CS231n-assignment3-LSTM
在前面的练习中,您实现了一个普通的RNN并将其应用于图像标题。在本笔记本中,您将实现LSTM更新规则并将其用于图像字幕。
ln[1]:
# Setup cell.
import time, os, json
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cs231n.gradient_check import eval_numerical_gradient, eval_numerical_gradient_array
from cs231n.rnn_layers import *
from cs231n.captioning_solver import CaptioningSolver
from cs231n.classifiers.rnn import CaptioningRNN
from cs231n.coco_utils import load_coco_data, sample_coco_minibatch, decode_captions
from cs231n.image_utils import image_from_url
#%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 8.0) # Set default size of plots.
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
def rel_error(x, y):
""" returns relative error """
return np.max(np.abs(x - y) / (np.maximum(1e-8, np.abs(x) + np.abs(y))))
Load MS-COCO data
ln[2]:
# Load COCO data from disk; this returns a dictionary
# We'll work with dimensionality-reduced features for this notebook, but feel
# free to experiment with the original features by changing the flag below.
data = load_coco_data(pca_features=True)
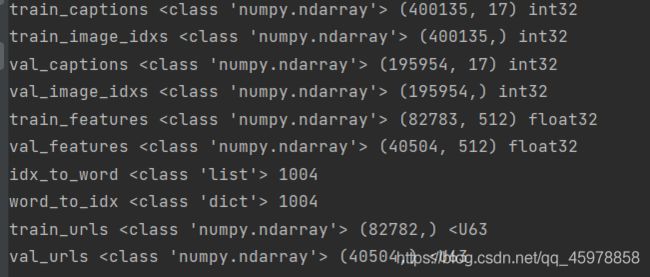
# Print out all the keys and values from the data dictionary
for k, v in data.items():
if type(v) == np.ndarray:
print(k, type(v), v.shape, v.dtype)
else:
print(k, type(v), len(v))
长短期记忆(Long short-term memory, LSTM)是一种特殊的RNN,主要是为了解决长序列训练过程中的梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题。简单来说,就是相比普通的RNN,LSTM能够在更长的序列中有更好的表现。
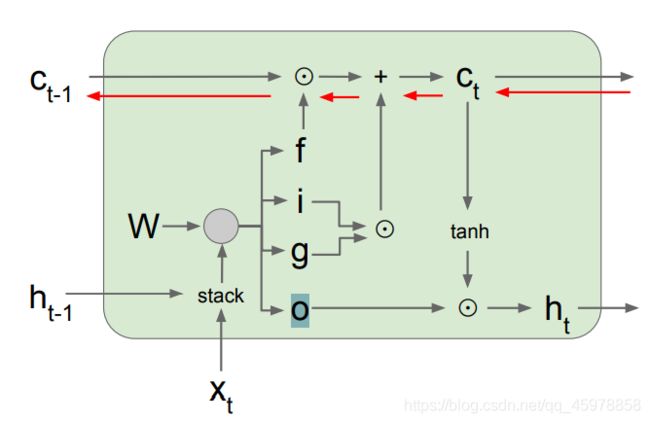
状态传递ct 和 隐藏状态 ht
LSTM: step forward
在文件cs231n/rnn_layers.py中的lstm_step_forward函数中实现LSTM的单个时间步长的forward传递。这应该类似于您在上面实现的rnn_step_forward函数,但使用的是LSTM更新规则。
def lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b):
"""Forward pass for a single timestep of an LSTM.
The input data has dimension D, the hidden state has dimension H, and we use
a minibatch size of N.
Note that a sigmoid() function has already been provided for you in this file.
Inputs:
- x: Input data, of shape (N, D)
- prev_h: Previous hidden state, of shape (N, H)
- prev_c: previous cell state, of shape (N, H)
- Wx: Input-to-hidden weights, of shape (D, 4H)
- Wh: Hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (H, 4H)
- b: Biases, of shape (4H,)
Returns a tuple of:
- next_h: Next hidden state, of shape (N, H)
- next_c: Next cell state, of shape (N, H)
- cache: Tuple of values needed for backward pass.
"""
next_h, next_c, cache = None, None, None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the forward pass for a single timestep of an LSTM. #
# You may want to use the numerically stable sigmoid implementation above. #
#############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N, H = prev_h.shape
h = x.dot(Wx) + prev_h.dot(Wh) + b # [Nx4H]
h[:, 0:3 * H] = sigmoid(h[:, 0:3 * H]) # [Nx4H]
h[:, 3 * H:4 * H] = np.tanh(h[:, 3 * H:4 * H]) # [Nx4H]
i, f, o, g = h[:, :H], h[:, H:2 * H], h[:, 2 * H:3 * H], h[:, 3 * H:4 * H] # [NxH]
next_c = f * prev_c + i * g # [NxH]
next_c_tanh = np.tanh(next_c) # [NxH]
next_h = o * next_c_tanh # [NxH]
cache = (x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b, h, next_c_tanh)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return next_h, next_c, cache
完成之后,运行以下命令对实现执行一个简单的测试。您应该看到e-8或更小的错误。
ln[3]:
N, D, H = 3, 4, 5
x = np.linspace(-0.4, 1.2, num=N*D).reshape(N, D)
prev_h = np.linspace(-0.3, 0.7, num=N*H).reshape(N, H)
prev_c = np.linspace(-0.4, 0.9, num=N*H).reshape(N, H)
Wx = np.linspace(-2.1, 1.3, num=4*D*H).reshape(D, 4 * H)
Wh = np.linspace(-0.7, 2.2, num=4*H*H).reshape(H, 4 * H)
b = np.linspace(0.3, 0.7, num=4*H)
next_h, next_c, cache = lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)
expected_next_h = np.asarray([
[ 0.24635157, 0.28610883, 0.32240467, 0.35525807, 0.38474904],
[ 0.49223563, 0.55611431, 0.61507696, 0.66844003, 0.7159181 ],
[ 0.56735664, 0.66310127, 0.74419266, 0.80889665, 0.858299 ]])
expected_next_c = np.asarray([
[ 0.32986176, 0.39145139, 0.451556, 0.51014116, 0.56717407],
[ 0.66382255, 0.76674007, 0.87195994, 0.97902709, 1.08751345],
[ 0.74192008, 0.90592151, 1.07717006, 1.25120233, 1.42395676]])
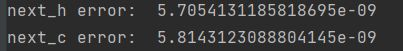
print('next_h error: ', rel_error(expected_next_h, next_h))
print('next_c error: ', rel_error(expected_next_c, next_c))
def lstm_step_backward(dnext_h, dnext_c, cache):
"""Backward pass for a single timestep of an LSTM.
Inputs:
- dnext_h: Gradients of next hidden state, of shape (N, H)
- dnext_c: Gradients of next cell state, of shape (N, H)
- cache: Values from the forward pass
Returns a tuple of:
- dx: Gradient of input data, of shape (N, D)
- dprev_h: Gradient of previous hidden state, of shape (N, H)
- dprev_c: Gradient of previous cell state, of shape (N, H)
- dWx: Gradient of input-to-hidden weights, of shape (D, 4H)
- dWh: Gradient of hidden-to-hidden weights, of shape (H, 4H)
- db: Gradient of biases, of shape (4H,)
"""
dx, dprev_h, dprev_c, dWx, dWh, db = None, None, None, None, None, None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the backward pass for a single timestep of an LSTM. #
# #
# HINT: For sigmoid and tanh you can compute local derivatives in terms of #
# the output value from the nonlinearity. #
#############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N, H = dnext_h.shape
x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b, h, next_c_tanh = cache
'''注意,这里ifog每个门对应的顺序和上图不是一一对应的哦,要对着上面的梯度图看,不然看不懂'''
i, f, o, g = h[:, :H], h[:, H:2 * H], h[:, 2 * H:3 * H], h[:, 3 * H:4 * H]
# dgate contains gradients w.r.t. each gate
dgate = h.copy()
# sigmoid gradient
dgate[:, :3 * H] = dgate[:, :3 * H] * (1 - dgate[:, :3 * H])
# tanh gradient
dgate[:, 3 * H:4 * H] = 1 - dgate[:, 3 * H:4 * H] ** 2
dnc_tanh = 1 - next_c_tanh ** 2
# calculate gradients in common
dnc_prod = dnext_h * o * dnc_tanh + dnext_c
dgate[:, :H] *= dnc_prod * g
dgate[:, H:2 * H] *= dnc_prod * prev_c
dgate[:, 2 * H:3 * H] *= dnext_h * next_c_tanh
dgate[:, 3 * H:4 * H] *= dnc_prod * i
# calculate final gradients
dx = dgate.dot(Wx.T)
dprev_h = dgate.dot(Wh.T)
dprev_c = dnext_c * f + dnext_h * o * dnc_tanh * f
dWx = x.T.dot(dgate)
dWh = prev_h.T.dot(dgate)
db = dgate.sum(axis=0)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return dx, dprev_h, dprev_c, dWx, dWh, db
完成之后,运行以下命令对实现执行数值梯度检查。你应该看到e-7或更小的错误。
ln[4]:
np.random.seed(231)
N, D, H = 4, 5, 6
x = np.random.randn(N, D)
prev_h = np.random.randn(N, H)
prev_c = np.random.randn(N, H)
Wx = np.random.randn(D, 4 * H)
Wh = np.random.randn(H, 4 * H)
b = np.random.randn(4 * H)
next_h, next_c, cache = lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)
dnext_h = np.random.randn(*next_h.shape)
dnext_c = np.random.randn(*next_c.shape)
fx_h = lambda x: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fh_h = lambda h: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fc_h = lambda c: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fWx_h = lambda Wx: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fWh_h = lambda Wh: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fb_h = lambda b: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fx_c = lambda x: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
fh_c = lambda h: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
fc_c = lambda c: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
fWx_c = lambda Wx: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
fWh_c = lambda Wh: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
fb_c = lambda b: lstm_step_forward(x, prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)[1]
num_grad = eval_numerical_gradient_array
dx_num = num_grad(fx_h, x, dnext_h) + num_grad(fx_c, x, dnext_c)
dh_num = num_grad(fh_h, prev_h, dnext_h) + num_grad(fh_c, prev_h, dnext_c)
dc_num = num_grad(fc_h, prev_c, dnext_h) + num_grad(fc_c, prev_c, dnext_c)
dWx_num = num_grad(fWx_h, Wx, dnext_h) + num_grad(fWx_c, Wx, dnext_c)
dWh_num = num_grad(fWh_h, Wh, dnext_h) + num_grad(fWh_c, Wh, dnext_c)
db_num = num_grad(fb_h, b, dnext_h) + num_grad(fb_c, b, dnext_c)
dx, dh, dc, dWx, dWh, db = lstm_step_backward(dnext_h, dnext_c, cache)
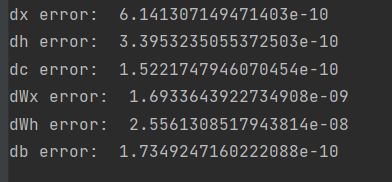
print('dx error: ', rel_error(dx_num, dx))
print('dh error: ', rel_error(dh_num, dh))
print('dc error: ', rel_error(dc_num, dc))
print('dWx error: ', rel_error(dWx_num, dWx))
print('dWh error: ', rel_error(dWh_num, dWh))
print('db error: ', rel_error(db_num, db))
LSTM: forward
在文件cs231n/rnn_layers.py中的函数lstm_forward中,实现lstm_forward函数,对整个时间序列的数据运行LSTM forward。
完成后,运行以下命令检查实现。你应该看到一个e-7或更小的错误。
def lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b):
"""Forward pass for an LSTM over an entire sequence of data.
We assume an input sequence composed of T vectors, each of dimension D. The LSTM uses a hidden
size of H, and we work over a minibatch containing N sequences. After running the LSTM forward,
we return the hidden states for all timesteps.
Note that the initial cell state is passed as input, but the initial cell state is set to zero.
Also note that the cell state is not returned; it is an internal variable to the LSTM and is not
accessed from outside.
Inputs:
- x: Input data of shape (N, T, D)
- h0: Initial hidden state of shape (N, H)
- Wx: Weights for input-to-hidden connections, of shape (D, 4H)
- Wh: Weights for hidden-to-hidden connections, of shape (H, 4H)
- b: Biases of shape (4H,)
Returns a tuple of:
- h: Hidden states for all timesteps of all sequences, of shape (N, T, H)
- cache: Values needed for the backward pass.
"""
h, cache = None, None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the forward pass for an LSTM over an entire timeseries. #
# You should use the lstm_step_forward function that you just defined. #
#############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N, T, D = x.shape
H = h0.shape[1]
prev_h = h0
prev_c = np.zeros(h0.shape)
h = np.zeros((N, T, H))
cache = []
for i in range(T):
next_h, next_c, cache_i = lstm_step_forward(x[:, i, :], prev_h, prev_c, Wx, Wh, b)
h[:, i, :] = next_h
prev_h, prev_c = next_h, next_c
cache.append(cache_i)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return h, cache
ln[5]:
N, D, H, T = 2, 5, 4, 3
x = np.linspace(-0.4, 0.6, num=N*T*D).reshape(N, T, D)
h0 = np.linspace(-0.4, 0.8, num=N*H).reshape(N, H)
Wx = np.linspace(-0.2, 0.9, num=4*D*H).reshape(D, 4 * H)
Wh = np.linspace(-0.3, 0.6, num=4*H*H).reshape(H, 4 * H)
b = np.linspace(0.2, 0.7, num=4*H)
h, cache = lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)
expected_h = np.asarray([
[[ 0.01764008, 0.01823233, 0.01882671, 0.0194232 ],
[ 0.11287491, 0.12146228, 0.13018446, 0.13902939],
[ 0.31358768, 0.33338627, 0.35304453, 0.37250975]],
[[ 0.45767879, 0.4761092, 0.4936887, 0.51041945],
[ 0.6704845, 0.69350089, 0.71486014, 0.7346449 ],
[ 0.81733511, 0.83677871, 0.85403753, 0.86935314]]])
print('h error: ', rel_error(expected_h, h))
LSTM: backward
在文件cs231n/rnn_layers.py中的lstm_backward函数中,对整个时间序列的数据实现LSTM的向后传递。
def lstm_backward(dh, cache):
"""Backward pass for an LSTM over an entire sequence of data.
Inputs:
- dh: Upstream gradients of hidden states, of shape (N, T, H)
- cache: Values from the forward pass
Returns a tuple of:
- dx: Gradient of input data of shape (N, T, D)
- dh0: Gradient of initial hidden state of shape (N, H)
- dWx: Gradient of input-to-hidden weight matrix of shape (D, 4H)
- dWh: Gradient of hidden-to-hidden weight matrix of shape (H, 4H)
- db: Gradient of biases, of shape (4H,)
"""
dx, dh0, dWx, dWh, db = None, None, None, None, None
#############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the backward pass for an LSTM over an entire timeseries. #
# You should use the lstm_step_backward function that you just defined. #
#############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N, T, H = dh.shape
D = cache[0][0].shape[1]
# initialize gradients
dnext_c = np.zeros((N, H))
dnext_h = np.zeros((N, H))
dx = np.zeros((N, T, D))
dWx = np.zeros((D, 4 * H))
dWh = np.zeros((H, 4 * H))
db = np.zeros(4 * H)
# use of lstm step backward per timestep
for i in range(T - 1, -1, -1):
dxi, dprev_h, dprev_c, dWxi, dWhi, dbi = lstm_step_backward(dnext_h + dh[:, i, :], dnext_c, cache[i])
dx[:, i, :] = dxi
dWx += dWxi
dWh += dWhi
db += dbi
dnext_h = dprev_h
dnext_c = dprev_c
dh0 = dnext_h
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return dx, dh0, dWx, dWh, db
完成后,运行以下命令对实现执行数值梯度检查。您应该看到e-8或更小的错误。(对于dWh,如果你的错误是在e-6或更小的顺序上,也没关系)。
ln[6]:
from cs231n.rnn_layers import lstm_forward, lstm_backward
np.random.seed(231)
N, D, T, H = 2, 3, 10, 6
x = np.random.randn(N, T, D)
h0 = np.random.randn(N, H)
Wx = np.random.randn(D, 4 * H)
Wh = np.random.randn(H, 4 * H)
b = np.random.randn(4 * H)
out, cache = lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)
dout = np.random.randn(*out.shape)
dx, dh0, dWx, dWh, db = lstm_backward(dout, cache)
fx = lambda x: lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fh0 = lambda h0: lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fWx = lambda Wx: lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fWh = lambda Wh: lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
fb = lambda b: lstm_forward(x, h0, Wx, Wh, b)[0]
dx_num = eval_numerical_gradient_array(fx, x, dout)
dh0_num = eval_numerical_gradient_array(fh0, h0, dout)
dWx_num = eval_numerical_gradient_array(fWx, Wx, dout)
dWh_num = eval_numerical_gradient_array(fWh, Wh, dout)
db_num = eval_numerical_gradient_array(fb, b, dout)
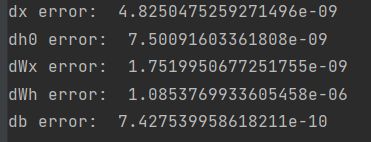
print('dx error: ', rel_error(dx_num, dx))
print('dh0 error: ', rel_error(dh0_num, dh0))
print('dWx error: ', rel_error(dWx_num, dWx))
print('dWh error: ', rel_error(dWh_num, dWh))
print('db error: ', rel_error(db_num, db))
内联的问题
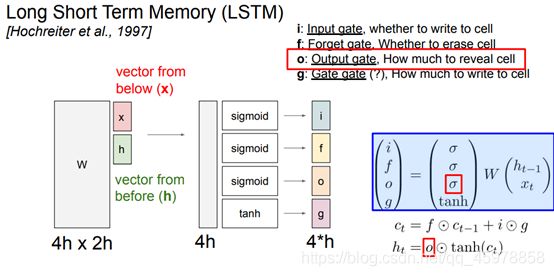
回想一下,在LSTM中,输入门i、忘记门f和输出门o都是sigmoid函数的输出。为什么我们不用ReLU激活函数而是sigmoid函数来计算这些值呢?
答:我们使用sigmoid函数,因为我们想要模拟一个开关,流动之前细胞(f)的value,在细胞(i)输入新的value,或使用细胞的当前value计算的下一个隐藏的状态。回想一下,sigmoid的输出值介于0和1之间。因此,它可以模拟一个开关并允许信息流动。另一方面,ReLU的输出值在0到+inf之间。因此,我们可能会遇到梯度爆炸的问题,没有模拟一个开关
LSTM captioning model
现在,您已经实现了一个LSTM,更新文件cs231n/classifier/rnn.py中CaptioningRNN类的丢失方法的实现,以处理self。cell_type lstm。这需要添加少于10行代码。
在上一个文章中有,大家可以移步Image Captioning with RNNs
完成此操作后,运行以下命令检查实现。你应该看到e-10或更少的顺序上的不同。
ln[7]:
N, D, W, H = 10, 20, 30, 40
word_to_idx = {'' : 0, 'cat': 2, 'dog': 3}
V = len(word_to_idx)
T = 13
model = CaptioningRNN(word_to_idx,
input_dim=D,
wordvec_dim=W,
hidden_dim=H,
cell_type='lstm',
dtype=np.float64)
# Set all model parameters to fixed values
for k, v in model.params.items():
model.params[k] = np.linspace(-1.4, 1.3, num=v.size).reshape(*v.shape)
features = np.linspace(-0.5, 1.7, num=N*D).reshape(N, D)
captions = (np.arange(N * T) % V).reshape(N, T)
loss, grads = model.loss(features, captions)
expected_loss = 9.82445935443
print('loss: ', loss)
print('expected loss: ', expected_loss)
print('difference: ', abs(loss - expected_loss))

Overfit LSTM captioning model
ln[8]:
np.random.seed(231)
small_data = load_coco_data(max_train=50)
small_lstm_model = CaptioningRNN(
cell_type='lstm',
word_to_idx=data['word_to_idx'],
input_dim=data['train_features'].shape[1],
hidden_dim=512,
wordvec_dim=256,
dtype=np.float32,
)
small_lstm_solver = CaptioningSolver(small_lstm_model, small_data,
update_rule='adam',
num_epochs=50,
batch_size=25,
optim_config={
'learning_rate': 5e-3,
},
lr_decay=0.995,
verbose=True, print_every=10,
)
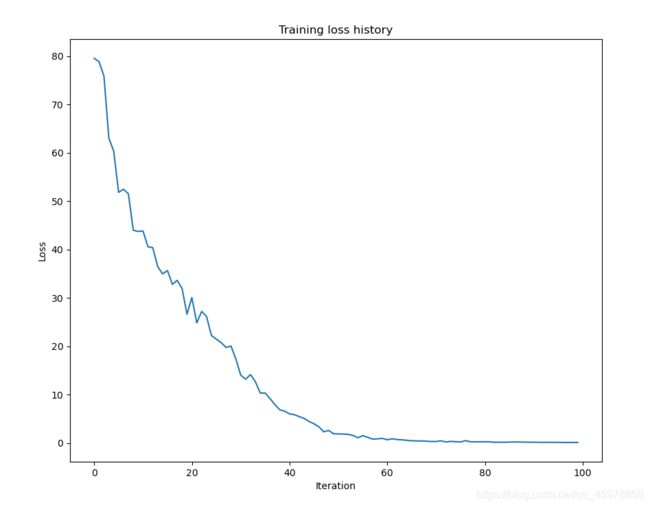
small_lstm_solver.train()
# Plot the training losses
plt.plot(small_lstm_solver.loss_history)
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training loss history')
plt.show()
LSTM test-time sampling
ln[9]:
for split in ['train', 'val']:
minibatch = sample_coco_minibatch(small_data, split=split, batch_size=2)
gt_captions, features, urls = minibatch
gt_captions = decode_captions(gt_captions, data['idx_to_word'])
sample_captions = small_lstm_model.sample(features)
sample_captions = decode_captions(sample_captions, data['idx_to_word'])
for gt_caption, sample_caption, url in zip(gt_captions, sample_captions, urls):
plt.imshow(image_from_url(url))
plt.title('%s\n%s\nGT:%s' % (split, sample_caption, gt_caption))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()