spring硬骨头-----解决循环依赖问题
目录
what?
spring中是如何解决循环依赖问题的?
整体思路:
spring中初始化时设置属性值的方法:set和构造的区别
那么三级缓存是怎么处理的呢?
实现细节:
总结:
1、三级缓存解决循环依赖问题的关键是什么?为什么提前暴露对象能够解决?
2、为什么使用三级缓存?只使用一个缓冲不行吗??
3、只使用二级缓存行不行?为什么使用三级缓存?
4、在创建代理对象时,如果某个Bean需要代理对象,会不会创建普通的Bean对象(通过实例化初始化产生的对象)?
5、为什么使用三级缓存就能解决这个问题?(4代理问题)
6、在什么时候使用?
最近在学习spring的源码,之前的文章已经把spring的整个流程进行了梳理。有了整体的脉络之后,学习起来就清晰明了了。如果没看过spring源码的同学,可以看一下鄙人整理的笔记。
spring源码讲解(简单易学)
今天记录一下spring的实现细节。这里想记录的是spring的一个难点------spring解决循环依赖问题。后面还会继续记录整个spring的其他实现细节。
what?
首先讲一下什么是循环依赖,循环依赖顾名思义就是两个类循环的引用了。举个
这里有两个类 类A引用了类B ,类B同时又引用了类A,这就是循环依赖。
spring中是如何解决循环依赖问题的?
相信大家在面试的过程当中,经常会被问到这个问题。这个问题也是spring源码中比较难的一个问题,接下来会把大致思路和实现的细节记录下来。
整体思路:
使用三级缓存解决了循环依赖问题。
一级缓存为:Map
二级缓存为:Map
三级缓存为:Map
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
//一级缓存
private final Map singletonObjects
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
//三级缓存
/** Cache of singleton factories: bean name to ObjectFactory. */
private final Map> singletonFactories
= new HashMap<>(16);
//二级缓存
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map earlySingletonObjects
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
spring中初始化时设置属性值的方法:set和构造的区别
1、set方法
2、构造方法,初始化
3、工厂方法
这里只说set和构造方法
相信大家都知道,set方法能够解决循环依赖问题,而构造方法不能解决循环依赖问题。
可以这么简单的理解,set方法首先完成对象的创建工作,之后通过set方法设置属性。
构造方法,创建出对象之后,立即就能够给对象一个属性值。
而解决循环依赖问题的关键就是能够把实例化和初始化分开,先给一个earlyBean(未设置值)的Bean待用(提前暴露对象),A依赖B B依赖A 只要有一个依赖一个不完整的Bean就能吧环打破,解决循环依赖问题。
那么三级缓存是怎么处理的呢?
一级缓存为:Map
二级缓存为:Map
三级缓存为:Map
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ObjectFactory {
T getObject() throws BeansException;} 函数式接口,能够传递匿名内部类/lambda。
能够执行getObject()方法, 实际调用的是createBean方法(看详细实现的代码就能知道)
ObjectFactory是一个函数式接口,仅有1个方法,可以传入lambda表达式,可以是匿名内部类,通过调研getObject()方法来执行具体的逻辑。
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();spring在创建对象之前,每次都是先从容器中查找,
找不到再创建
spring中重要的方法,
getBean-->doGetBean-->createBean-->doCreateBean
实现细节:
注意:下面的这个方法非常重要,会多次的递归调用。
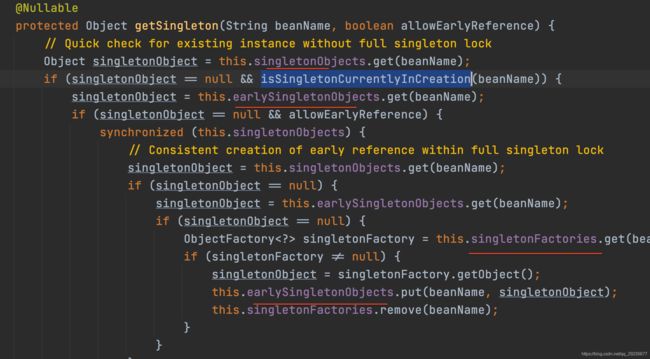
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
//先到一级缓存中查找
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
//没找到,并且正在创建当中(这个方法,循环引用创建时会用到)
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
//注意 B创建过程中给A付值的时候会调用这里,从三级缓存中取的stepA1 StepB1 都存在三级缓存中
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}getSingleton(beanName);第一次调用的是一个参数的方法---->allowEarlyReference为truegetSingleton(beanName, true);
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
//实际调用的是 lambda传入的 createBean方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException :
this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
} //实际调用的是 lambda传入的 createBean方法
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
里面有一个createBean方法
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java的createBean方法
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
try {
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,
// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);
}
}
下面的方法中有一个doCreateBean方法,是实际的创建Bean的方法
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//实例化Bean的方法,反射实现的 构造实现的(获取到一个所有属性都是null的空对象)
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//只是填充xml中配置的一些属性,,applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
} A对象地址A@1755
1、 //实例化Bean的方法,反射实现的 构造实现的(获取到一个所有属性都是null的空对象)
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
2、 addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
这里也使用了lambda表达式
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}使用了一级缓存singletonObjects(上锁)
1、如果存在这个beanName的话,将当前的BeanName缓存起来。三级缓存
2、把二级缓存earlySingletonObjects的缓存 去掉该Bean
runtimeBeanReference
总结:
1、三级缓存解决循环依赖问题的关键是什么?为什么提前暴露对象能够解决?
实例化和初始化分开,在中间过程给其他对象付值的时候,并不少一个完整的对象,而是吧半成品对象付值给了其他对象
(实例化A--初始化A--实例化B--初始化B--(之后能够找到A,把A拿过来只是半成品))
2、为什么使用三级缓存?只使用一个缓冲不行吗??
不能。
在整个处理过程中,缓存中放的是半成品和成品对象,成品和半成品都会放到一起,一级缓存中,获取到半成品对象,此时无法使用。
不能进行相关的处理,因此要把半成品和成品对象分割。
??为什么不加一个标记哪??
这样肯定会遍历操作,消耗性能。打标签太麻烦。
K String V Obj
3、只使用二级缓存行不行?为什么使用三级缓存?
多了一个getEarlyBeanReference(Beanname,lambda)
如果能够保证所有的Bean对象都不去调用此方法,使用缓存可以吗?
B对象没有调用lambda方法,如果都不调用getEarlyBeanReference方法是可以的。!!!
获取早期的Bean引用。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));方法, Obtain a reference for early access to the specified bean,
* typically for the purpose of resolving a circular reference.protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic()
&& hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
return exposedObject;
}里面有一个循环BeanPostProcessor方法
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean);
return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}进入到wrapIfNecessary方法
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
} else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
} else if (!this.isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) && !this.shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, (TargetSource)null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//动态代理
Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
} else {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
} else {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
}这里有一个创建代理的方法。
进入到该方法内部
protected Object createProxy(Class beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (this.shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
} else {
this.evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = this.buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
this.customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (this.advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) {
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader)classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
}
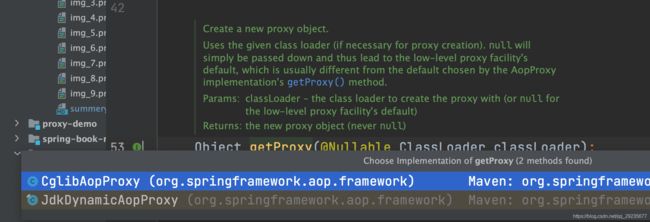
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return this.createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}有两个代理的实现。
那么为什么要加入三级缓存??
使用三级缓存的本质在于使用AOP,解决aop的代理问题?
4、在创建代理对象时,如果某个Bean需要代理对象,会不会创建普通的Bean对象(通过实例化初始化产生的对象)?
会。
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().smartInstantiationAware) {
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);
}
}
return exposedObject;
}会返回一个暴露的对象。
可能执行也可能不会执行。如果不执行代理,就是传过来的Bean,如果调用代理方法,则会讲之前的bean用代理产生的对象覆盖掉传入的Bean对象。
不配置AOP就不用代理。
如果没有循环依赖,使用AOP会调用getEarlyBeanReference吗?
5、为什么使用三级缓存就能解决这个问题?(4代理问题)
使用三级缓存的本质在于使用AOP,解决aop的代理问题?
当一个对象需要被代理的时候,在整个创建过程中是包含两个对象。一个是普通对象,应该是代理生成的对象,bean默认是单例对象,那么我在整个生命周期的处环节中,能对应一个beanName能对应两个对象吗??
显然不能,那么怎么办呢??
保证使用的时候,加一层判断,判断是否需要进行代理的处理。
exposedObject = bp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);这个方法就把之前的对象覆盖掉了。
6、在什么时候使用?
因为不知道,所以使用一个匿名内部类的方式,在调用的时候,直接对原对象(普通对象)进行覆盖操作,保证全局唯一。(什么时候用,再调用代理,覆盖)
就是本质问题。使用三级缓存的本质在于使用AOP,解决aop的代理问题?
三级缓存,为什么调用lambda value的值。 下图的stepA1的vlaue值。
为了给B对象的a属性进行付值操作。必须呀获取a对象,此时a的普通对象已经生成(半成品) getEarluBeanReference方法。
getEarluBeanReference方法内部会进行判断,是否需要使用AOP代理。getEarluBeanReference方法就保证了Bean的全局唯一。
一级缓存放成品对象
二级缓存放半成品对象(引用)
三级缓存放lambda表达式,来完成代理对象的覆盖过程。
代理怎么实现。a-b-c-a的环
嗯,差不多就到这里了。后面再完善spring的三层缓存问题解决循环问题。
如有问题也请大佬们纠正问题。