【NGINX入门指北】Nginx Web 架构实验
Nginx Web 架构实验
文章目录
- Nginx Web 架构实验
- 一、动态网站结构
- 二、LNMP 动态网站环境部署
- 三、fastcgi & php-fpm:
- 四、php-fpm初始化配置
- 五、Nginx Location、
- 六、Nginx Rewrite
- 七、CA&HTTPS
- 八、Nginx 的平滑升级
一、动态网站结构
资源
资源文件识别——语言识别——框架识别
-
index.php
开源的php:Windows/Linux+nginx+php+mysql -
index.py
开源的python:Windows/Linux+apache+python+mysql -
index.jsp
商业JAVA:Windows/Linux+tomcat+JDK+Oracle -
index.asp
商业 C#:Windows+iis+asp.net+sql-server/oracle/mogodb
二、LNMP 动态网站环境部署
1.linux部署
-
关闭防火墙
-
关闭selinux
2.nginx部署
- 安装nginx
[root@nginx1 ~]# yum list | grep nginx
Could not retrieve mirrorlist http://mirrors.elrepo.org/mirrors-elrepo.el7 error was
14: curl#7 - "Failed connect to mirrors.elrepo.org:80; 拒绝连接"
nginx.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx @nginx-stable
nginx-filesystem.noarch 1:1.20.1-10.el7 @epel
rh-nginx116-nginx.x86_64 1:1.16.1-6.el7 @centos-sclo-rh
rh-nginx116-runtime.x86_64 1.16-1.el7 @centos-sclo-rh
zabbix-nginx-conf-scl.noarch 5.0.28-1.el7 @zabbix-frontend
collectd-nginx.x86_64 5.8.1-1.el7 epel
munin-nginx.noarch 2.0.69-5.el7 epel
nginx-all-modules.noarch 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-debug.x86_64 1:1.8.0-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-debuginfo.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-mod-devel.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-mod-http-image-filter.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-mod-http-perl.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-mod-http-xslt-filter.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-mod-mail.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-mod-stream.x86_64 1:1.20.1-10.el7 epel
nginx-module-geoip.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-geoip-debuginfo.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-image-filter.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-image-filter-debuginfo.x86_64
1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-njs.x86_64 1:1.22.1+0.7.10-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-njs-debuginfo.x86_64 1:1.22.1+0.7.10-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-perl.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-perl-debuginfo.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-xslt.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-module-xslt-debuginfo.x86_64 1:1.22.1-1.el7.ngx nginx-stable
nginx-nr-agent.noarch 2.0.0-12.el7.ngx nginx-stable
pagure-web-nginx.noarch 5.13.3-2.el7 epel
pcp-pmda-nginx.x86_64 4.3.2-13.el7_9 updates
python2-certbot-nginx.noarch 1.11.0-1.el7 epel
sympa-nginx.x86_64 6.2.70-2.el7 epel
zabbix-nginx-conf-scl.noarch 5.0.31-1.el7 zabbix-frontend
[root@nginx1 ~]# yum install -y nginx
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 三 2023-02-08 23:46:45 CST; 2 days ago
Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 11615 ExecStop=/bin/sh -c /bin/kill -s TERM $(/bin/cat /var/run/nginx.pid) (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 11621 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 11623 (nginx)
Tasks: 2
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─11623 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
└─11624 nginx: worker process
2月 08 23:46:45 nginx1 systemd[1]: Stopped nginx - high performance web server.
2月 08 23:46:45 nginx1 systemd[1]: Starting nginx - high performance web server...
2月 08 23:46:45 nginx1 systemd[1]: PID file /var/run/nginx.pid not readable (yet?) after start.
2月 08 23:46:45 nginx1 systemd[1]: Started nginx - high performance web server.
[root@nginx1 ~]#
3.php-fpm部署
部署方式
- 方式一:RPM 部署
# php-fpm:php接收动态请求的程序
# php-mysql:php 连接mysql的程序
# php-gd:图形程序(GD库可以处理图片,或者生成图片)
[root@nginx1 ~]# yum install -y php-fpm php-mysql php-gd
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
Could not retrieve mirrorlist http://mirrors.elrepo.org/mirrors-elrepo.el7 error was
14: curl#7 - "Failed connect to mirrors.elrepo.org:80; 拒绝连接"
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* elrepo: elrepo.org
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
Ceph | 1.5 kB 00:00:00
Ceph-noarch | 1.5 kB 00:00:00
base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
ceph-source | 1.5 kB 00:00:00
http://repos.lax-noc.com/elrepo/elrepo/el7/x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] curl#7 - "Failed to connect to 2607:fcd0:0:a::2: 网络不可达"
正在尝试其它镜像。
elrepo | 3.0 kB 00:00:00
epel | 4.7 kB 00:00:00
extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
nginx-stable | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
percona-release-noarch | 1.5 kB 00:00:00
percona-release-x86_64 | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
prel-release-noarch | 1.5 kB 00:00:00
updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
zabbix | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
zabbix-frontend | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
zabbix-non-supported | 2.9 kB 00:00:00
软件包 php-mysql-5.4.16-48.el7.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 php-gd-5.4.16-48.el7.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 php-fpm.x86_64.0.5.4.16-48.el7 将被 安装
--> 解决依赖关系完成
依赖关系解决
=======================================================================================================
Package 架构 版本 源 大小
=======================================================================================================
正在安装:
php-fpm x86_64 5.4.16-48.el7 base 1.4 M
事务概要
=======================================================================================================
安装 1 软件包
总下载量:1.4 M
安装大小:4.5 M
Downloading packages:
php-fpm-5.4.16-48.el7.x86_64.rpm | 1.4 MB 00:00:06
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
正在安装 : php-fpm-5.4.16-48.el7.x86_64 1/1
验证中 : php-fpm-5.4.16-48.el7.x86_64 1/1
已安装:
php-fpm.x86_64 0:5.4.16-48.el7
完毕!
[root@nginx1 ~]#
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl status php-fpm
● php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 六 2023-02-11 21:35:07 CST; 5s ago
Main PID: 17515 (php-fpm)
Status: "Ready to handle connections"
Tasks: 6
CGroup: /system.slice/php-fpm.service
├─17515 php-fpm: master process (/etc/php-fpm.conf)
├─17519 php-fpm: pool www
├─17520 php-fpm: pool www
├─17521 php-fpm: pool www
├─17522 php-fpm: pool www
└─17523 php-fpm: pool www
2月 11 21:35:07 nginx1 systemd[1]: Starting The PHP FastCGI Process Manager...
2月 11 21:35:07 nginx1 systemd[1]: Started The PHP FastCGI Process Manager.
# 开机启动php-fpm
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl enable php-fpm
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service.
[root@nginx1 ~]# netstat -napt | grep 9000
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17515/php-fpm: mast
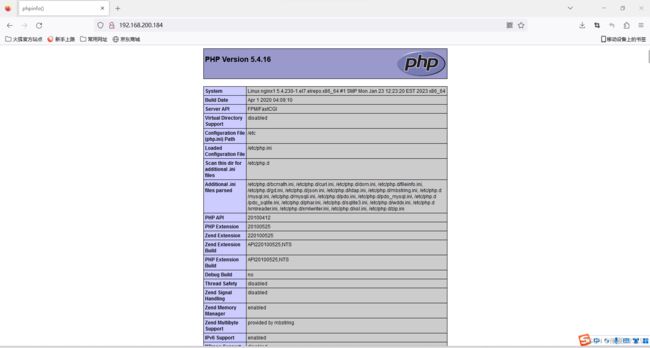
# 测试php页面(php基本信息)
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
# 增加PHP主页名称:index.php
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
location / {
...
index index.php index.html
...
}
}
# 启动nginx_fastcgi功能,去掉#注释修改权限即可
server {
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
- 方式二:源码部署
4.mysql部署
部署方式:
- RPM部署
# 安装mysql服务器程序和客户机程序
#yum install -y mariadb-server mariadb
#systemctl start mariadb
#systemctl enable mariadb
# 修改mysql的root密码为‘123456’
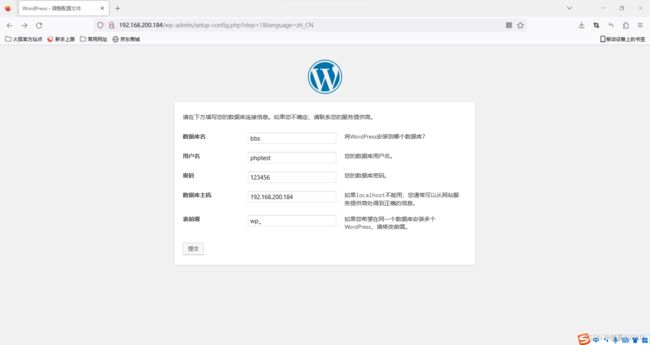
# 准备数据库,存放app
#mysqladmin password '123456' create database bbs;
#grant all on bbs.* to phptest@'192.168.200.184' identified by '123456';
#flush privileges;
测试php是否成功调用mysql
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
<?php
$link=mysql_connect('192.168.200.184','phptest','123456');
if($link)
echo "mysql connect Successfully!";
else
echo "mysql connect faile!";
mysql_close();
?>
[root@nginx1 ~]#
- 源码部署
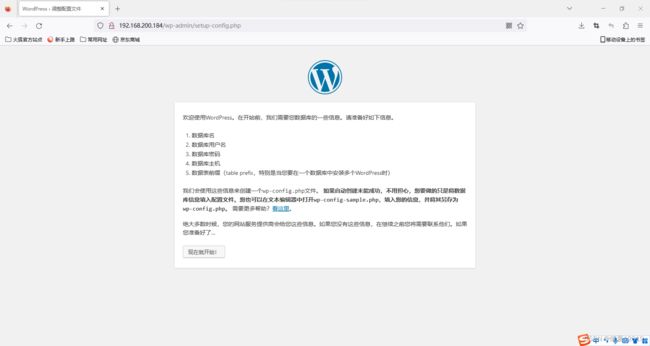
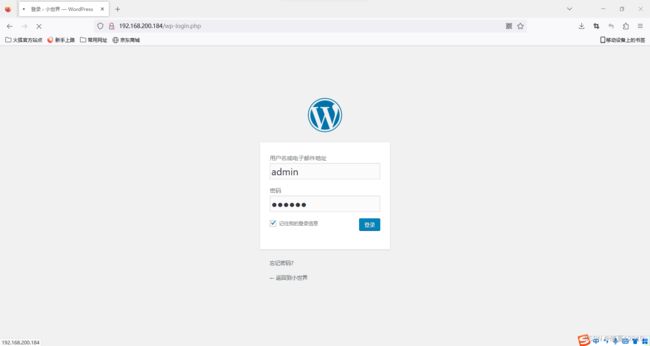
5.业务上线
[root@nginx1 ~]# wget https://cn.wordpress.org/wordpress-4.9.4-zh_CN.zip
[root@nginx1 ~]# unzip wordpress-4.9.4-zh_CN.zip
[root@nginx1 ~]# ls
nginx-1.22.1.tar.gz 公共 模板 桌面
wordpress 视频
wordpress-4.9.4-zh_CN.zip 图片 文档 下载 音乐
zabbix initial-setup-ks.cfg
[root@nginx1 ~]# rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
[root@nginx1 ~]# cp -rf /root/wordpress/* /usr/share/nginx/html
[root@nginx1 ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /usr/share/nginx/html/*
[root@nginx1 ~]# chmod 777 /usr/share/nginx/html

PHP开发相关内容
学习站点:https://www.w3school.com.cn/
- 技术点:
UI:构图
前端:通过表单,文本框,提交按钮,页面布局
后端:php连接函数
DBA:实现后台数据库的写入
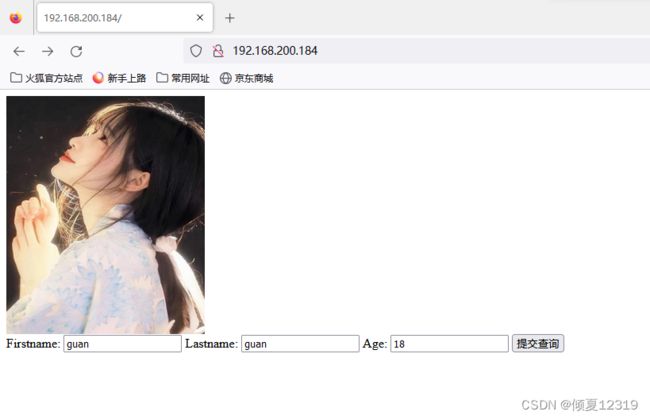
OP:业务上线 - 准备前台页面
[root@nginx1 conf]# cd /usr/share/nginx/html
[root@nginx1 html]# ls
index.html test.jpg
[root@nginx1 html]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
<html>
<body>
<img src="test.jpg" width="250" height="300" />
<form action="insert.php" method="post">
Firstname: <input type="text" name="firstname" />
Lastname: <input type="text" name="lastname" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
[root@nginx1 html]#
- 准备php中间件
[root@nginx1 html]#vim insert.php
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("192.168.200.184","root","123456");
if(!$con)
{
die('could not connectxulei:'.mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("test_db",$con);
$sql="INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName,LastName,Age) VALUES ('$_POST[firstname]','$_POST[lastname]','$_POST[age]')";
if(!mysql_query($sql,$con))
{
die('Error:'.mysql_error());
}
echo"A line of code is successfully executed.";
mysql_close($con);
?>
[root@nginx1 html]# ls
index.html insert.php test.jpg
[root@nginx1 html]#
- 准备表和库
mysql> create database test_db;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> use test_db;
Database changed
mysql> create table Persons(FirstName varchar(50),LastName varchar(50),Age int);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+-------------------+
| Tables_in_test_db |
+-------------------+
| Persons |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc Persons;
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| FirstName | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| LastName | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| Age | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+-----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> grant all on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> grant all on *.* to root@'192.168.200.184' identified by '123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql>
- 后台数据
登录数据库即可看到数据
mysql> use test_db;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from Persons;
+-----------+----------+------+
| FirstName | LastName | Age |
+-----------+----------+------+
| guan | guan | 18 |
+-----------+----------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
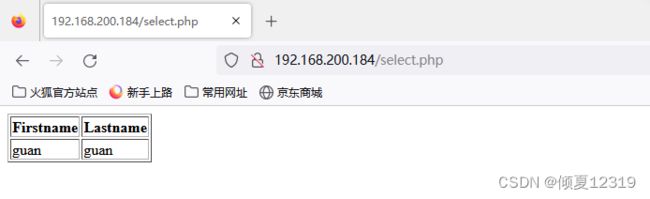
- 输出页面
[root@nginx1 html]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/select.php
[root@nginx1 html]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/select.php
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost","root","123456");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("test_db", $con);
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM Persons");
echo "
Firstname
Lastname
";
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo "";
echo "" . $row['FirstName'] . " ";
echo "" . $row['LastName'] . " ";
echo " ";
}
echo "
";
mysql_close($con);
?>
[root@nginx1 html]#
- 前台输出
三、fastcgi & php-fpm:
-
静态网站:nginx服务器能处理的是静态元素 .html .jpg .mp4 .css
-
Nginx模块:ngx_fastcgi_modul
ngx_fastcgi_modul:处理动态请求的接口。
nginx 通过ngx_fastcgi_modul模块 链接 php-fpm处理动态请求。 -
PHP :php-fpm
PHP-FPM(FastCGI Process Manager:FastCGI进程管理器)是一个PHP FastCGI管理器。
PHP通过php-fpm接收前台nginx的动态访问的请求,比如向后端Mysql进行查询请求后,将查询结果返回给前台nginx。 -
PHP-MYSQL
php-mysql:是php连接mysql的接口程序。 -
MYSQL存储数据
重要知识点:
1.什么是 FastCGI
2.Nginx+FastCGI运行原理
3.LNMP的运行原理
四、php-fpm初始化配置
- php-fpm相关配置文件
1.核心配置文件:
vim /etc/php.ini
date.timezone = PRC # 设置PHP的时区
open_basedir # 设置PHP脚本允许访问的目录.
open_basedir 将PHP所能打开的文件限制在指定的目录树中,包括文件本身。当程序要使用例如fopen()或file_get_contents()打开一个文件时,这个文件的位置将会被检查。当文件在指定的目录树之外,程序将拒绝打开。
2.全局配置文件:
vim /etc/php-fpm.conf
pid = /run/php-fpm/php-fpm.pid # 设置pid文件的位置
error_log = log/php-fpm.log # 记录错误日志的文件
log_level = notice # 记录日志的等级
# alert(必须立即处理), error(错误情况), warning(警告情况), notice(一般重要信息), debug(调试信息). 默认: notice.
process.max = 3 # 默认没设置
# process.max: 控制子进程最大数的全局变量, 后边的设置子进程数量的指令受到这个值的限制, 0表示无限制
daemonize = yes # 将fpm转至后台运行
3.扩展配置文件
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
user = nginx # 设置用户和用户组
listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1
# 允许访问FastCGI进程的IP,设置any为不限制IP,如果要设置其他主机的nginx也能访问这台FPM进程,listen处要设置成本地可被访问的IP。默认值是any。每个地址是用逗号分隔. 如果没有设置或者为空,则允许任何服务器请求连接
listen = 127.0.0.1:9000
# fpm监听端口,即nginx中php处理的地址,一般默认值即可。可用格式为: 'ip:port'
slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/$pool-slow.log # 开启慢日志
pm=dynamic # 动态模式进程管理开启
start_servers=5 # 最初开启多少进程
min_spare_server =5 # 最小的多余进程数。最少空闲。用户访问会消耗掉进程。然后为了满足后续游湖随时随地开启进程保持空闲数为5。
max_children = 50 # 最大进程数
# max_children是PHP-FPM Pool 最大的子进程数,他数值取决于你的服务器内存。 假设你打算给10G内存给当前配置的PHP-FPM Pool,一般一个PHP请求占用内存10M-40M,我们按站点每个PHP请求占用内存25M,这样max_children = 10G/25M = 409。所以,这个值可以根据情况算出来
max_spare_servers=10 # 最大的多余进程。大规模断开后,高并发访问过后,还剩多少。
max_requests = 500 # 每个子进程能响应的请求数量,到达此数字,该PHP进程就被释放掉了。
# max_requests是每个子进程重生之前处理的请求数, 默认值为unlimited(默认为1024),可以设置小一点(如500左右),这样可以避免内存泄露带来的问题
- 初始化php-fpm
初始化前
ps aux |grep php # 观察php程序存在十个进程。
vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf # 设置生产环境下常用数值
pm = dynamic # dynamic:启动动态管理模式
pm.start_servers = 32 # start_servers:初始启动32个进程
pm.max_children = 512 # max_children:最大进程数。(子进程数会在最大和最小数范围中变化)512个进程数是在大于16G内存的前提下。
pm.min_spare_servers = 32 # min_spare:随着用户访问的增加,保持32个空闲进程。
pm.max_spare_servers = 64 # max_spare:随着用户离去。杀死大量空闲进程来节约资源。
pm.max_requests = 1500 # max_requests:是每个子进程重生之前处理的请求数, 默认值为unlimited(为1024)
# max_children是PHP-FPM Pool 最大的子进程数,他数值取决于你的服务器内存。 假设你打算给10G内存给当前配置的PHP-FPM Pool,一般一个PHP请求占用内存10M-40M,我们按站点每个PHP请求占用内存25M,这样max_children = 10G/25M = 409。所以,这个值可以根据情况算出来
systemctl restart php-fpm
初始化后
ps aux |grep php
- 启动php状态监控页面功能
1.启动测试页功能
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
pm.status_path = /php_status # ;为php中的注释,去掉pm.status_path之前的逗号
2.nginx配置页面转发
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
location = /php_status {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl restart nginx php-fpm
[root@nginx1 ~]#
3.访问测试页:http://192.168.200.184/php_status
pool – fpm池子名称,大多数为www
process manager – 进程管理方式,值:static, dynamic or ondemand. dynamic
start time – 启动日期,如果reload了php-fpm,时间会更新
start since – 运行时长
accepted conn – 当前池子接受的请求数
listen queue – 请求等待队列,如果这个值不为0,那么要增加FPM的进程数量
max listen queue – 请求等待队列最高的数量
listen queue len – socket等待队列长度
idle processes – 空闲进程数量
active processes – 活跃进程数量
total processes – 总进程数量
max active processes – 最大的活跃进程数量(FPM启动开始算)
max children reached - 进程最大数量限制的次数,如果这个数量不为0,那说明你的最大进程数量太小了,请改大一点。
slow requests – 启用了php-fpm slow-log,缓慢请求的数量
五、Nginx Location、
前言:
通常网站的部分页面,需要特殊设置。
比如,/test.html 页面,需要用户访问控制(如allow all)。
location = /test.html {
allow all;
}
那部分页面该如何表达呢?
答案:就是位置 Location URL { module }. 其中URL的表达方式中使用的正则表达式,常会有冲突的情况,请通过下面的实验,了解常见的冲突符号,并掌握其中的优先级。
语法规则:
location [=|~|~*|!~|!~*|^~] /uri/ {
module;
module;
}
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| = | 表示精确匹配,优先级也是最高的 |
| ~ | 区分大小写的正则匹配 |
| ~* | 不区分大小写的正则匹配 |
| / | 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到 |
| ^~ | 以某些字符串开头 |
| !~ | 非(区分大小写匹配的正则) |
| !~* | 非(不区分大小写匹配的正则) |
Location优先级:
= >> ^~ >> ~|~*|!~|!~* >> /
# 精确匹配》字符开头》正则匹配》通配
Location 案例:
目的:通过不同的表达式,观察表达式间的优先级
server {
listen 192.168.200.184;
root /abcd;
index index.html;
location = / { index a.html; }
location ~ / { index b.html; }
location / { index c.html; }
}
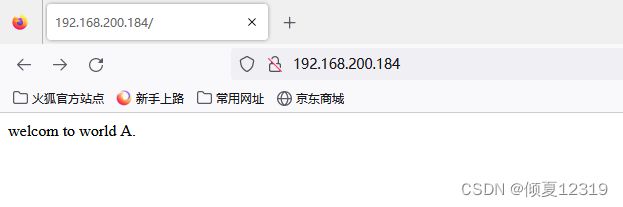
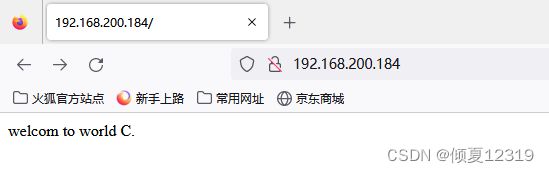
a.html、b.html、c.html分别存储不同内容。
访问页面,观察显示的内容。理解正则符号间的优先级。
# location / {
# expires 24h;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#index index.php index.html;
# root /app;
# random_index on;
# }
root /abc;
index index.html;
location = / {
index a.html;
}
location ~/ {
index b.html;
}
location / {
index c.html;
}
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /abc
[root@nginx1 ~]# cd /abc
[root@nginx1 abc]# ls
[root@nginx1 abc]# echo "welcom to world A." > a.html
[root@nginx1 abc]# echo "welcom to world B." > b.html
[root@nginx1 abc]# echo "welcom to world C." > c.html
[root@nginx1 abc]# ls
a.html b.html c.html
[root@nginx1 abc]#
[root@nginx1 abc]# systemctl restart nginx
# location / {
# expires 24h;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#index index.php index.html;
# root /app;
# random_index on;
# }
root /abc;
index index.html;
#location = / {
# index a.html;
# }
location ~/ {
index b.html;
}
location / {
index c.html;
}
# location / {
# expires 24h;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#index index.php index.html;
# root /app;
# random_index on;
# }
root /abc;
index index.html;
#location = / {
# index a.html;
# }
# location ~/ {
# index b.html;
# }
location / {
index c.html;
}
# location / {
# expires 24h;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#index index.php index.html;
# root /app;
# random_index on;
# }
root /abc;
index index.html;
#location = / {
# index a.html;
# }
# location ~/ {
# index b.html;
# }
# location / {
# index c.html;
# }
[root@nginx1 abc]# echo "welcom to world INDEX." > index.html
[root@nginx1 abc]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
[root@nginx1 abc]# systemctl restart nginx
基于用户(username&password)
module:ngx_http_auth_basic_module
语法:
Syntax:auth_basic string | off;
Context: http,server,location,limit_execpt
Syntax:auth_basic_user_file file;
Context: http,server,location,limit_execpt
启用控制
- 建立认证文件
[root@node3 conf.d]# yum install -y httpd-tools
```bash
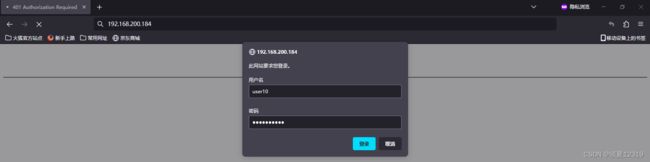
[root@nginx1 ~]# htpasswd -cm /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd user10
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user user10
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd
user10:$apr1$IElgoR53$WTFSAWMmIfZo985jrlcxM.
[root@nginx1 ~]#
- 启动认证
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
auth_basic "welcom to big world!";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd;
...
}
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
...
location = /php_status {
auth_basic "welcom to big world!";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/passwd;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
六、Nginx Rewrite
Nginx URL重写
- 什么是Rewrite
-
URL Rewrite最常见的应用是URL伪静态化,是将动态页面显示为静态页面方式的一种技术。比如
http://www.123.com/news/index.php?id=123 使用URLRewrite 转换后可以显示为 http://www.123
.com/news/123.html对于追求完美主义的网站设计师,就算是网页的地址也希望看起来尽量简洁明快。
理论上,搜索引擎更喜欢静态页面形式的网页,搜索引擎对静态页面的评分一般要高于动态页面。所
以,UrlRewrite可以让我们网站的网页更容易被搜索引擎所收录。 -
从安全角度上讲,如果在URL中暴露太多的参数,无疑会造成一定量的信息泄漏,可能会被一些黑客
利用,对你的系统造成一定的破坏,所以静态化的URL地址可以给我们带来更高的安全性。 -
实现网站地址跳转,例如用户访问360buy.com,将其跳转到jd.com。
- Rewrite相关指令
重定向:rewrite
将用户的访问(url),更换成指定的文件。
if 语句
应用环境:server,location
语法:if (condition) { … }
条件判断
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| ~* | 正则匹配 (不区分大小写) |
| !~ | 非正则匹配 (区分大小写) |
| !~* | 非正则匹配 (不区分大小写) |
| -f 和!-f | 用来判断是否存在文件 |
| -d 和!-d | 用来判断是否存在目录 |
| -e 和!-e | 用来判断是否存在文件或目录 |
| -x 和!-x | 用来判断文件是否可执行 |
全局变量
| $document_root | 针对当前请求的根路径设置值 |
| $remote_addr | 客户端地址 |
| $request_filename | 当前请求的文件路径名(带网站的主目录/usr/local/nginx/html/images/test.jpg) |
| $request_uri | 当前请求的文件路径名(不带网站的主目录/images/test.jpg) |
| $scheme | 用的协议,比如http或者是https |
| $server_name | 请求到达的服务器名 |
| $args | 请求中的参数 |
| $host | 请求信息中的"Host",如果请求中没有Host行,则等于设置的服务器名 |
| $limit_rate | 对连接速率的限制; |
| $request_method | 请求的方法,比如"GET"、"POST"等 |
| $remote_port | 客户端端口号 |
| $remote_user | 客户端用户名,认证用 |
| $query_string | 与$args相同 |
| $server_protocol | 请求的协议版本,“HTTP/1.0"或"HTTP/1.1” |
| $server_addr | 服务器地址,如果没有用listen指明服务器地址,使用这个变量将发起一次系统调用以取得地址(造成资源浪费) |
| $document_uri | 与$uri一样,URI地址 |
| $server_port | 请求到达的服务器端口号 |
-
Rewrite flag
-
Rewrite匹配参考示例
案例1:
目的:当用户访问http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html地址时,
通过redirect 重定向至http://192.168.200.184/ccc/c.com/c.html
注意:
1.还原默认站点
#cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen 80;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.php;
}
}
#vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html # 默认主页
2.配置地址重写
# 创建待测试目录
[root@nginx1 html]#mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/abc/aaa/a.com/ -p
[root@nginx1 html]#mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/ccc/a.com/ -p
# 创建待测试目标页面
[root@nginx1 html]#vim /usr/share/nginx/html/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html
[root@nginx1 a.com]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html
welcom to world A.
[root@nginx1 html]#vim /usr/share/nginx/html/ccc/c.com/c.html
[root@nginx1 a.com]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/ccc/c.com/c.html
welcom to world C.
[root@nginx1 a.com]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
location /abc {
rewrite .* /ccc/c.com/c.html permanent;
}
...
[root@nginx1 a.com]# systemctl restart nginx
3.访问旧页面进行测试
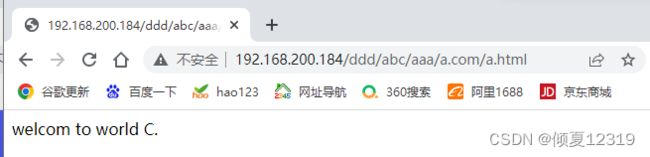
浏览器访问:http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html
结果如下:说明重定向成功,由网址http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html 重定向到http://192.168.200.184/ccc/c.com/c.html

4.关于permanent
permanent 会将地址显示为新的URL地址(重定向之后的URL)
没有添加permanent之前
添加上permanenturl被替换生成两次请求。
服务器只转换了url,客户端重新申请。

添加permanent之后

不添加permanent
url是老的服务器内部转换请求。
服务器内部转换URL,内部转换页面。
5.请思考表达式问题1
用以下匹配方式,对URL(http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html )进行匹配有什么区别
Location = /abc
通过此URL:http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html访问服务器,结果是否会重定向
答案:不可行,因为需要完全匹配
Location ~ /abc
通过此URL:http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html 访问服务器,结果是否会重定向
答案:可行,因为部分匹配即可
Location ^~ /abc
通过此URL:http://192.168.200.184/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html 访问服务器,结果是否会重定向
答案:可行,因为部分匹配即可
6.请思考表达式问题2
用户访问如下URL( http://192.168.200.184/bbb/abc/aaa/a.com/a.html )是否会这样的语句(Location ~ /abc)匹配
如何阻止这样的url重定向:location ~ ^/abc

案例2:
目的:利用正则中的”()和\1 “,
替换url中一部分的内容。
将http://192.168.200.184/2016/a/b/c/test.html
换http://192.168.200.184/2017/a/b/c/test.html
方法:
location /2016 {
rewrite ^/2016/(.*)$ /2017/$1 permanent;
}
1.注释掉上一个实验中的重定向部分。
避免实验出现交叉影响
2.配置地址重写
# 准备目标目录
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/2017/a/b/c/ -p
# 准备目标 页面
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/2017/a/b/c/test.html
[root@nginx1 a.com]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
location /abc {
rewrite ^/abc/(.*)$ /efg/$1 permanent;
}
3.访问旧页面进行测试
在浏览器输入:192.168.200.184/2016/a/b/c/test.html


url因为permanent被重新改写,请求也变为2次。客户端重新申请了两次
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /var/log/nginx/access.log
192.168.200.1 - user10 [12/Feb/2023:16:22:25 +0800] "GET /2016/a/b/c/test.html HTTP/1.1" 301 169 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/109.0" "-"
192.168.200.1 - user10 [12/Feb/2023:16:22:25 +0800] "GET /2017/a/b/c/test.html HTTP/1.1" 200 13 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:109.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/109.0" "-"
案例3:
目的:了解判断在重定向中的使用方法。
location { rewrite } 只能替换url中的目录路径,
使用if (){rewrite}可以替换协议主机目录全部能容。
将http://www.qianfeng.com换为http://jd.com
1.注释掉上一个实验中的重定向部分。
2.配置地址重写
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
if ( $host ~* qianfeng.com ) {
rewrite .* http://jd.com permanent;
}
[root@nginx1 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
3.访问旧页面进行测试
注意:客户端 guan.com的域名解析,和jd.com的域名解析。
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.200.184 guan.com a.com b.com nginx1
浏览器输入guan.com

案例4
目的:上一个试验中,不论输入的url中页面内容是什么:
http://guan.com/1.html
http://guan.com/2.html
其结果。把主机地址由guan.com换成cloud.com。$request全部都重定向至
http://cloud.com/1.html主页。
http://cloud.com/2.html
需求:如果希望替换掉域名中的主机,保留后端url路径。可以使用nginx内置变量调用老的url目录路径。
示例:
将http://qianfeng.com/ccc/bbb/2.html
换成http://cloud.com/ccc/bbb/2.html
1.延续上一个实验
准备一个新网站cloud.com
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/cloud.com.conf
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/cloud.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name cloud.com;
location / {
root /cloud;
index index.html;
}
}
新页面aaa/bbb/test.html
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /cloud
[root@nginx1 ~]# cd /cloud
[root@nginx1 cloud]# vim index.html
[root@nginx1 cloud]# cat index.html
welcome to cloud!
[root@nginx1 cloud]# mkdir aaa/bbb -p
[root@nginx1 cloud]# vim aaa/bbb/test.html
[root@nginx1 cloud]# pwd
/cloud
[root@nginx1 cloud]# vim aaa/bbb/test.html
[root@nginx1 cloud]# cat aaa/bbb/test.html
welcome to /cloud/aaa/bbb/test.html!
[root@nginx1 cloud]#
2.配置地址重写
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
if ( $host ~* guan.com ) {
rewrite .* http://cloud.com$request_uri permanent;
}
注意客户端解析cloud.com的问题。
注意:因为无法管理京东站点。
这次实验中的目的站点,使用的自己管理的cloud.com/aaa/bbb/test.html
3.访问旧页面进行测试
浏览器访问:http://guan.com/aaa/bbb/test.html
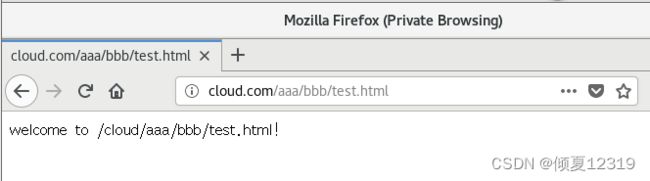
案例5:
目的:在访问的url是目录时,在URL自动添加一个“/” (如果不是目录,则不加/)
(但是先做个判断,是目录才需要加,不是目录就不加。)
当用户访问网站时,输入的URL不完整。
1.输入的URL是目录时,自动添加“/”
http://www.baidu.com/abc
2.输入的URL是文件时,不添加“/”
http://www.baidu.com/abc/index.html
3.输入的URL是目录,但已经添加"/"时,不添加“/”
http://www.baidu.com/abc/
1.注释掉上一个实验中的重定向部分。
2.配置地址重写
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
if (-d $request_filename) {
rewrite ^(.*)([^/])$ http://$host$1$2/ permanent;
}
准备目标目录
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/dir
[root@nginx1 ~]# echo 'welcome to /usr/share/nginx/html/dir' > /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/index.html
3.访问页面进行测试
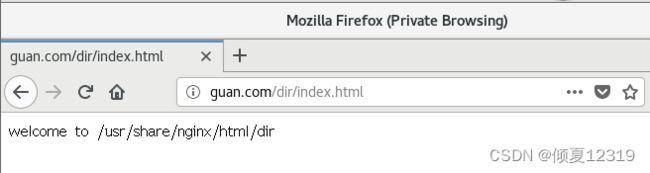
访问目录:http://guan.com/dir/

注意发生重定向现象,观察url后方多了“/”。
访问文件:http://guan.com/dir/index.html
案例6(了解):
目的:将旧url中的字段,引入重定向后新url中。
http://www.tianyun.com/login/tianyun.html
转为 http://www.tianyun.com/reg/login.php?user=tianyun
演示:
location /login {
rewrite ^/login/(.*)\.html$ /reg/login.php?user=$1;
}
因涉及动态站点环境,理解概念即可。
案例7:
目的:目录的表达方式发生变化,原先的“-”分割,变成了“/"目录层次。
将http://www.tianyun.com/qf/11-22-33/1.html
转换为http://www.tianyun.com/qf/11/22/33/1.html
1.注释掉上一个实验中的重定向部分。
2.配置地址重写
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
location /dir {
rewrite ^/dir/([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)(.*)$ /dir/$1/$2/$3$4 permanent;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
准备目标目录
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/ -p
准备目标页面
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/test.html
[root@nginx1 ~]# echo 'welcome to /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/test.html ' > /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/test.html
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/test.html
welcome to /usr/share/nginx/html/dir/123/456/789/test.html
3.访问页面进行测试
在浏览器输入:http://guan.com/dir/123-456-789/test.html

案例8:
目的:引用原URL当中的信息,重定向至目标的URL
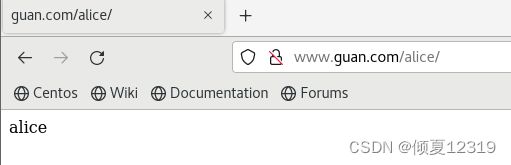
http://alice.guan.com ==> http://www.guan.com/alice
http://jack.guan.com ==> http://www.guan.com/jack
1.注释掉上一个实验中的重定向部分。
2.配置地址重写
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
if ($host ~* "^www.guan.com$" ) {
break;
}
if ($host ~* "^(.*)\.guan\.com$" ) {
set $user $1;
rewrite .* http://www.guan.com/$user permanent;
}
这里break是为了跳出循环,如不加break,每一次重写后,主机名都符合if的判断结果,会再次被重写。
set 指令是用于定义一个变量,并且赋值。应用于server,location,if环境。
准备目标页面
[root@nginx1 ~]# mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/{jack,alice}
[root@nginx1 ~]# echo "jack" > /usr/share/nginx/html/jack/index.html
[root@nginx1 ~]# echo "alice" > /usr/share/nginx/html/alice/index.html
准备客户端DNS记录
[root@nginx1 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
[root@nginx1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
192.168.200.184 guan.com nginx1 cloud.com jack.guan.com alice.guan.com www.guan.com
案例9:
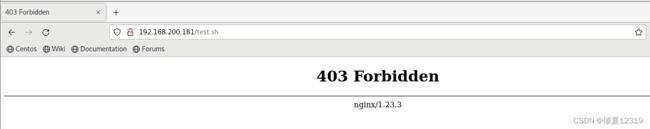
目的:如果访问服务器中的特殊文件。
如:.sh结尾的文件,则返回403操作拒绝错误
1.阅读理解示例
[root@node1 html]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/test.sh
[root@node1 html]# cat /usr/share/nginx/html/test.sh
echo "hello world."
2.示例
[root@node1 html]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
location ~* \.sh$ {
return 403;
#return 301 http://www.guan.com;
}
[root@node1 html]# systemctl restart nginx
目的:last标记
1.准备三个页面
[root@node1 html]# mkdir /usr/share/nginx/html/test
[root@node1 html]# echo 'break' > /usr/share/nginx/html/test/break.html
[root@node1 html]# echo 'last' > /usr/share/nginx/html/test/last.html
[root@node1 html]# echo 'test' > /usr/share/nginx/html/test/test.html
2.邀请break,last标记
[root@node1 html]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
...
server_name guan.com
....
location /break {
rewrite .* /test/break.html break;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
location /last {
rewrite .* /test/last.html last;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
location /test {
rewrite .* /test/test.html break;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
[root@node1 html]# systemctl restart nginx
3.验证,理解last
http://192.168.200.181/break

http://192.168.200.181/last
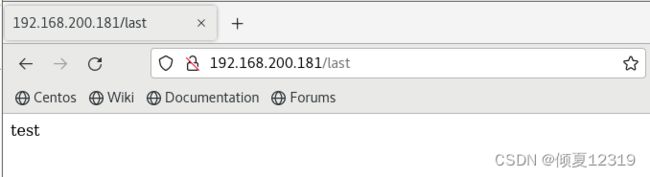
last 新的URL是个开始。拿新UR匹配(下一个URL),结果匹配到test了。
注意:last标记在本条rewrite规则执行完后,会对其所在的server { … } 标签重新发起请求;
break标记则在本条规则匹配完成后,停止匹配,不再做后续的匹配。
另有些时候必须使用last,比如在使用alias指令时,而使用proxy_pass指令时则必须使用break。
如果location中rewrite后,还需要进行其他处理,如动态fastcgi请求(.PHP,.jsp)等,要用last继续发起新的请求
(根的location使用last比较好, 因为如果有.php等fastcgi请求还要继续处理)
http://192.168.200.181/test
案例11(了解):
目的:80 ======> 443
1 申请证书
2 上传到服务器上
3 解压证书
4 启动证书功能
https的独立server{}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.xuleicloud.top;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html;
}
ssl on;
ssl_certificate cert/214025315060640.pem;
ssl_certificate_key cert/214025315060640.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
}
把这个文件解压后,会有两个文件,分别为***.pem和***.key(可以修改成你需要的名字),将这两个文件拷贝到你的Nginx根目录下的cert文件夹内(自己创建的,也可以命名成其他名字)。
或者拷贝到绝对路径也可以。/abc/aaa.pem
5 配置地址重写
http的独立server{}
方式1:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.xuleicloud.top xuleicloud.top;
return 301 https://www.xuleicloud.top$request_uri;
}
方式2:
rewrite ^(.*) https://$server_name$1 permanent;
6访问http 跳转到https了
http://www.xuleicloud.top:8080
案例12(了解):
目的:apache 开启重定向,开启443
[root@aliyun ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/discuz.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
RewriteEngine on
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://www.xuleicloud.top$1 [R=301,L]
</VirtualHost>
七、CA&HTTPS
私有CA
前言:
CA 证书颁发机构(CA, Certificate Authority), 基于https的协议工作的一中虚拟主机,要构建这样的网站需要mod_ssl模块的支持。且需要提供两个文件:证书文件和私钥文件,证书文件是标识这个网站服务器身份的,私钥文件主要用来实现在服务器端对数据进行加密,然后在网站中传输的。证书在生产生活中需要到对应的机构去申请,在实验环境中本应该搭建一台证书服务器。
1、生成证书及秘钥文件
1.准备存放证书和秘钥的目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir -p /etc/nginx/ssl
2.生成私钥
使用openssl生成基于rsa数学算法长度为1024bit的秘钥,文件必须以key为结尾
[root@nginx ~]# openssl genrsa 1024 > /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus
...............................................................++++++
................................................................++++++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
3.使用秘钥文件生成证书-申请书
[root@nginx ~]# openssl req -new -key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key > /etc/nginx/ssl/server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN ###国家名(两个字
State or Province Name (full name) []:BJ ###省会(两个字
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BJ ###城市
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]::GG ###组织名
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:cloud ##组织单位名
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:nginx.linux.com ##服务器的名字或者你的名字
Email Address []:[email protected] ###可选
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []: ###密码为空
An optional company name []: ####密码为空
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []: ###公司名空
查看申请书
[root@nginx ~]# ls /etc/nginx/ssl/
server.csr (证书申请) server.key (私钥)
4.同意申请,生成证书
[root@nginx ~]# openssl req -x509 -days 365 -key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key -in /etc/nginx/ssl/server.csr > /etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt
注释:
-x509:证书的格式,固定的
days:证书的有效期,生产生活中时间不同,价格不同
key:指定秘钥文件
in:指定证书申请文件
查看证书
[root@nginx ~]# ll /etc/nginx/ssl/
总用量 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1021 7月 12 17:31 server.crt ####证书文件
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 676 7月 12 17:30 server.csr ####申请书。可以销毁
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 887 7月 12 17:12 server.key ####私钥文件
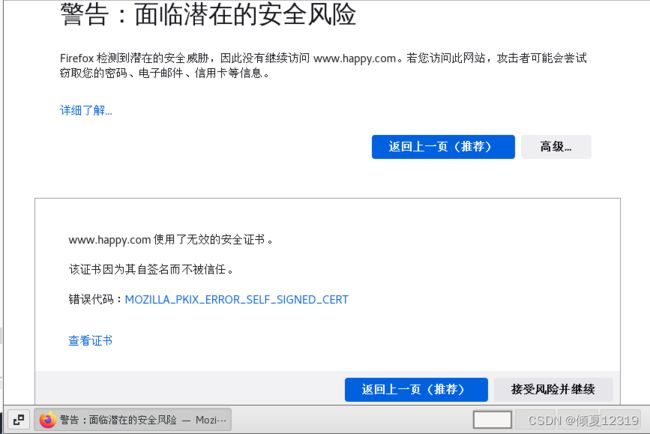
2、私有CA的https部署实战
1.创建目录
[root@nginx ~]# mkdir /happy
[root@nginx ~]# echo "happy ssl web" > /happy/index.html
2.编辑nginx.conf文件
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/happy.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.bj.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/server.crt; ##路径自定义
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/server.key;
location / {
root /happy;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -t
[root@nginx ~]# nginx -s reload
[root@nginx ~]# ss -antp | grep nginx
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* users:(("nginx",pid=11700,fd=6),("nginx",pid=11699,fd=6),("nginx",pid=8347,fd=6))
LISTEN 0 128 *:443 *:* users:(("nginx",pid=11700,fd=20),("nginx",pid=11699,fd=20),("nginx",pid=8347,fd=20))
3、测试访问
公网CA
[root@xiaochen ~]# ll /etc/nginx/214194377980730.*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1679 May 11 14:41 /etc/nginx/214194377980730.key
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3916 May 11 14:41 /etc/nginx/214194377980730.pem
[root@xiaochen ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.xuleicloud.top ;
return 301 https://www.xuleicloud.top$request_uri;
# rewrite .* https://www.xuleicloud.top$request_uri permanent;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/214194377980730.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/214194377980730.key;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.php;
}
}
[root@xiaochen ~]# systemctl restart nginx
八、Nginx 的平滑升级
原理:
当需要将正在运行中的nginx升级,添加/删除服务模块时,可以在不中断服务的情况下,使用新版本,重编译的Nginx可执行程序替换旧版本的可执行程序,步骤如下:
• 使用新的可执行程序替换旧的可执行程序,对于编译安装的Nginx,可以将新版本编译安装到旧版本的nginx安装路径中.替换之前,最好备份一下旧的可执行程序
• 发送以下指令: Kill –USR2 旧版本的nginx主进程号
• 旧版本的主进程将重命名它的pid文件为.oldbin (例如:/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin),然后执行新版本的nginx可执行程序,依次启动新的主进程和新的工作进程.
• 此时,新,旧版本的nginx实例会同时运行,共同处理输入的请求.要逐步停止旧版本的nginx实例,你必须发送WINCH信号给旧的主进程,然后,它的工作进程就将开始从容关闭:kill –WINCH 旧版本的Nginx主进程号
• 一段时间后,旧的工作进程(worker process)处理了所有已连接的请求后退出,仅由新的工作进程来处理输入的请求了.
• 这时候,我们可以决定是使用新版本,还是恢复到旧的版本;
Kill –HUP 旧的主进程号:Nginx将在不重载配置文件的情况下启动它的工作进程;
Kill –QUIT 新的主进程号:从容关闭其他工作进程(woker process);
Kill –TERM 新的主进程号:强制退出;
Kill 新的主进程号或旧的主进程号:如果因为某些原因新的工作进程不能退出,则向其发送kill信号.
新的主进程退出后,旧的主进程会移除.oldbin前缀,恢复为他的.pid文件,这样,一切就都恢复到升级之前了,如果尝试升级成功,而你也希望保留新的服务器时,可发送QUIT信号给旧的主进程,使其退出而只留下新的服务器运行:
平滑升级1.12版本到1.14版本
1、编译安装新版本的nginx,指定安装目录为新目录
[root@server nginx]# tar xf nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@server nginx]# cd /usr/local/src/nginx-1.14.2/
[root@server nginx-1.14.2]# ./configure --user=nginx --group=nginx --prefix=/usr/local/nginx14 --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module && make && make install
2、查看就的nginx的主进程号和工作进程号
[root@server ~]# ps aux |grep ngin[x]
root 68595 0.0 0.1 20640 1548 ? Ss 12:12 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 75083 0.0 0.1 21060 1632 ? S 12:17 0:00 nginx: worker process
3、替换旧的执行程序
[root@server ~]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx{,.bak}
[root@server ~]# cp /usr/local/nginx14/sbin/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@server ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.14.2
4、 给主进程发送USR2信号
[root@server ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
68595
[root@server ~]# kill -USR2 68595
[root@server ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin
68595
旧版本的主进程将重命名它的pid文件为.oldbin (例如:/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid.oldbin),然后执行新版本的nginx可执行程序,依次启动新的主进程和新的工作进程.
5、给进程发送WINCH信号
[root@server ~]# kill -WINCH 68595
[root@server ~]# ps aux |grep ngin[x]
root 58943 0.0 0.3 45940 3260 ? S 13:34 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 58944 0.0 0.1 46388 1888 ? S 13:34 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 68595 0.0 0.1 20640 1548 ? Ss 12:12 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
一段时间后,旧的工作进程(worker process)处理了所有已连接的请求后退出,仅由新的工作进程来处理输入的请求了.
回退到以前版本
这时因为旧的服务器还尚未关闭它监听的套接字,所以通过下面的几步还可以恢复旧版本:
• 发送 HUP 信号给旧的主进程 - 它将在不重加载配置文件的情况下启动它的工作进程。
• 发送 QUIT 信号给新的主进程,要求其从容关闭其工作进程
• 发送 TERM 信号给新的主进程,迫使其退出
• 如果因为某些原因新的工作进程不能退出,则直接将其杀死 KILL 信号
第一步
[root@server ~]# kill -HUP 68595
[root@server ~]# ps aux |grep ngin[x]
root 58943 0.0 0.3 45940 3260 ? S 13:34 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx 58944 0.0 0.1 46388 1888 ? S 13:34 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 68595 0.0 0.1 20640 1548 ? Ss 12:12 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 80008 0.0 0.1 21060 1388 ? S 13:50 0:00 nginx: worker process
第二步
[root@server ~]# kill -QUIT 58943
[root@server ~]# ps aux |grep ngin[x]
root 68595 0.0 0.1 20640 1548 ? Ss 12:12 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 80008 0.0 0.1 21060 1388 ? S 13:50 0:00 nginx: worker process
[root@server ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
68595
总结: 新的主进程退出后,旧的主进程会自动移除 .oldbin 后缀,恢复为.pid的后缀名,如此:一切就都恢复到升级之前了。如果尝试升级成功,而你也希望保留新的服务器时,发送 QUIT 信号给旧的主进程使其退出而只留下新的服务器运行。