分布式搜索--elasticsearch
一、初识 elasticsearch
1. 了解 ES
① elasticsearch 是一款非常强大的开源
搜索引擎,可以帮助我们从海量数据中
快速找到需要的内容
② elasticsearch 结合 kibana、Logstash、
Beats,也就是 elastic stack (ELK),被
广泛应用在日志数据分析、实时监控等
领域
③ elasticsearch 是elastic stack的核心,
负责存储、搜索、分析数据
(2) Lucene 与 elasticsearch 的区别
Lucene 是一个Java语言的搜索引擎类库
Lucene的优势:
① 易扩展
② 高性能 (基于倒排索引)
Lucene的缺点:
① 只限于 Java 语言开发
② 学习曲线陡峭
③ 不支持水平扩展
相比于 lucene,elasticsearch 具备下列
优势:
① 支持分布式,可水平扩展
② 提供 Restful 接口,可被任何语言
调用
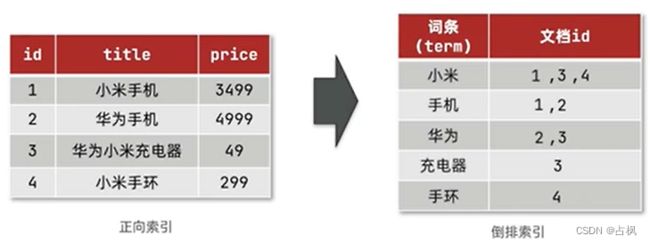
2. 倒排索引
传统数据库 (如MySQL) 采用正向索引,
局部搜索会在表上逐条数据进行扫描,
非常的繁琐
elasticsearch 采用倒排索引:
会形成一个新的表,由两部分构成,进
行两次搜索,先搜词条再搜文档
文档 (document):每条数据就是一个文档
词条 (term):文档按照语义分成的词语
倒排索引中包含两部分内容:
词条词典 (Term Dictionary):记录所有词条,
以及词条与倒排列表 (Posting List) 之间的关
系,会给词条创建索引,提高查询和插入效
率
倒排列表 (Posting List):记录词条所在的文
档 id、词条出现频率 、词条在文档中的位置
等信息
文档 id:用于快速获取文档
词条频率 (TF):文档在词条出现的次数,
用于评分
3. es 的一些概念
(1) es 与 mysql 对比
(2) 架构
Mysql:擅长事务类型操作,可以确保
数据的安全和一致性
Elasticsearch:擅长海量数据的搜索、
分析、计算
4. 安装 es、kibana
(1) 部署单点 es
(2) 部署 kibana
kibana 可以提供一个 elasticsearch 的可
视化界面
(3) 安装 IK 分词器
1) 分词器的作用
① 创建倒排索引时对文档分词
② 用户搜索时,对输入的内容分词
2) 默认的分词语法说明:
在 kibana 的 DevTools 中测试:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "床前明月光,疑是地上霜!"
}
① POST:请求方式
② /_analyze:请求路径,这里省略了,
有 kibana 帮我们补充
③ 请求参数,json风格:
analyzer:分词器类型,这里是默
认的 standard 分词器
text:要分词的内容
默认将文字拆除一个字一个字的,对中
文分词很不友好,所以用 IK 分词器
3) ik 分词器包含两种模式:
ik_smart:最少切分,粗粒度
ik_max_word:最细切分,细粒度
一般情况下,为了提高搜索的效果,
需要这两种分词器配合使用,既建
索引时用 ik_max_word 尽可能多的
分词,而搜索时用 ik_smart 尽可能
提高匹配准度,让用户的搜索尽可
能的准确
4) ik 分词器扩展词条
要拓展ik分词器的词库,只需要修改一
个 ik 分词器目录中的 config 目录中的
IkAnalyzer.cfg.xml 文件:
IK Analyzer 扩展配置
ext.dic
然后在名为 ext.dic 的文件中,添加想要
拓展的词语即可
5) 停用词条
在 stopword.dic 文件中,添加想要拓展的
词语即可:
IK Analyzer 扩展配置
ext.dic
stopword.dic
(4) 部署 es 集群
直接使用 docker-compose 来完成
二、索引库操作
1. mapping 映射属性
(1) mapping 是对索引库中文档的约束,常
见的 mapping 属性包括:
① type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
字符串:text (可分词的文本)、keyword
(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip 地址)
数值:long、integer、short、byte、
double、float
布尔:boolean
日期:date
对象:object
② index:是否创建索引,默认为 true
③ analyzer:使用哪种分词器
④ properties:该字段的子字段
2. 索引库的 CRUD
(1) 创建索引库
ES 中通过 Restful 请求操作索引库、
文档,请求内容用 DSL 语句来表示
创建索引库和 mapping 的 DSL 语法如下:
PUT /索引库名称
PUT /索引库名称
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"字段名":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"字段名2":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"字段名3":{
"properties": {
"子字段": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
// ...略
}
}
}
(2) 查看索引库
GET /索引库名
(3) 修改索引库
索引库和 mapping 一旦创建无法修改,
但是可以添加新的字段,语法如下:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"新字段名":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
(4) 删除索引库
DELETE /索引库名
三、文档操作
1. 新增文档
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
"字段3": {
"子属性1": "值3",
"子属性2": "值4"
},
// ...
}
2. 查询文档
GET /索引库名/_doc/文档id
3. 删除文档
DELETE /索引库名/_doc/文档id
4. 修改文档
(1) 全量修改
删除旧文档,添加新文档
本质是:根据指定的 id 删除文档,新增
一个相同 id 的文档
PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
// ... 略
}
(2) 增量修改
修改指定字段值
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id
{
"doc": {
"字段名": "新的值",
}
}
5. Dynamic Mapping
我们向 ES 中插入文档时,如果文档中
字段没有对应的 mapping,ES 会帮助
我们字段设置 mapping
| JSON类型 | Elasticsearch类型 |
|---|---|
| 字符串 | ① 日期格式字符串:mapping 为 date 类型 ② 普通字符串:mapping 为 text 类型,并添加 keyword 类型子字段 |
| 布尔值 | boolean |
| 浮点数 | float |
| 整数 | long |
| 对象嵌套 | object,并添加 properties |
| 数组 | 由数组中的第一个非空类型决定 |
| 空值 | 忽略 |
四、RestClient 操作索引库
RESTClient 是一款用于测试各种 Web
服务的插件,它可以向服务器发送各种
HTTP请求(用户也可以自定义请求方式),
并显示服务器响应
本质就是组装 DSL 语句,通过 http请求
发送给 ES
1. 创建索引库
(1) 导入数据库
(2) 分析数据结构
mapping 要考虑的问题:
字段名、数据类型、是否参与搜索、是
否分词,如果分词,分词器是什么
(3) 初始化 JavaRestClient
① 引入依赖
org.elasticsearch.client
elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client
1.8
7.12.1
② 初始化
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
(4) 创建索引库代码
@Testvoid testCreateHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.请求参数,MAPPING_TEMPLATE是静态常量字符串,内容是创建索引库的DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发起请求, indices 返回的对象中包含索引库操作的所有方法
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
2. 删除索引库代码
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发起请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
3. 判断索引库是否存在
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发起请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.out.println(exists);
}
五、RestClient 操作文档
1. 初始化
public class ElasticsearchDocumentTest {
// 客户端
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
}
2. 新增文档
@Test
void testIndexDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.创建request对象
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("indexName").id("1");
// 2.准备JSON文档
request.source("{\"name\": \"Jack\", \"age\": 21}", XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
3. 查询文档
@Test
void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.创建request对象
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("indexName", "1");
// 2.发送请求,得到结果
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.解析结果
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
System.out.println(json);
}
4. 修改文档
@Test
void testUpdateDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.创建request对象
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("indexName", "1");
// 2.准备参数,每2个参数为一对 key value
request.doc(
"age", 18,
"name", "Rose"
);
// 3.更新文档
client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
5. 删除文档
@Test
void testDeleteDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.创建request对象
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("indexName", "1");
// 2.删除文档
client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
6. 批量导入文档
@Test
void testBulk() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Bulk请求
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
// 2.添加要批量提交的请求:这里添加了两个新增文档的请求
request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel")
.id("101").source("json source", XContentType.JSON));
request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel")
.id("102").source("json source2", XContentType.JSON));
// 3.发起bulk请求
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}