redis源码阅读-rehash详解
背景
今天群里有个小伙伴问rehash的事。翻看下源码,解密下rehash。
我们小了解下rehash是什么
rehash有两个目的:
- (扩容)扩容防止hash冲突后,形成链表带来的性能下降,时间复杂度提升(5倍容量后才扩容);
- (缩容)大量key被回收后,大量的空闲空间,通过rehash节省空间(1/10以下使用量才缩容);
redis为了防止大的dict rehash的时候影响性能,使用了渐进式rehash(并不是一下子执行完,而是通过周期性能任务或访问dict的时候执行搬迁)
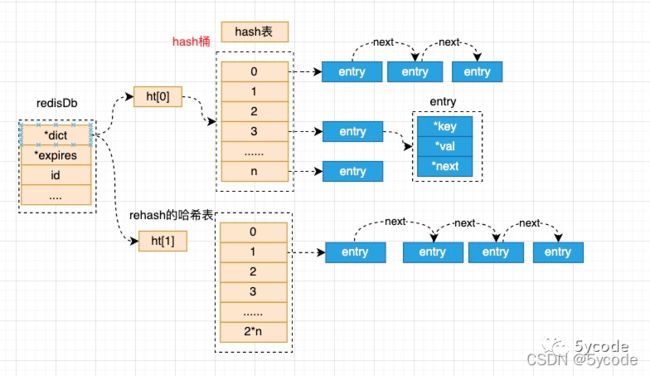
我们先把redis的数据结构摆上
//hash表结构
typedef struct dictht {
//dictEntry 数组,hash桶
dictEntry **table;
//桶的个数
unsigned long size;
//用来取模(size-1)
unsigned long sizemask;
//记录添加的进桶的数量
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
/**
* 位置为0的是保存rehash之前的
* 位置为1的保存rehash过程中的
*/
dictht ht[2];
/**
* rehash时候表示搬迁的槽位,默认为-1,表示没有搬迁
*/
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
//当前迭代的标识,默认为0,为了防止并发
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
- rehash的时候,是吧ht[0]的数据搬迁到ht[1]中
- 搬迁以后会根据hash重新选择对应的桶
rehash的触发时机
rehash的扩容时机
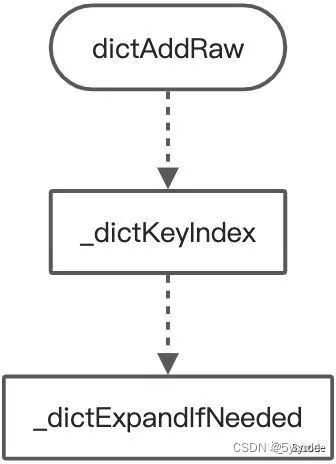
在dict.c中有这么一个方法_dictExpandIfNeeded
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d){
//已经在rehash了,就直接拦截返回成功
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK;
//如果size为零,说明初始化以后,么有插入元素,直接扩展到4
if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE);
/**
* 1,已经插入的元素数量大于总容量
* 2,dict_can_resize 没有被设置为0 ,设置为0禁止resize
* 3, 已插入的元素数量是桶容量的5倍
*/
if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size &&(dict_can_resize ||
d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio)){
//扩展到已用容量的2倍,相当于至少是size的10倍(同时内部还会进行修正)
return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2);
}
return DICT_OK;
}
static long _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key, uint64_t hash, dictEntry **existing){
unsigned long idx, table;
dictEntry *he;
if (existing) *existing = NULL;
/* Expand the hash table if needed */
/**
* 判断是否需要扩容
*/
if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR)
return -1;
//从两个hash表中查找
for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) {
idx = hash & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
......
}
}
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing){
/**
* @brief 根据key计算hash值,如果存在返回-1,
* existing 为对应的指针
*/
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
//正在rehash的时候,选择哪个槽
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
}
- 只有在添加添加元素的时候才会去判断是否需要扩容
- 只有当used是size的5的倍的时候才触发扩容(负载因子:dict_force_resize_ratio)
rehash缩容
在serverCron 的databaseCron 函数中
void databasesCron(void) {
//rehash只在未持久化的时候执行
if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1) {
//申明两个全局变量
static unsigned int resize_db = 0;
static unsigned int rehash_db = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
int j;
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
//是否缩容
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
tryResizeHashTables(resize_db % server.dbnum);
resize_db++;
}
//开始执行rehash的搬迁动作
if (server.activerehashing) {
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
int work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db);
if (work_done) {
break;
} else {
//记录下本次执行到的db,下次执行
rehash_db++;
rehash_db %= server.dbnum;
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 尝试进行rehash以节省内存,主要是缩容
* @param dbid
*/
void tryResizeHashTables(int dbid) {
//使用量小于总槽数的1/10触发缩容
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].dict))
dictResize(server.db[dbid].dict);
if (htNeedsResize(server.db[dbid].expires))
dictResize(server.db[dbid].expires);
}
/**
* 缩容时的判断条件
* @param dict
* @return
*/
int htNeedsResize(dict *dict) {
long long size, used;
size = dictSlots(dict);
used = dictSize(dict);
//当used的容量小于总hash槽总数的1/10的时候,返回true,最小为4
return (size > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(used*100/size < HASHTABLE_MIN_FILL));
}
int dictResize(dict *d){
int minimal;
//已经在rehash 就直接返回
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
//当前使用容量
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
**
* hash桶扩缩容,并创建hash表
* @param d 对应的hash表
* @param size 扩容的大小,内部会修正为2的倍数
* 扩容时传入的是2倍size
* 缩容时传入的是当前使用的大小
* @return
*/
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size){
//已经rehash,进行拦截
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
//重置后的容量,2倍增长,最小为4,相当于一次校验,必须是2的倍数,
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */
//没有变化,就直接返回
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
//新hash表的大小
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
//如果执行完了,就直接置换
d->ht[1] = n;
//设置rehash的索引,从第0个桶开始
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
总结:
- 在周期的任务中,会触发缩容判断,如果已用小于1/10,则进行缩容
- 其次如果已经激活了rehash,则会进行一次搬迁
- 在dictAddRaw的时候,触发扩容判断
- 不管扩容还是缩容,如果触发了,只要是已经在rehash了,就直接拦截,也就是在rehash未进行完之前不会进行第二次
rehash的执行
我们看下rehash执行的源代码
/**
* @brief 渐进式rehash搬迁
* @param d
* @param n 执行次数
* @return int
*/
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
//先判断是否需要rehash,=-1的时候返回true,不等-1就拦截了
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
/**
* 执行次数 并且没有搬空
*/
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
//挨个轮训
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
//获取到对应的桶
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
//获取在新的hash表的位置
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
//采用头插法
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de;
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
//hash索引
d->rehashidx++;
}
/**
* 如果已经搬迁完了,释放ht[0]空间,并将 d->ht[1] 赋值给ht[0]
* 重置ht[1]空间
* 将hash索引 d->rehashidx设置为-1
*/
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
- 通过传入n 表示一次从ht[0]搬几个hash桶的数据到ht[1]
- while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) 主要没有搬迁完就会循环执行
- 搬迁完成以后就会将ht[0]空间释放,将ht[1]赋值给ht[0],ht[1]重置,最后将d->rehashidx 置为-1
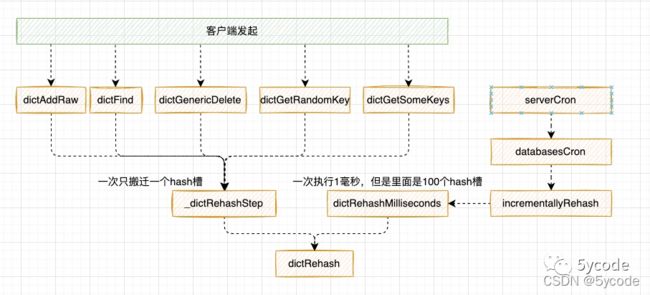
我们看下调用
在调用dict的方法时,一次只搬迁一个hash槽
/**
* 一次只搬迁一个hash槽
* @param d
*/
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
在周期性任务serverCron中
/**
* 执行rehash多少毫秒
* @param d
* @param ms 搬迁执行的毫秒数
* @return
*/
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) {
long long start = timeInMilliseconds();
int rehashes = 0;
//最少搬迁100个桶
while(dictRehash(d,100)) {
rehashes += 100;
//如果超时,就中断循环
if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break;
}
return rehashes;
}
int incrementallyRehash(int dbid) {
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].dict)) {
//1次执行1毫秒
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].dict,1);
return 1;
}
/* Expires */
if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].expires)) {
//1次执行1毫秒
dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].expires,1);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
rehash的搬迁
- 一个是客户端发起的所有的dict的操作方法(不管是get、set、等都绕不开),一次只搬迁1个桶
- 一个是redis在轮训的时候serverCron中的调用,一次执行1毫秒,最少搬迁100个桶
- rehash的时候,如果在此触碰rehash,直接拦截
redis系列文章
redis源码阅读-入门篇
redis源码阅读二-终于把redis的启动流程搞明白了
redis源码阅读三-终于把主线任务执行搞明白了
redis源码阅读四-我把redis6里的io多线程执行流程梳理明白了
redis源码阅读五-为什么大量过期key会阻塞redis?
redis源码六-redis中的缓存淘汰策略处理分析
redis源码阅读-之哨兵流程
redis源码阅读-持久化之RDB
redis源码阅读-持久化之aof
阅读redis源码的时候一些c知识
阅读redis持久化RDB源码的时候一些c知识
linux中的文件描述符与套接字socket
redis中的IO多路复用select和epoll
Reactor模式详解及redis如何使用
redis的key过期了还能取出来?
本文是Redis源码剖析系列博文,有想深入学习Redis的同学,欢迎star和关注;
Redis中文注解版:https://github.com/yxkong/redis/tree/5.0
如果觉得本文对你有用,欢迎一键三连;
同时可以关注微信公众号5ycode获取第一时间的更新哦;