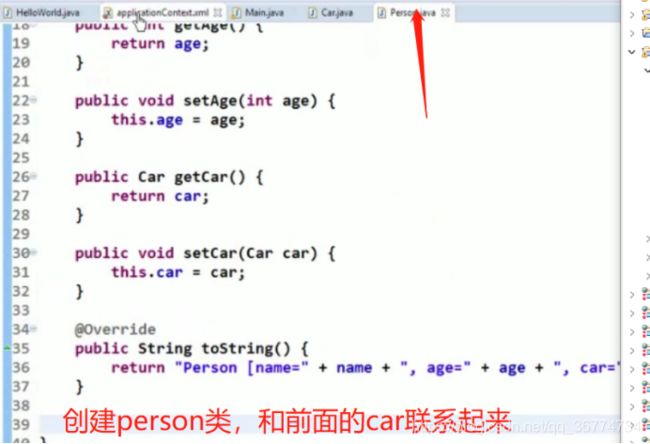
创建car.java
package com.atguigu.spring.helloworld;
public class Car {
private String company;
private String brand;
private int maxSpeed;
private float price;
public Car(String company, String brand, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public Car(String company, String brand, int maxSpeed, float price) {
super();
this.company = company;
this.brand = brand;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [company=" + company + ", brand=" + brand + ", maxSpeed="
+ maxSpeed + ", price=" + price + "]";
}
}
按索引匹配入参
按类型匹配入参
字面值
字面值:可用字符串表示的值,可以通过
基本数据类型及其封装类、String 等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式
若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用 把字面值包裹起来。
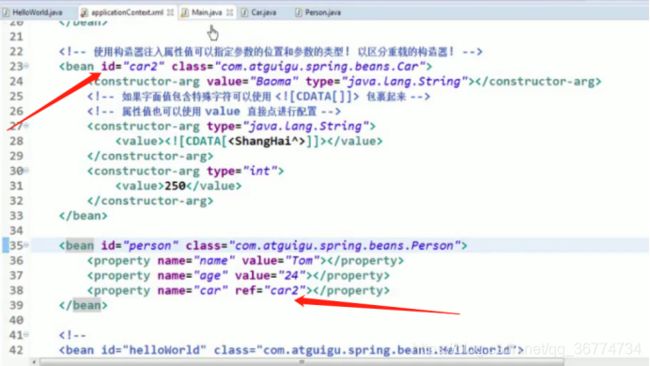
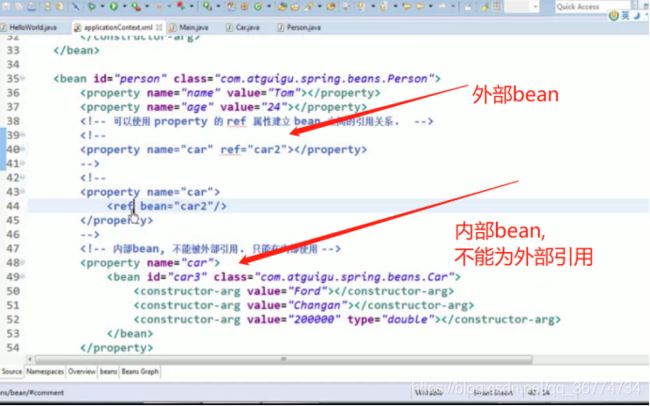
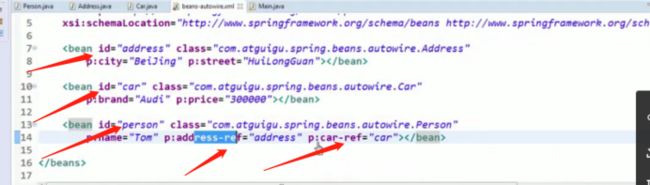
引用其它 Bean
组成应用程序的 Bean 经常需要相互协作以完成应用程序的功能. 要使 Bean 能够相互访问, 就必须在 Bean 配置文件中指定对 Bean 的引用
在 Bean 的配置文件中, 可以通过 元素或 ref 属性为 Bean 的属性或构造器参数指定对 Bean 的引用.
也可以在属性或构造器里包含 Bean 的声明, 这样的 Bean 称为内部 Bean
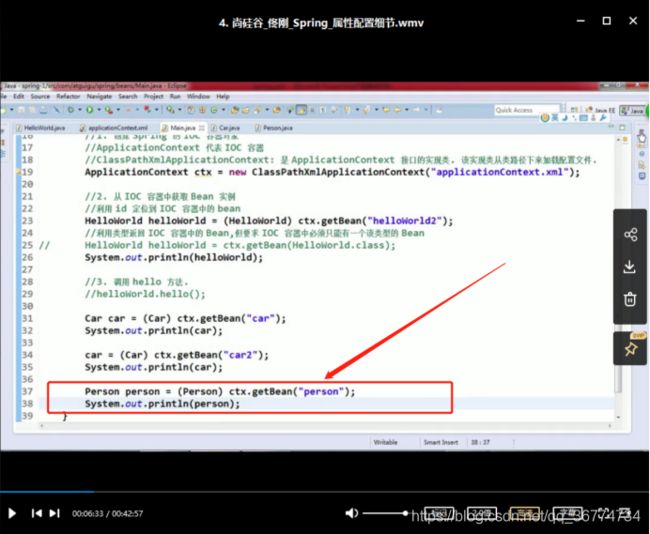
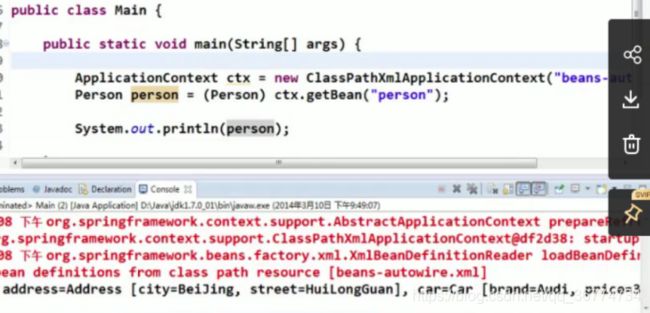
Src/applicationContext.xml
在main.java类里面测试
结果
内部 Bean
当 Bean 实例仅仅给一个特定的属性使用时, 可以将其声明为内部 Bean. 内部 Bean 声明直接包含在
内部 Bean 不能使用在任何其他地方
第二种
设置级联属性
集合属性
]]>
集合属性
在 Spring中可以通过一组内置的 xml 标签(例如: ,
配置 java.util.List 类型的属性, 需要指定 标签, 在标签里包含一些元素. 这些标签可以通过
数组的定义和 List 一样, 都使用
配置 java.util.Set 需要使用
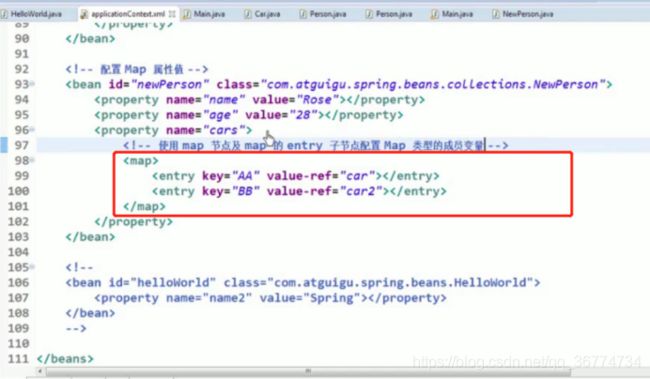
Java.util.Map 通过
必须在
因为键和值的类型没有限制, 所以可以自由地为它们指定
可以将 Map 的键和值作为
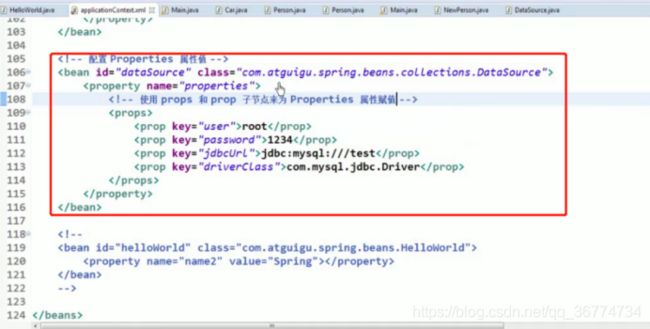
使用
使用props和prop子节点来为properties属性赋值
Main.java测试
使用 utility scheme 定义集合
使用基本的集合标签定义集合时, 不能将集合作为独立的 Bean 定义, 导致其他 Bean 无法引用该集合, 所以无法在不同 Bean 之间共享集合.
可以使用 util schema 里的集合标签定义独立的集合 Bean. 需要注意的是, 必须在
使用 p 命名空间
为了简化 XML 文件的配置,越来越多的 XML 文件采用属性而非子元素配置信息。
Spring 从 2.5 版本开始引入了一个新的 p 命名空间,可以通过
使用 p 命名空间后,基于 XML 的配置方式将进一步简化
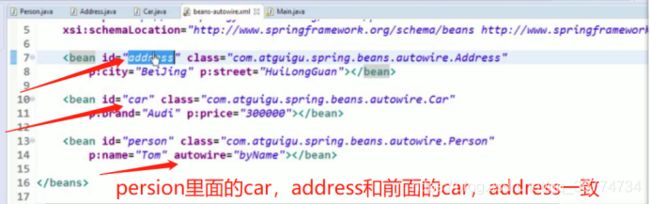
XML 配置里的 Bean 自动装配
Spring IOC 容器可以自动装配 Bean. 需要做的仅仅是在
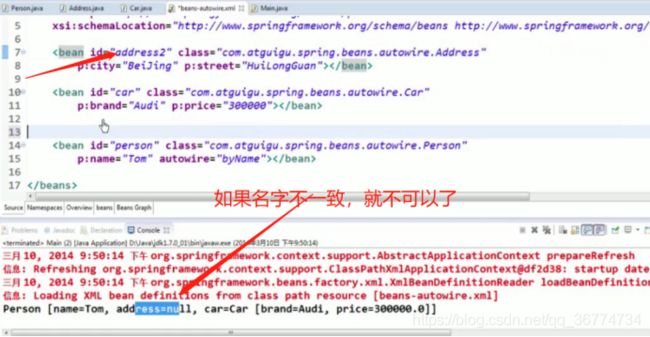
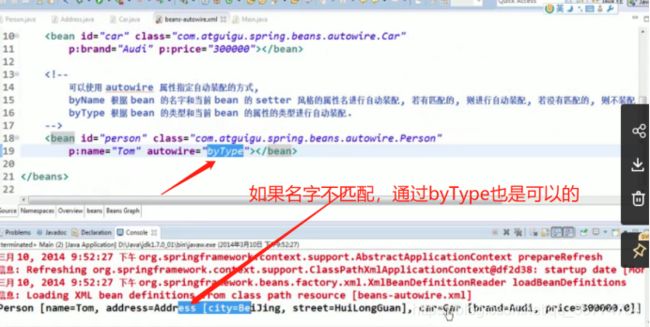
byType(根据类型自动装配): 若 IOC 容器中有多个与目标 Bean 类型一致的 Bean. 在这种情况下, Spring 将无法判定哪个 Bean 最合适该属性, 所以不能执行自动装配.
byName(根据名称自动装配): 必须将目标 Bean 的名称和属性名设置的完全相同.
constructor(通过构造器自动装配): 当 Bean 中存在多个构造器时, 此种自动装配方式将会很复杂. 不推荐使用
若ioc容器中有1个以上的类型匹配的bean,则抛弃异常
XML 配置里的 Bean 自动装配的缺点
在 Bean 配置文件里设置 autowire 属性进行自动装配将会装配 Bean 的所有属性. 然而, 若只希望装配个别属性时, autowire 属性就不够灵活了.
autowire 属性要么根据类型自动装配, 要么根据名称自动装配, 不能两者兼而有之.
一般情况下,在实际的项目中很少使用自动装配功能,因为和自动装配功能所带来的好处比起来,明确清晰的配置文档更有说服力一些
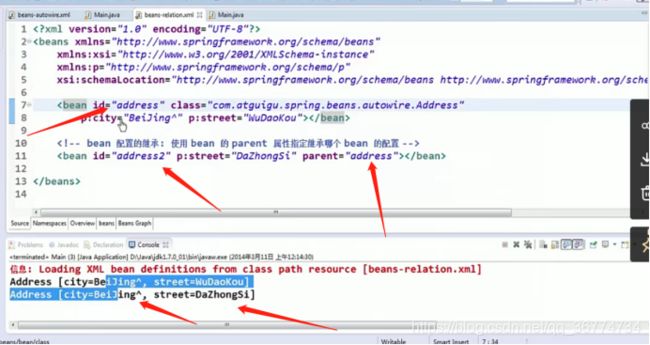
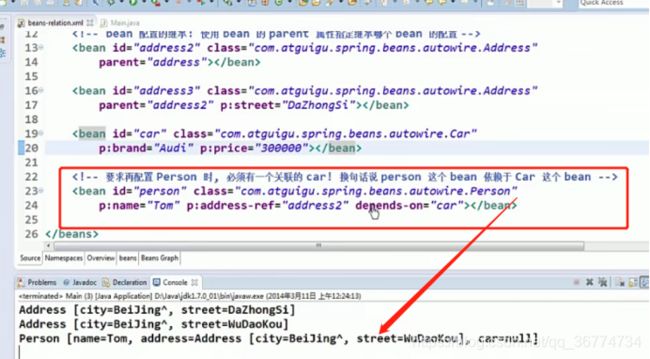
继承 Bean 配置
Spring 允许继承 bean 的配置, 被继承的 bean 称为父 bean. 继承这个父 Bean 的 Bean 称为子 Bean
子 Bean 从父 Bean 中继承配置, 包括 Bean 的属性配置
子 Bean 也可以覆盖从父 Bean 继承过来的配置
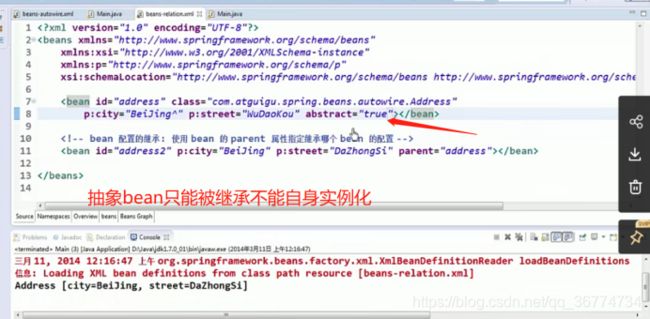
父 Bean 可以作为配置模板, 也可以作为 Bean 实例. 若只想把父 Bean 作为模板, 可以设置
并不是
也可以忽略父 Bean 的 class 属性, 让子 Bean 指定自己的类, 而共享相同的属性配置. 但此时 abstract 必须设为 true
依赖 Bean 配置
Spring 允许用户通过 depends-on 属性设定 Bean 前置依赖的Bean,前置依赖的 Bean 会在本 Bean 实例化之前创建好
如果前置依赖于多个 Bean,则可以通过逗号,空格或的方式配置 Bean 的名称
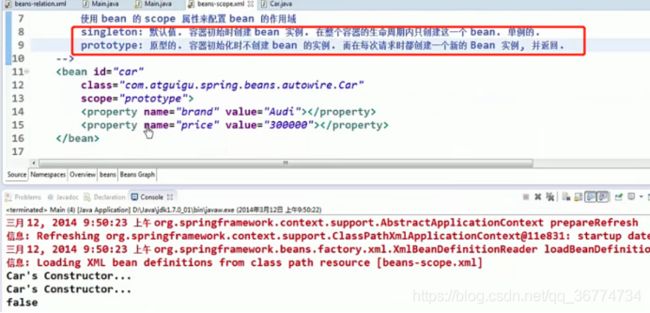
Bean 的作用域
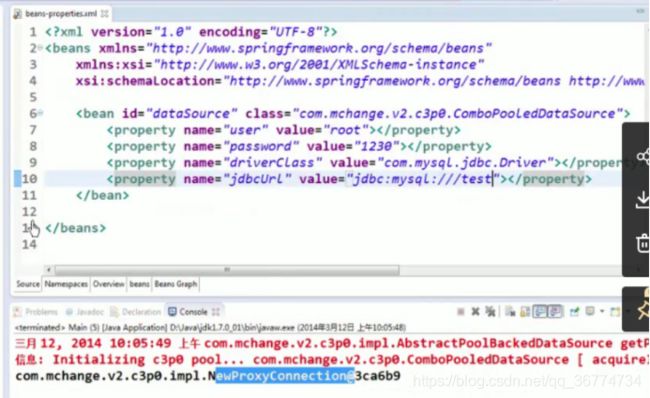
使用外部属性文件
在配置文件里配置 Bean 时, 有时需要在 Bean 的配置里混入系统部署的细节信息(例如: 文件路径, 数据源配置信息等). 而这些部署细节实际上需要和 Bean 配置相分离
Spring 提供了一个 PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 的 BeanFactory 后置处理器, 这个处理器允许用户将 Bean 配置的部分内容外移到属性文件中. 可以在 Bean 配置文件里使用形式为 ${var} 的变量, PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 从属性文件里加载属性, 并使用这些属性来替换变量.
Spring 还允许在属性文件中使用 ${propName},以实现属性之间的相互引用。
抽离出来
db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=1230
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///test
jdbc.initPoolSize=5
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10Src/eans-properties.xml
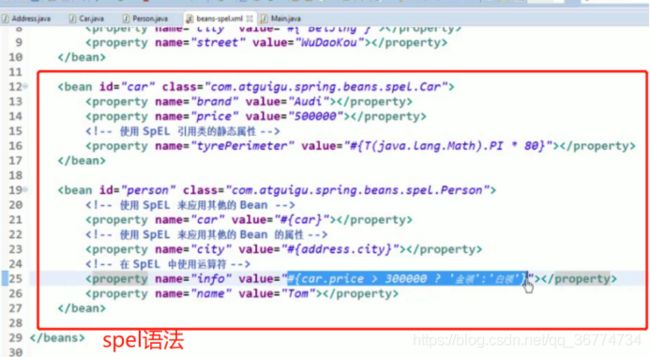
Spring表达式语言:SpEL
Spring 表达式语言(简称SpEL):是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
语法类似于 EL:SpEL 使用 #{…} 作为定界符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是 SpEL
SpEL 为 bean 的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利
通过 SpEL 可以实现:
通过 bean 的 id 对 bean 进行引用
调用方法以及引用对象中的属性
计算表达式的值
正则表达式的匹配
SpEL:字面量
字面量的表示:
整数:
小数:
科学计数法:
String可以使用单引号或者双引号作为字符串的定界符号:
Boolean:
SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法(1)
字面值
<bean id="girl" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User">
<property name="userName" value="周迅">property>
bean>
<bean id="boy" class="com.atguigu.spring.helloworld.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="userName" value="高胜远">property>
<property name="wifeName" value="#{girl.userName}">property>
bean>
IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期方法
Spring IOC 容器可以管理 Bean 的生命周期, Spring 允许在 Bean 生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务.
Spring IOC 容器对 Bean 的生命周期进行管理的过程:
通过构造器或工厂方法创建 Bean 实例
为 Bean 的属性设置值和对其他 Bean 的引用
调用 Bean 的初始化方法
Bean 可以使用了
当容器关闭时, 调用 Bean 的销毁方法
在 Bean 的声明里设置 init-method 和 destroy-method 属性, 为 Bean 指定初始化和销毁方法.
创建 Bean 后置处理器
添加 Bean 后置处理器后 Bean 的生命周期
Spring IOC 容器对 Bean 的生命周期进行管理的过程:
通过构造器或工厂方法创建 Bean 实例
为 Bean 的属性设置值和对其他 Bean 的引用
将 Bean 实例传递给 Bean 后置处理器的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
调用 Bean 的初始化方法
将 Bean 实例传递给 Bean 后置处理器的 postProcessAfterInitialization方法
Bean 可以使用了
当容器关闭时, 调用 Bean 的销毁方法
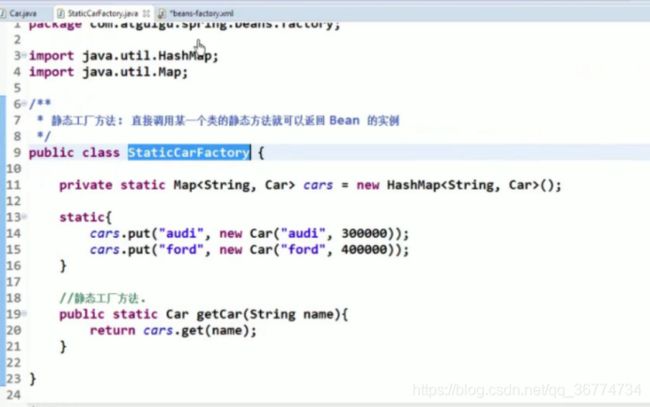
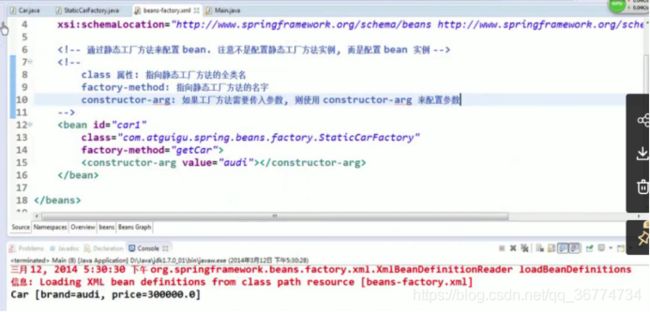
通过调用静态工厂方法创建 Bean
调用静态工厂方法创建 Bean是将对象创建的过程封装到静态方法中. 当客户端需要对象时, 只需要简单地调用静态方法, 而不同关心创建对象的细节.
要声明通过静态方法创建的 Bean, 需要在 Bean 的 class 属性里指定拥有该工厂的方法的类, 同时在 factory-method 属性里指定工厂方法的名称. 最后, 使用
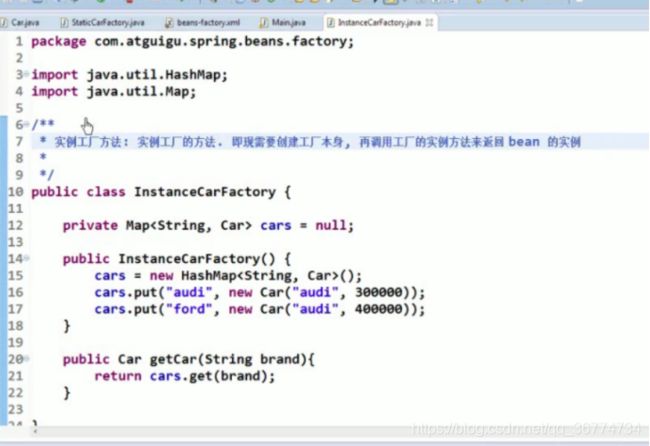
通过调用实例工厂方法创建 Bean
实例工厂方法: 将对象的创建过程封装到另外一个对象实例的方法里. 当客户端需要请求对象时, 只需要简单的调用该实例方法而不需要关心对象的创建细节.
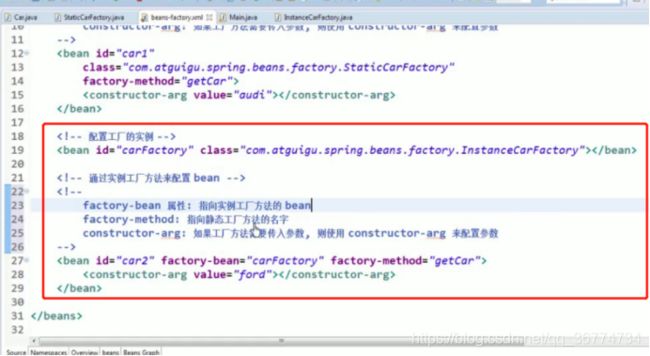
要声明通过实例工厂方法创建的 Bean
在 bean 的 factory-bean 属性里指定拥有该工厂方法的 Bean
在 factory-method 属性里指定该工厂方法的名称
使用 construtor-arg 元素为工厂方法传递方法参数
实例工厂的方法
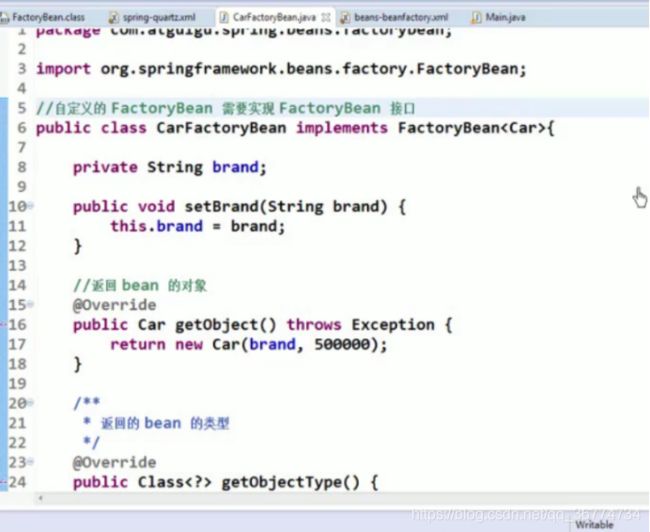
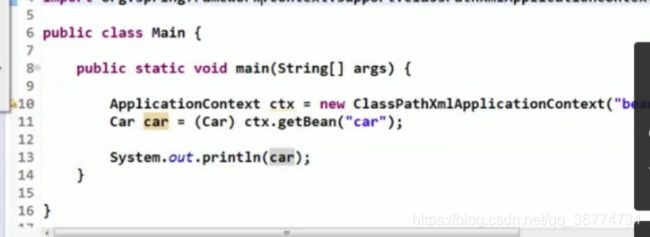
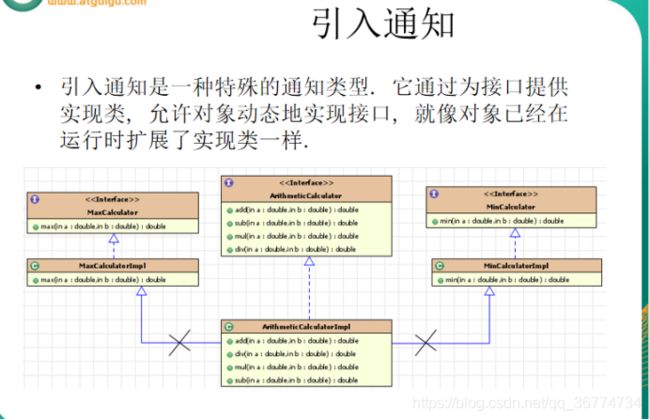
实现 FactoryBean 接口在 Spring IOC 容器中配置 Bean
基于注解的方式
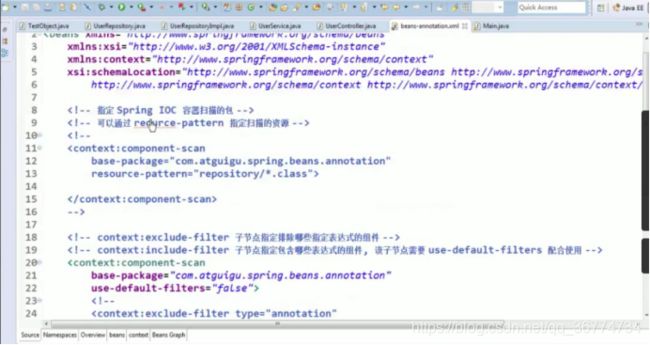
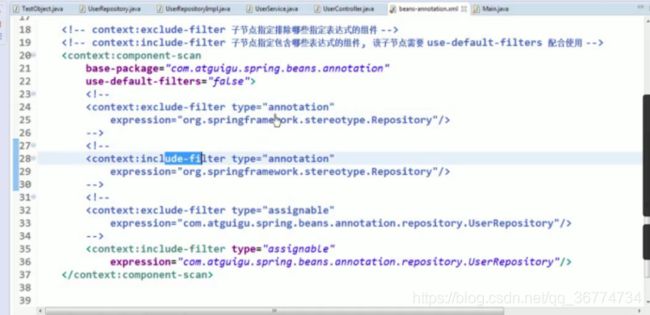
在 classpath 中扫描组件
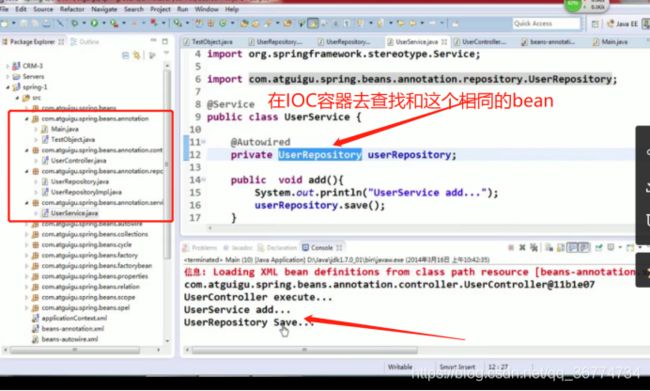
组件扫描(component scanning): Spring 能够从 classpath 下自动扫描, 侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件.
特定组件包括:
@Component: 基本注解, 标识了一个受 Spring 管理的组件
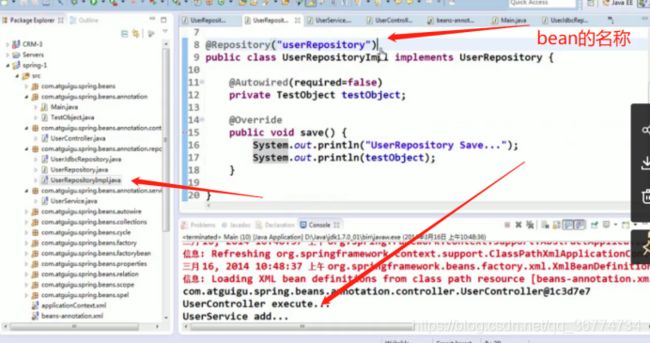
@Respository: 标识持久层组件
@Service: 标识服务层(业务层)组件
@Controller: 标识表现层组件
对于扫描到的组件, Spring 有默认的命名策略: 使用非限定类名, 第一个字母小写. 也可以在注解中通过 value 属性值标识组件的名称
![]()
组件装配
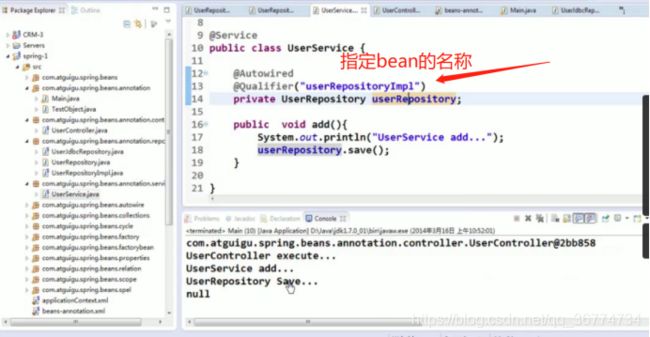
使用 @Resource 或 @Inject
自动装配 Bean
Spring 还支持 @Resource 和 @Inject 注解,这两个注解和 @Autowired 注解的功用类似
@Resource 注解要求提供一个 Bean 名称的属性,若该属性为空,则自动采用标注处的变量或方法名作为 Bean 的名称
@Inject 和 @Autowired 注解一样也是按类型匹配注入的 Bean, 但没有 reqired 属性
建议使用 @Autowired 注解
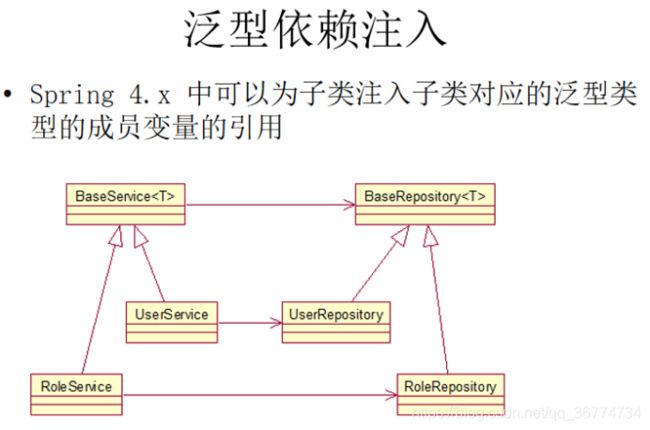
泛型依赖注入
Spring AOP 基于注解的方式
目录
applicationContext.xml
ArithmeticCalculator.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop;
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
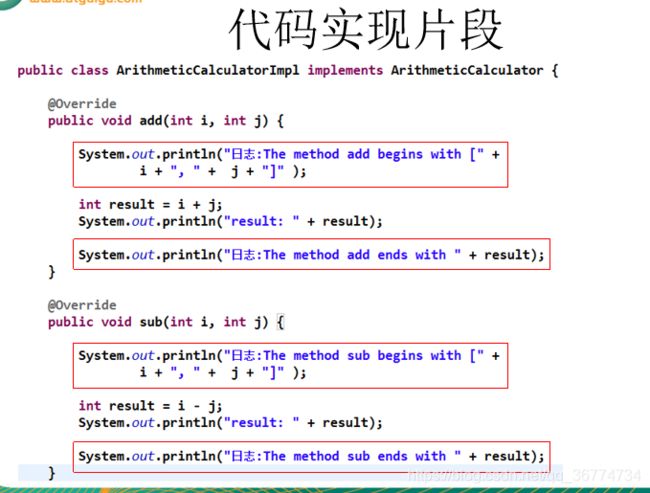
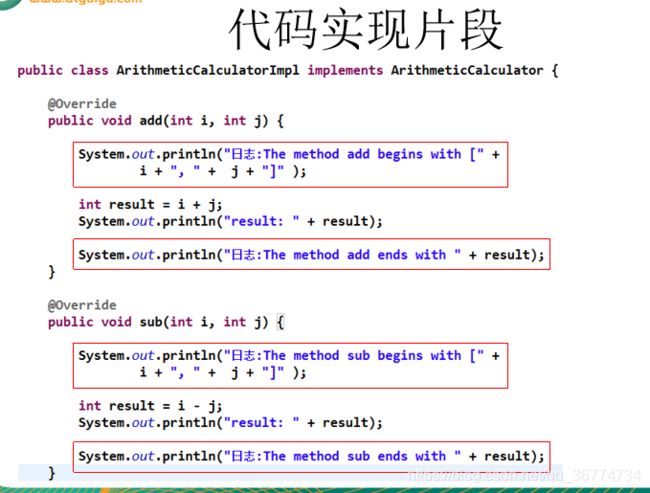
}ArithmeticCalculatorImpl.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("arithmeticCalculator")
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}
LoggingAspect.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 可以使用 @Order 注解指定切面的优先级, 值越小优先级越高
*/
@Order(2)
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
/**
* 定义一个方法, 用于声明切入点表达式. 一般地, 该方法中再不需要添入其他的代码.
* 使用 @Pointcut 来声明切入点表达式.
* 后面的其他通知直接使用方法名来引用当前的切入点表达式.
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void declareJointPointExpression(){}
/**
* 在 com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator 接口的每一个实现类的每一个方法开始之前执行一段代码
*/
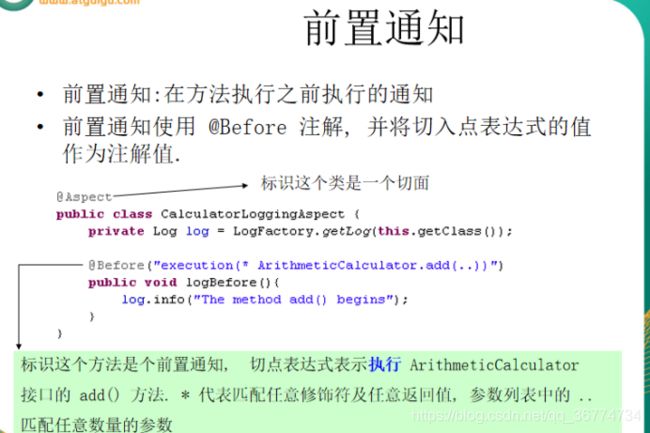
@Before("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args));
}
/**
* 在方法执行之后执行的代码. 无论该方法是否出现异常
*/
@After("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends");
}
/**
* 在方法法正常结束受执行的代码
* 返回通知是可以访问到方法的返回值的!
*/
@AfterReturning(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
returning="result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result);
}
/**
* 在目标方法出现异常时会执行的代码.
* 可以访问到异常对象; 且可以指定在出现特定异常时在执行通知代码
*/
@AfterThrowing(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
throwing="e")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs excetion:" + e);
}
/**
* 环绕通知需要携带 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数.
* 环绕通知类似于动态代理的全过程: ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数可以决定是否执行目标方法.
* 且环绕通知必须有返回值, 返回值即为目标方法的返回值
*/
/**
@Around("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd){
Object result = null;
String methodName = pjd.getSignature().getName();
try {
//前置通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(pjd.getArgs()));
//执行目标方法
result = pjd.proceed();
//返回通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs exception:" + e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//后置通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends");
return result;
} */
}Main.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
System.out.println(arithmeticCalculator.getClass().getName());
int result = arithmeticCalculator.add(1, 2);
System.out.println("result:" + result);
result = arithmeticCalculator.div(1000, 10);
System.out.println("result:" + result);
}
}VlidationAspect.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Order(1)
@Aspect
@Component
public class VlidationAspect {
@Before("com.atguigu.spring.aop.LoggingAspect.declareJointPointExpression()")
public void validateArgs(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("-->validate:" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}解析:
Aop之前
代码混乱:越来越多的非业务需求(日志和验证等)加入后, 原有的业务方法急剧膨胀. 每个方法在处理核心逻辑的同时还必须兼顾其他多个关注点.
代码分散: 以日志需求为例, 只是为了满足这个单一需求, 就不得不在多个模块(方法)里多次重复相同的日志代码. 如果日志需求发生变化, 必须修改所有模块.
AOP 简介
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程): 是一种新的方法论, 是对传统 OOP(Object-Oriented Programming, 面向对象编程) 的补充.
AOP 的主要编程对象是切面(aspect), 而切面模块化横切关注点.
在应用 AOP 编程时, 仍然需要定义公共功能, 但可以明确的定义这个功能在哪里, 以什么方式应用, 并且不必修改受影响的类. 这样一来横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里.
AOP 的好处:
每个事物逻辑位于一个位置, 代码不分散, 便于维护和升级
业务模块更简洁, 只包含核心业务代码.
AOP 术语
切面(Aspect): 横切关注点(跨越应用程序多个模块的功能)被模块化的特殊对象
通知(Advice): 切面必须要完成的工作
目标(Target): 被通知的对象
代理(Proxy): 向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象
连接点(Joinpoint):程序执行的某个特定位置:如类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法抛出异常后等。连接点由两个信息确定:方法表示的程序执行点;相对点表示的方位。例如 ArithmethicCalculator#add() 方法执行前的连接点,执行点为 ArithmethicCalculator#add(); 方位为该方法执行前的位置
切点(pointcut):每个类都拥有多个连接点:例如 ArithmethicCalculator 的所有方法实际上都是连接点,即连接点是程序类中客观存在的事务。AOP 通过切点定位到特定的连接点。类比:连接点相当于数据库中的记录,切点相当于查询条件。切点和连接点不是一对一的关系,一个切点匹配多个连接点,切点通过 org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
Spring AOP
AspectJ:Java 社区里最完整最流行的 AOP 框架.
在 Spring2.0 以上版本中, 可以使用基于 AspectJ 注解或基于 XML 配置的 AOP
在 Spring 中启用 AspectJ 注解支持
要在 Spring 应用中使用 AspectJ 注解, 必须在 classpath 下包含 AspectJ 类库: aopalliance.jar、aspectj.weaver.jar 和 spring-aspects.jar
将 aop Schema 添加到
要在 Spring IOC 容器中启用 AspectJ 注解支持, 只要在 Bean 配置文件中定义一个空的 XML 元素
当 Spring IOC 容器侦测到 Bean 配置文件中的
用 AspectJ 注解声明切面
要在 Spring 中声明 AspectJ 切面, 只需要在 IOC 容器中将切面声明为 Bean 实例. 当在 Spring IOC 容器中初始化 AspectJ 切面之后, Spring IOC 容器就会为那些与 AspectJ 切面相匹配的 Bean 创建代理.
在 AspectJ 注解中, 切面只是一个带有 @Aspect 注解的 Java 类.
通知是标注有某种注解的简单的 Java 方法.
AspectJ 支持 5 种类型的通知注解:
@Before: 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
@After: 后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行
@AfterRunning: 返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
@AfterThrowing: 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后
@Around: 环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
利用方法签名编写 AspectJ 切入点表达式
最典型的切入点表达式时根据方法的签名来匹配各种方法:
execution * com.atguigu.spring.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..): 匹配 ArithmeticCalculator 中声明的所有方法,第一个 * 代表任意修饰符及任意返回值. 第二个 * 代表任意方法. .. 匹配任意数量的参数. 若目标类与接口与该切面在同一个包中, 可以省略包名.
execution public * ArithmeticCalculator.*(..): 匹配 ArithmeticCalculator 接口的所有公有方法.
execution public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(..): 匹配 ArithmeticCalculator 中返回 double 类型数值的方法
execution public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, ..): 匹配第一个参数为 double 类型的方法, .. 匹配任意数量任意类型的参数
execution public double ArithmeticCalculator.*(double, double): 匹配参数类型为 double, double 类型的方法.
环绕通知
环绕通知是所有通知类型中功能最为强大的, 能够全面地控制连接点. 甚至可以控制是否执行连接点.
对于环绕通知来说, 连接点的参数类型必须是 ProceedingJoinPoint . 它是 JoinPoint 的子接口, 允许控制何时执行, 是否执行连接点.
在环绕通知中需要明确调用 ProceedingJoinPoint 的 proceed() 方法来执行被代理的方法. 如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了, 但目标方法没有被执行.
注意: 环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果, 即调用 joinPoint.proceed(); 的返回值, 否则会出现空指针异常
重用切入点定义
在编写 AspectJ 切面时, 可以直接在通知注解中书写切入点表达式. 但同一个切点表达式可能会在多个通知中重复出现.
在 AspectJ 切面中, 可以通过 @Pointcut 注解将一个切入点声明成简单的方法. 切入点的方法体通常是空的, 因为将切入点定义与应用程序逻辑混在一起是不合理的.
切入点方法的访问控制符同时也控制着这个切入点的可见性. 如果切入点要在多个切面中共用, 最好将它们集中在一个公共的类中. 在这种情况下, 它们必须被声明为 public. 在引入这个切入点时, 必须将类名也包括在内. 如果类没有与这个切面放在同一个包中, 还必须包含包名.
其他通知可以通过方法名称引入该切入点.
Spring AOP 基于配置文件xml的方式
applicationContext-xml.xml
ArithmeticCalculator.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop.xml;
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}ArithmeticCalculatorImpl.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop.xml;
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
return result;
}
}LoggingAspect.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop.xml;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
public class LoggingAspect {
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args));
}
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends");
}
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result);
}
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs excetion:" + e);
}
@Around("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd){
Object result = null;
String methodName = pjd.getSignature().getName();
try {
//前置通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(pjd.getArgs()));
//执行目标方法
result = pjd.proceed();
//返回通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
//异常通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs exception:" + e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//后置通知
System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends");
return result;
}
}Main.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop.xml;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-xml.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
System.out.println(arithmeticCalculator.getClass().getName());
int result = arithmeticCalculator.add(1, 2);
System.out.println("result:" + result);
result = arithmeticCalculator.div(1000, 10);
System.out.println("result:" + result);
}
}
VlidationAspect.java
package com.atguigu.spring.aop.xml;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
public class VlidationAspect {
public void validateArgs(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("-->validate:" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}解析
用基于 XML 的配置声明切面
除了使用 AspectJ 注解声明切面, Spring 也支持在 Bean 配置文件中声明切面. 这种声明是通过 aop schema 中的 XML 元素完成的.
正常情况下, 基于注解的声明要优先于基于 XML 的声明. 通过 AspectJ 注解, 切面可以与 AspectJ 兼容, 而基于 XML 的配置则是 Spring 专有的. 由于 AspectJ 得到越来越多的 AOP 框架支持, 所以以注解风格编写的切面将会有更多重用的机会.
除了使用 AspectJ 注解声明切面, Spring 也支持在 Bean 配置文件中声明切面. 这种声明是通过 aop schema 中的 XML 元素完成的.
正常情况下, 基于注解的声明要优先于基于 XML 的声明. 通过 AspectJ 注解, 切面可以与 AspectJ 兼容, 而基于 XML 的配置则是 Spring 专有的. 由于 AspectJ 得到越来越多的 AOP 框架支持, 所以以注解风格编写的切面将会有更多重用的机会.
当使用 XML 声明切面时, 需要在
在 Bean 配置文件中, 所有的 Spring AOP 配置都必须定义在
切面 Bean 必须有一个标示符, 供
基于 XML ---- 声明切入点
切入点使用
切入点必须定义在
定义在
定义在
基于 XML 的 AOP 配置不允许在切入点表达式中用名称引用其他切入点.
基于 XML ---- 声明通知
在 aop Schema 中, 每种通知类型都对应一个特定的 XML 元素.
通知元素需要使用
Spring 对 JDBC 的支持
案例
db.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=1230
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///spring
jdbc.initPoolSize=5
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10applicationContext.xml
Department.java
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Department [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
DepartmentDao.java
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 不推荐使用 JdbcDaoSupport, 而推荐直接使用 JdbcTempate 作为 Dao 类的成员变量
*/
@Repository
public class DepartmentDao extends JdbcDaoSupport{
@Autowired
public void setDataSource2(DataSource dataSource){
setDataSource(dataSource);
}
public Department get(Integer id){
String sql = "SELECT id, dept_name name FROM departments WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Department.class);
return getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id);
}
} Employee.java
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer dpetId;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public Integer getDpetId() {
return dpetId;
}
public void setDpetId(Integer dpetId) {
this.dpetId = dpetId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email="
+ email + ", dpetId=" + dpetId + "]";
}
}EmployeeDao.java
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Employee get(Integer id){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id);
return employee;
}
} JDBCTest.java
package com.atguigu.spring.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
public class JDBCTest {
private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) ctx.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
employeeDao = ctx.getBean(EmployeeDao.class);
departmentDao = ctx.getBean(DepartmentDao.class);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate = ctx.getBean(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.class);
}
/**
* 使用具名参数时, 可以使用 update(String sql, SqlParameterSource paramSource) 方法进行更新操作
* 1. SQL 语句中的参数名和类的属性一致!
* 2. 使用 SqlParameterSource 的 BeanPropertySqlParameterSource 实现类作为参数.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate2(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) "
+ "VALUES(:lastName,:email,:dpetId)";
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("XYZ");
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setDpetId(3);
SqlParameterSource paramSource = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramSource);
}
/**
* 可以为参数起名字.
* 1. 好处: 若有多个参数, 则不用再去对应位置, 直接对应参数名, 便于维护
* 2. 缺点: 较为麻烦.
*/
@Test
public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) VALUES(:ln,:email,:deptid)";
Map paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("ln", "FF");
paramMap.put("email", "[email protected]");
paramMap.put("deptid", 2);
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramMap);
}
@Test
public void testDepartmentDao(){
System.out.println(departmentDao.get(1));
}
@Test
public void testEmployeeDao(){
System.out.println(employeeDao.get(1));
}
/**
* 获取单个列的值, 或做统计查询
* 使用 queryForObject(String sql, Class requiredType)
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForObject2(){
String sql = "SELECT count(id) FROM employees";
long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
/**
* 查到实体类的集合
* 注意调用的不是 queryForList 方法
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForList(){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email FROM employees WHERE id > ?";
RowMapper rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
List employees = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowMapper,5);
System.out.println(employees);
}
/**
* 从数据库中获取一条记录, 实际得到对应的一个对象
* 注意不是调用 queryForObject(String sql, Class requiredType, Object... args) 方法!
* 而需要调用 queryForObject(String sql, RowMapper rowMapper, Object... args)
* 1. 其中的 RowMapper 指定如何去映射结果集的行, 常用的实现类为 BeanPropertyRowMapper
* 2. 使用 SQL 中列的别名完成列名和类的属性名的映射. 例如 last_name lastName
* 3. 不支持级联属性. JdbcTemplate 到底是一个 JDBC 的小工具, 而不是 ORM 框架
*/
@Test
public void testQueryForObject(){
String sql = "SELECT id, last_name lastName, email, dept_id as \"department.id\" FROM employees WHERE id = ?";
RowMapper rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Employee.class);
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, 1);
System.out.println(employee);
}
/**
* 执行批量更新: 批量的 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
* 最后一个参数是 Object[] 的 List 类型: 因为修改一条记录需要一个 Object 的数组, 那么多条不就需要多个 Object 的数组吗
*/
@Test
public void testBatchUpdate(){
String sql = "INSERT INTO employees(last_name, email, dept_id) VALUES(?,?,?)";
List batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"AA", "[email protected]", 1});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"BB", "[email protected]", 2});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"CC", "[email protected]", 3});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"DD", "[email protected]", 3});
batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"EE", "[email protected]", 2});
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
}
/**
* 执行 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
String sql = "UPDATE employees SET last_name = ? WHERE id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "Jack", 5);
}
@Test
public void testDataSource() throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DataSource.class);
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
}
} 事务基于注解
package com.atguigu.spring.tx;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("bookShopService")
public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService {
@Autowired
private BookShopDao bookShopDao;
//添加事务注解
//1.使用 propagation 指定事务的传播行为, 即当前的事务方法被另外一个事务方法调用时
//如何使用事务, 默认取值为 REQUIRED, 即使用调用方法的事务
//REQUIRES_NEW: 事务自己的事务, 调用的事务方法的事务被挂起.
//2.使用 isolation 指定事务的隔离级别, 最常用的取值为 READ_COMMITTED
//3.默认情况下 Spring 的声明式事务对所有的运行时异常进行回滚. 也可以通过对应的
//属性进行设置. 通常情况下去默认值即可.
//4.使用 readOnly 指定事务是否为只读. 表示这个事务只读取数据但不更新数据,
//这样可以帮助数据库引擎优化事务. 若真的事一个只读取数据库值的方法, 应设置 readOnly=true
//5.使用 timeout 指定强制回滚之前事务可以占用的时间.
// @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,
// isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,
// noRollbackFor={UserAccountException.class})
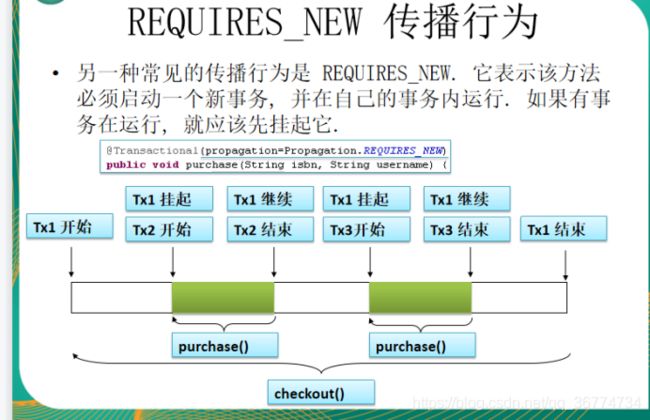
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,
isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,
readOnly=false,
timeout=3)
@Override
public void purchase(String username, String isbn) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
//1. 获取书的单价
int price = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn);
//2. 更新数的库存
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn);
//3. 更新用户余额
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username, price);
}
}事务基于配置文件
SpringTransactionTest.java
package com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.service.BookShopService;
import com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.service.Cashier;
public class SpringTransactionTest {
private ApplicationContext ctx = null;
private BookShopDao bookShopDao = null;
private BookShopService bookShopService = null;
private Cashier cashier = null;
{
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-tx-xml.xml");
bookShopDao = ctx.getBean(BookShopDao.class);
bookShopService = ctx.getBean(BookShopService.class);
cashier = ctx.getBean(Cashier.class);
}
@Test
public void testTransactionlPropagation(){
cashier.checkout("AA", Arrays.asList("1001", "1002"));
}
@Test
public void testBookShopService(){
bookShopService.purchase("AA", "1001");
}
}BookShopServiceImpl.java
package com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.service.impl;
import com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.BookShopDao;
import com.atguigu.spring.tx.xml.service.BookShopService;
public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService {
private BookShopDao bookShopDao;
public void setBookShopDao(BookShopDao bookShopDao) {
this.bookShopDao = bookShopDao;
}
@Override
public void purchase(String username, String isbn) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
//1. 获取书的单价
int price = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn);
//2. 更新数的库存
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn);
//3. 更新用户余额
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username, price);
}
}applicationContext-tx-xml.xml
解析
JdbcTemplate 简介
为了使 JDBC 更加易于使用, Spring 在 JDBC API 上定义了一个抽象层, 以此建立一个 JDBC 存取框架.
作为 Spring JDBC 框架的核心, JDBC 模板的设计目的是为不同类型的 JDBC 操作提供模板方法. 每个模板方法都能控制整个过程, 并允许覆盖过程中的特定任务. 通过这种方式, 可以在尽可能保留灵活性的情况下, 将数据库存取的工作量降到最低.
使用 JdbcTemplate 更新数据库
使用 JdbcTemplate 查询数据库
使用 JdbcTemplate 查询数据库
简化 JDBC 模板查询
每次使用都创建一个 JdbcTemplate 的新实例, 这种做法效率很低下.
JdbcTemplate 类被设计成为线程安全的, 所以可以再 IOC 容器中声明它的单个实例, 并将这个实例注入到所有的 DAO 实例中.
JdbcTemplate 也利用了 Java 1.5 的特定(自动装箱, 泛型, 可变长度等)来简化开发
Spring JDBC 框架还提供了一个 JdbcDaoSupport 类来简化 DAO 实现. 该类声明了 jdbcTemplate 属性, 它可以从 IOC 容器中注入, 或者自动从数据源中创建.
注入 JDBC 模板示例代码
扩展 JdbcDaoSupport 示例代码
在 JDBC 模板中使用具名参数
在经典的 JDBC 用法中, SQL 参数是用占位符 ? 表示,并且受到位置的限制. 定位参数的问题在于, 一旦参数的顺序发生变化, 就必须改变参数绑定.
在 Spring JDBC 框架中, 绑定 SQL 参数的另一种选择是使用具名参数(named parameter).
具名参数: SQL 按名称(以冒号开头)而不是按位置进行指定. 具名参数更易于维护, 也提升了可读性. 具名参数由框架类在运行时用占位符取代
具名参数只在 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 中得到支持
在 JDBC 模板中使用具名参数
Spring 中的事务管理
事务简介
事务管理是企业级应用程序开发中必不可少的技术, 用来确保数据的完整性和一致性.
事务就是一系列的动作, 它们被当做一个单独的工作单元. 这些动作要么全部完成, 要么全部不起作用
事务的四个关键属性(ACID)
原子性(atomicity): 事务是一个原子操作, 由一系列动作组成. 事务的原子性确保动作要么全部完成要么完全不起作用.
一致性(consistency): 一旦所有事务动作完成, 事务就被提交. 数据和资源就处于一种满足业务规则的一致性状态中.
隔离性(isolation): 可能有许多事务会同时处理相同的数据, 因此每个事物都应该与其他事务隔离开来, 防止数据损坏.
持久性(durability): 一旦事务完成, 无论发生什么系统错误, 它的结果都不应该受到影响. 通常情况下, 事务的结果被写到持久化存储器中.
Spring 中的事务管理
作为企业级应用程序框架, Spring 在不同的事务管理 API 之上定义了一个抽象层. 而应用程序开发人员不必了解底层的事务管理 API, 就可以使用 Spring 的事务管理机制.
Spring 既支持编程式事务管理, 也支持声明式的事务管理.
编程式事务管理: 将事务管理代码嵌入到业务方法中来控制事务的提交和回滚. 在编程式管理事务时, 必须在每个事务操作中包含额外的事务管理代码.
声明式事务管理: 大多数情况下比编程式事务管理更好用. 它将事务管理代码从业务方法中分离出来, 以声明的方式来实现事务管理. 事务管理作为一种横切关注点, 可以通过 AOP 方法模块化. Spring 通过 Spring AOP 框架支持声明式事务管理.
Spring 中的事务管理器
Spring 从不同的事务管理 API 中抽象了一整套的事务机制. 开发人员不必了解底层的事务 API, 就可以利用这些事务机制. 有了这些事务机制, 事务管理代码就能独立于特定的事务技术了.
Spring 的核心事务管理抽象是 它为事务管理封装了一组独立于技术的方法. 无论使用 Spring 的哪种事务管理策略(编程式或声明式), 事务管理器都是必须的.
Spring 中的事务管理器的不同实现
用事务通知声明式地管理事务
事务管理是一种横切关注点
为了在 Spring 2.x 中启用声明式事务管理, 可以通过 tx Schema 中定义的
声明了事务通知后, 就需要将它与切入点关联起来. 由于事务通知是在
由于 Spring AOP 是基于代理的方法, 所以只能增强公共方法. 因此, 只有公有方法才能通过 Spring AOP 进行事务管理.
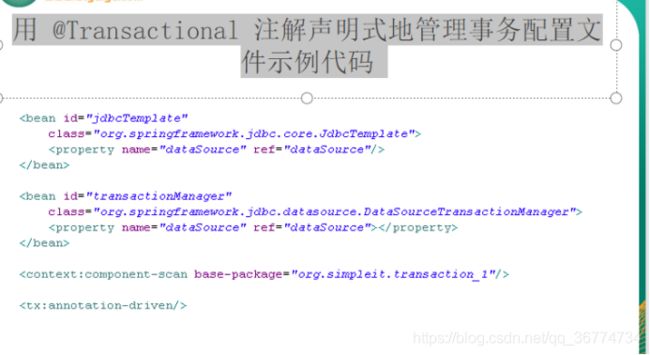
@Transactional 注解声明式地管理事务
除了在带有切入点, 通知和增强器的 Bean 配置文件中声明事务外, Spring 还允许简单地用 @Transactional 注解来标注事务方法.
为了将方法定义为支持事务处理的, 可以为方法添加 @Transactional 注解. 根据 Spring AOP 基于代理机制, 只能标注公有方法.
可以在方法或者类级别上添加 @Transactional 注解. 当把这个注解应用到类上时, 这个类中的所有公共方法都会被定义成支持事务处理的.
在 Bean 配置文件中只需要启用
如果事务处理器的名称是 transactionManager, 就可以在
事务传播属性
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时, 必须指定事务应该如何传播. 例如: 方法可能继续在现有事务中运行, 也可能开启一个新事务, 并在自己的事务中运行.
事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定. Spring 定义了 7 种类传播行为.
并发事务所导致的问题
当同一个应用程序或者不同应用程序中的多个事务在同一个数据集上并发执行时, 可能会出现许多意外的问题
并发事务所导致的问题可以分为下面三种类型:
脏读: 对于两个事物 T1, T2, T1 读取了已经被 T2 更新但 还没有被提交的字段. 之后, 若 T2 回滚, T1读取的内容就是临时且无效的.
不可重复读:对于两个事物 T1, T2, T1 读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 更新了该字段. 之后, T1再次读取同一个字段, 值就不同了.
幻读:对于两个事物 T1, T2, T1 从一个表中读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 在该表中插入了一些新的行. 之后, 如果 T1 再次读取同一个表, 就会多出几行.
事务的隔离级别
从理论上来说, 事务应该彼此完全隔离, 以避免并发事务所导致的问题. 然而, 那样会对性能产生极大的影响, 因为事务必须按顺序运行.
在实际开发中, 为了提升性能, 事务会以较低的隔离级别运行.
事务的隔离级别可以通过隔离事务属性指定
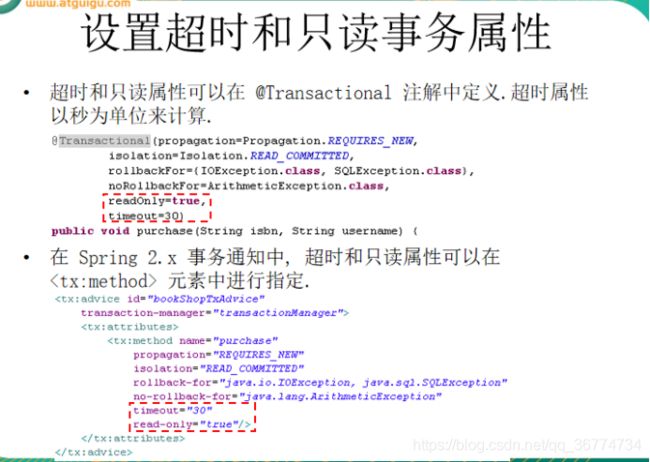
超时和只读属性
由于事务可以在行和表上获得锁, 因此长事务会占用资源, 并对整体性能产生影响.
如果一个事物只读取数据但不做修改, 数据库引擎可以对这个事务进行优化.
超时事务属性: 事务在强制回滚之前可以保持多久. 这样可以防止长期运行的事务占用资源.
只读事务属性: 表示这个事务只读取数据但不更新数据, 这样可以帮助数据库引擎优化事务.
设置超时和只读事务属性
spring整合hibernate
这里只放关键代码
applicationContext.xml
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
true
true
update
BookShopDaoImpl.java
package com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.dao.impl;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.dao.BookShopDao;
import com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.exceptions.BookStockException;
import com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.exceptions.UserAccountException;
/**hql语句进行参数绑定的两种方式
* 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/lewky_liu/article/details/75452516
* 使用hibernate的createQuery进行增删查改
*参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44830627/article/details/106443974
*https://www.cnblogs.com/ryelqy/p/10104027.html
*/
@Repository
public class BookShopDaoImpl implements BookShopDao {
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
//不推荐使用 HibernateTemplate 和 HibernateDaoSupport
//因为这样会导致 Dao 和 Spring 的 API 进行耦合
//可以移植性变差
// private HibernateTemplate hibernateTemplate;
//获取和当前线程绑定的 Session.
private Session getSession(){
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
/**
* 这里还要注意一下
* 注意1,applicationContext.xml 文件里面的
*
*
*
*是给所有service加了事务
*,2,BookShopServiceImpl里面的那段话,因为开启了事务才有可使用的session,若不用事务,则也无法获取session
*
*/
}
/**
* getSession().createQuery(hql).setString(0, isbn) uniqueResult()方法讲解
* Hibernate的Query接口,如何正确使用uniqueResult()方法,有很多人不懂。参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq15577969/article/details/82716747
* hibernate的参考手册中,query接口提供了一个更好的方法 uniqueResult () 用来获取实例,如果查询结果有多个值则抛出错误;结果有且只有一个值,返回一个object; 如果没值,返回null
*/
@Override
public int findBookPriceByIsbn(String isbn) {
String hql = "SELECT b.price FROM Book b WHERE b.isbn = ?";
Query query = getSession().createQuery(hql).setString(0, isbn);
return (Integer)query.uniqueResult();
}
@Override
public void updateBookStock(String isbn) {
//验证书的库存是否充足.
String hql2 = "SELECT b.stock FROM Book b WHERE b.isbn = ?";
int stock = (int) getSession().createQuery(hql2).setString(0, isbn).uniqueResult();
if(stock == 0){
throw new BookStockException("库存不足!");
}
String hql = "UPDATE Book b SET b.stock = b.stock - 1 WHERE b.isbn = ?";
getSession().createQuery(hql).setString(0, isbn).executeUpdate();
}
/**executeUpdate 修改
* 使用hibernate的createQuery进行增删查改
*参考: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44830627/article/details/106443974
*/
@Override
public void updateUserAccount(String username, int price) {
//验证余额是否足够
String hql2 = "SELECT a.balance FROM Account a WHERE a.username = ?";
int balance = (int) getSession().createQuery(hql2).setString(0, username).uniqueResult();
if(balance < price){
throw new UserAccountException("余额不足!");
}
String hql = "UPDATE Account a SET a.balance = a.balance - ? WHERE a.username = ?";
getSession().createQuery(hql).setInteger(0, price).setString(1, username).executeUpdate();
}
}
BookShopServiceImpl.java
package com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.dao.BookShopDao;
import com.atguigu.spring.hibernate.service.BookShopService;
@Service
public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService {
@Autowired
private BookShopDao bookShopDao;
/**
* Spring hibernate 事务的流程
* 1. 在方法开始之前
* ①. 获取 Session
* ②. 把 Session 和当前线程绑定, 这样就可以在 Dao 中使用 SessionFactory 的
* getCurrentSession() 方法来获取 Session 了
* ③. 开启事务
*
* 2. 若方法正常结束, 即没有出现异常, 则
* ①. 提交事务
* ②. 使和当前线程绑定的 Session 解除绑定
* ③. 关闭 Session
*
* 3. 若方法出现异常, 则:
* ①. 回滚事务
* ②. 使和当前线程绑定的 Session 解除绑定
* ③. 关闭 Session
*/
@Override
public void purchase(String username, String isbn) {
int price = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn);
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn);
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username, price);
}
}