python爬虫-逆向实例小记-1
注意!!!!某政府网站逆向实例仅作为学习案例,禁止其他个人以及团体做谋利用途!!!!
案例分析
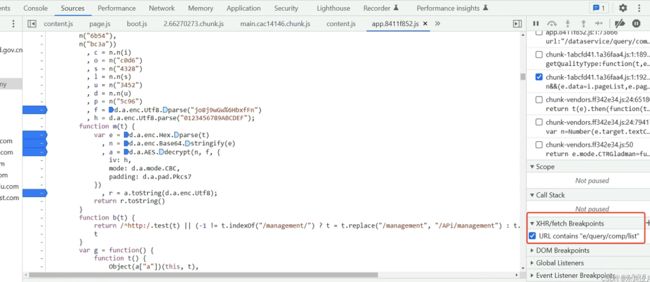
第一步:下图标注出来的是获取请求断点,断点出自 请求url
第二步:有点玄学了(鄙人才疏学浅,所以会通篇进行手动实现响应这个过程可以看到一些重要信息)。手动实现断点后响应过程
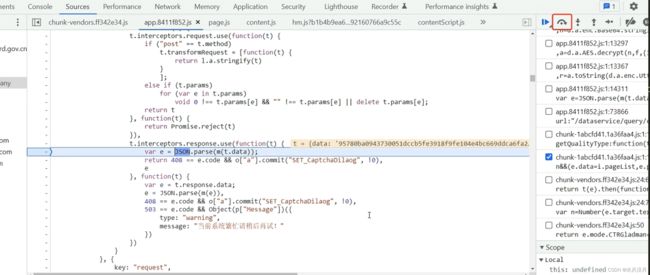
第三步:通过手动进行下一步会得到每一步的操作后的内容(与调试debug是一样的)
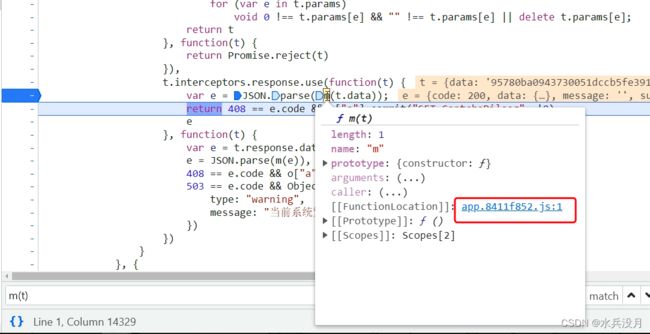
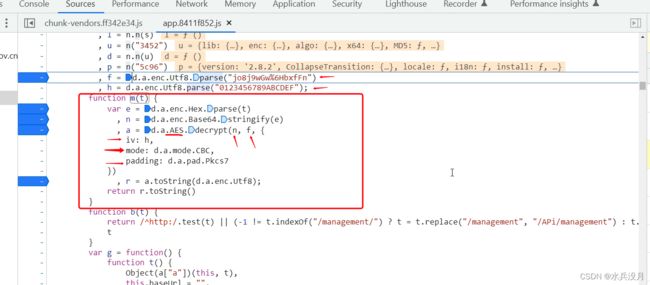
第四步:从一大串响应内容到得到页面正常的内容,调用了f m(t)函数, 鼠标放在该位置,会得到相关的.js 文件。点进去即可
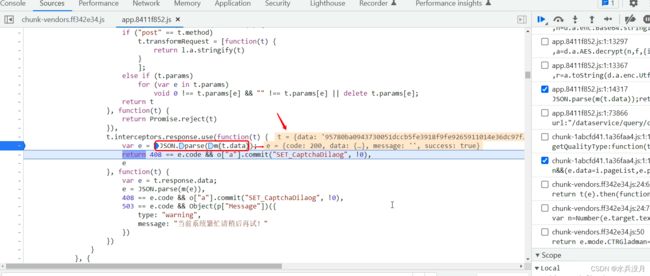
第五步:展示一下: f m(t) 函数。通过这个函数可以很肯定的是,使用了AES CBC模式pkcs7 填充。从下图可知,f 是key ,h 是偏移量(vi), n 是通过hex 和base64 包装后的一大串内容
第六步:一步一步执行,就可以看到从“乱码”到内容的关键过程。
代码
python AES部分参考https://blog.csdn.net/yt_xy/article/details/108863258 博主
# 十六进制转base64
import codecs
hex_string = '' # 十六进制数值
b64_string = codecs.encode(codecs.decode(hex_string, 'hex'), 'base64').decode()
# 解密
# !!!!!!!!
# 本人参考https://blog.csdn.net/yt_xy/article/details/108863258 博主
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import base64
class Encrypt:
def __init__(self, key, iv):
self.key = key.encode('utf-8')
self.iv = iv.encode('utf-8')
# @staticmethod
def pkcs7padding(self, text):
"""明文使用PKCS7填充 """
bs = 16
length = len(text)
bytes_length = len(text.encode('utf-8'))
padding_size = length if (bytes_length == length) else bytes_length
padding = bs - padding_size % bs
padding_text = chr(padding) * padding
self.coding = chr(padding)
return text + padding_text
def aes_encrypt(self, content):
""" AES加密 """
cipher = AES.new(self.key, AES.MODE_CBC, self.iv)
# 处理明文
content_padding = self.pkcs7padding(content)
# 加密
encrypt_bytes = cipher.encrypt(content_padding.encode('utf-8'))
# 重新编码
result = str(base64.b64encode(encrypt_bytes), encoding='utf-8')
return result
def aes_decrypt(self, content):
"""AES解密 """
self.pkcs7padding(content)
cipher = AES.new(self.key, AES.MODE_CBC, self.iv)
content = base64.b64decode(content)
text = cipher.decrypt(content).decode('utf-8')
return text.rstrip(self.coding)
if __name__ == '__main__':
key = '******'
iv = '****'
a = Encrypt(key=key, iv=iv)
d = a.aes_decrypt(b64_string)
print("解密:", d)