JWT的深入理解
1、JWT是什么
JWT(JSON Web Token)是一种开放标准(RFC 7519),用于在不同实体之间安全地传输信息。它由三部分组成,即头部(Header)、载荷(Payload)和签名(Signature)。以下是JWT的基本概念和使用方式:
-
头部(Header):头部通常由两部分组成,算法类型和令牌类型。例如:
{ "alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT" }在上述示例中,
alg表示使用的签名算法,typ表示令牌的类型。 -
载荷(Payload):载荷包含需要传输的信息,可以自定义添加一些标准或私有的声明。例如:
{ "sub": "user123", "name": "John Doe", "role": "admin", "exp": 1625102873 }在上述示例中,
sub表示主题(subject),name表示名称,role表示角色,exp表示过期时间。 -
签名(Signature):签名用于验证令牌的真实性和完整性。它是对头部和载荷进行签名的结果,使用私钥进行签名。例如:
HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret )在上述示例中,通过对头部和载荷进行签名,使用一个秘密密钥(secret)生成签名。
使用JWT的基本流程如下:
-
用户认证:用户向服务器发送认证请求,服务器验证用户的身份和凭证。
-
生成JWT:服务器根据用户的身份信息生成JWT,并将其返回给客户端。
-
客户端存储JWT:客户端将收到的JWT保存在本地,通常使用cookie或本地存储(如localStorage)。
-
后续请求:客户端在每次请求中将JWT作为身份凭证附加到请求的头部(通常是
Authorization头)。 -
服务器验证:服务器在接收到请求时,解析JWT并验证其真实性和有效性。
-
响应请求:服务器根据JWT中的信息进行相应的操作,并返回相应的响应结果。
JWT的优势在于它是自包含的,即令牌本身携带了用户信息和验证信息,减少了对服务器端存储和查找用户信息的开销。同时,JWT可以在跨域环境中使用,具有可扩展性和灵活性。
需要注意的是,为了保证安全性,JWT的签名部分应该使用安全的密钥进行签名,并且需要进行合适的过期时间设置和刷新机制来保护令牌的安全性。
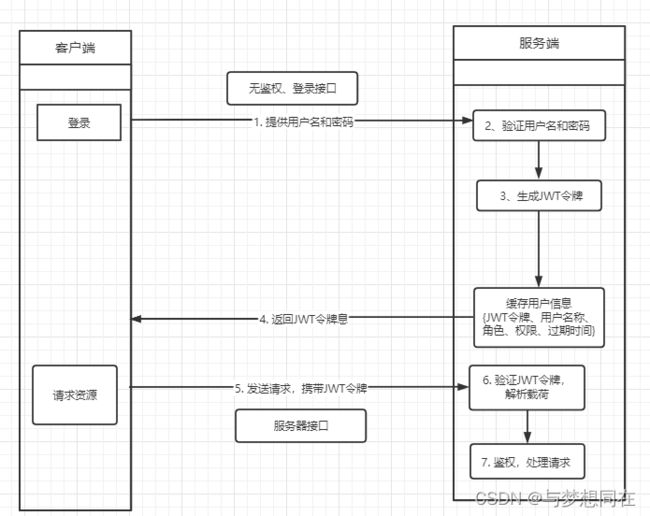
2、JWT流程
在这个过程中,JWT令牌作为身份凭证被生成并在客户端和服务器之间传递。服务器验证JWT的签名和有效性,并从中提取用户的身份信息来进行鉴权和授权操作。JWT的特点是自包含的,减少了服务器端的存储和查找开销,并提供了无状态的身份验证机制。
需要注意的是,为了保证JWT的安全性,应使用安全的密钥对JWT进行签名,并根据需求设置适当的过期时间和刷新机制,以保护令牌的安全性。
3、实操代码
登录的接口实现,伪代码:
public UserVo login(String account, String password, boolean isRememberMe, HttpServletResponse response) {
// 数据库用户校验
User dbUser = userMapper.selectOne(new QueryWrapper().eq(User.ACCOUNT, account));
if (dbUser == null) {
throw new GlobalException(BaseResultEnum.USER_NOT_EXISTS);
}
checkUser(dbUser);
checkPassword(dbUser, password);
// 角色校验
Long userId = dbUser.getId();
List dbRoles = getRoles(userId);
if (CollectionUtil.isEmpty(dbRoles)) {
throw new GlobalException(BaseResultEnum.NO_AUTHORITY_ROLE);
}
// 权限校验
Set roleIDs = dbRoles.stream().map(Role::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set dbPermission = getPermissions(roleIDs);
if (CollectionUtil.isEmpty(dbPermission)) {
throw new GlobalException(BaseResultEnum.NO_AUTHORITY_ROLE);
}
// 封装用户信息
AuthUser authUser = getAuthUser(dbUser, userId, dbPermission, roles, LoginSourceType.PC.getName());
authUser.setLoginType(LoginSourceType.PC.getType());
// 获取用户设置的有效时间
authUser.setExpiredTime(User.getValidTimeByType(authUser.getValidTimeType()));
// 生成令牌
String accessKey = UUIDUtils.getUUID();
// 缓存令牌与信息
cacheToken(authUser, accessKey, LoginSourceType.PC.getType());
// header存储accessKey,返回JWT令牌
response.addHeader(ShiroConstants.TOKEN_NAME_FOR_HTTP_HEADER, accessKey);
// 是否记住密码
if (isRememberMe) {
addRememberMeCookie(account, password, response);
}
// 返回的用户信息,用于Cookie保存
UserVo userVo = getUserVo(dbUser);
Set perms = dbPermission.stream().map(Permission::getCode).collect(Collectors.toSet());
userVo.setPerms(perms);
userVo.setToken(accessKey);
return userVo;
}
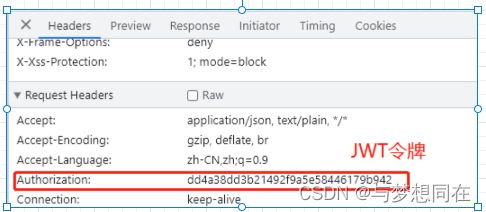
结果情况如下:
Shiro、JWT的拦截
定义一个拦截器类,继承 BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter 类。 BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter 类又继承情况如下:最终实现了Filter与继承自ServletContextSuper。
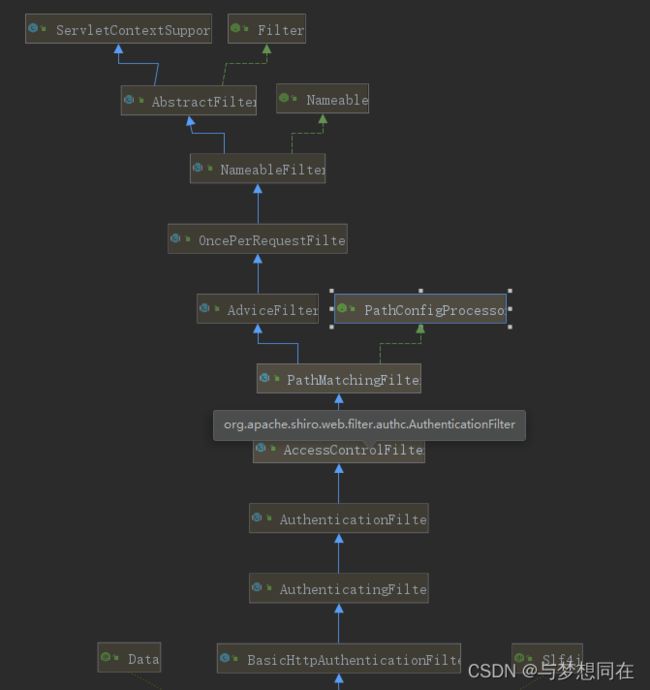
重写BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter 类的 preHandle()->isAccessAllowed()->isLoginAttempt()->executeLogin() 方法。
使用shiro组件
配置Shiro的配置文件,注册ShiroFilterFactoryBean(),
@Bean("shiroFilter")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean factory() {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 添加自己的过滤器并且取名为jwt
Map filterMap = new HashMap<>();
filterMap.put("jwt", new JWTFilter());
factoryBean.setFilters(filterMap);
factoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager());
factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noLogin");
// 用LinkedHashMap添加拦截的uri,其中authc指定需要认证的uri,anon指定排除认证的uri
LinkedHashMap filterRuleMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filterRuleMap.put("/login", "anon");
factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterRuleMap);
return factoryBean;
}
/**
DefaultWebSecurityManager类主要定义了设置subjectDao,获取会话模式,设置会话模式,设置会话管理器,是否是http会话模式等操作,它继承了DefaultSecurityManager类,实现了WebSecurityManager接口
*/
@Bean("securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setRealm(jwtRealm);
DefaultSubjectDAO subjectDAO = new DefaultSubjectDAO();
DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator defaultSessionStorageEvaluator = new DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator();
defaultSessionStorageEvaluator.setSessionStorageEnabled(false);
subjectDAO.setSessionStorageEvaluator(defaultSessionStorageEvaluator);
manager.setSubjectDAO(subjectDAO);
return manager;
}
参考地址:http://shiro.apache.org/web.html#urls-
shiro:DefaultWebSecurityManager详解
Shiro的认证与授权
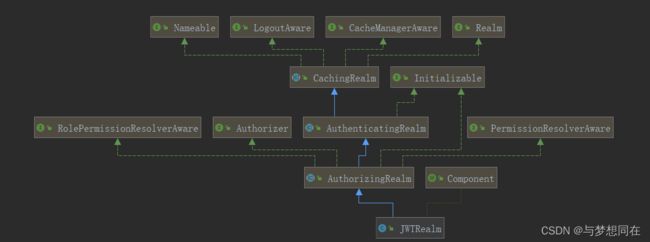
定义一个配置JWTRealm类,继承AuthorizingRealm类
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token instanceof JWTToken;
}
/**
* 授权
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
AuthUser authUser = (AuthUser) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
if (authUser == null) {
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
Set perms = authUser.getPerms();
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(perms)) {
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(perms);
}
Set roles = authUser.getRoles();
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(roles)) {
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRoles(roles);
}
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
/**
* 认证
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken auth) throws AuthenticationException {
String accessKey = (String) auth.getCredentials();
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(accessKey)) {
throw new AuthenticationException(BaseResultEnum.NON_LOGIN.getMessage());
}
String userString = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(String.format(RedisKey.USER_TOKEN_KEY, accessKey));
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(userString)) {
throw new AuthenticationException(BaseResultEnum.TOKEN_EXPIRED.getMessage());
}
AuthUser user = JSON.parseObject(userString, AuthUser.class);
if (user == null) {
throw new AuthenticationException(BaseResultEnum.TOKEN_EXPIRED.getMessage());
}
// 判断是否登陆过
/* String userTokenMappingKey = String.format(RedisKey.USER_TOKEN_MAPPING_KEY, user.getId(), LoginSourceType.PC.getType());
//用户关联的token
String lastAccessKey = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(userTokenMappingKey);
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(lastAccessKey)||!lastAccessKey.equals(accessKey)) {
throw new AuthenticationException(BaseResultEnum.TOKEN_EXPIRED.getMessage());
}*/
/*
//刷新当前token过期时间
stringRedisTemplate.expire(String.format(RedisKey.USER_TOKEN_KEY, accessKey), user.getExpiredTime(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);*/
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, accessKey, getName());
}