计算机网络 day11 tcpdump - 传输层 - netstat - socket - nc - TCP/UDP头部
目录
故障排查
tcpdump抓包工具
传输层(TCP和UDP协议)
传输层的作用
应用程序和端口号有什么关系?
传输层端对端连接实现拓扑图
如何查看自己的linux机器开放了哪些端口?
1、netstat(network status 网络的状态)
netstat查看本机开放的端口:
socket 槽、套接字(接口)
2、ss命令:
3、lsof命令
如何查看其他机器开放了哪些端口?
nc、nmap命令
如何知道这个ip地址175.6.49.131(不是本机)对应的主机开放了哪些端口?
nc命令
nmap命令
TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) 传输控制协议
UDP(User Datagram Protocol) 用户数据报协议
TCP的封装格式
数据传输的过程:
UDP的封装格式:
故障排查
在进行网络故障排查时,需要有耐心和系统性地逐步排查。根据具体情况,也可能需要使用其他工具和技术来帮助诊断和解决问题。
tcpdump抓包工具
tcpdump 进行网络诊断的时候的工具(类似于医院里的CT、B超、核磁共振)
tcpdump抓包命令:
tcpdump -i ens33 tcp dst port 80 and src host 192.168.1.142
#抓取从ens33接口进来的数据包,协议是tcp协议 目的端口是80 同时 源ip地址是192.168.1.142src host 192.168.1.142 源ip地址是192.168.1.142 source 源
dst port 80 目的端口是80and 前面的条件和后面的条件都要满足
or 2个条件满足一个就可以了
tcpdump -i ens33 arp
tcpdump -i ens33 icmp
tcpdump -i ens33 arp or icmp
ping 和 tcpdump 是网络诊断的2大神器。传输层(TCP和UDP协议)
传输层的作用
(网络层)IP层提供点到点的连接,而传输层提供端到端的连接。
它主要负责在源主机和目标主机之间提供端到端的数据传输服务,并确保可靠、有序地传输数据。
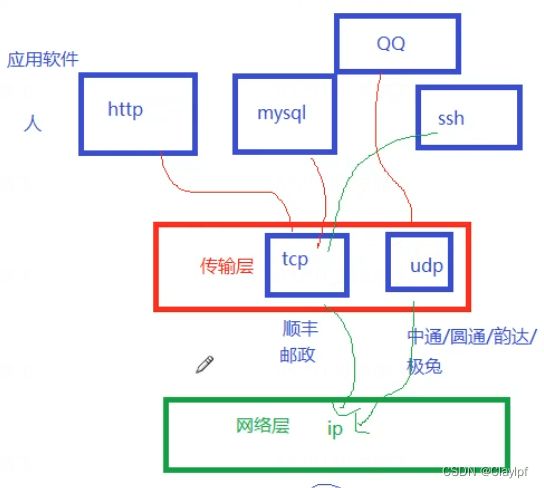
应用程序和端口号有什么关系?
应用程序其实就是运行一个程序提供某个服务
一个应用程序 --》 背后就是一个服务 --》落实到进程来实现 --》进程会监听某个端口
(可以理解为打开一个窗户或者一扇门(端口),这样别人(数据)就可以进来了)
QQ --》实现即时通信(聊天发消息)--》UDP协议
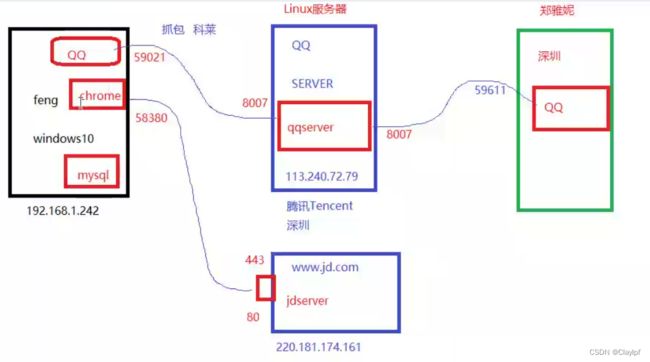
传输层端对端连接实现拓扑图
一台电脑里可以同时运行很多的应用程序
不同的程序不能占用相同的端口号
上图中的 应用程序 和 端口号 绑定了
我们不知道QQ的端口号,我们需要使用抓包工具(科莱),找到QQ的TCP包或者UDP包,从而获取QQ的端口号,IP地址和协议
qq server --》8007 --》UDP
如何查看自己的linux机器开放了哪些端口?
使用netstat、ss(不如netstat好用)、lsof等工具
1、netstat(network status 网络的状态)
netstat可以查看本机开放了哪些端口
应用程序--》服务---》进程--》占用一个端口(监听某个端口)
下载netstat:
[root@sc-server ~]# yum install net-tools -ynetstat查看本机开放的端口:
[root@sc-server ~]# netstat -anplut
-a all
-n --numeric 数字的形式显示
-p --program
[--tcp|-t] tcp信息
[--udp|-u] udp信息
[--listening|-l] 处于监听状态的信息[root@sc-server ~]# netstat -anplut
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:23 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 967/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1677/sendmail: acce
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1257/mysqld
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1670/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1670/nginx: master
tcp 0 36 192.168.50.1:23 192.168.50.9:60013 ESTABLISHED 3845/sshd: root@pts
tcp6 0 0 :::23 :::* LISTEN 967/sshd
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 1670/nginx: master
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:* 693/chronyd
udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::* 693/chronyd 其中的名词解释:
ESTABLISHED 建立连接
LISTEN 听(监听) 监控某个端口看是否有人连接过来(监听)Proto 代表使用的是什么协议
Recv-Q 接受数据的队列里有多少数据 receive queue -->表示我们的应用程序还没有处理的数据
Send-Q 发送数据的队列里有多少数据 Send queue -->我们发生出去的数据,远程主机没有确认的数据Local Address 表示本地的IP地址和端口号
Foreign Address 表示外部机器的IP地址和端口号
State 代表现在连接处于什么状态
PID/Program PID代表进程号 Program代表程序名字
0.0.0.0 代表任意ip地址
127.0.0.1:35 代表只是在127.0.0.1这个ip上开放35号端口 --》代表只能自己访问
0.0.0.0:* 代表任意ip地址和任意端口号 *代表任意端口号
杀死进程:
[root@sc-server ~]# kill -9 1677 强制杀死pid是1677进程
-9 表示告诉linux内核强制杀死某个进程
9) SIGKILL 本质上属于一种信号signal kill状态解释:
Recv-Q
Established: The count of bytes not copied by the user program connected to this socket. Listening: Since
Kernel 2.6.18 this column contains the current syn backlog.
Send-Q
Established: The count of bytes not acknowledged by the remote host. Listening: Since Kernel 2.6.18 this col‐
umn contains the maximum size of the syn backlog.
Local Address
Address and port number of the local end of the socket. Unless the --numeric (-n) option is specified, the
socket address is resolved to its canonical host name (FQDN), and the port number is translated into the cor‐
responding service name.
Foreign Address
Address and port number of the remote end of the socket. Analogous to "Local Address."
State
The state of the socket. Since there are no states in raw mode and usually no states used in UDP and UDPLite,
this column may be left blank. Normally this can be one of several values:
ESTABLISHED
The socket has an established connection.
SYN_SENT
The socket is actively attempting to establish a connection.
SYN_RECV
A connection request has been received from the network.
FIN_WAIT1
The socket is closed, and the connection is shutting down.
FIN_WAIT2
Connection is closed, and the socket is waiting for a shutdown from the remote end.
TIME_WAIT
The socket is waiting after close to handle packets still in the network.
Recv-Q
Established:连接到此套接字的用户程序未复制的字节数。聆听:自
内核2.6.18本列包含当前的syn积压。
Send-Q
Established:未被远程主机确认的字节数。监听:自内核2.6.18起,此参数为0
Umn包含syn积压的最大大小。
Local Address
socket本端地址和端口号。除非指定了——numeric (-n)选项
socket地址被解析为它的规范主机名(FQDN),端口号被转换成响应的服务名称。
Foreign Address
套接字远端地址和端口号。类似于“本地地址”。
State
socket的状态。由于在原始模式下没有状态,通常在UDP和UDPLite中没有使用状态,
这一栏可以留空。通常,这可以是以下几个值之一:
ESTABLISHED
socket已建立连接。
SYN_SENT
socket正在积极尝试建立连接。
SYN_RECV
已从网络接收到连接请求。
FIN_WAIT1
socket已关闭,连接正在关闭。
FIN_WAIT2
连接已关闭,socket正在等待远程端关闭。
TIME_WAIT
socket在关闭后等待处理仍在网络中的数据包。socket 槽、套接字(接口)
socket = ip+port --》接口
Socket(套接字)是计算机网络编程中的一种编程接口,用于实现网络通信
它提供了一种机制,使不同计算机之间或同一计算机上的不同进程之间可以进行数据交换和通信。
它基于网络协议栈(如TCP/IP协议栈)实现了数据传输的底层细节。
2、ss命令:
[root@sc-server ~]# ss -anptul
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 *:* users:(("chronyd",pid=693,fd=5))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::1]:323 [::]:* users:(("chronyd",pid=693,fd=6))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:23 *:* users:(("sshd",pid=967,fd=3))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* users:(("nginx",pid=1672,fd=8),("nginx",pid=1671,fd=8),("nginx",pid=1670,fd=8))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:8080 *:* users:(("nginx",pid=1672,fd=7),("nginx",pid=1671,fd=7),("nginx",pid=1670,fd=7))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:23 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=967,fd=4))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:80 [::]:* users:(("nginx",pid=1672,fd=9),("nginx",pid=1671,fd=9),("nginx",pid=1670,fd=9))
[root@sc-server ~]# 3、lsof命令
查看单个端口是否被占据了:使用lsof命令:
下载lsof:
[root@sc-server ~]# yum install lsof net-tools -ylsof的使用:
[root@sc-server ~]# lsof -i:80 查看80端口被那个进程占用了
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
nginx 1670 root 8u IPv4 21644 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 1670 root 9u IPv6 21645 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 1671 nginx 8u IPv4 21644 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 1671 nginx 9u IPv6 21645 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 1672 nginx 8u IPv4 21644 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
nginx 1672 nginx 9u IPv6 21645 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
[root@sc-server ~]# lsof -i:22
[root@sc-server ~]# lsof -i:23
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
sshd 967 root 3u IPv4 20037 0t0 TCP *:telnet (LISTEN)
sshd 967 root 4u IPv6 20039 0t0 TCP *:telnet (LISTEN)
sshd 3845 root 3u IPv4 72900 0t0 TCP sc-server:telnet->192.168.50.9:60013 (ESTABLISHED)
[root@sc-server ~]# 如何查看其他机器开放了哪些端口?
nc、nmap命令
如何知道这个ip地址175.6.49.131(不是本机)对应的主机开放了哪些端口?
下载nc 和 namp:
[root@sc-server ~]# yum install nc nmap -ync命令
nc(netcat)是一个强大的网络工具,可以在命令行下进行网络连接、数据传输和端口扫描等操作
连接到指定主机和端口:
nc示例:连接到主机 example.com 的 80 端口
nc example.com 80等待连接并监听指定端口:
nc -l示例:监听本地主机的 12345 端口
nc -l 12345发送文件:
nc -w< 示例:将本地文件 example.txt 发送到远程主机的 12345 端口
nc -w 3 example.com 12345 < example.txt接收文件:
nc -l> 示例:接收来自远程主机的文件并保存为 example.txt
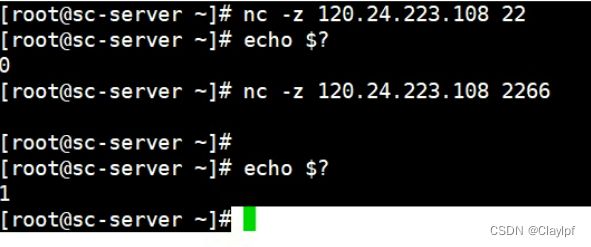
nc -l 12345 > example.txt端口扫描:
nc -zv- 示例:扫描 example.com 主机的 1 到 1000 端口
nc -zv example.com 1-1000
-z 表示没有返回值,但是我们可以通过echo $?来判断该机器的端口是否打开了
nmap命令
nmap 会对某个ip地址进行常用端口号的扫描,一个一个端口去试是否开放 0~1024+常用端口(对该台机器的端口进行遍历查询)
端口号的范围: 0~65535
[root@sc-server ~]# nmap 120.24.223.108
Starting Nmap 6.40 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2023-07-19 15:17 CST
Nmap scan report for 120.24.223.108
Host is up (0.025s latency).
Not shown: 995 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
443/tcp open https
3306/tcp open mysql
3389/tcp closed ms-wbt-server
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 9.44 seconds
[root@sc-server ~]#TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) 传输控制协议
可靠的、面向连接的协议
传输效率低
UDP(User Datagram Protocol) 用户数据报协议
不可靠的、无连接的服务
传输效率高
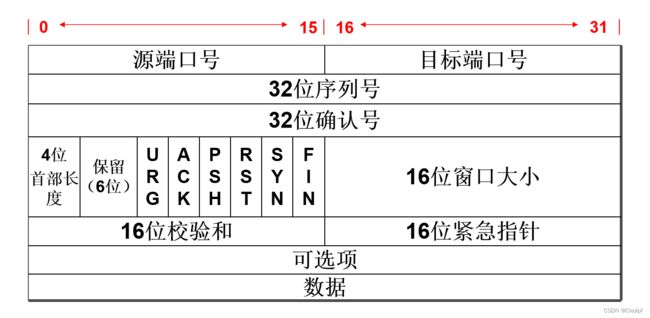
TCP的封装格式
源端口号:发送TCP进程对应的端口号
目标端口号:目标端接收进程的端口号
32位序列号:0 ~ 2^32-1范围内,数据段标记,用于到目的端对到达包的重组
32位确认号:0 ~ 2^32-1范围内,对发送端的确认信息,告诉发送端这个序号之前的数据段都收到了
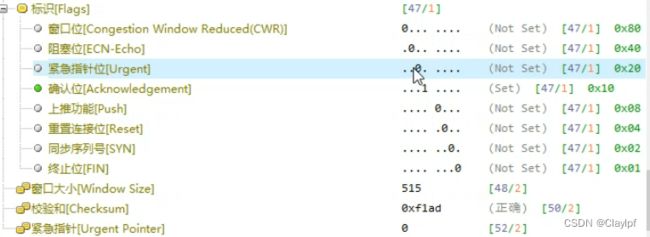
6个控制位:(标志位:作用就是表达某个意思,双方沟通的时候使用)
U R G:紧急指针有效位,与16位紧急指针配合使用(紧急指针位)
A C K:确认序列号有效位,表明该数据包包含确认信息(确认位)
P S H:通知接收端立即将数据提交给用户进程,不在缓存中停留,等待更多的数据(push上推位)
R S T:为1时,请求重新建立TCP连接(重置连接位)
S Y N:为1时,请求建立连接(同步序列号位)
F I N:为1时,数据发送完毕,请求断开连接(结束位、终止位)
16位窗口大小:滑动窗口的大小,指明本地可接收数据的字节数
16位校验和:用于验证数据的完整性和检测传输过程中是否出现错误
16位紧急指针:与控制位U R G有关
TCP头部:20个字节
IP头部:20个字节
帧头部:18个字节
MTU:最大字节数为1500(包含了头部信息)
数据:1500-20-20=1460字节
抓包(TCP包)
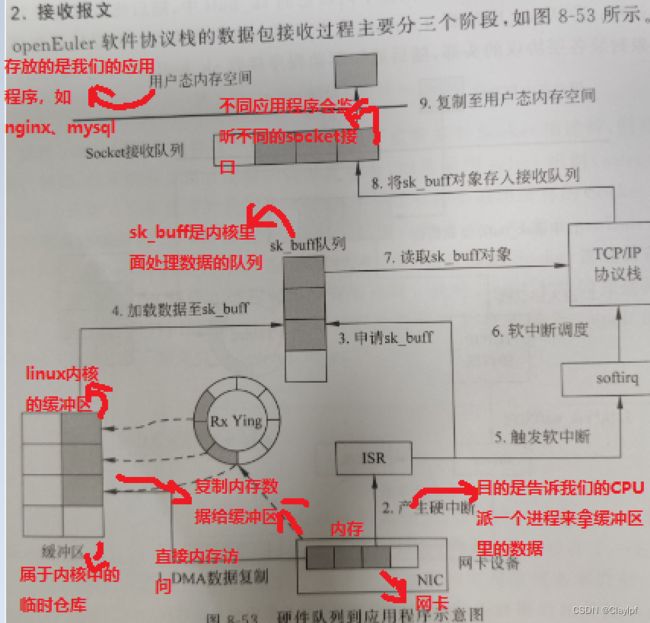
数据传输的过程:
NIC 网卡(network interface card)
DMA 直接内存访问(directly memory access):直接将网卡存储芯片里的数据复制到内存里
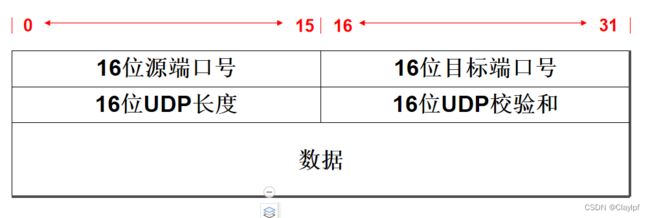
UDP的封装格式:
16位源端口号:发送端的UDP进程端口号
16位目标端口号:接收端的UDP进程端口号
16位UDP长度:包含数据的长度,可以算出数据的结束位置
16位UDP校验和:UDP的差错控制(可选)