java方法详解
1. 方法概述
1.1 什么是方法
方法(method)是将具有独立功能的代码块组织成为一个整体,使其具有特殊功能的代码集
注意:
- 方法必须先创建才可以使用,该过程称为方法定义
- 方法创建后并不是直接运行的,需要手动使用后才执行,该过程称为方法调用
2. 方法的定义和调用
2.1 方法的定义
格式:
public static void 方法名(){ //方法体 }例如:
public static void Number(){ //方法体 }
2.2 方法的调用
格式:方法名();
例如:Number();
案例一:
package yj.com.itheima_01; /* 方法在main方法中调用 方法要先创建才能使用, */ public class MethodDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //调用方法 Number(); } public static void Number(){ //定义变量 int number = 58; //判断 if(number%2==0){ System.out.println(true); }else{ System.out.println(false); } } }案例二:打印两个数中的较大值
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { getMax(); } public static void getMax() { int a = 50; int b = 80; if (a > b){ System.out.println(a); }else { System.out.println(b); } } }
3. 带参数方法的定义和调用
3.1 带参数方法的定义
格式:
public static void 方法名(参数){......}格式(单个参):
public static void 方法名(数据类型 变量名){......}单个参数范例:
public static void Number(int number) {......}格式(多个参)
public static void 方法名(数据类型 变量名1,数据类型 变量名2,.....){......}多个参数范例:
public static void getMax(int number1,int number2,int number3){......}注意
- 方法定义时,参数中的数据类型与变量名都不能缺少
- 方法定义时,多个参数之间使用逗号(,)分隔
3.2 带参数方法的调用
格式:方法名(参数);
单个参数格式:方法名(变量/常量值);
单个参数案例:Number(5);
多个参数格式:方法名(变量名1/常量值1,变量名2/常量值2);
单个参数案例:Number(5,6);
注意:
方法调用时,参数的数量与类型必须与方法定义中的设置相匹配,否则程序将报错。如int调int。
例如:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Number(65); //常量值调用 int a = 56; //变量的调用 Number(a); } public static void Number(int number) { if (number % 2 == 0) { System.out.println(true); } else { System.out.println(false); } } }
3.3 形参和实参
形参:方法定义中的参数。等同于变量定义格式,例如:int number,数据类型和变量名组成
实参:方法调用中的参数。等同于使用变量或常量,例如: 10 number,不带数据类型,常量或者是变量名。
例如:打印两个数中的较大值
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { MaxNumber(10, 20); int a = 25; int b = 35; MaxNumber(a, b); } public static void MaxNumber(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { System.out.println(a); } else { System.out.println(b); } } }
4. 带返回值方法的定义和调用
4.1 返回值方法的定义
格式:
public static 数据类型 方法名(参数){ return数据; }例1:
public static boolean Number(int number) { return true; }例2:
public static int getMax(int a, int b){ return 1000; }注意:
方法定义时return后面的返回值与方法定义上的数据类型要匹配,否则程序将报错
4.2 带返回值方法的调用
格式1:方法名(参数);
例如:Number(10);
格式2:数据类型 变量名 = 方法名(参数);
例如:boolean flag = Number(10);
注意:
方法的返回值通常会使用变量接收,否则返回值将毫无意义。
例如:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.方法名 Number(50); //true //2. 数据类型 变量名 = 方法名(参数); boolean b = Number(60); // boolean b = true; System.out.println(b); } //定义一个方法,该方法接收一个参数,判断该数据是否是偶数,并且返回真假值 public static boolean Number(int a) { if (a % 2 == 0) { return true; } else { return false; } } }结果:
true
例二:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { //在main()方法中调用定义好的方法并使用变量保存 int result = MaxNumber(20, 50); System.out.println(result); //在main()方法中调用定好的方法并直接打印结果 System.out.println(MaxNumber(20, 50)); } public static int MaxNumber(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return a; } else { return b; } } }
5. 方法的注意事项
5.1 方法注意事项
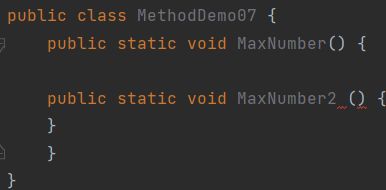
1.方法是平级关系不能嵌套定义
错误演示:
正确演示:
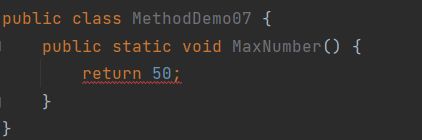
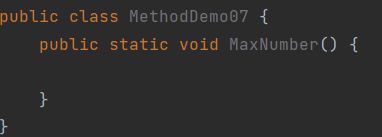
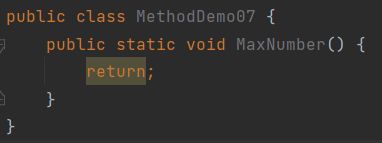
2.void表示无返回值,可以省略return,也可以单独的书写return,后面不加数据
错误演示:
正确演示:
5.2 方法的通用格式
格式:
public static 返回值类型 方法名(参数){ 方法体 return数据; }
- public static: 修饰符
- 返回值类型:方法操作完毕之后返回的数掘的数据类型。如果方法操作完毕,没有数据返回,这里写void,而且方法体中一般不写return
- 方法名:调用方法时候使用的标识
- 参数:由数据类型和变量名组成,多个参数之间用逗号隔开
- 方法体:完成功能的代码块
- return:如果方法操作完毕,有数据返回,用于把数据返回给调用者
定义方法时,要做到两个明确
- 明确返回值类型:主要是明确方法操作完毕之后是否有数据返回,如果没有,写void;如果有,写对应的数据类型
- 明确参数:主要是明确参数的类型和数量
调用方法时
- void类型的方法,直接调用即可
- 非void类型的方法,推荐用变量接收调用
6. 方法重载
6.1 方法重载的概述
方法重载指同一个类中定义的多个方法之间的关系,满足下列条件的多个方法相互构成重载
- 多个方法在同一个类中
- 多个方法具有相同的方法名
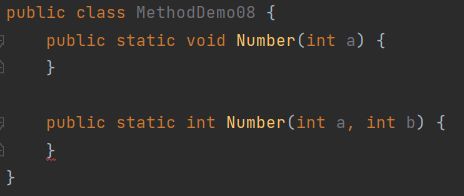
- 多个方法的参数不相同,类型不同或者数量不同
6.2 方法重载的特点
- 重载仅对应方法的定义,与方法的调用无关,调用方式参照标准格式
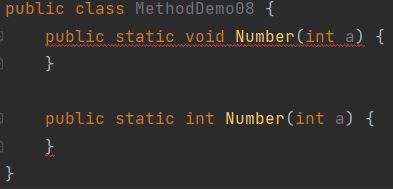
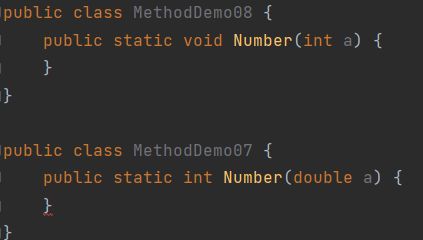
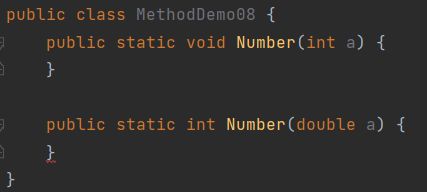
- 重载仅针对同一个类中方法的名称与参数进行识别,与返回值无关,换句话说不能通过返回值来判定两个方法是否相互构成重载
错误演示:
正确演示:
例如:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { //调用 int result = Number(20, 50); System.out.println(result); double result2 = Number(20.0, 50.0); System.out.println(result2); int result3 = Number(20, 50, 80); System.out.println(result3); } public static int Number(int a, int b) { return a + b; } public static double Number(double a, double b) { return a + b; } public static int Number(int a, int b, int c) { return a + b + c; } }结果:
例二:
package yj.com.itheima_01; /* 使用方法重载的思想,设计比较两个整数是否相同的方法,兼容全整数类型(byte,short,int long) */ public class MethodDemo09 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(compare(10, 20)); System.out.println(compare(10L, 20L)); System.out.println(compare((byte) 10, (byte) 20)); System.out.println(compare((short) 10, (short) 20)); } public static boolean compare(int a, int b) { System.out.println("int"); // System.out.println(compare(10, 20));走的这个方法 return a == b; } public static boolean compare(long a, long b) { System.out.println("long"); // System.out.println(compare(10L, 20L));走的这个方法 return a == b; } public static boolean compare(byte a, byte b) { System.out.println("byte"); //System.out.println(compare((byte) 10, (byte) 20));走的这个方法 return a == b; } public static boolean compare(short a, short b) { System.out.println("short"); // System.out.println(compare((short) 10, (short) 20));走的这个方法 return a == b; } }结果:
7. 方法的参数传递
7.1 方法参数传递(基本类型)
对于基本数据类型的参数,形式参数的改变,不影响实际参数的值。
例如:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 30; System.out.println("调用age方法之前" + number); age(number); System.out.println("调用age方法之后" + number); } public static void age(int number) { number = 50; } }结果:
7.2 方法参数的传递(引用类型)
对于引用类型的参数,形式参数的改变,影响实际参数的值
例如:
package yj.com.itheima_01; public class MethodDemo11 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {30, 50, 80}; System.out.println("调用age方法之前" + arr[1]); age(arr); System.out.println("调用age方法之前" + arr[1]); } public static void age(int[] arr) { arr[1] = 45; } }结果: