SpringBoot源码分析(5)--createApplicationContext创建应用上下文
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、ApplicationContext简述
-
- 2.1、Spring IOC容器实现方式
- 三、createApplicationContext/创建应用上下文
-
- 3.1、DefaultResourceLoader
- 3.2、AbstractApplicationContext
- 3.3、GenericApplicationContext
-
- 3.3.1、SimpleAliasRegistry
- 3.3.2、DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
- 3.3.3、FactoryBeanRegistrySupport
- 3.3.4、AbstractBeanFactory
- 3.3.5、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
- 3.3.6、DefaultListableBeanFactory
- 3.4、GenericWebApplicationContext
- 3.5、ServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 3.6、AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
-
- 3.6.1、创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
-
- 3.6.1.1、创建ConditionEvaluator
- 3.6.1.2、注册annotation后处理器
- 3.6.2、创建ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
-
- 3.6.2.1、注册缺省过滤器
- 3.6.2.2、设置Environment
- 3.6.2.3、设置ResourceLoader
- 四、总结
一、前言
本文基于spring-boot-2.2.14.BUILD-SNAPSHOT源码分析,createApplicationContext方法。ApplicationContext是spring容器的核心,其实一般我们所说的spring容器,一般也可以说是ApplicationContext,具体点就是ApplicationContext里的DefaultListableBeanFactory,后面在bean的创建时候会详细介绍的,现在就先了解下ApplicationContext的创建,以及在创建时候做的一些初始化工作。
二、ApplicationContext简述
ApplicationContext代表IOC容器,也就是我们常说的上下文,在SpringIOC容器中读取Bean配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化,只有在容器实例化后才可以从IOC容器里获取Bean实例并使用。
Spring容器主要有BeanFactory和ApplicationContext两种类型
2.1、Spring IOC容器实现方式
Spring 提供了两种类型的IOC容器实现:
- BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现,BeanFacotry是Spring中比较原始的Factory。
- ApplicationContext:ApplicationContext继承自BeanFactory接口,是BeanFactory的子接口。拥有更多的企业级方法,原始的BeanFactory无法支持Spring的许多插件,如AOP功能、Web应用等, 所以在实际应用中推荐使用ApplicationContext。
两种方式比较:
- BeanFactory:BeanFactory是Spring框架的基础设施,面向Spring本身
- ApplicationContext : 面向使用Spring框架的开发者,几乎所有的应用场合都直接使用ApplicationContext而非底层的BeanFactory。 无论使用何种方式,配置文件是相同的。
三、createApplicationContext/创建应用上下文
springBoot启动流程创建ApplicationContext的源码
public static final String DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot."
+ "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context."
+ "annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext";
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
// 判断指定的实现类是否存在,不存在则根据应用类型选择,根据名字反射创建ConfigurationApplicationContext具体的实例
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
// 根据webApplicationType类型加载class文件
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
// 创建无参的对象
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
根据上下文中webApplicationType的类型创建实例化对象,对于webApplicationType的类型我们在前面已经分析过了。一般我们都是web服务,所以启动都是servlet类型的。所以这里加载出来的contextClass是
class org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> clazz) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null");
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
return instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor());
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
Constructor<T> ctor = findPrimaryConstructor(clazz);
if (ctor != null) {
return instantiateClass(ctor);
}
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Unresolvable class definition", err);
}
}
进入到类的实例化函数中instantiateClass()
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
//用于确定构造函数的可用。
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is it an abstract class?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Is the constructor accessible?", ex);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Illegal arguments for constructor", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(ctor, "Constructor threw exception", ex.getTargetException());
}
}
大段大段都是异常处理。
1.ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor) 用于确定构造函数的可用。
public static void makeAccessible(Constructor<?> ctor) {
if ((!Modifier.isPublic(ctor.getModifiers()) ||
!Modifier.isPublic(ctor.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) && !ctor.isAccessible()) {
ctor.setAccessible(true);
}
}
2.判断代码是否kotlin
3.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext创建新实例
要了解AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的实例化过程中都做了什么,先要了解其继承结构。下面是其类图。

我们知道子类实例化的时候先实例化父类的构造方法,我们从上往下来看各个父类的构造方法

3.1、DefaultResourceLoader
DefaultResourceLoader: 默认资源加载器,获取默认的类加载器,获取的是当前线程的上下文类加载器。
3.2、AbstractApplicationContext
private ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver;
//构造方法
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
在构造方法中实例化一个resourcePatternResolver ,参数就是PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver是一个Ant模式通配符的Resource查找器,可以用来查找类路径下或者文件系统中的资源。在其中会实例化一个AntPathMatcher,该类实现Ant风格的路径模式(类似于 **/*.xml)
resourcePatternResolver: 也就是资源模式解析器;实际类型是PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver,它是基于模式匹配的,默认使用AntPathMatcher进行路径匹配,它除了支持ResourceLoader支持的前缀外,还额外支持classpath*:用于加载所有匹配的类路径Resource。
3.3、GenericApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext: 通用应用上下文
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
记住这个DefaultListableBeanFactory,非常重要,spring加载的bean都会放到这里面去。
这里直接new一个 DefaultListableBeanFactory 对象,这个对象就是IOC容器最开始的样子,这里其实是已经创建了 bean 工厂, DefaultListableBeanFactory 这个类里面有一个beanDefinitionMap,就是用来存放bean对象的。
在构造方法中会实例化一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
官方注释里说了,GenericApplicationContext与为每次刷新创建新的内部beanfactory实例的其他applicationContext实现不同,此上下文的内部beanfactory从一开始就可用,以便能够在其上注册bean定义。只能调用一次refresh()。在后面刷新上下文的时候,相对于其他上下文在每次刷新的时候都重新创建一个BeanFactory,GenericApplicationContext则不用,在其刷新BeanFactory的方法中,方法上的注释说了Do nothing,什么都不做。在后面的上下文刷新中会详细记录。
我们看一下GenericApplicationContext初始化属性beanFactory,其类型是DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory类图如下:

同样的,在实例化DefaultListableBeanFactory的时候先实例化父类的构造方法。
3.3.1、SimpleAliasRegistry
SimpleAliasRegistry: 简单别名注册器,没有明确的定义构造方法,也就是只有默认的无参构造方法,我们可认为只是实例化了自己。提供了bean别名的增删改查功能
public class SimpleAliasRegistry implements AliasRegistry {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
//key是bean别名
//value是原始bean名称
private final Map<String, String> aliasMap = new ConcurrentHashMap(16);
public SimpleAliasRegistry() {
}
}
3.3.2、DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry: 默认单例bean注册器, 提供了单例bean增删改查等功能,用于注册共享的单例bean,没有明确的定义构造方法,也就是只有默认的无参构造方法,我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
private static final int SUPPRESSED_EXCEPTIONS_LIMIT = 100;
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new Ha
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(256);
private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
private final Set<String> inCreationCheckExclusions =
Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
@Nullable
private Set<Exception> suppressedExceptions;
private boolean singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;
private final Map<String, Object> disposableBeans = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Set<String>> containedBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependentBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
private final Map<String, Set<String>> dependenciesForBeanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
public DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry(){
}
3.3.3、FactoryBeanRegistrySupport
FactoryBeanRegistrySupport: 工厂bean注册器支持,用于注册工厂bean单例,没有明确的定义构造方法,也就是只有默认的无参构造方法,我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
public abstract class FactoryBeanRegistrySupport extends DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry {
private final Map<String, Object> factoryBeanObjectCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(16);
public FactoryBeanRegistrySupport() {
}
}
3.3.4、AbstractBeanFactory
AbstractBeanFactory: 抽象bean工厂。无参构造方法体内为空,我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
//自定义PropertyEditorRegistrar属性编辑器注册器
//用于编辑Factory下的所有bean
private final Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> propertyEditorRegistrars = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
//自定义PropertyEditor属性编辑器
private final Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> customEditors = new HashMap<>(4);
//String值解析器
private final List<StringValueResolver> embeddedValueResolvers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
//Bean创建处理器
private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
//Bean Scope范围支持
//父接口ConfigurableBeanFactory中定义了两个SCOPE
//SCOPE_SINGLETON = "singleton";
//SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = "prototype";
//WebApplicationContext接口中定义了三个SCOPE
//SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
//SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
//SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application"
private final Map<String, Scope> scopes = new LinkedHashMap<>(8);
public AbstractBeanFactory(){
}
}
3.3.5、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory: 抽象的有自动装配装配能力的bean工厂,赋予了自动装配功能,该类提供bean创建(具有构造函数解析),属性填充,接线(包括自动装配)和初始化。 处理运行时bean引用,解析托管集合,调用初始化方法等。支持自动装配构造函数,按名称的属性和按类型的属性。无参构造方法中,添加了三个非自动装配的接口:BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware和BeanClassLoaderAware。
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
private InstantiationStrategy instantiationStrategy = new CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy();
@Nullable
private ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
private boolean allowCircularReferences = true;
private boolean allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping = false;
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyTypes = new HashSet<>();
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyInterfaces = new HashSet<>();
private final NamedThreadLocal<String> currentlyCreatedBean = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Currently created bean");
private final ConcurrentMap<String, BeanWrapper> factoryBeanInstanceCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Method[]> factoryMethodCandidateCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, PropertyDescriptor[]> filteredPropertyDescriptorsCache =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
//自动装配忽略BeanNameAware接口
this.ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
//自动装配忽略BeanFactoryAware接口
this.ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
//自动装配忽略BeanClassLoaderAware接口
this.ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
}
3.3.6、DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory: ListableBeanFactory的默认实现,该类用于注册所有bean定义、也可用作独立的bean工厂,当然也可以用作我们自定义bean工厂的父类。无参构造方法中也只是调用了super(),我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
public DefaultListableBeanFactory() {
super();
}
}
3.4、GenericWebApplicationContext
GenericWebApplicationContext: 通用web应用上下文,在GenericApplicationContext基础上增加web支持,无参构造方法中,只是调用了super(),我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
public GenericWebApplicationContext() {
super();
}
3.5、ServletWebServerApplicationContext
ServletWebServerApplicationContext: servlet web服务应用上下文,能够从自身引导,创建,初始化和运行WebServer,无参构造方法中是空内容,我们可认为只是实例化了自己。
public ServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
}
3.6、AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
//创建一个读取注解的Bean定义读取器
//什么是 Bean 定义?BeanDefinition 完成了 spring 内部 Bean 的 BeanDefinition 的注册(主要是后置处理器)
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//创建 BeanDefinition 扫描器,可以用来扫描包或者类,继而转换为BeanDefinition ,
//spring 默认的扫描器其实不是这个 scanner 对象,而是在后面自己又重新 new 了一个 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//spring 在执行工程后置器 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 时,去扫描包时会 new一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
//这里 scanner 仅仅是为了 程序员可以手动调用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 对象的 scanner方法
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);// 实例化类路径bean定义扫描器
}
构造方法中的内容就是实例化两个bean,并赋值给自己的属性。我们接着往下看,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner到底是什么,构造方法中到底做了什么?
3.6.1、创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader

在看这个方法之前,我们先打个断点,然后看下this里面的 beanDefinitionMap 里面是否有有值,即IOC容器中是否有bean对象,可以看到,到这一步还是没有值的,即还没有bean实例存在IOC容器中。接着我们继续往下看

到这一步的时候可以看到 beanDefinitionMap 已经有bean存进去了,接下来我们重点看下
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 构造方法 都做了哪些事情。
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = AnnotationBeanNameGenerator.INSTANCE;
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
private ConditionEvaluator conditionEvaluator;
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
}
官方对这个类的解释是:
是一个方便的编程式注册bean的适配器。他是ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的另一种选择,对注解应用同样的解决方案,只不过要手动显式注册。
从类注释上来看,作用就是用于编程式注解bean的注册,例如我们平时用到的@Component,还有@Configuration类下的@Bean等。
在这个类中会实例化一个AnnotationBeanNameGenerator和一个AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver。
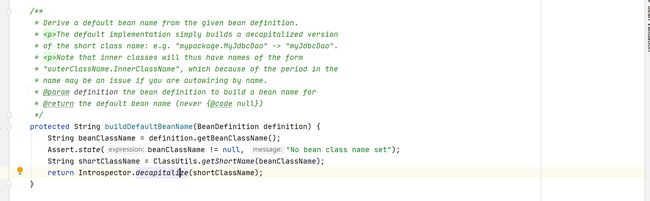
AnnotationBeanNameGenerator: 见名知意,生成beanName。如果属于注解bean定义,即获取注解定义的beanName,不是就获取默认的beanName,即类名首字母小写。isStereotypeWithNameValue()方法会判断注解类型是否是Component或者元注解中是否有Component或者注解类型是否是ManagedBean和Named,且attributes不为空,attributes存在value值。
private static final String COMPONENT_ANNOTATION_CLASSNAME = "org.springframework.stereotype.Component";
@Override
public String generateBeanName(BeanDefinition definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (definition instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
String beanName = determineBeanNameFromAnnotation((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) definition);
if (StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
// Explicit bean name found.
return beanName;
}
}
// Fallback: generate a unique default bean name.
return buildDefaultBeanName(definition, registry);
}
/**
* Derive a bean name from one of the annotations on the class.
* @param annotatedDef the annotation-aware bean definition
* @return the bean name, or {@code null} if none is found
*/
@Nullable
protected String determineBeanNameFromAnnotation(AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedDef) {
AnnotationMetadata amd = annotatedDef.getMetadata();
Set<String> types = amd.getAnnotationTypes();
String beanName = null;
for (String type : types) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(amd, type);
if (attributes != null) {
Set<String> metaTypes = this.metaAnnotationTypesCache.computeIfAbsent(type, key -> {
Set<String> result = amd.getMetaAnnotationTypes(key);
return (result.isEmpty() ? Collections.emptySet() : result);
});
if (isStereotypeWithNameValue(type, metaTypes, attributes)) {
Object value = attributes.get("value");
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = (String) value;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(strVal)) {
if (beanName != null && !strVal.equals(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Stereotype annotations suggest inconsistent " +
"component names: '" + beanName + "' versus '" + strVal + "'");
}
beanName = strVal;
}
}
}
}
}
return beanName;
}
AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver 即Scope注解元数据解析。扫描Scope注解并设置值。

是否属于注解定义,是就转为注解定义并得到attributes对象,该对象包含了注解信息,如果attributes不为空,得到value值即Scope的取值,并设置到ScopeName,再设置代理模式,最后返回Scopemetadata对象。

回到构造方法

上面看官方注释的时候说了方便的适配器,在构造方法中的参数类型是BeanDefinitionRegistry,实际传进来的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,这就是对象的适配。通过看类图可以知道AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的父类GenericApplicationContext实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口。所以这里AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext可以被当做一个registry。
这里的registry就是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext本身, 因为AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext是新创建的,所以getOrCreateEnvironment(registry)返回的一定是一个新的StandardEnvironment。而将之前创建的Environment注入到这里是在准备ApplicationContext阶段进行的。
这边还有个问题,在createApplicationContext()方法之前的prepareEnvironment方法中已经读取了环境变量,为什么这里还要再重新创建一个?这个问题在最后的总结中将给出答案。

public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// 推断ApplicationContext所需要的BeanFactory,Classloader等
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
// 注册annotation postprocessor
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader实例的构造方法一共有2行逻辑, 首先会根据registry创建BeanFactory,Classloader等,然后给registry也就是ApplicationContext注册所有相关的annotation postprocessor,下面我们先来看看如果推断出BeanFactory和各种loader的
3.6.1.1、创建ConditionEvaluator
@Conditional注解的条件评估器, 评估是否满足条件
//@Conditional注解的解析器
//也可用于@ConditionalOnBean,@ConditionalOnClass,@ConditionalOnExpression,@ConditionalOnMissingBean等子注解
class ConditionEvaluator {
//内部类
private final ConditionContextImpl context;
//构造函数
public ConditionEvaluator(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.context = new ConditionContextImpl(registry, environment, resourceLoader);
}
//判断是否应该跳过
public boolean shouldSkip(@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) {
if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) {
//metadata为空或者没有使用@Conditional注解,不跳过
return false;
}
if (phase == null) {
//ConfigurationPhase对象为空,也就是没有设置生效条件
if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata &&
ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) {
//如果是注解的话,使用PARSE_CONFIGURATION配置验证是否跳过
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION);
}
//不是注解的话,使用REGISTER_BEAN配置验证是否跳过
return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN);
}
List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历配置类的条件注解,得到条件数据,放到conditions集合中
for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) {
for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) {
Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader());
conditions.add(condition);
}
}
//按Order注解排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions);
//条件排序
for (Condition condition : conditions) {
ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null;
if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) {
requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase();
}
//添加验证满足,那就跳过
if ((requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) && !condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//私有静态内部类
private static class ConditionContextImpl implements ConditionContext {
public ConditionContextImpl(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
//传入的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext对象
this.registry = registry;
this.beanFactory = deduceBeanFactory(registry);
this.environment = (environment != null ? environment : deduceEnvironment(registry));
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null ? resourceLoader : deduceResourceLoader(registry));
this.classLoader = deduceClassLoader(resourceLoader, this.beanFactory);
}
//推断获取beanFactory
@Nullable
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory deduceBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
return (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) source;
}
if (source instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
//AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext
//调用了GenericApplicationContext中的getBeanFactory方法
//获取到一个DefaultListableBeanFactory对象
return (((ConfigurableApplicationContext) source).getBeanFactory());
}
return null;
}
//获取环境
private Environment deduceEnvironment(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
//AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContex实现了EnvironmentCapable
//调用了AbstractApplicationContext中的getEnvironment方法
//获取到了StandardEnvironment实例
return ((EnvironmentCapable) source).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
//获取ResourceLoader
private ResourceLoader deduceResourceLoader(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry source) {
if (source instanceof ResourceLoader) {
//AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContex实现了ResourceLoader
//所以直接强转
return (ResourceLoader) source;
}
return new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
//获取ClassLoader
@Nullable
private ClassLoader deduceClassLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
@Nullable ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//传入ResourceLoader为null
if (resourceLoader != null) {
ClassLoader classLoader = resourceLoader.getClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
return classLoader;
}
}
if (beanFactory != null) {
//获取到beanFactory不为null
//使用beanFactory中的classloader
return beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader();
}
return ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
}
public ConditionContextImpl(@Nullable BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
@Nullable Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
// 推断哪种beanFactory
this.beanFactory = deduceBeanFactory(registry);
// 推断哪种environment
this.environment = (environment != null ? environment : deduceEnvironment(registry));
// 推断哪种resourceLoader
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null ? resourceLoader : deduceResourceLoader(registry));
// 推断哪种classLoader
this.classLoader = deduceClassLoader(resourceLoader, this.beanFactory);
}
- beanFactory: 根据registry的类型推断出哪种beanFactory,前面我们已经提到registry就是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext是ConfigurableApplicationContext的子类,所以最后得到的是DefaultListableBeanFactory
- environment:前面我们已经得到了一个新的StandardEnvironment,这里直接设置
- resourceLoader:这里和environment类似,因为AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext本身就是ResourceLoader的子类,所以返回的就是它本身
- classLoader: 将返回beanFactory上的beanClassLoader
3.6.1.2、注册annotation后处理器
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
在registerAnnotationConfigProcessors()方法中,设置了DependencyComparator(依赖比较器),AutowireCandidateResolver(Autowire注解候选解析,即解析@Qualifier注解),以及注册了几个bean定义。AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext被当做registry用来注册bean定义,实际调用的是DefaultListableBeanFactory的registerBeanDefinition方法。
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
/**
* 注册所有相关的注解后处理器annotation postprocessor
*/
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
// 设置DependencyComparator @Order,@Priority的处理bean
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
// 设置AutowireCandidateResolver @Lazy,@Qualifier的处理bean
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
// 注册一个可以处理有@Configuration注解的类到spring的BeanDefinitionMap中,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 注册一个对于@AutoWired和@Value的解析类 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
// 创建一个可以处理有一般类型注解的类的postprocessor,并注册到RootBeanDefinition
//java 自有注解的处理,如@Resource,@PostConstruct,@PreDestroy等
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
// 创建一个可以处理有@Persistence注解的类的postprocessor,并注册到RootBeanDefinitior
// JPA相关注解的处理
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 注册解析@EventListener的类
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 事件工厂的默认实现
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
registerPostProcessor方法主要是将beanDefinition放入beanFactory的beanDefinitionMap属性
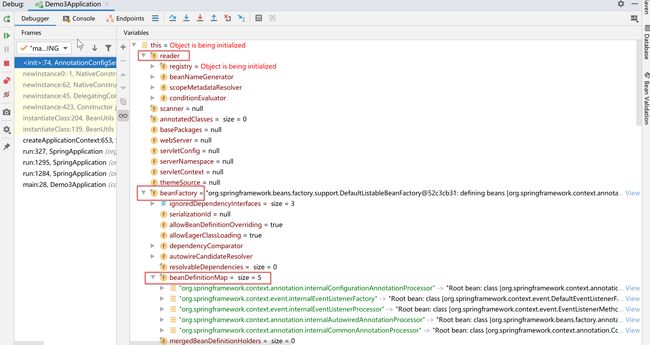
这里是对于几个类加到spring容器中,具体干嘛后面会用到,这里只是先了解下,注册的beanDefinition如下:
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor:对于应用程序下所有Bean解析并且注入到容器中,比如@Component以及被@Component注解的@Service,@Controller,@Repository等,还有@Bean,@Import注解等加到bean定义的map中去。这个后置处理器非常重要,基本上类上面的注解都在这里面判断并解析,spring的包扫描也在里面完成
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:对于@Autowired注解修饰的字段或者方法解析,加入到bean定义的map中
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:对于@Resource注解修饰的字段或者方法解析,加入到spring容器中,并且解析@PostConstruct,@PreDestory注解。这两个注解分别用作Bean初始化和销毁时候用的。后面说到源码时候再说。
- PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 持久性注释Bean后置处理器
对jpa的处理,所以需要引入spring-orm的包,没有引入的话则spring不会注册这个类 - EventListenerMethodProcessor,DefaultEventListenerFactory:这两个类主要用于spring中事件的发布。一般我们在使用spring事件的时候,都是实现ApplicationListener,具体源码逻辑《SpringBoot源码分析(2)–SpringBoot启动源码(万字图文源码debug讲解springboot启动原理)》说过了,可以去看下。但是后来版本中Spring又加了一个@EventListener的注解,这个注解可以放到方法上去。这样就简化了对于事件的使用,就不需要再去实现ApplicationListener了,事件多的时候比较优雅,不然同一个事件,不同的处理方式,就要实现很多的ApplicationListener类了。
3.6.2、创建ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
创建类扫描器ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner会对指定路径下的所有class进行扫描,将符合条件的转成BeanDefinition并注册到ApplicationContext中,这部分会在以后的文章中讲解,下面我们先来看一下如何创建一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner。
/**
* 创建一个新的ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
*/
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// 定义扫描过滤器
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();
}
// 设置环境
setEnvironment(environment);
// 设置resourceLoader
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
3.6.2.1、注册缺省过滤器
首先我们会先注册一个缺省的过滤器Filter,缺省的Filter会检查所有有以下几种注解的类
- @Component
- @Repository
- @Service
- @Controller
- @ManagedBean
- @Named
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
this.includeFilters.add(newAnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));这段代码看上去去只加了Component注解,实际上它会找到所有有Component注解的注解,如Repository,Service,Controller
3.6.2.2、设置Environment
这里Environment的作用是,当有条件注解或者有占位符注解的component类时,可以用Environment里的变量来替代
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.environment = environment;
this.conditionEvaluator = null;
}
3.6.2.3、设置ResourceLoader
设置ResourceLoader是为了后面处理需要加载各种properties里的变量时使用
public void setResourceLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourcePatternResolver = ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader);
this.componentsIndex = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.loadIndex(this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader());
}
该类中同样有BeanDefinitionRegistry,AnnotationBeanNameGenerator,AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver对象。
好的我们再回头再总结下:
createApplicationContext最终创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,方法依次从父类会实例化AbstractApplicationContext–》GenericApplicationContext–》GenericWebApplicationContext–》ServletWebServerApplicationContext–》AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,
其中GenericApplicationContext初始化属性beanFactory,其类型DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory从父类开始初始化,SimpleAliasRegistry–》DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry–》FactoryBeanRegistrySupport–》AbstractBeanFactory–》AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory–》DefaultListableBeanFactory
而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContextt构造方法中初始化了
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader与ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
前者是注解bean定义读取器,用于编程式注解bean的注册;后者是类路径bean定义扫描器,用于检测类路径上的bean候选者。
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReade用来加载class类型的配置,在它初始化的时候,会预先注册一些BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor,这些处理器会在接下来的spring初始化流程中被调用。ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner是一个扫描指定类路径中注解Bean定义的扫描器,在它初始化的时候,会初始化一些需要被扫描的注解。
四、总结
1、文中疑问
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader中为什么还要实例化一个StandardServletEnvironment?
我们可以把这个问题变一下,为什么不把SpringApplication中的environment直接注入到AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader,而是要在AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader中实例化新的StandardServletEnvironment?
我们看下类所在的包可知,SpringApplication是Spring boot的特有的类,而AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader是spring中的类,我们知道spring boot依赖spring,但spring不依赖spring boot,那么我们在spring中能用spring boot特有的内容吗?我们可能又有另外的疑问了,那为什么不先实例化spring中的StandardServletEnvironment,然后将它赋值给SpringApplication,就目前而言,我也不知道,不过在后续应该能找到答案,我们暂且先当一个疑问留着。
2、AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader与ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
前者是注解bean定义读取器,用于编程式注解bean的注册;后者是类路径bean定义扫描器,用于检测类路径上的bean候选者。
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReade用来加载class类型的配置,在它初始化的时候,会预先注册一些BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor,这些处理器会在接下来的spring初始化流程中被调用。ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner是一个扫描指定类路径中注解Bean定义的扫描器,在它初始化的时候,会初始化一些需要被扫描的注解。
3、BeanDefinition
Spring容器里通过BeanDefinition对象来表示Bean,BeanDefinition描述了Bean的配置信息;根据BeanDefinition实例化bean,并放到bean缓存中。
4、spring bean配置方式
有三种:基于XML的配置方式 、基于注解的配置方式和基于Java类的配置方式。
- 基于XML,这个我们都很熟,类似:
- 基于注解,这个我们也用的比较多,入@Component、@Service、@Controller等
- 基于java类,spring的推荐配置方式,@Configuration配合@Bean
5、createApplicationContext到底做了什么
说的简单点:创建web应用上下文,对其部分属性:reader、scanner、beanFactory进行了实例化;reader中实例化了属性conditionEvaluator;scanner中添加了两个AnnotationTypeFilter:一个针对@Component,一个针对@ManagedBean;beanFactory中注册了5个注解配置处理器到DefaultListableBeanFactory的beanDefinitionMap集合中。这些就目前而言,可能没体现其作用,后续肯定会用到的。
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22162093/article/details/106364051