【C++】二叉搜索树
文章目录
- Insert()函数
- Inorder()函数
- Find()函数
- 拷贝构造
- 析构函数
- operator=
- 整体代码
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。二叉搜索树作为一种经典的数据结构,它既有链表的快速插入与删除操作的特点,又有数组快速查找的优势;所以应用十分广泛,例如在文件系统和数据库系统一般会采用这种数据结构进行高效率的排序与检索操作。
为什么叫做排序树?因为中序遍历的结果就是排序的结果。
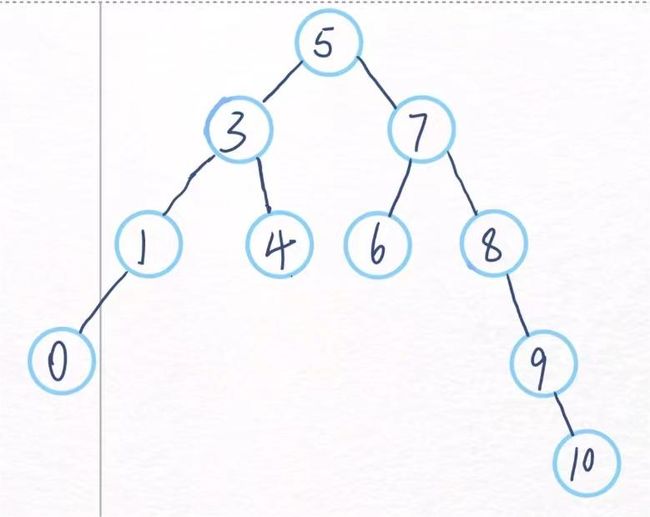
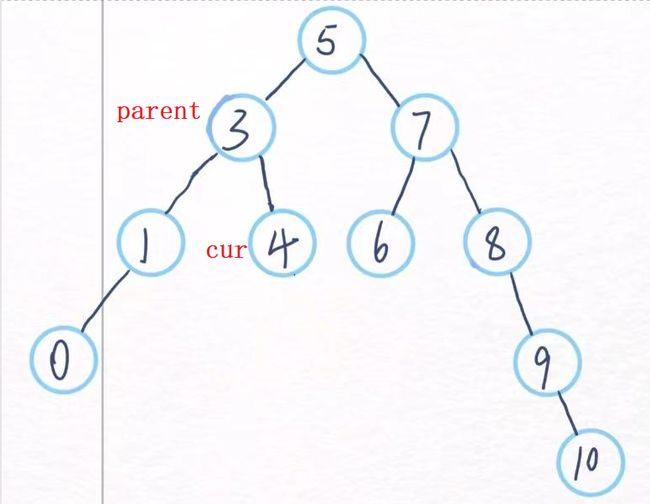
这就是一颗二叉搜索树,左子树的值小于当前节点,右子树的值大于当前节点。
中序遍历的顺序:左 中 右
对上述的搜索二叉树进行中序遍历就是0->1->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->10
首先定义出搜索二叉树的节点,由于需要在类外访问到成员,所以最好定义成strcut。
template
struct TreeNode
{
TreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_key(key)
{}
TreeNode* _left;
TreeNode* _right;
K _key;
};
再定义出一个搜索二叉树的类,里面存好根节点和接口函数。
template
class BSTree
{
typedef TreeNode Node;
public:
private:
Node* _root=nullptr;//根节点
};
Insert()函数
分析:首先判断当前这颗搜索二叉树是否有节点,即判断根节点是否为nullptr,如果为nullptr,直接new一个新节点给root即可。
其次就是判断要插入的值和当前值哪个大?
最重要的就是如何将其连接起来。
需要一个parent指针记录父节点,一个cur记录当前节点,最后利用parent将其连接起来。
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//判断根节点是否为nullptr
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//有相同的值了,不插入
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
if (key < parent->_key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}
然后为了确保正确将节点插入到搜索二叉树当中,再实现一个中序遍历。
Inorder()函数
按照C语言当中应该是如下实现的。
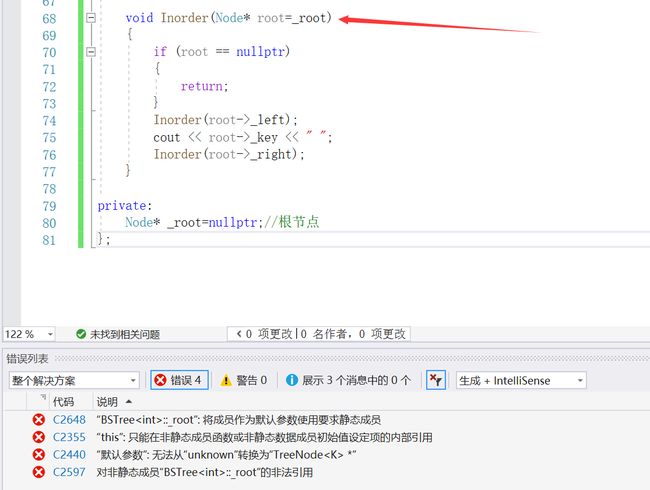
void Inorder(Node* root=_root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
Inorder(root->_right);
}
这里报错的点在于缺省参数不能是成员变量(缺省参数必须是常量),这里可以自己实现一个
get_root()来解决这个问题,但也可以嵌套一层,再一个Inorder()函数里面调用真正的中序遍历_Inorder()。
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
对代码进行测试
BSTree t;
int a[] = { 1,9,8,5,7,2,3,12,13,17,98,91,100,520,521,1314 };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
t.Inorder();
可以看到排序是正常的,说明插入建立搜索二叉树是没有问题的。
然后就是删除某个节点了
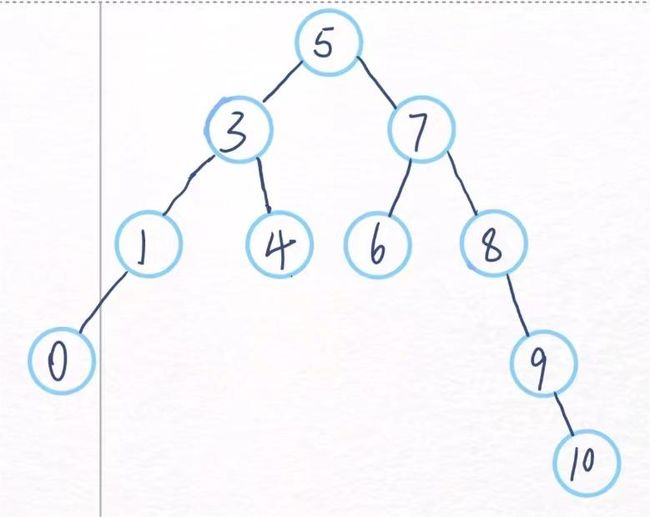
对于图中值为10的节点,如果要删除掉这个节点很简单,直接
delete即可,简单粗暴,这就是第一种情况。case1:要删除的节点为叶子节点,没有左右子树的节点,直接delete。
如果要删除图中值为9的节点,直接将9的父亲节点8指向9的子节点10就行了,然后delete节点9
case2:要删除的节点只有左/右子节点,将当前节点的父亲节点指向当前节点的子节点即可。
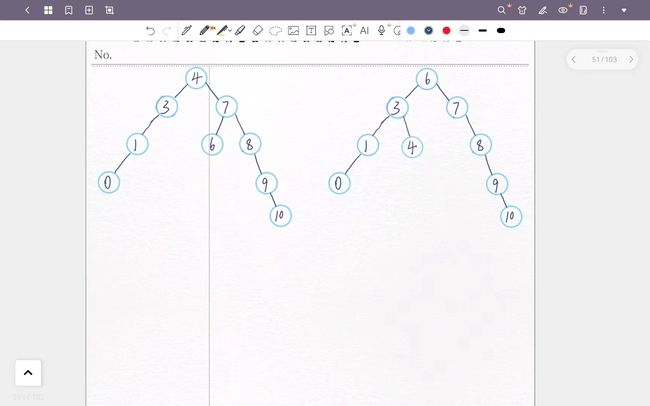
如果要删除5这个节点,如果还继续使用修改指向的方法那会相当的复杂,所以要改变思考方向,直接找值替换掉然后再删除那个节点不就好了。
如图满足替换条件的就是4和6,分别是左子树的最大值和右子树的最小值。
可以看到,是满足二叉搜索树的性质的。
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//已经找到了key,准备删除
//1.没有左儿子
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
//如果当前节点是根节点,那么就无法利用parent来删除节点,而是直接删除
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)//如果在父节点左边
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)//如果在父节点右边
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
}
//2.没有右儿子
else if(cur->_right==nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
}
else
{
//如果存在左右子节点,用右边的最小值替换
Node* minParent = cur;
Node* min = cur->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
minParent = min;
min = min->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, min->_key);
//删除节点
if (minParent->_left == min)
{
minParent->_left = min->_right;
}
else
{
minParent->_right = min->_right;
}
delete min;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
在上述代码当中,如果要删除叶子节点->没有左右儿子的节点,直接走第一个if即可。
模拟一下删除4节点的过程
parent指向3,cur指向4,这时候4的left和right都是nullptr,然后把parent->right指向4的右儿子,就是nullptr,也完成了删除,最后释放cur的空间。
Find()函数
利用递归实现,思路很简单,大于当前值就往左边递归,小于当前值就往右边递归
bool Find(const K& key)
{
return _Find(_root, key);
}
bool _Find(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key == key)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _Find(root->_right, key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Find(root->_left, key);
}
}
#EraseR()函数,递归实现
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
//要删除当前节点
//1.如果是没有左儿子
Node* del = root;//要释放空间的节点,提前记录
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
//如果有左右节点
Node* cur = root->_right;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, root->_key);
//然后再去删除替换后的节点
return _EraseR(root->right, cur->_key);
}
delete del;
del = nullptr;
return true;
}
}
问题1:为什么要用
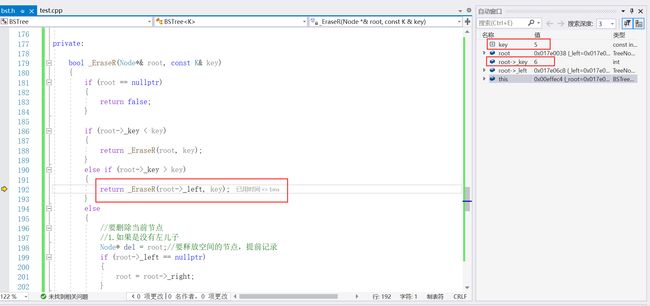
(root->right, cur->_key);而不能_EraseR(root, cur->_key);假如我要删除5,如果用后面那个代码会发生什么?
因为我是在右子树去找最小值,所以就是用5和6交换,然后最后删除右子树的5节点。
可以发现递归没有往右边去找5了,因为这个时候没有将5删掉之前都已经不满足二叉搜索树的性质了,因为此时根节点是6,5比6小自然就往左边找去了,但是左边压根就没有5呀,所以会导致删除失败,因此我们要给一个方向,5是存在又子树,那么就去右边找。
问题2:为什么要传引用?
因为传引用会特别方便,能够直接将节点删除,假如我要删除8这个节点,传递过去的8这个节点又是**
7->right的别名,那么我直接将7->right指向8->right**不就好了吗?也不用去记录父亲节点了。
拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root ==nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* CopyRoot = new Node(root->_key);
CopyRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
CopyRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return CopyRoot;
}
因为同一份数据去构造搜索二叉树却不同的顺序去构造搜索二叉树会导致树的结构不一样,所以不能够采用中序遍历的方式去构造搜索二叉树,而是采用前序遍历。
但如果写了拷贝构造之后编译器就不会生成默认的构造函数了,因为拷贝构造也属于构造,因此可以利用一下C++11的特性,强制编译器生成一个默认的拷贝构造
BSTree() = default;
析构函数
void _Destroy(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
~BSTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
}
采用后序遍历的方式来删除,从下往上删。
operator=
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
直接采用现代写法,再传参的时候会去调用一次拷贝构造给t,但t是局部变量,出了作用域会自动销毁,因此直接把拷贝构造的t的root给_root,等出了作用域还能顺带销毁t,一举两得。
整体代码
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
//class BinarySearchTree
template
class BSTreeNode
{
public:
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_key(key)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
{}
BSTreeNode* _left;
BSTreeNode* _right;
K _key;
};
template
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode Node;
public:
//强制生成默认构造函数
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree& t)
{
_root = _Copy(t._root);
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur!=nullptr)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key == cur->_key)
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (key > parent->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else if (key < parent->_key)
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
//准备删除
//1、没有左儿子
//2、没有右儿子
//3、有左右儿子
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = _root->_right;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (_root == cur)
{
_root = _root->_left;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
}
else
{
Node* minParent = cur;
Node* min = cur->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
minParent = min;
min = min->_left;
}
swap(cur->_key, min->_key);
if (minParent->_left == min)
{
minParent->_left = min->_right;
}
else
{
minParent->_right = min->_right;
}
delete min;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
return _Find(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root,key);
}
~BSTree()
{
_Destroy(_root);
}
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
private:
Node* _Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root ==nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* CopyRoot = new Node(root->_key);
CopyRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);
CopyRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);
return CopyRoot;
}
void _Destroy(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Destroy(root->_left);
_Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;//记录要删除的节点,释放空间
//找到了要删除的节点了
//如果左儿子为空
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* min = root->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, min->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
_InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
_InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool _Find(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (root->_key == key)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _Find(root->_right, key);
}
else if(root->_key > key)
{
return _Find(root->_left, key);
}
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root=nullptr;
};