golang学习之gin(四):参数绑定、文件上传、其他数据格式输出、自定义HTTP配置
文章目录
- 一、参数绑定:
-
- 1. 什么是参数绑定:
- 2. ShouldBind:
- 3. ShouldBindWith
- 4. ShouldBindQuery
- 二、文件上传:
-
- 1. form表单上传单文件&&多文件:
- 2. ajax上传单文件&&多文件:
- 三、其他数据格式输出:
-
- 1. JSON:
- 2. AsciiJSON:
- 3. JSONP:
- 4. PureJSON:
- 5. SecureJSON
- 6. XML:
- 7. YAML:
- 8.ProtoBuf:
- 四、自定义HTTP配置:
-
- 1.http请求补充:
- 2. 设置启动参数
一、参数绑定:
1. 什么是参数绑定:
能够基于请求自动提取JSON、form表单和QueryString类型的数据,并把值绑定到指定的结构体对象
2. ShouldBind:
./
├── chapter04
│ └── post.go
├── main.go
│ ├── css
│ │ └── index.css
│ ├── images
│ └── js
└── template
├── chapter04
│ └── user_add.html
./main.go
package main
import (
"gin_project/chapter04"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
// 注册模板
engine.LoadHTMLGlob("template/**/*")
// 注册静态文件
engine.Static("./static", "static")
// 注册路由
// POST
engine.GET("/to_user_add", chapter04.ToUserAdd4) // 获取请求页面
engine.POST("/user_add", chapter04.PostForm4)
engine.Run(":9000")
}
./chapter04/post.go
package chapter04
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type User struct {
// structTag:指定字段名称,不用使用首字母大写的
Id int `form:"id" json:"id"`
Name string `form:"username" json:"username`
Age string `form:"age" json:"age`
Address string `form:"address" json:"address"`
}
// post
func ToUserAdd4(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "chapter04/user_add.html", nil)
}
func PostForm4(ctx *gin.Context) {
var userInfo User
err := ctx.ShouldBind(&userInfo)
fmt.Println(err) //./template/chapter04/user_add.html
{{ define "chapter04/user_add.html" }}
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<title>post请求练习title>
<style>
.userForm {
width: 480px;
height: 360px;
margin: 20px 200px;
}
input {
margin: 5px 0;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="userForm">
<h2>添加用户h2>
<form action="/user_add" method="post">
<span>用户名: span><input type="text" name="username"><br>
<span>年 龄: span><input type="text" name=" "><br>
<span>地 址: span><input type="text" name="address"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
div>
body>
html>
{{ end }}
3. ShouldBindWith
可以使用显式绑定声明绑定 multipart form:
c.ShouldBindWith(&form, binding.Form)
或者简单地使用 ShouldBind 方法自动绑定
4. ShouldBindQuery
ShouldBindQuery函数只绑定 url 查询参数而忽略 post 数据
二、文件上传:
1. form表单上传单文件&&多文件:
.
├── chapter04
│ ├── file_upload.go
│ └── post.go
├── main.go
├── static
│ ├── css
│ ├── images
│ └── js
├── template
│ ├── chapter04
│ │ ├── fileUpload.html
│ │ └── user_add.html
└── upload
├── timg.jpeg
├── ttt.jpg
└── �\217\220示�\237�2.mp3
./main.go
package main
import (
"gin_project/chapter04"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
// 注册模板
engine.LoadHTMLGlob("template/**/*")
// 注册静态文件
engine.Static("./static", "static")
// 注册路由
// 文件上传
engine.GET("/to_fileUpload", chapter04.ToFileUpload)
engine.POST("/fileUpload", chapter04.FileUpload) // 表单单文件
engine.POST("/fileUploads", chapter04.FileUploads) // 表单多文件
engine.Run(":9000")
}
./chapter04/file_upload.go
package chapter04
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func ToFileUpload(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "chapter04/fileUpload.html", nil)
}
// 接收单文件
func FileUpload(ctx *gin.Context) {
file, _ := ctx.FormFile("file") // 获取文件
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
time_unix := strconv.FormatInt(time.Now().Unix(), 10) // 获取时间戳并转成字符串
file_path := "upload/" + time_unix + file.Filename // 设置保存文件的路径,不要忘了后面的文件名
ctx.SaveUploadedFile(file, file_path) // 保存文件
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, "上传成功")
}
// 接收多文件
func FileUploads(ctx *gin.Context) {
form, _ := ctx.MultipartForm()
files := form.File["file"] // 获取文件
for _, file := range files {
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
file_path := "upload/" + file.Filename // 设置保存文件的路径,不要忘了后面的文件名
ctx.SaveUploadedFile(file, file_path) // 保存文件
}
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, "上传成功")
}
./template/chapter04/fileUpload.html
{{ define "chapter04/fileUpload.html" }}
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<title>文件上传练习title>
<style>
.fileForm {
width: 300px;
margin: 100px auto;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="fileForm">
<h2>上传单文件h2>
<form action="/fileUpload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<span>文件: span><input type="file" name="file"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
div>
<div class="fileForm">
<h2>上传多文件h2>
<form action="/fileUploads" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<span>文件1: span><input type="file" name="file"><br>
<span>文件2: span><input type="file" name="file"><br>
<span>文件3: span><input type="file" name="file"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
div>
body>
html>
{{ end }}
2. ajax上传单文件&&多文件:
./
├── chapter04
│ ├── file_upload.go
├── main.go
├── static
│ ├── css
│ ├── images
│ └── js
├── template
│ ├── chapter04
│ │ ├── ajaxFile.html
│ │ ├── fileUpload.html
└── upload
./main.go
package main
import (
"gin_project/chapter04"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
engine := gin.Default()
// 注册模板
engine.LoadHTMLGlob("template/**/*")
// 注册静态文件
engine.Static("./static", "static")
// 注册路由
engine.GET("/to_user_add", chapter04.ToUserAdd4) // 获取请求页面
engine.POST("/user_add", chapter04.PostForm4)
// 文件上传
engine.GET("/to_ajaxFileUpload", chapter04.ToAjaxFileUpload)
engine.POST("/ajaxFileUpload", chapter04.AjaxFileUpload) // ajax单文件
engine.POST("/ajaxFileUploads", chapter04.AjaxFileUploads) // ajax多文件
engine.Run(":9000")
}
./chapter04/file_upload.go
package chapter04
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func ToAjaxFileUpload(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.HTML(http.StatusOK, "chapter04/ajaxFile.html", nil)
}
func AjaxFileUpload(ctx *gin.Context) {
file, _ := ctx.FormFile("file") // 获取文件
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
time_unix := strconv.FormatInt(time.Now().Unix(), 10) // 获取时间戳并转成字符串
file_path := "upload/" + time_unix + file.Filename // 设置保存文件的路径,不要忘了后面的文件名
ctx.SaveUploadedFile(file, file_path) // 保存文件
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, "上传成功")
}
func AjaxFileUploads(ctx *gin.Context) {
form, _ := ctx.MultipartForm()
files := form.File["file"] // 获取文件
for _, file := range files {
fmt.Println(file.Filename)
file_path := "upload/" + file.Filename // 设置保存文件的路径,不要忘了后面的文件名
ctx.SaveUploadedFile(file, file_path) // 保存文件
}
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, "上传成功")
}
./template/chapter04/ajaxFile.html
{{ define "chapter04/ajaxFile.html" }}
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<title>ajax文件上传练习title>
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/2.0.0/jquery.min.js">script>
<style>
.fileForm {
width: 300px;
margin: 100px auto;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="fileForm">
<h2>ajax上传单文件h2>
<form>
<span>文件: span><input type="file" name="file" id="file"><br>
<input type="button" id="file_btn" value="提交">
form>
div>
<div class="fileForm">
<h2>ajax上传多文件h2>
<form>
<span>文件1: span><input type="file" name="files" class="files"><br>
<span>文件2: span><input type="file" name="files" class="files"><br>
<span>文件3: span><input type="file" name="files" class="files"><br>
<input type="button" value="提交" id="files_btn">
form>
div>
<script>
// 上传单个文件
var file_btn = document.getElementById("file_btn");
file_btn.onclick = function (ev) {
var file = $("#file")[0].files[0];
var form_data = new FormData();
form_data.append("file",file);
// ajax中需要加两个参数:
// contentType:false,
// processData:false,
$.ajax({
url:"/ajaxFileUpload",
type:"POST",
data:form_data,
contentType:false,
processData:false,
success:function (data) {
alert(data);
},
fail:function (data) {
console.log(data);
}
})
}
// 上传多个文件
var files_btn = document.querySelector("#files_btn")
files_btn.onclick = function(ev) {
var files = document.querySelectorAll(".files")
console.log(files);
var form_data = new FormData();
for(let file in files) {
form_data.append("file",file);
}
$.ajax({
url:"/ajaxFileUploads",
type:"POST",
data:form_data,
contentType:false,
processData:false,
success:function (data) {
alert(data);
},
fail:function (data) {
console.log(data);
}
})
}
script>
body>
html>
{{ end }}
三、其他数据格式输出:
1. JSON:
func OutJson(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"msg": "提交成功",
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
// {"code":200,"html":"\u003cb\u003eHello, world!\u003c/b\u003e","msg":"提交成功","tag":"\u003cbr\u003e"}
}
2. AsciiJSON:
生成具有转义的非 ASCII 字符的 ASCII-only JSON
func OutAsciiJson(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.AsciiJSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"msg": "提交成功",
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
// {"code":200,"html":"\u003cb\u003eHello, world!\u003c/b\u003e","msg":"\u63d0\u4ea4\u6210\u529f","tag":"\u003cbr\u003e"}
}
3. JSONP:
使用 JSONP 向不同域的服务器请求数据。如果查询参数存在回调,则将回调添加到响应体中;
如果传输的数据在两个不同的域,由于在javascript里无法跨域获取数据,所以一般采取script标签的方式获取数据,传入一些callback来获取最终的数据,这就有可能造成敏感信息被劫持;
func OutJsonp(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.AsciiJSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"msg": "提交成功",
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
// {"code":200,"html":"\u003cb\u003eHello, world!\u003c/b\u003e","msg":"提交成功","tag":"\u003cbr\u003e"}
}
4. PureJSON:
func OutPureJSON(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.PureJSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"msg": "提交成功",
})
// {"code":200,"html":"Hello, world!","msg":"提交成功","tag":"
"}
}
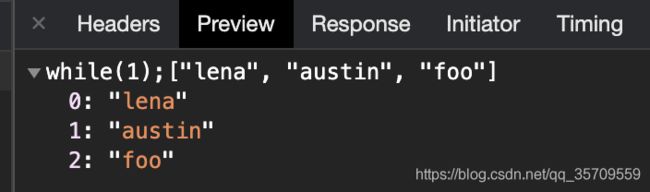
5. SecureJSON
使用 SecureJSON 防止 json 劫持。如果给定的结构是数组值,则默认预置 “while(1),” 到响应体;
json劫持:利用网站的cookie未过期,然后访问了攻击者的虚假页面,那么该页面就可以拿到json形式的用户敏感信息;
func OutSecureJSON(ctx *gin.Context) {
names := []string{"lena", "austin", "foo"}
ctx.SecureJSON(http.StatusOK, names)
}
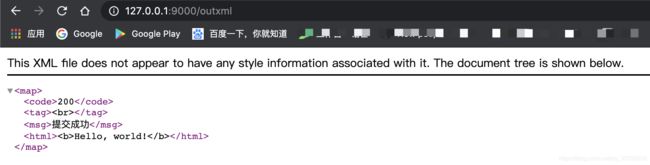
6. XML:
func OutXML(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.XML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"msg": "提交成功",
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
}
7. YAML:
func OutYML(ctx *gin.Context) {
ctx.YAML(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"code": 200,
"tag": "
",
"user": gin.H{"name": "zhiliao", "age": 18},
"html": "Hello, world!",
})
}
8.ProtoBuf:
四、自定义HTTP配置:
1.http请求补充:
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/someGet", getting)
router.POST("/somePost", posting)
router.PUT("/somePut", putting)
router.DELETE("/someDelete", deleting)
router.PATCH("/somePatch", patching)
router.HEAD("/someHead", head)
router.OPTIONS("/someOptions", options)
2. 设置启动参数
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
...
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", router)
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
...
s := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8080",
Handler: router,
ReadTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
s.ListenAndServe()
}