C语言常用时间相关函数
首先讲一下#include 和#include 的区别,前者是C99标准库函数,后者是Linux系统函数,如果Windows平台装了MinGW(Minimalist GNU for Windows)工具也是可以使用
获取时间戳-time
函数原型:
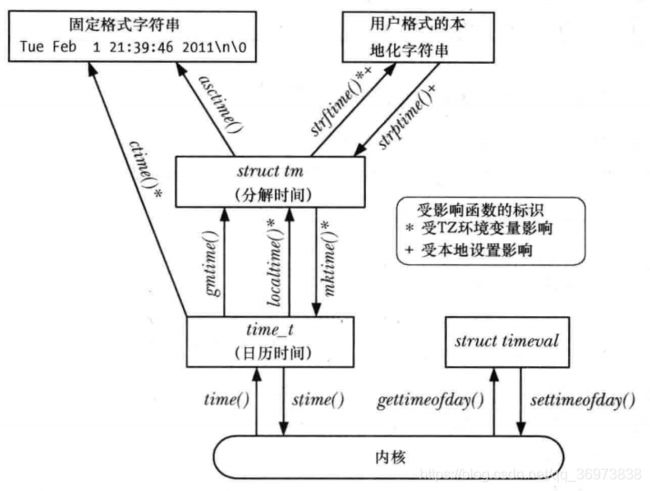
time_t time(time_t *timer)
变量time_t实际上是long类型,使用时既可以传入变量指针,又可以直接利用其返回值。
使用范例
#include 或者
time_t timer;
time(&timer);
printf("time = %d", timer);
获取微秒级时间戳-gettimeofday
函数原型:
int gettimeofday(struct timeval*tv,struct timezone *tz )
struct timeval
{
long tv_sec;
long tv_usec;
};
使用范例
#include 时间戳 to 本地时间-localtime
根据系统的时区信息转换成本地时间
函数原型:
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer)
struct tm
{
int tm_sec; /* 秒 – 取值区间为[0,59] */
int tm_min; /* 分 - 取值区间为[0,59] */
int tm_hour; /* 时 - 取值区间为[0,23] */
int tm_mday; /* 一个月中的日期 - 取值区间为[1,31] */
int tm_mon; /* 月份(从一月开始,0代表一月) - 取值区间为[0,11] */
int tm_year; /* 年份,其值等于实际年份减去1900 */
int tm_wday; /* 星期 – 取值区间为[0,6],其中0代表星期天,1代表星期一 */
int tm_yday; /* 从每年1月1日开始的天数– 取值区间[0,365],其中0代表1月1日 */
int tm_isdst; /* 夏令时标识符,夏令时tm_isdst为正;不实行夏令时tm_isdst为0 */
};
使用范例
#include 时间戳 to UTC-gmtime
函数原型:
struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timer)
使用方法类比localtime。
struct tm to时间戳
函数原型:
time_t mktime(struct tm *tmp)
使用范例
#include 时间戳to 时间字符串
char *ctime(const time_t *timep)
使用范例
#include struct tm to 时间字符串
函数原型:
char *asctime(const struct tm *timeptr)
使用范例
#include 延时函数
Windows
头文件#include
函数原型:
void Sleep(unsigned long time)
单位毫秒。
Linux
头文件#include
函数原型:
unsigned int sleep(unsigned int seconds);
单位秒;
返回值:若进程/线程挂起到参数所指定的时间则返回0,若有信号中断则返回剩余秒数;
void usleep(unsigned long usec);
单位微秒。