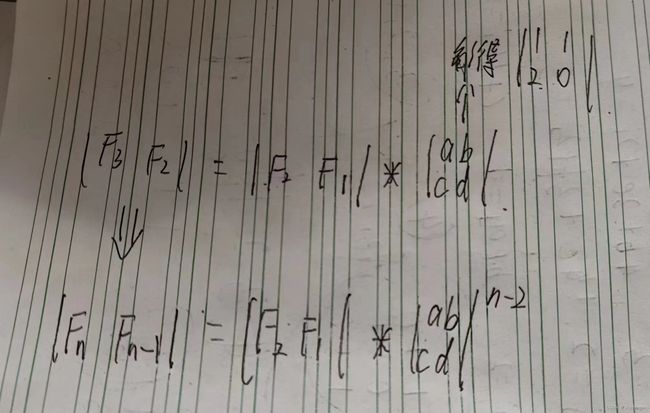左神算法 重要技巧:递归的加速技巧(斐波那契数列套路)以及推广
目录
【案例1】【十分重要 : 斐波那契递归套路,只要像斐波那契这种严格递归都可以进行类似的优化】
【有严格的递归项后,通过线性代数的知识进行优化】
【代码实现】
【技巧推广】
【实例1 使用这个技巧】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【实例2】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】 代码没有考虑死亡,考虑了也很简单,你们可以尝试自己写一下,不会可以私信博主。
【实例3】
【题目描述】 【此题给出一个很好的思路】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【实例4】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例1】【十分重要 : 斐波那契递归套路,只要像斐波那契这种严格递归都可以进行类似的优化】
斐波那契数列递归的加速技巧。除了初始项,后序的每一项都有严格都有严格的递归项的所有问题,都可以进行递归优化
【有严格的递归项后,通过线性代数的知识进行优化】
求解后得到 | F(n) F(n-1) | = | F(2) F(1) | * ![]() ^ (n-2)
^ (n-2)
假如矩阵![]() ^ (n-2)求出的值为
^ (n-2)求出的值为 ![]() ,则F(N) = a + c
,则F(N) = a + c
然后现在如果要优化时间,就需要找到一种方法使得这样的矩阵的某次方算得更快。
先考虑10 ^ 75, 可以将 75 转为二进制 1001011, 然后 t = 10 ^ 1,每次t = t*t;如果上面的数字,在二进制中出现了就相乘。
矩阵也可以按照这种策略得到。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex1
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/13 8:35
*/
public class Ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fibonacci(5));
}
// 斐波那契数列求解
public static int fibonacci(int n){
if (n < 1){
return 0;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2){
return 1;
}
int[][] base = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int[][] res = matrixPower(base, n -2);
return res[0][0] + res[1][0];
}
// 矩阵的幂函数
public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] base, int n){
int[][] t = base;
// 先构建一个单位矩阵
int[][] res = new int[base.length][base.length];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i][i] = 1;
}
for (; n != 0 ; n >>= 1) {
if ((n & 1) == 1){
res = matrixMultiply(res, t);
}
t = matrixMultiply(t, t);
}
return res;
}
// 只要 a 和 b的矩阵规模是常数矩阵,时间复杂度就是O(1)
public static int[][] matrixMultiply(int[][] a, int[][] b){
int[][] res = new int[a.length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
res[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}【技巧推广】
【实例1 使用这个技巧】
【题目描述】
一个农场,第一年有一个母牛,后每年一个母牛可以生一头母牛,新生的母牛三年后便就有了生育能力,假设牛不会死亡。问第N年有多少头牛。
【思路解析】
列出前几年的牛的数列 1 2 3 4 6 9 13 ....., 则f当N>3时 , F(N) = F(N-1) + F(N-3)
所以
然后进行矩阵乘法的加速。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex2
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/13 9:53
*/
public class Ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(cowProm(7));
}
// 斐波那契数列求解
public static int cowProm(int n){
if (n < 1){
return 0;
}
if (n <= 3){
return n;
}
int[][] base = {{1, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1}, {1, 0, 0}};
int[][] res = matrixPower(base, n - 3);
return res[0][0] * 3 + 2 * res[1][0] + res[2][0];
}
// 矩阵的幂函数
public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] base, int n){
int[][] t = base;
// 先构建一个单位矩阵
int[][] res = new int[base.length][base.length];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i][i] = 1;
}
for (; n != 0 ; n >>= 1) {
if ((n & 1) == 1){
res = matrixMultiply(res, t);
}
t = matrixMultiply(t, t);
}
return res;
}
// 只要 a 和 b的矩阵规模是常数矩阵,时间复杂度就是O(1)
public static int[][] matrixMultiply(int[][] a, int[][] b){
int[][] res = new int[a.length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
res[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
【实例2】
【题目描述】
有一只母兔,每年生两只母兔,兔子两年之后就有了生育能力,开始生育,问第N年后有几只兔子。 (如果五年后死亡),如果考虑死亡,然后算上死亡的兔子数亮,可以列出一个严格的递归式,然后再看是几阶矩阵,然后带入求解即可。
【思路解析】
列出前几年的兔子数量 1 3 5 11 21 43 .... N>= 3 时 F(N) = F(N-1) + 2 * F(N-2) - F(N-5) 。
矩阵乘法加速思路相同。
【代码实现】 代码没有考虑死亡,考虑了也很简单,你们可以尝试自己写一下,不会可以私信博主。
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex2
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/13 9:53
*/
public class Ex3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(doeProm(6));
}
// 斐波那契数列求解
public static int doeProm(int n){
if (n < 1){
return 0;
}
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if(n==2){
return 3;
}
int[][] base = {{1,1},{2,0}};
int[][] res = matrixPower(base, n - 2);
return res[0][0] * 3 + res[1][0];
}
// 矩阵的幂函数
public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] base, int n){
int[][] t = base;
// 先构建一个单位矩阵
int[][] res = new int[base.length][base.length];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i][i] = 1;
}
for (; n != 0 ; n >>= 1) {
if ((n & 1) == 1){
res = matrixMultiply(res, t);
}
t = matrixMultiply(t, t);
}
return res;
}
// 只要 a 和 b的矩阵规模是常数矩阵,时间复杂度就是O(1)
public static int[][] matrixMultiply(int[][] a, int[][] b){
int[][] res = new int[a.length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
res[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
【实例3】
【题目描述】 【此题给出一个很好的思路】
【思路解析】
这是原理分析
先写出前几个数据,也容易看出规律。
如果没有找出规律,也可以使用暴力尝试,但时间复杂度极高。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex4
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/13 8:35
*/
public class Ex4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fibonacci(6));
}
// 斐波那契数列求解
public static int fibonacci(int n){
if (n < 1){
return 0;
}
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if(n == 2){
return 2;
}
int[][] base = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int[][] res = matrixPower(base, n -2);
return res[0][0] * 2+ res[1][0];
}
// 矩阵的幂函数
public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] base, int n){
int[][] t = base;
// 先构建一个单位矩阵
int[][] res = new int[base.length][base.length];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i][i] = 1;
}
for (; n != 0 ; n >>= 1) {
if ((n & 1) == 1){
res = matrixMultiply(res, t);
}
t = matrixMultiply(t, t);
}
return res;
}
// 只要 a 和 b的矩阵规模是常数矩阵,时间复杂度就是O(1)
public static int[][] matrixMultiply(int[][] a, int[][] b){
int[][] res = new int[a.length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
res[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
【实例4】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
如果n=6, 就是我有 1 2 3 4 5 6,这几个木棍,要使任意三根都不能组成三角形,即任意两根不能大于第三根,等于的情况,就是去掉最少的情况。所以又可以总结为斐波那契数列问题。里面去掉所有木棍后,剩下的木棍长度可以组成一个斐波那契数列。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex5
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/13 11:48
*/
public class Ex5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getMin(18));
}
public static int getMin(int n){
int i = 0;
while (fibonacci(i) <= n){
i++;
}
return n - (i - 1);
}
// 斐波那契数列求解
public static int fibonacci(int n){
if (n < 1){
return 0;
}
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
if(n == 2){
return 2;
}
int[][] base = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int[][] res = matrixPower(base, n -2);
return res[0][0] * 2+ res[1][0];
}
// 矩阵的幂函数
public static int[][] matrixPower(int[][] base, int n){
int[][] t = base;
// 先构建一个单位矩阵
int[][] res = new int[base.length][base.length];
for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) {
res[i][i] = 1;
}
for (; n != 0 ; n >>= 1) {
if ((n & 1) == 1){
res = matrixMultiply(res, t);
}
t = matrixMultiply(t, t);
}
return res;
}
// 只要 a 和 b的矩阵规模是常数矩阵,时间复杂度就是O(1)
public static int[][] matrixMultiply(int[][] a, int[][] b){
int[][] res = new int[a.length][a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
res[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
}
}
}
return res;
}
}