DataWhale“深入浅出PyTorch”第八章
教程前四章的打卡记录:深入迁出pytorch专栏
该教程的GitHub地址:深入浅出PyTorch
哔哩哔哩视频地址:深入浅出Pytorch
DataWhale“深入浅出PyTorch”第八章——PyTorch生态简介
PyTorch之所以会在短短的几年时间里发展成为主流的深度学习框架,除去框架本身的优势,还在于PyTorch有着良好的生态圈。
1.图像——torchvision
torchvision经常用来调用预训练模型,加载数据集,对图片进行数据增强的操作。
带 *的部分是我们经常会使用到的一些库,所以在下面的部分我们对这些库进行一个简单的介绍:
- torchvision.datasets *
- torchvision.models *
- torchvision.tramsforms *
- torchvision.io
- torchvision.ops
- torchvision.utils
1.1 torchvision.datasets
torchvision.datasets主要包含了一些我们在计算机视觉中常见的数据集,在0.10.0版本的torchvision下,有以下的数据集:
| Caltech | CelebA | CIFAR | Cityscapes |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMNIST | FakeData | Fashion-MNIST | Flickr |
| ImageNet | Kinetics-400 | KITTI | KMNIST |
| PhotoTour | Places365 | QMNIST | SBD |
| SEMEION | STL10 | SVHN | UCF101 |
| VOC | WIDERFace |
1.2 torchvision.transforms
我们知道在计算机视觉中处理的数据集有很大一部分是图片类型的,如果获取的数据是格式或者大小不一的图片,则需要进行归一化和大小缩放等操作,这些是常用的数据预处理方法。除此之外,当图片数据有限时,我们还需要通过对现有图片数据进行各种变换,如缩小或放大、水平或垂直翻转等,这些是常见的数据增强方法。而torchvision.transforms中就包含了许多这样的操作。
from torchvision import transforms
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToPILImage(), # 这一步取决于后续的数据读取方式,如果使用内置数据集则不需要
transforms.Resize(image_size),
transforms.ToTensor()
])
除了上面提到的几种数据增强操作,在torchvision官方文档里提到了更多的操作,具体使用方法也可以参考本节配套的”transforms.ipynb“,在这个notebook中我们给出了常见的transforms的API及其使用方法,更多数据变换的操作我们可以点击这里进行查看。
1.载入图片
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 加载原始图片
img = Image.open("./figures/Lenna.jpg")
print(img.size)
plt.imshow(img)
2.沿中心切割transforms.CenterCrop(size)
# 对给定图片进行沿中心切割
# 对图片沿中心放大切割,超出图片大小的部分填0
img_centercrop1 = transforms.CenterCrop((500,500))(img)
print(img_centercrop1.size)
# 对图片沿中心缩小切割,超出期望大小的部分剔除
img_centercrop2 = transforms.CenterCrop((224,224))(img)
print(img_centercrop2.size)
plt.subplot(1,3,1),plt.imshow(img),plt.title("Original")
plt.subplot(1,3,2),plt.imshow(img_centercrop1),plt.title("500 * 500")
plt.subplot(1,3,3),plt.imshow(img_centercrop2),plt.title("224 * 224")
plt.show()
3.改变图片的亮度,对比度,饱和度和色调transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0)
# 对图片的亮度,对比度,饱和度,色调进行改变
#随机改变
img_CJ = transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=1,contrast=0.5,saturation=0.5,hue=0.5)(img)
print(img_CJ.size)
plt.imshow(img_CJ)
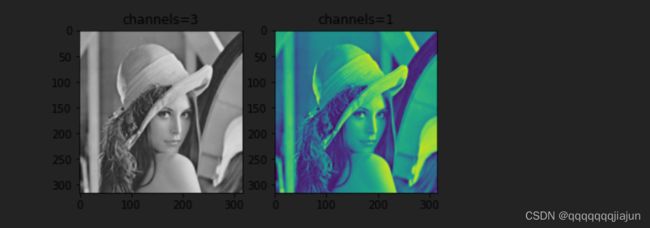
4.灰度变换transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels)
img_grey_c3 = transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=3)(img)
img_grey_c1 = transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1)(img)
plt.subplot(1,2,1),plt.imshow(img_grey_c3),plt.title("channels=3")
plt.subplot(1,2,2),plt.imshow(img_grey_c1),plt.title("channels=1")
plt.show()
5.缩放transforms.Resize
# 等比缩放
img_resize = transforms.Resize(999)(img)
print(img_resize.size)
plt.imshow(img_resize)
6.另一种不推荐的缩放transforms.Scale
# 等比缩放 不推荐使用此转换以支持调整大小
img_scale = transforms.Scale(224)(img)
print(img_scale.size)
plt.imshow(img_scale)
7.随机裁剪 transforms.RandomCrop
# 随机裁剪成指定大小
# 设立随机种子
import torch
torch.manual_seed(31)
# 随机裁剪
img_randowm_crop1 = transforms.RandomCrop(224)(img)
img_randowm_crop2 = transforms.RandomCrop(224)(img)
print(img_randowm_crop1.size)
plt.subplot(1,2,1),plt.imshow(img_randowm_crop1)
plt.subplot(1,2,2),plt.imshow(img_randowm_crop2)
plt.show()
8.随机裁剪transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip
# 随机左右旋转
# 设立随机种子,可能不旋转
import torch
#torch.manual_seed(41)#随机种子
img_random_H = transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip()(img)
print(img_random_H.size)
plt.imshow(img_random_H)
9.随机垂直裁剪
# 随机垂直方向旋转
img_random_V = transforms.RandomVerticalFlip()(img)
print(img_random_V.size)
plt.imshow(img_random_V)
10.随机裁剪成指定大小
# 随机裁剪成指定大小
img_random_resizecrop = transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224,scale=(0.5,0.5))(img)
print(img_random_resizecrop.size)
plt.imshow(img_random_resizecrop)
11.对图片进行组合变化 tranforms.Compose()
# 对一张图片的操作可能是多种的,我们使用transforms.Compose()将他们组装起来
transformer = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.transforms.RandomResizedCrop((224), scale = (0.5,1.0)),
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(),
transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=1,contrast=0.5,saturation=0.5,hue=0.5)
])
img_transform = transformer(img)
plt.imshow(img_transform)
1.3 torchvision.models
为了提高训练效率,减少不必要的重复劳动,PyTorch官方也提供了一些预训练好的模型供我们使用,可以点击这里进行查看现在有哪些预训练模型,下面我们将对如何使用这些模型进行详细介绍。 此处我们以torchvision0.10.0 为例,如果希望获取更多的预训练模型,可以使用使用pretrained-models.pytorch仓库。现有预训练好的模型可以分为以下几类:
- Classification
在图像分类里面,PyTorch官方提供了以下模型,并正在不断增多。
| AlexNet | VGG | ResNet | SqueezeNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet | Inception v3 | GoogLeNet | ShuffleNet v2 |
| MobileNetV2 | MobileNetV3 | ResNext | Wide ResNet |
| MNASNet | EfficientNet | RegNet | 持续更新 |
这些模型是在ImageNet-1k进行预训练好的,具体的使用我们会在后面进行介绍。除此之外,我们也可以点击这里去查看这些模型在ImageNet-1k的准确率。
- Semantic Segmentation
语义分割的预训练模型是在COCO train2017的子集上进行训练的,提供了20个类别,包括background, aeroplane, bicycle, bird, boat, bottle, bus, car, cat, chair, cow, diningtable, dog, horse, motorbike, person, pottedplant, sheep, sofa,train, tvmonitor。
| FCN ResNet50 | FCN ResNet101 | DeepLabV3 ResNet50 | DeepLabV3 ResNet101 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LR-ASPP MobileNetV3-Large | DeepLabV3 MobileNetV3-Large | 未完待续 |
具体我们可以点击这里进行查看预训练的模型的mean IOU和global pixelwise acc
- Object Detection,instance Segmentation and Keypoint Detection
物体检测,实例分割和人体关键点检测的模型我们同样是在COCO train2017进行训练的,在下方我们提供了实例分割的类别和人体关键点检测类别:
COCO_INSTANCE_CATEGORY_NAMES = [
'__background__', 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus','train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light', 'fire hydrant', 'N/A', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow', 'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'N/A', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'N/A', 'N/A','handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee', 'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball','kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard', 'tennis racket','bottle', 'N/A', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl','banana', 'apple', 'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza','donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch', 'potted plant', 'bed', 'N/A', 'dining table','N/A', 'N/A', 'toilet', 'N/A', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone','microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'N/A', 'book','clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier', 'toothbrush']
COCO_PERSON_KEYPOINT_NAMES =['nose','left_eye','right_eye','left_ear','right_ear','left_shoulder','right_shoulder','left_elbow','right_elbow','left_wrist','right_wrist','left_hip','right_hip','left_knee','right_knee','left_ankle','right_ankle']
| Faster R-CNN | Mask R-CNN | RetinaNet | SSDlite |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 未完待续 |
同样的,我们可以点击这里查看这些模型在COCO train 2017上的box AP,keypoint AP,mask AP
- Video classification
视频分类模型是在 Kinetics-400上进行预训练的
| ResNet 3D 18 | ResNet MC 18 | ResNet (2+1) D |
|---|---|---|
| 未完待续 |
同样我们也可以点击这里查看这些模型的Clip acc@1,Clip acc@5
1.4 torchvision.io
在torchvision.io提供了视频、图片和文件的 IO 操作的功能,它们包括读取,写入,编解码处理操作。随着torchvision的发展,io也增加了更多底层的高效率的API。在使用torchvision.io的过程中,我们需要注意以下几点:
- 不同版本之间,
torchvision.io有着较大变化,因此在使用时,需要查看下我们的torchvision版本是否存在你想使用的方法。 - 除了read_video()等方法,torchvision.io为我们提供了一个细粒度的视频API torchvision.io.VideoReader() ,它具有更高的效率并且更加接近底层处理。在使用时,我们需要先安装ffmpeg然后从源码重新编译torchvision我们才能我们能使用这些方法。
- 在使用Video相关API时,我们最好提前安装好PyAV这个库。
1.5 torchvision.ops
torchvision.ops 为我们提供了许多计算机视觉的特定操作,包括但不仅限于NMS,RoIAlign(MASK R-CNN中应用的一种方法),RoIPool(Fast R-CNN中用到的一种方法)。在合适的时间使用可以大大降低我们的工作量,避免重复的造轮子,想看更多的函数介绍可以点击这里进行细致查看。
1.6 torchvision.utils
torchvision.utils 为我们提供了一些可视化的方法,可以帮助我们将若干张图片拼接在一起、可视化检测和分割的效果。具体方法可以点击这里进行查看。
总的来说,torchvision的出现帮助我们解决了常见的计算机视觉中一些重复且耗时的工作,并在数据集的获取、数据增强、模型预训练等方面大大降低了我们的工作难度,可以让我们更加快速上手一些计算机视觉任务。
2.视频——torchbvideo
后面两节不太了解直接上链接了
详细查看:链接
3.文本——torchtext
详细查看:链接