左神算法中级提升(4) 超级重点:动态规划的空间压缩技巧
【案例1】
【题目描述】【以后出现这种的题型 概率很低】
【案例2】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
构建两个栈,一个栈存放基本数据,一个栈存放最小值数据。每次加入一个数据时,当前元素和栈顶元素比较,谁小谁进入。 然后弹出时,两个栈同步弹出。
【代码实现】
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex2
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 8:47
*/
public class Ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static class MyStack {
Stack stack;
Stack minStack;
public MyStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int v) {
stack.push(v);
if (minStack.isEmpty()) { // 如果最小栈为空就直接加入
minStack.push(v);
} else {
int min = Math.min(minStack.peek(), v);
minStack.push(min);
}
}
public int pop() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈已经为空,无法弹出有效信息");
return -1;
} else {
int cur = stack.pop(); // 同步弹出
minStack.pop();
return cur;
}
}
public int getMin() {
if (minStack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈已经为空,无法弹出有效信息");
return -1;
} else {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
}
} 【案例3】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
队列实现栈结构,使用两个队列,每次加入时都加在有数据的队列,然后弹出时,将除了最后一个数据全部加载到另一个空队列,然后弹出最后一个元素。
栈实现队列结构,在一个栈中加入数据,弹出时将数据全部加载到另一个空栈里,然后弹出,如果弹出栈不为空,就直接弹出。
【代码实现】
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex3
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 9:02
*/
public class Ex3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueen myQueen = new MyQueen();
myQueen.push(5);
System.out.println(myQueen.pop());
myQueen.push(3);
System.out.println(myQueen.peek());
System.out.println(myQueen.peek());
myQueen.push(2);
myQueen.push(1);
myQueen.push(0);
System.out.println(myQueen.pop());
System.out.println(myQueen.pop());
System.out.println(myQueen.pop());
System.out.println(myQueen.pop());
System.out.println("========");
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(5);
myStack.push(3);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(1);
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
}
public static class MyQueen{
public Stack stackPush;
public Stack stackPop;
public MyQueen(){
this.stackPush = new Stack<>();
this.stackPop = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int v){
stackPush.push(v);
process();
}
public int pop(){
process();
if(stackPop.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queen is empty!!!");
}
return stackPop.pop();
}
public int peek(){
process();
if(stackPop.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queen is empty!!!");
}
return stackPop.peek();
}
private void process(){
if(stackPop.isEmpty()){
while (!stackPush.isEmpty()){
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
}
}
}
public static class MyStack{
public LinkedList list1;
public LinkedList list2;
public int k = 1; // 指定现在加入数据的列表是那个
public MyStack(){
list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int v){
if(k == 1){
list1.add(v);
}else {
list2.add(v);
}
}
public int pop(){
int cur;
if(k == 1){
cur = list1.remove();
while (!list1.isEmpty()){
list2.add(cur);
cur = list1.remove();
}
k = 2;
}else {
cur = list2.remove();
while (!list2.isEmpty()){
list1.add(cur);
cur = list2.remove();
}
k = 1;
}
return cur;
}
}
} 【案例4】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【动态规划的空间压缩技巧】【只能减少空间的使用】
如果一个位置只依赖它左边的和上边的数据,则我们可以只用一个数组表示第一行,让这个数组自更新即可,这样就可以得到我们想要的数据。同样,也可以用一个数组表示第一列,来做列的自更新。 有时可以用部分变量来记录某些数据,帮助完成自更新。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex4
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 10:26
*/
public class Ex4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {{2,5,7,9,11},{2,3,4,5,3},{1,5,6,7,9}};
System.out.println(getMin(matrix));
}
public static int getMin(int[][] matrix){
// 这里假设行和列规模相似,
// 如果规模差距很大,如n行m列 n >>> m,我们选择行更新,数组大小为m, m >>> n,我们选择列更新,数组大小为n
int n = matrix.length;
int m = matrix[0].length;
int[] arr = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { // 初始化数组
arr[i] = matrix[0][i];
if (i > 0){
arr[i] += arr[i-1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { // 自更新
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (j == 0){
arr[j] = arr[j] + matrix[i][j];
}else {
arr[j] = Math.min(arr[j-1], arr[j]) + matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
return arr[m-1];
}
}
【案例5】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
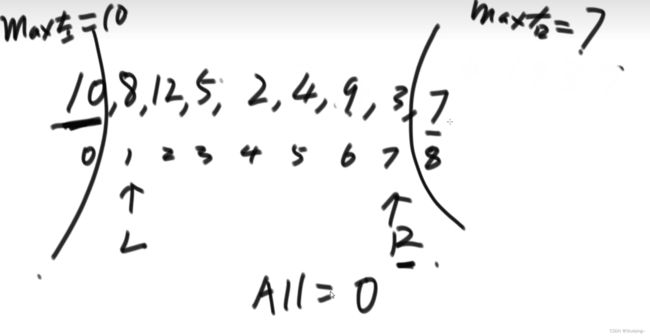
如果常规思维我们去寻找那些地方有可能有水是非常麻烦的。所以我们去求每个位置的水量来做累加即可。对于一个i位置,它的左边最大值假设为maxL,右边最大值为maxR,容易想到此时的水量为max{min{maxL,maxR}-arr[i],0}。
所以第一种思路使用两个数组分别记录每个位置的左边最大值和右边最大值。空间复杂度为O(N)
第二种思路,空间复杂度为O(1),记录目前已经遍历的左边最大值maxL和右边最大值maxR
(1)maxL < maxR,
则L索引位置上的桶边界已经确定,因为water = max{min{maxL,maxR}-arr[i],0}。maxR可能更大,但是他并不影响min{maxL,maxR}-arr[i]。
(2)maxL > maxR
则R索引位置上的桶边界已经确定
(3) maxL == maxR
则L和R索引位置上的桶边界都已经确定
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex5
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 10:42
*/
public class Ex5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3,1,2,5,2,4};
System.out.println(water1(arr));
System.out.println(water2(arr));
}
public static int water1(int[] arr) {
// 使用两个数组来记录每个位置的左最大值和右最大值
int n = arr.length;
int[] left = new int[n];
int[] right = new int[n];
left[1] = arr[0];
right[n - 2] = arr[n - 1];
for (int i = 2; i < n - 1; i++) {
left[i] = Math.max(left[i - 1], arr[i - 1]);
}
for (int i = n - 3; i > 0; i--) {
right[i] = Math.max(right[i + 1], arr[i + 1]);
}
int total = 0;
// 因为1位置和末位置都没有约束,不可能装水
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
total += Math.max(Math.min(right[i], left[i]) - arr[i], 0);
}
return total;
}
public static int water2(int[] arr) {
// 使用两个数组来记录每个位置的左最大值和右最大值
int n = arr.length;
int left = arr[0];
int right = arr[n - 1];
int L = 1;
int R = n - 2;
int total = 0;
// 因为1位置和末位置都没有约束,不可能装水
while (L <= R){
if (left > right){
total += Math.max(right - arr[R], 0);
right = Math.max(right, arr[R--]);
}else if(right > left){
total += Math.max(left - arr[L], 0);
left = Math.max(left, arr[L++]);
}else {
total += Math.max(right - arr[R], 0);
right = Math.max(right, arr[R--]);
total += Math.max(left - arr[L], 0);
left = Math.max(left, arr[L++]);
}
}
return total;
}
}
【案例6】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
对于每个数组,他都有一个全局最大值,如果全局最大值在左部分,则我们应使右部分的最大值尽可能小,右部分至少包含一个元素arr【n-1】,所以右部分最大值>=arr[n-1],我们要是右部分尽可能小,所以让右部分只包含唯一一个元素。最大值在右部分情况类似。但是如果最大值在左边界,则只能在左部分,如果在右边界只能在右部分。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex6
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 11:57
*/
public class Ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static int getMax(int[] arr){
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max){
max = arr[i];
index = i;
}
}
int ans;
if(index == 0){
ans = max - arr[arr.length - 1];
} else if (index == arr.length - 1) {
ans = max - arr[0];
}else {
ans = Math.max(max - arr[arr.length - 1], max - arr[0]);
}
return ans;
}
}【案例7】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
当字符串a、b长度不相等时,直接返回false。长度相等时,使a = a + a,然后使用KMP算法查询b是否在a上面。
【KMP算法详解】
详解并查集和KMP算法_Studying~的博客-CSDN博客
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex7
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 13:23
*/
public class Ex7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "12345";
String b = "44123";
System.out.println(rotateStr(a, b));
}
public static boolean rotateStr(String a, String b){
if (a.length() != b.length()){
return false;
}
a = a + a;
int[] next = getNext(b);
int p1 = 0;
int p2 = 0;
char[] aChar = a.toCharArray();
char[] bChar = b.toCharArray();
while (p1 < aChar.length && p2 < bChar.length){
if (aChar[p1] == bChar[p2]){
p1 ++;
p2++;
} else if (next[p2] != -1) {
p2 = next[p2];
}else {
p1++;
}
}
return p2 == bChar.length;
}
public static int[] getNext(String str){
if (str.length() == 1){
return new int[] {-1};
}
int n = str.length();
char[] chars = new char[n];
int[] next = new int[n];
next[0] = -1;
next[1] = 0;
int i = 2;
int cn = 0;
while (i < n) {
if(chars[cn] == chars[i-1]){
next[i++] = ++cn;
} else if (cn > 0) {
cn = next[cn];
}else {
next[i++] = 0;
}
}
return next;
}
}
【案例8】
【题目描述】 【2019 京东面试题】
给你一个正数数组,每个正数代表一个咖啡机冲一杯咖啡所需要的时间,一个咖啡机同时只能冲一杯咖啡。给你一个正数N,代表有n个人想喝咖啡,每个人只喝一杯。有一个洗咖啡杯的机器,一次只能洗一个,所需时间为a。咖啡杯不洗,也能通过自然挥发变干净所需要的时间b。返回所有人喝完咖啡,并且所有咖啡杯清洗干净所需要的最少时间。
【思路分析】
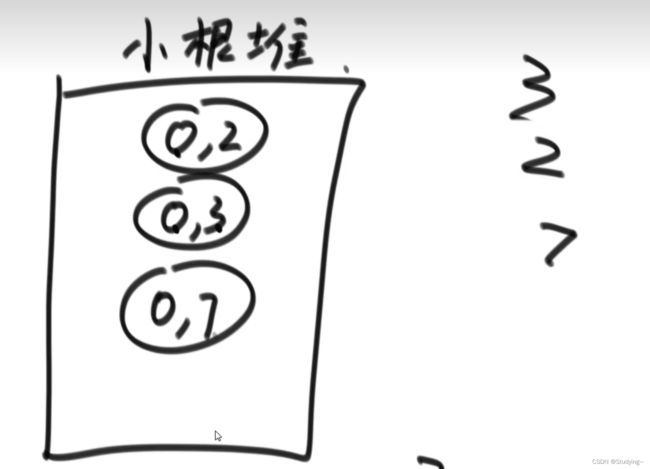
每个人喝咖啡的时间可以通过小根堆得到,小根堆里面存放一个Coffee结构,如(0,2)第一个数字代表咖啡机能使用的时间,第二个数字代表咖啡机冲一杯咖啡所需的时间。小根堆根据两个数字的和来进行维护。
得到每个人得到咖啡的时间后,根据洗咖啡杯的两种策略来进行决定。
【代码实现】
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex8
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 14:10
*/
public class Ex8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 7};
System.out.println(minTime(arr, 5, 2, 3));
}
public static class Coffee {
public int time;
public int need;
public Coffee(int time, int need) {
this.time = time;
this.need = need;
}
}
public static int minTime(int[] arr, int n, int a, int b) {
int[] drink = drink(arr, n);
return dpWash(drink, a, b, n);
}
public static int[] drink(int[] arr, int n) { // 得到n个人喝到咖啡的时间
PriorityQueue coffees = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Coffee o1, Coffee o2) {
return (o1.need + o1.time) - (o2.need + o2.time);
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Coffee cur = new Coffee(0, arr[i]);
coffees.add(cur);
}
int[] drink = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Coffee cur = coffees.poll();
cur.time += cur.need;
drink[i] = cur.time;
coffees.add(cur);
}
return drink;
}
public static int wash(int[] drink, int a, int b, int index, int washTime) {
// index 代表现在洗到第几个杯子了
// washTime代表洗咖啡机 在多久可以使用
// 对每个杯子都有两种策略。 要么洗干净,要么不洗等他挥发干净。 返回两种情况中用时最少的那个
// a 是洗杯子所用时间, b是自然挥发所用时间
if (index == drink.length) {
return 0;
}
int wash1 = Math.max(washTime, drink[index]) + a;
int next1 = wash(drink, a, b, index + 1, wash1);
int time1 = Math.max(wash1, next1);
int wash2 = drink[index] + b;
int next2 = wash(drink, a, b, index + 1, washTime);
int time2 = Math.max(wash2, next2);
return Math.min(time1, time2);
}
public static int dpWash(int[] drink, int a, int b, int n) {
if (a >= b) {
return drink[n - 1] + b;
}
int[][] times = new int[n][drink[n - 1] + n * a];
for (int i = 0; i < times[0].length; i++) {
times[n-1][i] = Math.min(drink[n - 1] + b, Math.max(i, drink[n-1]) + a);
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
int washTime = drink[i] + (i + 1) * a;
for (int j = 0; j < washTime; j++) {
int wash = Math.max(j, drink[i]) + a;
times[i][j] = Math.min(Math.max(wash, times[i + 1][wash]), Math.max(drink[i] + b, times[i + 1][drink[i] + b]));
}
}
return times[0][0];
}
}
【案例9】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
每个数字都一定可以分为奇数(有a个),和只有一个2因子的数(有b个),和含有多个2因子的数(有c个)。
(1) b == 0
a == 1, c >= 1; a > 1, c >= a - 1
(2) b != 0
c >= a; if (b == 1) c >= Math.max{1, a};
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex9
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/12 16:29
*/
public class Ex9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static boolean arr4(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length == 0) {
return false;
}
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0) {
if (arr[i] % 4 == 0) {
c++;
} else {
b++;
}
} else {
a++;
}
}
if (b == 0) {
if (a == 0) {
return true;
} else if (a == 1) {
return c >= 1;
} else {
return c >= a - 1;
}
} else {
if (b == 1) {
return c >= Math.max(1, a);
} else {
return c >= a;
}
}
}
}