MySQL第五章、索引事务
目录
一、索引
1.1 概念
1.2 作用
1.3 使用场景
1.4 使用
1.5 案例
二、索引背后的数据结构
2.1 B-树(B树)
2.2 B+树(MySQL背后数据结构)
三、事务
3.1 为什么使用事务
3.2 事务的概念
3.3 使用
3.4并发执行事务产生的问题
3.4.1脏读问题
3.4.2不可重复读
3.4.3幻读
3.4.4隔离级别
一、索引
1.1 概念
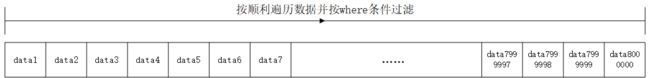
索引是一种特殊的文件,包含着对数据表里所有记录的引用指针。可以对表中的一列或多列创建索引,并指定索引的类型,各类索引有各自的数据结构实现。
1.2 作用
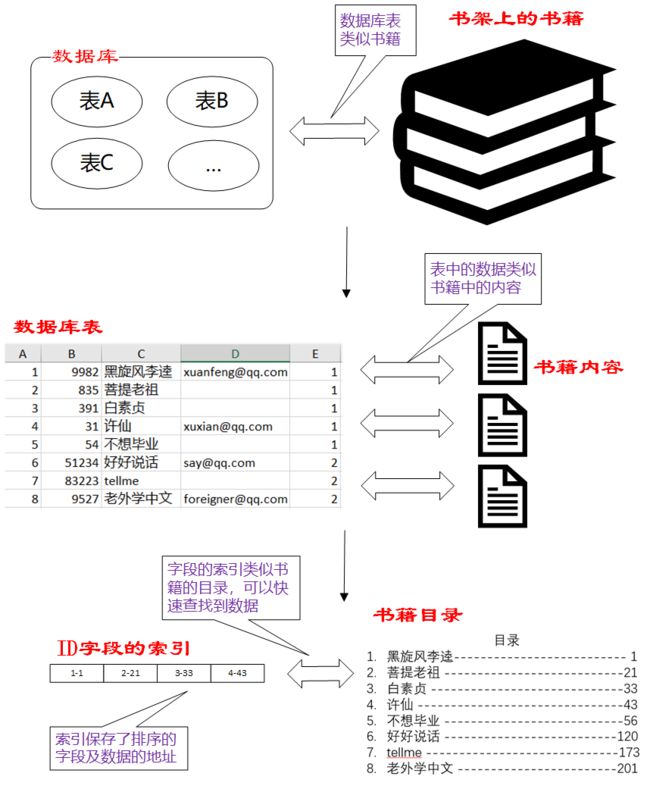
- 数据库中的表、数据、索引之间的关系,类似于书架上的图书、书籍内容和书籍目录的关系。
- 索引所起的作用类似书籍目录,可用于快速定位、检索数据。
- 索引对于提高数据库的性能有很大的帮助。
1.3 使用场景
要考虑对数据库表的某列或某几列创建索引,需要考虑以下几点:
- 数据量较大,且经常对这些列进行条件查询。
- 该数据库表的插入操作,及对这些列的修改操作频率较低。
- 索引会占用额外的磁盘空间。
满足以上条件时,考虑对表中的这些字段创建索引,以提高查询效率。反之,如果非条件查询列,或经常做插入、修改操作,或磁盘空间不足时,不考虑创建索引。
1.4 使用
创建主键约束(PRIMARY KEY)、唯一约束(UNIQUE)、外键约束(FOREIGN KEY)时,会自动创建对应列的索引。
- 查看索引
show index from 表名;- 创建索引
对于非主键、非唯一约束、非外键的字段,可以创建普通索引
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段名);- 删除索引
drop index 索引名 on 表名;1.5 案例
-- 创建用户表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_user;
CREATE TABLE test_user (
id_number INT,
name VARCHAR(20) comment '姓名',
age INT comment '年龄',
create_time timestamp comment '创建日期'
);-- 构建一个8000000条记录的数据
-- 构建的海量表数据需要有差异性,所以使用存储过程来创建, 拷贝下面代码就可以了,暂时不用理解
-- 产生名字
drop function if exists rand_name;
delimiter $$
create function rand_name(n INT, l INT)
returns varchar(255)
begin
declare return_str varchar(255) default '';
declare i int default 0;
while i < n do
if i=0 then
set return_str = rand_string(l);
else
set return_str =concat(return_str,concat(' ', rand_string(l)));
end if;
set i = i + 1;
end while;
return return_str;
end $$
delimiter ;
-- 产生随机字符串
drop function if exists rand_string;
delimiter $$
create function rand_string(n INT)
returns varchar(255)
begin
declare lower_str varchar(100) default
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz';
declare upper_str varchar(100) default
'ABCDEFJHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
declare return_str varchar(255) default '';
declare i int default 0;
declare tmp int default 5+rand_num(n);
while i < tmp do
if i=0 then
set return_str
=concat(return_str,substring(upper_str,floor(1+rand()*26),1));
else
set return_str
=concat(return_str,substring(lower_str,floor(1+rand()*26),1));
end if;
set i = i + 1;
end while;
return return_str;
end $$
delimiter ;
-- 产生随机数字
drop function if exists rand_num;
delimiter $$
create function rand_num(n int)
returns int(5)
begin
declare i int default 0;
set i = floor(rand()*n);
return i;
end $$
delimiter ;
-- 向用户表批量添加数据
drop procedure if exists insert_user;
delimiter $$
create procedure insert_user(in start int(10),in max_num int(10))
begin
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit = 0;
repeat
set i = i + 1;
insert into test_user values ((start+i) ,rand_name(2,
5),rand_num(120),CURRENT_TIMESTAMP);
until i = max_num
end repeat;
commit;
end $$
delimiter ;
-- 执行存储过程,添加8000000条用户记录
call insert_user(1, 8000000);查询 id_number 为778899的用户信息:
-- 可以看到耗时4.93秒,这还是在本机一个人来操作,在实际项目中,如果放在公网中,假如同时有1000
个人并发查询,那很可能就死机。
select * from test_user where id_number=556677;可以使用explain来进行查看SQL的执行:
explain select * from test_user where id_number=556677;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: test_user
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL <== key为null表示没有用到索引
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 6
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)为提供查询速度,创建 id_number 字段的索引:
create index idx_test_user_id_number on test_user(id_number);换一个身份证号查询,并比较执行时间:
select * from test_user where id_number=776655;可以使用explain来进行查看SQL的执行:
explain select * from test_user where id_number=776655;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: test_user
type: ref
possible_keys: idx_test_user_id_number
key: idx_test_user_id_number <= key用到了idx_test_user_id_number
key_len: NULL
ref: const
rows: 1
Extra: Using where
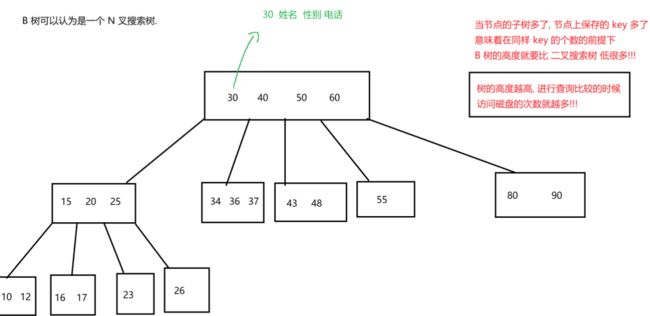
1 row in set (0.00 sec)索引保存的数据结构主要为B+树,及hash的方式,实现原理会在以后数据库原理的部分讲解。
二、索引背后的数据结构
2.1 B-树(B树)
2.2 B+树(MySQL背后数据结构)
三、事务
3.1 为什么使用事务
准备测试表:
drop table if exists accout;
create table accout(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) comment '账户名称',
money decimal(11,2) comment '金额'
);
insert into accout(name, money) values
('阿里巴巴', 5000),
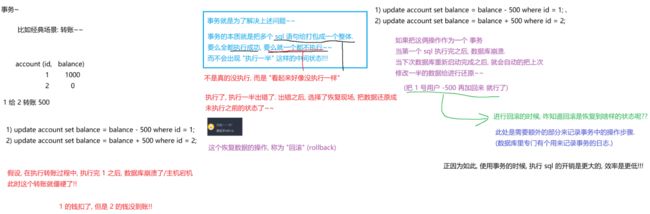
('四十大盗', 1000);比如说,四十大盗把从阿里巴巴的账户上偷盗了2000元
-- 阿里巴巴账户减少2000
update accout set money=money-2000 where name = '阿里巴巴';
-- 四十大盗账户增加2000
update accout set money=money+2000 where name = '四十大盗';假如在执行以上第一句SQL时,出现网络错误,或是数据库挂掉了,阿里巴巴的账户会减少2000,但是四十大盗的账户上就没有了增加的金额。
解决方案:使用事务来控制,保证以上两句SQL要么全部执行成功,要么全部执行失败。
3.2 事务的概念
事务指逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
在不同的环境中,都可以有事务。对应在数据库中,就是数据库事务。
3.3 使用
(1)开启事务:start transaction;
(2)执行多条SQL语句
(3)回滚或提交:rollback/commit;
说明:rollback即是全部失败,commit即是全部成功。
start transaction;
-- 阿里巴巴账户减少2000
update accout set money=money-2000 where name = '阿里巴巴';
-- 四十大盗账户增加2000
update accout set money=money+2000 where name = '四十大盗';
commit;事务的特性及设置,会在后续 数据库原理 部分进一步讲解。
3.4并发执行事务产生的问题
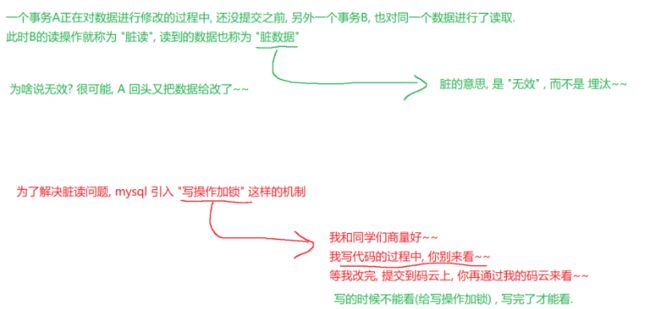
3.4.1脏读问题
加锁操作:降低了并发程度(降低了效率),提高了隔离性(提高了数据的准确性)
3.4.2不可重复读
读加锁操作:进一步降低事务的并发处理能力(处理效率也降低),提高了事务的隔离性(数据的准确性又提高了)