力扣 1 至 100 中等
欢迎访问我的博客首页。
力扣 1 至 100 中等
- 1. LeetCode 2.两数相加
- 2. LeetCode 3.无重复字符的最长子串
- 3. LeetCode 5.最长回文子串
- 4. LeetCode 6.Z 字形变换
- 5. LeetCode 8.字符串转换整数
- 6. LeetCode 11.盛最多水的容器
- 7. LeetCode 12.整数转罗马数字
- 8. LeetCode 15.三数之和
- 9. LeetCode 16.最接近的三数之和
- 10. LeetCode 17.电话号码的字母组合
- 11. LeetCode 18.四数之和
- 12. LeetCode 19.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(未实现)
- 13. LeetCode 22.括号生成
- 14. LeetCode 24.两两交换链表中的结点(未实现)
- 15. LeetCode 29.两数相除
- 16. LeetCode 31.下一个排列
- 17. LeetCode 33.搜索旋转排序数组
- 18. LeetCode 34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置(未实现)
- 19. LeetCode 36.有效的数独
- 20. LeetCode 38.外观数列
- 21. LeetCode 39.组合总和
- 22. LeetCode 40.组合总和Ⅱ(未实现)
- 23. LeetCode 43.字符串相乘
- 24. LeetCode 45.跳跃游戏Ⅱ
- 25. LeetCode 64.最小路径
1. LeetCode 2.两数相加
题目。
分析:因为是两个整数,且按逆序储存,所以题目比较简单,只需遍历链表即可。注意考虑 4 种情况:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if (l1 == nullptr)
return l2;
if (l2 == nullptr)
return l1;
ListNode *res = nullptr, *work = nullptr;
int sum, carry = 0;
// 1.链表l1和链表l2都没结束。
while (l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr) {
sum = l1->val + l2->val + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
if (res == nullptr) {
res = new ListNode(sum);
work = res;
}
else {
work->next = new ListNode(sum);
work = work->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
// 2.链表l2结束。
while (l1 != nullptr) {
sum = l1->val + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
work->next = new ListNode(sum);
work = work->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
// 3.链表l1结束。
while (l2 != nullptr) {
sum = l2->val + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
work->next = new ListNode(sum);
work = work->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
// 4.链表l1和链表l2都结束,检查进位是否为0。
if (carry != 0) {
work->next = new ListNode(carry);
work = work->next;
}
return res;
}
};
性能:时间复杂度是 O ( m a x ( m + n ) ) O(max(m+n)) O(max(m+n)),空间复杂度 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
2. LeetCode 3.无重复字符的最长子串
详细内容在这里。
3. LeetCode 5.最长回文子串
题目:给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。牛客只求长度。相关题目《LeetCode 132.分割回文串Ⅱ》。
分析:最长回文子串有时间复杂度为 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3)、 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)、 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 的 3 类算法。时间复杂度为 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3) 的算法使用两层循环获取子串 s[i: j],再使用一层循环判断 s[i: j] 是否为回文字符串。时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) 的算法有中心扩散法和动态规划法。时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 的算法有 Manacher 算法,这个算法太复杂,这里不讨论。
中心扩散法:遍历字符串中的每个字符 c,求以 c 为中心的回文字串长度。注意以 c 为中心的回文子串有 “aca” 和 “acca” 两种形式。
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string str) {
if (str.size() < 2)
return str;
string res = str.substr(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
// 1.以str[i]为中心。
string res1 = find(str, i - 1, i + 1);
res = res.size() >= res1.size() ? res : res1;
// 2.以str[i]str[i+1]为中心。
if (str[i] == str[i + 1]) {
string res2 = find(str, i - 1, i + 2);
res = res.size() >= res2.size() ? res : res2;
}
}
return res;
}
private:
string find(string& str, int left, int right) {
while (true) {
if (left < 0 || right >= str.size())
break;
if (str[left] == str[right]) {
left--;
right++;
}
else
break;
}
return str.substr(left + 1, right - left - 1);
}
};
性能:第 1 个字符最多需要 0 次判断,第 2 个字符最多需要 1 次判断,…,第 n/2 个字符最多需要 (n/2)-1 次判断,所以最多需要 2 × ( 0 + 1 + ⋯ + n / 2 − 1 ) = n 2 ÷ 2 2 \times (0 + 1 + \cdots + n/2-1) = n^2 \div 2 2×(0+1+⋯+n/2−1)=n2÷2 次判断,所以时间复杂度是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。因为使用了临时空间存放结果, 所以空间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。如果使用两个数表示回文子串而不是使用临时空间 temp,空间复杂度就可以变为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
下面使用动态规划算法。
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string& str) {
if (str.size() < 2)
return str;
int N = str.size(), begin = 0, maxlen = 1;
vector<vector<int>> dp(N, vector<int>(N));
// 1.长度为1的回文子串。
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
dp[i][i] = 1;
// 2.长度大于等于3的回文子串。
for (int len = 2; len <= N; len++) {
for (int start = 0; start + len <= N; start++) {
int end = start + len - 1;
// 3.str[start]与str[end]不相等。
if (str[start] != str[end])
continue;
// 4.str[start+1:end-1]不是回文字符串。
if (dp[start + 1][end - 1] != end - start - 1)
continue;
// 5.str[start]与str[end]相等且str[start+1:end-1]是回文字符串。
dp[start][end] = dp[start + 1][end - 1] + 2;
if (dp[start][end] > maxlen) {
maxlen = dp[start][end];
begin = start;
}
}
}
return str.substr(begin, maxlen);
}
};
为了保证 end-1>= start+1,即 start+len-1>=start+1,我们让 len 从 2 开始递增。于是我们要给出最小问题 len=1 的解。上面的动态规划算法中,第一层循环让回文子串的长度递增,第二层循环让回文子串的起始位置递增。总之要保证先处理的问题比后处理的问题的规模更小。
该题说明在设计动态规划算法时,一点要理清问题的增长方向,才能知道循环怎么写。一般的动态规划问题中,循环都是从小到大的,本题的两个循环都从小到大是不行的。
本题还有另一种更好理解地划分问题的方法,代码如下。
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string& str) {
if (str.size() < 2)
return str;
int N = str.size(), begin = 0, maxlen = 1;
vector<vector<int>> dp(N, vector<int>(N));
for (int start = N - 1; start >= 0; start--) {
for (int end = start; end < N; end++) {
if (start == end)
dp[start][end] = 1;
else if (str[start] == str[end] && dp[start + 1][end - 1] == end - start - 1)
dp[start][end] = dp[start + 1][end - 1] + 2;
if (dp[start][end] > maxlen) {
maxlen = dp[start][end];
begin = start;
}
}
}
return str.substr(begin, maxlen);
}
};
4. LeetCode 6.Z 字形变换
题目。将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。

图 4.1 Z 字 形 变 换 图\ 4.1\quad Z 字形变换 图 4.1Z字形变换
分析:我们把一竖列和后面斜向上的部分分为一组,如图 4.1,相连的一条竖直红线和一条斜线经过的元素称为一组。显然一组的元素个数最多是 l e n G r o u p s = 2 × n u m R o w s − 2 lenGroups = 2 \times numRows -2 lenGroups=2×numRows−2,一共有 numGroups = ceil(1.0 * s.size() / lenGroups) 个这样的组。
还可以发现,每组其实包含两列。在每组中,除了第一行和最后一行外,每行最多有两个元素:第一个元素在原数组中的下标是 l e n G r o u p s × x + y lenGroups \times x + y lenGroups×x+y;第二个元素在原数组中的下标是 l e n G r o u p s × ( x + 1 ) − y lenGroups \times (x + 1) - y lenGroups×(x+1)−y。其中 x 是从 0 开始的行数的下标,y 是从 0 开始的组数的下标。这样我们就确定了转换后每行每列的元素。
class Solution {
public:
string convert(string s, int numRows) {
if (s.size() == 0 || numRows <= 0)
return "";
// 1.如果numRows为1,下面会出现除0的情况。
if (numRows == 1)
return s;
// 2.numRows大于1。
string res = "";
int lenGroups = 2 * numRows - 2;
int numGroups = ceil(1.0 * s.size() / lenGroups);
for (int y = 0; y < numRows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < numGroups; x++) {
// 2.1竖直向下的元素。
int index1 = lenGroups * x + y;
if (index1 >= s.size())
continue;
res.push_back(s[index1]);
// 2.2斜向上的元素。
if (y > 0 && y < numRows - 1) {
int index2 = lenGroups * (x + 1) - y;
if (index2 >= s.size())
continue;
res.push_back(s[index2]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
分析:时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),空间复杂度是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
5. LeetCode 8.字符串转换整数
题目:输入的字符串形式是:(0 或多个空格,0 或 1 个正负号,0 或多个数字字符,0 或多个非数字字符)。
注意:遇到非数字字符就停止解析。
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
if (s.size() == 0)
return 0;
// 1.获取符号和第一个数字的下标。
bool positive = true;
int start = -1, end;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '+') {
if (s[i] == '-')
positive = false;
if (i == s.size() - 1 || s[i + 1]<'0' || s[i + 1]>'9')
return 0;
start = i + 1;
break;
}
// 找到第一个数字。
else if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9') {
start = i;
break;
}
// 遇到非空格字符就停止解析。
else if (s[i] != ' ')
return 0;
}
if (start == -1)
return 0;
// 2.获取最后一个数字的下标。
end = start;
while (end < s.size() && s[end] >= '0' && s[end] <= '9') {
end++;
}
// 3.获取有效的数字部分。
s = s.substr(start, end - start);
// 4.存放结果。
int sum = 0;
int len = s.size();
// 5.处理正数。
int max = INT_MAX;
if (positive == true) {
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s[i] == '0')
continue;
int exponent = len - 1 - i;
if (exponent > 9)
return INT_MAX;
if (exponent == 9 && s[i] > '2')
return INT_MAX;
int numi = (s[i] - '0') * pow(10, exponent);
if (numi >= INT_MAX - sum)
return INT_MAX;
sum += numi;
}
return sum;
}
// 6.处理负数。
else {
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s[i] == '0')
continue;
int exponent = len - 1 - i;
if (exponent > 9)
return INT_MIN;
if (exponent == 9 && s[i] > '2')
return INT_MIN;
int numi = (s[i] - '0') * pow(10, exponent);
if (numi - 1 >= INT_MAX - sum) // 注意这里是INT_MAX而不是INT_MIN。
return INT_MIN;
sum += numi;
}
return -1 * sum;
}
}
};
处理越界问题:INT_MAX = 2147483647,INT_MIN = -2147483648,最高位是 2 乘 10 的 9 次方。因为这两个边界的绝对值不相同,所以我们分开讨论,如第 5 部分和第 6 部分。每一部分我们都这样处理:
- 先确保加数 numi 不越界。如果一个数的某个数位上的数大于 0 且下标(低位从 0 开始)大于 9 则一定越界,如第 46 行。如果数位下标等于 9 且数位上的数字大于 2 则也越界,如第 48 行。
- 加数 numi 不越界,但和 sum 的和仍可能越界,所以加数 numi 不能超过 INT_MAX - sum。
6. LeetCode 11.盛最多水的容器
题目。
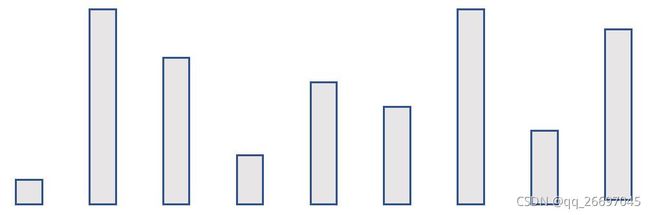
图 6 盛 最 多 水 的 容 器 图\ 6 \quad 盛最多水的容器 图 6盛最多水的容器
分析:使用两层循环穷举任意两条线组成的容器,保留最大容积。这样的方法时间复杂度是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。
双指针法:容器的容积由宽和高共同决定。在本题中,高是无序的,宽是有序的。所以我们可以按宽由大到小的顺序考察:第 1 条线和最后 1 条线组成的容器宽度最大,宽度确定后,容器的容积就由最短的边决定。因为第 1 条线比最后 1 条线短,所以可以得出结论:以第 1 条线为边界的容器,其最大容积是它的长度乘以它与最后 1 条线的距离。这样我们就把第 1 条线的情况考虑完了。
根据上面的讨论可以总结规律:使用两个指针分别指向第 1 条线和第 n 条线,其容积为较短的那条线的长度乘以宽度,然后指向较短的那条线的指针移动一次,把较短的线排除。以此类推直到两个指针相邻。
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
if (height.size() < 2)
return 0;
int res = 0, left = 0, right = height.size() - 1, width = height.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
res = max(res, min(height[left], height[right]) * width);
if (height[left] < height[right])
left++;
else
right--;
width--;
}
return res;
}
};
性能:时间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),空间复杂度是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
7. LeetCode 12.整数转罗马数字
题目。
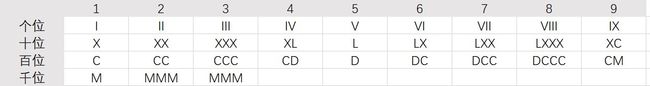
表 7 整 数 转 罗 马 数 字 表\ 7 \quad 整数转罗马数字 表 7整数转罗马数字
分析:由表 7 可以看出,整数转罗马数字时,可以把整数的每个数位上的数 x 分为 5 种情况处理:1<=x<=3、x=4、x=5、6<=x<=8、x=9。当 1<=x<=3 时,x 转换为 x 个 ‘I’、‘X’、‘C’ 或 ‘M’;当 x=4 时,x 转换为 “IV”、“XL”、或 “CD”;当 x=5 时,x 转换为 “V”、“L”、或 “D”;…
个位上的 ‘I’,‘V’,‘X’ 相对于十位上的 ‘X’,‘L’,‘C’,相对于百位上的 ‘C’,‘D’,‘M’,相对于千位上的 ‘M’,’-’,’-’。其中 ‘-’ 用不到。所以我们把这四组存在二维数组中。
class Solution {
public:
string intToRoman(int num) {
if (num < 1)
return "";
char rome[][3] = { { 'I','V','X' },{ 'X','L','C' },{ 'C','D','M' },{'M','-','-'} };
vector<string> res;
string str;
int x, index = 0;
while (num != 0) {
int x = num % 10;
str.clear();
if (x <= 3) {
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) {
str.push_back(rome[index][0]);
}
}
else if (x == 4) {
str.push_back(rome[index][0]);
str.push_back(rome[index][1]);
}
else if (x == 5) {
str.push_back(rome[index][1]);
}
else if (x >= 6 && x <= 8) {
str.push_back(rome[index][1]);
for (int i = 6; i <= x; i++)
str.push_back(rome[index][0]);
}
else {
str.push_back(rome[index][0]);
str.push_back(rome[index][2]);
}
res.push_back(str);
num /= 10;
index++;
}
string res_str;
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res_str += res[i];
return res_str;
}
};
8. LeetCode 15.三数之和
题目。
注意:以某个数 x 开头的三元组可能有多个。
分析:如果不排序,可以使用时间复杂度为 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3) 的算法。如果排序,因为使用双指针法可以设计时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) 的算法在有序数组中找出和为某个数的所有二元组,所以本题使用双指针法可以实现时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) 的算法。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 3)
return{};
// 1.排序。
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res, temp;
// 2.避免重复:先执行一次获取last。
temp = twoSum(nums, 0);
for (auto x : temp)
res.push_back(x);
int last = nums[0];
// 3.主要部分。
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0)
break;
if (nums[i] == last)
continue;
temp.clear();
// 4.固定一个数,查找二元组。
temp = twoSum(nums, i);
for (auto x : temp)
res.push_back(x);
last = nums[i];
}
// 5.如果三元组个数大于2,要去重复。
if (res.size() < 2)
return res;
vector<vector<int>> no_repeat_res = { res[0] };
int i = 0;
for (auto vec : res)
if (vec[0] != no_repeat_res[i][0] || vec[1] != no_repeat_res[i][1] || vec[2] != no_repeat_res[i][2]) {
no_repeat_res.push_back(vec);
i++;
}
return no_repeat_res;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int index) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
int left = index + 1, right = nums.size() - 1;
int target = 0 - nums[index];
while (left < right) {
if (nums[left] + nums[right]>target)
right--;
else if (nums[left] + nums[right] < target)
left++;
else {
res.push_back({ nums[index],nums[left],nums[right] });
left++;
}
}
return res;
}
};
注意:第 2 步和第 5 步都是为了去重复,这两个都不能少。如果没有第 5 步,输入 [0,0,0,0] 会 输出 [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]。twoSum 函数中 left 从 index + 1 开始,而不是从 0 开始。
9. LeetCode 16.最接近的三数之和
题目。
分析:这一题和 LeeCode15 算法相同,所以时间复杂度也是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),但这一题的结果只是一个数,不用考虑结果是否有重复,所以更简单一些。
class Solution {
public:
int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
if (nums.size() < 3)
return{};
// 1.排序。
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int res, min = INT_MAX;
// 2.固定一个数,查找二元组。
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
twoSum(nums, target, i, min, res);
return res;
}
private:
void twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target, int index, int& min, int& res) {
int left = index + 1, right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int three_num_sum = nums[index] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (abs(three_num_sum - target) < min) {
res = three_num_sum;
min = abs(three_num_sum - target);
}
if (three_num_sum > target)
right--;
else
left++;
}
}
};
10. LeetCode 17.电话号码的字母组合
题目。
分析:该问题是求 n 个在指定范围内取值的字符的组合。类似于投掷 n 个骰子,求向上一面点数的集合。这既不是排列问题也不是组合问题,而是一个 n 重循环加回溯问题。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
if (digits.size() == 0)
return {};
// 1.完整的键盘。
vector<vector<char>> keyboard = {
{'a', 'b', 'c'}, {'d', 'e', 'f'},
{'g', 'h', 'i'}, {'j', 'k', 'l'}, {'m', 'n', 'o'},
{'p', 'q', 'r', 's'}, {'t', 'u', 'v'}, {'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'} };
// 2.用到的按键。
vector<vector<char>> keys;
for (char ch : digits)
keys.push_back(keyboard[ch - '2']);
// 3.求按键上字母的组合。
vector<string> res;
permutation(keys, res);
return res;
}
private:
void permutation(vector<vector<char>>& keys, vector<string>& res, int index = 0, string yi = string{}) {
if (index == keys.size()) {
res.push_back(yi);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < keys[index].size(); i++) {
yi.push_back(keys[index][i]);
permutation(keys, res, index + 1, yi);
yi.pop_back();
}
}
};
11. LeetCode 18.四数之和
分析:这个题和《LeetCode 1.两数之和》、《LeetCode 15.三数之和》、《LeetCode 16.最接近的三数之和》方法相同。使用双指针法,求 m 数之和的时间复杂度为 O ( n m − 1 ) O(n^{m-1}) O(nm−1)。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
if (nums.size() < 4)
return {};
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
set<vector<int>> res;
for (int idx1 = 0; idx1 < nums.size() - 3; idx1++)
for (int idx2 = idx1 + 1; idx2 < nums.size() - 2; idx2++) {
int idx3 = idx2 + 1, idx4 = nums.size() - 1;
while (idx3 < idx4) {
int sum = nums[idx1] + nums[idx2] + nums[idx3] + nums[idx4];
if (sum == target) {
res.insert({ nums[idx1], nums[idx2], nums[idx3], nums[idx4] });
idx3++;
idx4--;
}
else if (sum < target)
idx3++;
else
idx4--;
}
}
return vector<vector<int>>(res.begin(), res.end());
}
};
力扣的测试数据范围是 − 1 0 9 -10^9 −109 到 1 0 9 10^9 109,所以第 12 行使用 int 会越界,可以使用 long long 类型,也可以这样:
int sum12 = nums[idx1] + nums[idx2];
int sum34 = nums[idx3] + nums[idx4];
if (sum12 == target - sum34)
重复的结果。为了避免结果中包含重复的四元数,先把结果存放在 set 中,再转移到 vector。
12. LeetCode 19.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(未实现)
使用先后指针只需遍历一次。
13. LeetCode 22.括号生成
这一题可以用回溯法解决。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
if (n < 1)
return {};
vector<string> res;
backtrack(n, n, res);
return res;
}
private:
void backtrack(int left, int right, vector<string>& res, string yi = string{}) {
if (left == 0 && right == 0) {
res.push_back(yi);
return;
}
// 1.只要左括号还有剩余,就可以放左括号。
if (left > 0) {
yi.push_back('(');
backtrack(left - 1, right, res, yi);
yi.pop_back();
}
// 2.只有剩余的右括号多于剩余的左括号时,才可以放右括号。
if (right > left) {
yi.push_back(')');
backtrack(left, right - 1, res, yi);
yi.pop_back();
}
}
};
回溯法的时间复杂度复杂,这里不讨论。我们的算法使用 yi 存放结果的一种可能,所以空间复杂度是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
14. LeetCode 24.两两交换链表中的结点(未实现)
15. LeetCode 29.两数相除
这个题与求快速幂的 LeetCode50:《Pow(x, n)》求解思想相同。
商的意义是被除数中包含几个除数。不用除法求商,可以用被除数减除数,直到被除数小于除数,被除数减除数的次数就是商的整数部分。这种方法可行,但效率低,我们可以仿造快速幂的思想提高效率。先来看个例子,求 100 除以 3 的整数部分:
- 100 大于 3 说明 100 中至少有 1 个 3,100 大于 6 说明 100 中至少有 2 个 3,100 大于 12 说明 100 中至少有 4 个 3,…,100 大于 96 说明 100 中至少有 32 个 3,100 小于 192 说明 100 中没有 192 个 3。至此我们只用 6 步就发现 100 中包含 32 个 3,这比每次减 3 需要 32 步快多了。然后 100 减去 32 个 3 得 4,因为 4 比 3 大,我们还要继续判断 4 中包含多少个 3。
- 4 大于 3 说明 4 中至少有 1 个 3,4 小于 6 说明 4 中没有 2 个 3。至此我们发现 4 中包含 1 个 3。然后 4 减 3 得 1,因为 1 比 3 小,所以剩下的数中不包含 3 了,结束寻找过程。
在第 1 步找到 32 个 3,在第 2 步找到 1 个 3,所以 100 中共有 33 个 3。上面的寻找过程主要是逐步判断被除数是否大于除数、除数的 2 倍,除数的 4 倍,除数的 8 倍…
class Solution {
public:
int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
if (divisor == 0)
throw exception("Divisor can not be zero!");
// 1.确定符号。
bool positive = (dividend ^ divisor) >= 0 ? true : false;
// 2.转换成正数。
long long lldividend = dividend, lldivisor = divisor, res = 0;
lldividend = abs(lldividend), lldivisor = abs(lldivisor);
// 3.核心算法。
while (lldividend >= lldivisor) {
// 4.求最大的 i,使 lldivisor * 2^i <= lldividend。
long long lldivisor_pow2i = lldivisor;
int left_move_time = 0;
while ((lldivisor_pow2i << 1) <= lldividend) {
lldivisor_pow2i <<= 1;
left_move_time++;
}
res += pow(2, left_move_time);
lldividend -= lldivisor_pow2i;
}
// 5.检查越界。
res = positive == true ? res : 0 - res;
if (res >= INT_MAX)
return INT_MAX;
else if (res <= INT_MIN)
return INT_MIN;
else
return res;
}
};
越界问题。第 2 部分把负数转换成正数。 I N T _ M I N = − 2 31 , I N T _ M A X = 2 31 − 1 INT\_MIN = - 2^{31}, INT\_MAX = 2^{31} - 1 INT_MIN=−231,INT_MAX=231−1,当负数是 INT_MIN 时,32 位的 int 类型无法存放其相反数,只能使用 64 位长整型 long long 存放。一定要先转换成长整型再取绝对值,而不能先取绝对值再转换成长整型,因为对 INT_MIN 取绝对值会越界:abs(INT_MIN) = INT_MIN。
16. LeetCode 31.下一个排列
这一题是求全排列的非递归算法的关键,详细的分析过程在全排列。
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() < 2)
return;
// 1.从尾部开始找出第一个长度为2的递增子串。
int p = nums.size() - 1;
while (p > 0) {
if (nums[p - 1] < nums[p])
break;
p--;
}
// 2.当前的排列是最大的,翻转它得到下一个最小排列。
if (p == 0) {
reverse(nums, 0);
return;
}
// 3.从递减子串nums[p:n-1]的尾部开始查找第一个大于nums[p-1]的元素nums[min_index]。
int min_index = nums.size() - 1;
while (nums[min_index] <= nums[p - 1])
min_index--;
// 4.交换nums[p-1]与nums[min_index]。
swap(nums[p - 1], nums[min_index]);
// 5.把递减子串nums[p:n-1]翻转成递增子串。
reverse(nums, p);
}
private:
void reverse(vector<int>& nums, int start) {
int end = nums.size() - 1;
while (start < end) {
swap(nums[start], nums[end]);
start++;
end--;
}
}
};
特别注意第 20 行是小于等于号,不要写成小于号。
17. LeetCode 33.搜索旋转排序数组
这一题考察在旋转数组中查找 target。因为有序,所以可以使用二分查找。
这一题的数组中的元素各不相同,也就是说旋转数组的前后两个递增子串都是严格递增的。LeetCode 81《搜索旋转排序数组 II》没有限制输入的元素各不相同,增加了难度。
与旋转数组相关的题目还有 LeetCode 189《旋转数组》,考察怎么用 O(1) 的空间复杂度生成旋转数组;《剑指 Offer 第2版》第 11 题《旋转数组的最小数字》查找旋转数组的最小值。
这里的 3.2 节详细讲解了在旋转数组中查找最小值、最大值和任意值的算法。
18. LeetCode 34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置(未实现)
19. LeetCode 36.有效的数独
遍历三次、使用一个长度最长为 9 的 set:每次遍历时,使用 set 保存一行、一列或一个小区域内的字符以便检查重复。
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if (board.size() != 9 || board[0].size() != 9)
return false;
unordered_set<char> ust;
// 1.检查每一行。
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
ust.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
if (ust.count(board[i][j]) == 1)
return false;
ust.insert(board[i][j]);
}
}
// 2.检查每一列。
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
ust.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
if (ust.count(board[i][j]) == 1)
return false;
ust.insert(board[i][j]);
}
}
// 3.检查每个小区域。
for (int cx = 1; cx < 9; cx += 3) {
for (int cy = 1; cy < 9; cy += 3) {
ust.clear();
for (int i = cx - 1; i <= cx + 1; i++) {
for (int j = cy - 1; j <= cy + 1; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
if (ust.count(board[i][j]) == 1)
return false;
ust.insert(board[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
遍历一次、使用 27 个长度最长为 9 的 set:
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
if (board.size() != 9 || board[0].size() != 9)
return false;
vector<unordered_multiset<char>> usts(27);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.')
continue;
if (usts[i].count(board[i][j]) > 0)
return false;
if (usts[9 + j].count(board[i][j]) > 0)
return false;
if (usts[18 + i / 3 * 3 + j / 3].count(board[i][j]) > 0)
return false;
usts[i].insert(board[i][j]);
usts[9 + j].insert(board[i][j]);
usts[18 + i / 3 * 3 + j / 3].insert(board[i][j]);
}
}
return true;
}
};
20. LeetCode 38.外观数列
class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
if (n <= 0)
return "";
string res = "1";
vector<pair<int, char>> statistics;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
// 1.统计外观数列的每个组。
statistics.push_back({ 1,res[0] });
char last_char = res[0];
for (int j = 1; j < res.size(); j++) {
if (res[j] == last_char)
statistics.back().first++;
else {
statistics.push_back({ 1,res[j] });
last_char = res[j];
}
}
// 2.根据统计结果生成新的外观数列。
res.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < statistics.size(); i++) {
res.push_back(statistics[i].first + '0');
res.push_back(statistics[i].second);
}
statistics.clear();
}
return res;
}
};
21. LeetCode 39.组合总和
该题的数据量和数据范围都比较小,意味着除分治算法外,难以找到其它好方法。
该题和《LeetCode 1.两数之和》、《LeetCode 15.三数之和》、《LeetCode 16.最接近的三数之和》、《LeetCode 18.四数之和》同是求和,区别在于该题求和的加数个数没有限制,这就类似《LeetCode 10.正则表达式匹配》,可以使用分治算法。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.size() == 0)
return{};
set<vector<int>> pre_res;
DAC(candidates, target, pre_res);
backtrack(candidates, target, pre_res);
vector<vector<int>> res(pre_res.begin(), pre_res.end());
return res;
}
private:
void DAC(vector<int>& candidates, int target, set<vector<int>>& res, vector<int> yi = {}, int index = 0, int sum = 0) {
if (sum > target || index >= candidates.size())
return;
if (sum == target) {
res.insert(yi);
return;
}
DAC(candidates, target, res, yi, index + 1, sum);
yi.push_back(candidates[index]);
sum += candidates[index];
DAC(candidates, target, res, yi, index, sum);
DAC(candidates, target, res, yi, index + 1, sum);
}
void backtrack(vector<int>& candidates, int target, set<vector<int>>& res, vector<int>& yi = vector<int>{}, int index = 0, int sum = 0) {
if (sum > target || index >= candidates.size())
return;
if (sum == target) {
res.insert(yi);
return;
}
// 1.不使用candidates[index]。
backtrack(candidates, target, res, yi, index + 1, sum);
// 2.使用candidates[index]。
yi.push_back(candidates[index]);
sum += candidates[index];
// 2.1继续使用candidates[index]。
backtrack(candidates, target, res, yi, index, sum);
// 2.2不再使用candidates[index]。
backtrack(candidates, target, res, yi, index + 1, sum);
// 撤销2。
// sum -= yi.back();
yi.pop_back();
}
};
该题还给出了回溯算法版的分治算法。它们的区别在于形参 yi,分治算法中的 yi 是值传递,递归函数栈中的每个函数都会有一个 yi 副本;回溯算法中的 yi 是引用传递,所有递归函数共享一个 yi 的实参,这样节省的内存是很明显的:
本题中函数的形参尽量都使用默认参数。函数 backtrack 的第 4 个引用类型的形参 yi 也被赋予默认参数,有些编译器是不支持这样的,比如力扣。这时需要传递过来一个实参。
题目中说了 candidates 中的元素是正整数,如果没有限定正数,不应该在 “sum > target” 时 return。为了避免结果中出现重复,本题先把结果保存在 set 中,再把 set 中的结果放入 vector。
22. LeetCode 40.组合总和Ⅱ(未实现)
23. LeetCode 43.字符串相乘
分析与解决在 数学算法。
24. LeetCode 45.跳跃游戏Ⅱ
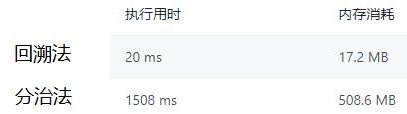
我首先想到的是下面的分治算法。题目限定 1 <= nums.length <= 10000,所以下面的分治算法果然在长度为 39 的第 73/106 个测试数据 x73 上超时了。经测试,使用 x73 的后 35 个元素可以在几秒内计算出答案,但使用完整的 x73 等待很久还是不能得出答案。
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() <= 1)
return 0;
int res = INT_MAX;
DAC(nums, res);
return res;
}
private:
void DAC(vector<int>& nums, int& step, int yi = 0, int location = 0) {
if (location >= nums.size())
return;
if (location == nums.size() - 1)
step = min(step, yi);
for (int i = 1; i <= nums[location]; i++)
DAC(nums, step, yi + 1, location + i);
}
};
// vector x73 = { 5,6,4,4,6,9,4,4,7,4,4,8,2,6,8,1,5,9,6,5,2,7,9,7,9,6,9,4,1,6,8,8,4,4,2,0,3,8,5 };
上面的分治算法是一种穷举算法,它枚举了所有可能的跳跃。下面我们找高效的枚举方法。
分析数组 nums = { 2,5,3,1,1,1,9,1,1,1}。我们很容易知道最少需要 3 步就能到达末尾,其中第 3 步要从 9 开始跳。现在我们从头分析,第 1 步可以调到 5 和 3,我们应该跳到哪一个呢?如果跳到 5,下一步可以跳的范围是 (nums[2], nums[6]);如果跳到 3,下一步可以跳的范围是 (nums[3], nums[5])。因为通过前者可以跳得更远,下次选择的范围更大,所以应该跳到 5。
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() <= 1)
return 0;
return DAC1(nums);
}
private:
int DAC1(vector<int>& nums, int location = 0) {
if (location == nums.size() - 1)
return 0;
if (location + nums[location] >= nums.size() - 1)
return 1;
int min_stop = location + 1, max_stop = location + nums[location];
int stop = find_stop(nums, min_stop, max_stop);
return 1 + DAC1(nums, stop);
}
int DAC2(vector<int>& nums, int location = 0, int last_max_stop = 0) {
if (location == nums.size() - 1)
return 0;
if (location + nums[location] >= nums.size() - 1)
return 1;
int min_stop = last_max_stop + 1, max_stop = location + nums[location];
int stop = find_stop(nums, min_stop, max_stop);
return 1 + DAC2(nums, stop, max_stop);
}
int find_stop(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end) {
int stop = start, next_span = start + nums[start];
for (int i =start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
if (i + nums[i] > next_span) {
stop = i;
next_span = i + nums[i];
}
}
return stop;
}
};
25. LeetCode 64.最小路径
本题求的是从左上角到右下角的最小路径,可以直接返回 dp[H - 1][W - 1]。如果求的是从左上角到底部的最小路径,应该返回 dp[H - 1] 的最小值。
class Solution {
public:
int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
if (grid.size() == 0)
return 0;
int H = grid.size(), W = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(H, vector<int>(W));
for (int y = 0; y < H; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < W; x++) {
if (y == 0 && x == 0)
dp[y][x] = grid[y][x];
else if (y == 0)
dp[y][x] = dp[y][x - 1] + grid[y][x];
else if (x == 0)
dp[y][x] = dp[y - 1][x] + grid[y][x];
else
dp[y][x] = min(dp[y][x - 1], dp[y - 1][x]) + grid[y][x];
}
}
return dp[H - 1][W - 1];
}
};