LangChain for LLM Application Development 课程要点
课程链接: https://learn.deeplearning.ai/langchain/
第一节 Introduction
简介了一下 LangChain 等。
第二节 Model, Prompts and parsers
LangChain 提供的一个关键能力就是 output parsing,如果需要返回结构化(JSON)的结果,可以考虑使用 ResponseSchema、StructuredOutputParser。
第三节 Memory
提到了几种memory,重点讲上下文 Conversation Memory,由于大模型有token长度限制,上下文是有限的。
- ConversationBufferWindowMemory 可以按上下文回合数控制上下文记忆长度
- ConversationTokenBufferMemory 可以按token长度来控制上下文记忆长度
- ConversationSummaryMemory 可以对上下文进行摘要处理(压缩)
第四节 Chains
主要讲解了三类 Chain 的用法
LLMChain
这是调用大模型的一个基础用法,使用 Prompt 对输入进行调整。
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the best name to describe \
a company that makes {product}?"
)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
product = "Queen Size Sheet Set"
chain.run(product)
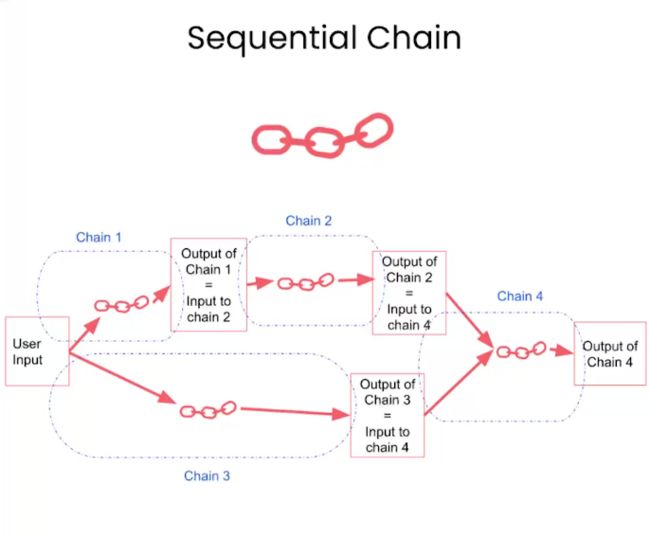
Sequential Chains
将多条 chain 串起来,以实现一个较为复杂的任务。
SimpleSequentialChain
简单的顺序调用
from langchain.chains import SimpleSequentialChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# prompt template 1
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the best name to describe \
a company that makes {product}?"
)
# Chain 1
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt)
# prompt template 2
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a 20 words description for the following \
company:{company_name}"
)
# chain 2
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt)
overall_simple_chain = SimpleSequentialChain(chains=[chain_one, chain_two],
verbose=True
)
overall_simple_chain.run(product)
SequentialChain
将多个 chain 进行组合,其顺序由 input_keys 和 output_keys 决定。
from langchain.chains import SequentialChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# prompt template 1: translate to english
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Translate the following review to english:"
"\n\n{Review}"
)
# chain 1: input= Review and output= English_Review
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt,
output_key="English_Review"
)
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Can you summarize the following review in 1 sentence:"
"\n\n{English_Review}"
)
# chain 2: input= English_Review and output= summary
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt,
output_key="summary"
)
# prompt template 3: translate to english
third_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What language is the following review:\n\n{Review}"
)
# chain 3: input= Review and output= language
chain_three = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=third_prompt,
output_key="language"
)
# prompt template 4: follow up message
fourth_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a follow up response to the following "
"summary in the specified language:"
"\n\nSummary: {summary}\n\nLanguage: {language}"
)
# chain 4: input= summary, language and output= followup_message
chain_four = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=fourth_prompt,
output_key="followup_message"
)
# overall_chain: input= Review
# and output= English_Review,summary, followup_message
overall_chain = SequentialChain(
chains=[chain_one, chain_two, chain_three, chain_four],
input_variables=["Review"],
output_variables=["English_Review", "summary","followup_message"],
verbose=True
)
review = df.Review[5]
overall_chain(review)
Router Chain
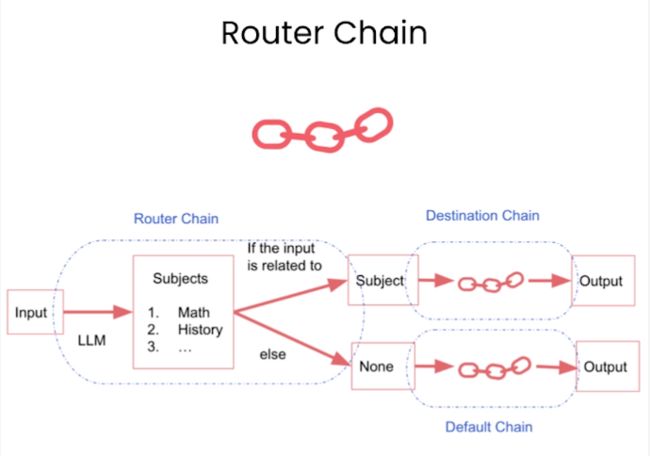
Router Chain 会有多个 destination chains 和一个 default chain, 实际上是使用 LLM 来去对问题进行分类然后选择对应的 destination chain,如果没有匹配上那么就回落到 default chain,他的例子:
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise\
and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit\
that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. \
You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down \
hard problems into their component parts,
answer the component parts, and then put them together\
to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
history_template = """You are a very good historian. \
You have an excellent knowledge of and understanding of people,\
events and contexts from a range of historical periods. \
You have the ability to think, reflect, debate, discuss and \
evaluate the past. You have a respect for historical evidence\
and the ability to make use of it to support your explanations \
and judgements.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
computerscience_template = """ You are a successful computer scientist.\
You have a passion for creativity, collaboration,\
forward-thinking, confidence, strong problem-solving capabilities,\
understanding of theories and algorithms, and excellent communication \
skills. You are great at answering coding questions. \
You are so good because you know how to solve a problem by \
describing the solution in imperative steps \
that a machine can easily interpret and you know how to \
choose a solution that has a good balance between \
time complexity and space complexity.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
prompt_infos = [
{
"name": "physics",
"description": "Good for answering questions about physics",
"prompt_template": physics_template
},
{
"name": "math",
"description": "Good for answering math questions",
"prompt_template": math_template
},
{
"name": "History",
"description": "Good for answering history questions",
"prompt_template": history_template
},
{
"name": "computer science",
"description": "Good for answering computer science questions",
"prompt_template": computerscience_template
}
]
from langchain.chains.router import MultiPromptChain
from langchain.chains.router.llm_router import LLMRouterChain,RouterOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
destination_chains = {}
for p_info in prompt_infos:
name = p_info["name"]
prompt_template = p_info["prompt_template"]
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template=prompt_template)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
destination_chains[name] = chain
destinations = [f"{p['name']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
destinations_str = "\n".join(destinations)
default_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("{input}")
default_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=default_prompt)
MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE = """Given a raw text input to a \
language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. \
You will be given the names of the available prompts and a \
description of what the prompt is best suited for. \
You may also revise the original input if you think that revising\
it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
<< FORMATTING >>
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
```json
{{{{
"destination": string \ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"
"next_inputs": string \ a potentially modified version of the original input
}}}}
REMEMBER: “destination” MUST be one of the candidate prompt
names specified below OR it can be “DEFAULT” if the input is not
well suited for any of the candidate prompts.
REMEMBER: “next_inputs” can just be the original input
if you don’t think any modifications are needed.
<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>
{destinations}
<< INPUT >>
{{input}}
<< OUTPUT (remember to include the ```json)>>“”"
router_template = MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE.format(
destinations=destinations_str
)
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=[“input”],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser(),
)
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(llm, router_prompt)
chain = MultiPromptChain(router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=destination_chains,
default_chain=default_chain, verbose=True
)
```python
chain.run("What is black body radiation?")
chain.run("what is 2 + 2")
chain.run("Why does every cell in our body contain DNA?")
第五节 Q&A over Documents
使用 langchain 的一些内置工具做一个简单的文档问答,会使用OpenAI的Embeddings API。
RetrievalQA 有多种方法,比如最简单的 stuff method:

以及三种更多的方法:
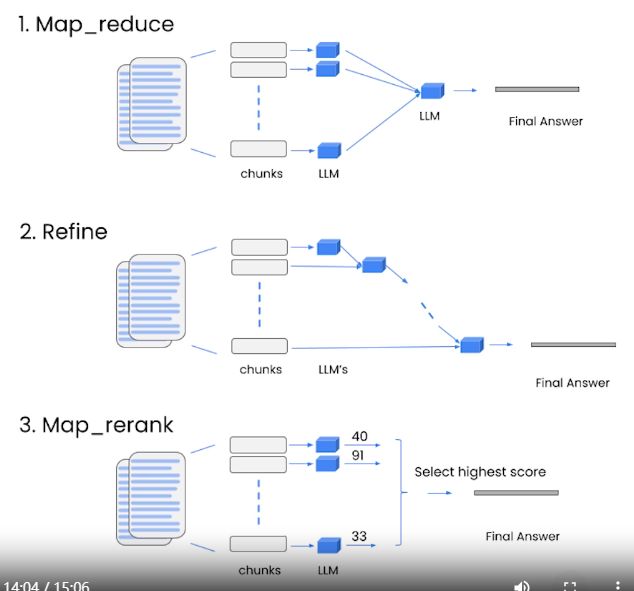
其中 Map_reduce 并行化地去处理数据块,然后再汇总到一个LLM得出最终回答,
Refine 则是串行地去处理数据块,每一次都带上之前的结果,最后得出最终回答,
Map_rerank 也是并行化去处理数据块,然后打分后选择一个最高分的作为最终回答。
这三种方法都比较消耗token,其中并行化的 Map_reduce 跟 Map_rerank 速度会快一些,Refine 速度是最慢的,但处理的质量最佳。
第六节 Evaluation
生成样本、评估和调试、LLM辅助的评估。
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv()) # read local .env file
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.document_loaders import CSVLoader
from langchain.indexes import VectorstoreIndexCreator
from langchain.vectorstores import DocArrayInMemorySearch
file = 'OutdoorClothingCatalog_1000.csv'
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=file)
data = loader.load()
index = VectorstoreIndexCreator(
vectorstore_cls=DocArrayInMemorySearch
).from_loaders([loader])
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature = 0.0)
qa = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=index.vectorstore.as_retriever(),
verbose=True,
chain_type_kwargs = {
"document_separator": "<<<<>>>>>"
}
)
examples = [
{
"query": "Do the Cozy Comfort Pullover Set\
have side pockets?",
"answer": "Yes"
},
{
"query": "What collection is the Ultra-Lofty \
850 Stretch Down Hooded Jacket from?",
"answer": "The DownTek collection"
}
]
from langchain.evaluation.qa import QAGenerateChain
example_gen_chain = QAGenerateChain.from_llm(ChatOpenAI())
new_examples = example_gen_chain.apply_and_parse(
[{"doc": t} for t in data[:5]]
)
examples += new_examples
import langchain
langchain.debug = True
qa.run(examples[0]["query"])
predictions = qa.apply(examples)
from langchain.evaluation.qa import QAEvalChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
eval_chain = QAEvalChain.from_llm(llm)
graded_outputs = eval_chain.evaluate(examples, predictions)
for i, eg in enumerate(examples):
print(f"Example {i}:")
print("Question: " + predictions[i]['query'])
print("Real Answer: " + predictions[i]['answer'])
print("Predicted Answer: " + predictions[i]['result'])
print("Predicted Grade: " + graded_outputs[i]['text'])
print()
第七节 Agent
langchain内置了一些agent比如进行搜索、Wikipedia、执行python等。
我们也可以自定义自己的工具agent,比如自定义一个时间工具可以得到今天的时间:
from langchain.agents import tool
from datetime import date
@tool
def time(text: str) -> str:
"""Returns todays date, use this for any \
questions related to knowing todays date. \
The input should always be an empty string, \
and this function will always return todays \
date - any date mathmatics should occur \
outside this function."""
return str(date.today())
agent= initialize_agent(
tools + [time],
llm,
agent=AgentType.CHAT_ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
verbose = True)