融合正余弦和柯西变异的麻雀搜索算法,并与灰狼算法,粒子群算法比较
今天的主角是:融合正余弦和柯西变异的麻雀搜索算法麻雀优化算法
在麻雀算法的基础上,改进点如下:
①采用折射反向学习策略初始化麻雀算法个体,基本思想是通过计算当前解的反向解来扩大搜索范围,借此找出给定问题更好的备选解;
②采用正余弦策略替换原始麻雀算法的发现者位置更新公式。当发现者搜寻的食物位于局部最优时,大量的跟随者会涌入到该位置,此时发现者与整个群体停滞不前,造成种群位置多样性出现损失;
③对正余弦策略的步长搜索因子进行改进;原始步长搜索因子呈线性递减趋势,不利于进一步平衡SSA的全局搜索和局部开发能力。
④采用柯西变异策略替换原始麻雀算法的跟随者位置更新公式。柯西分布与标准的正态分布相似,为连续的概率分布,在原点处值较小,两端较为扁长,逼近零速率较慢, 因而相比于正态分布能产生更大的扰动。因此,利用柯西变异对麻雀位置更新中的个体进行扰动,从而扩大麻雀算法的搜索规模,进而提升算法跳出局部最优能力。
原理公式及思路参考文献:
参考文献:[1] 李爱莲, 全凌翔, 崔桂梅, 等. 融合正余弦和柯西变异的麻雀搜索算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(3): 91-99.
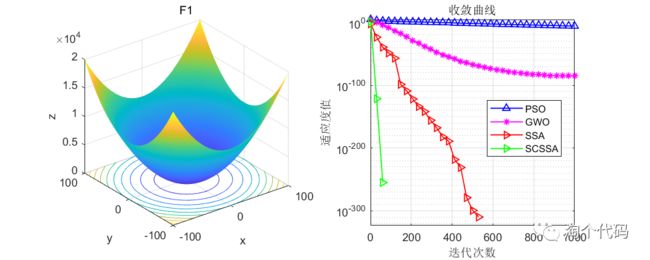
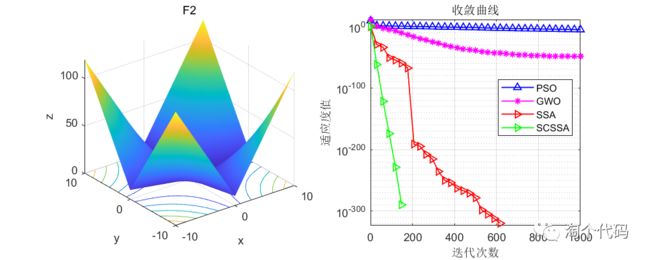
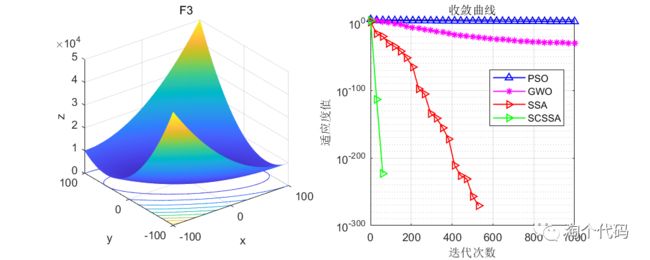
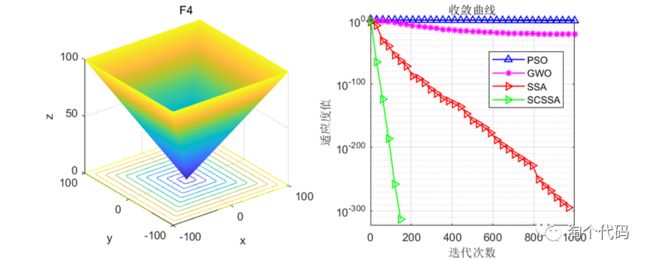
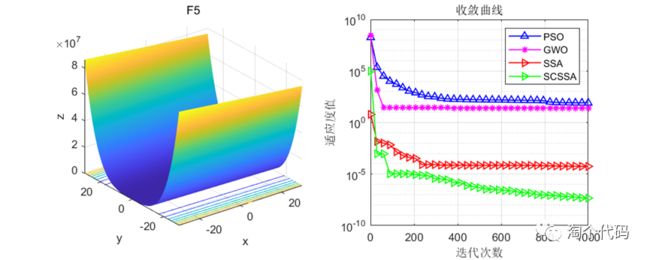
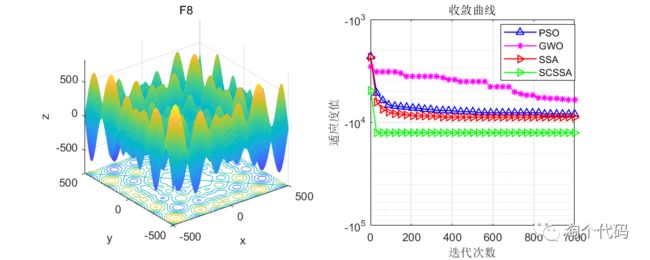
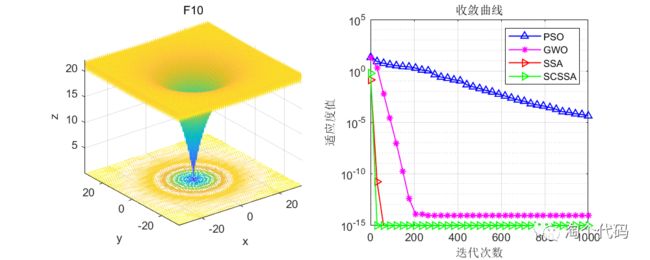
在CEC2005函数集上进行测试,结果如下:其中SCSSA为本文所提改进算法,SSA是原始的麻雀优化算法,GWO是灰狼优化算法,PSO是粒子群优化算法。
算法迭代1000次,每种算法的粒子数设置为100。
结果分析:在单峰值函数与多峰值函数的测试中可以看到,这篇文献提到的改进思路确实很强,大家也可以将柯西变异和正余弦策略用于其他算法的改进。
代码展示:
%%
clear all
close all
clc
N=100; % Number of search agents
Function_name='F1'; % Name of the test function, range from F1-F23
iter=1000; % Maximum number of iteration times
% Load details of the selected benchmark function
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=CEC2005(Function_name);
%% SSA
[fMin , bestX,SSA_Convergence_curve ] =SSA(N,iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by SSA for ' [num2str(Function_name)],' is : ', num2str(fMin)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by SSA: %s\n', num2str(bestX,'%e '));
%% GWO
[Best_score,Best_pos,PSO_curve]=PSO(N,iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % Calculating the solution of the given problem using PSO
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by PSO for ', [num2str(Function_name)],' is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by PSO: %s\n', num2str(Best_pos,'%e '));
%% gwo
[Alpha_score,Alpha_pos,GWO_Convergence_curve]=GWO(N,iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % Calculating the solution of the given problem using gwo
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by GWO for ', [num2str(Function_name)],' is : ', num2str(Alpha_score)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by GWO: %s\n', num2str(Alpha_pos,'%e '));
%% SCSSA
[SCSSA_fMin , SCSSA_bestX,SCSSA_Convergence_curve ] =SCSSA(N,iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by SCSSA for ' [num2str(Function_name)],' is : ', num2str(SCSSA_fMin)]);
fprintf ('Best solution obtained by SCSSA: %s\n', num2str(SCSSA_bestX,'%e '));
%Draw objective space
%% Figure
figure1 = figure('Color',[1 1 1]);
G1=subplot(1,2,1,'Parent',figure1);
func_plot(Function_name)
title(Function_name)
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
zlabel('z')
subplot(1,2,2)
G2=subplot(1,2,2,'Parent',figure1);
CNT=35;
k=round(linspace(1,iter,CNT)); %随机选CNT个点
% 注意:如果收敛曲线画出来的点很少,随机点很稀疏,说明点取少了,这时应增加取点的数量,100、200、300等,逐渐增加
% 相反,如果收敛曲线上的随机点非常密集,说明点取多了,此时要减少取点数量
iter=1:1:iter;
semilogy(iter(k),PSO_curve(k),'b-^','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),GWO_Convergence_curve(k),'m-*','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),SSA_Convergence_curve(k),'r->','linewidth',1);
hold on
semilogy(iter(k),SCSSA_Convergence_curve(k),'g->','linewidth',1);
grid on;
title('收敛曲线')
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('适应度值');
box on
legend('PSO','GWO','SSA','SCSSA')
set (gcf,'position', [300,300,800,320])function [fMin , bestX,Convergence_curve ] = SSA(pop, M,c,d,dim,fobj )
P_percent = 0.2; % The population size of producers accounts for "P_percent" percent of the total population size
pNum = round( pop * P_percent ); % The population size of the producers
lb= c.*ones( 1,dim ); % Lower limit/bounds/ a vector
ub= d.*ones( 1,dim ); % Upper limit/bounds/ a vector
%Initialization
for i = 1 : pop
x( i, : ) = lb + (ub - lb) .* rand( 1, dim );
fit( i ) = fobj( x( i, : ) ) ;
end
pFit = fit;
pX = x; % The individual's best position corresponding to the pFit
[ fMin, bestI ] = min( fit ); % fMin denotes the global optimum fitness value
bestX = x( bestI, : ); % bestX denotes the global optimum position corresponding to fMin
% Start updating the solutions.
for t = 1 : M
[ ans, sortIndex ] = sort( pFit );% Sort.
[fmax,B]=max( pFit );
worse= x(B,:);
r2=rand(1);
if(r2<0.8)
for i = 1 : pNum % Equation (3)
r1=rand(1);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )*exp(-(i)/(r1*M));
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
else
for i = 1 : pNum
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )+randn(1)*ones(1,dim);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
end
[ fMMin, bestII ] = min( fit );
bestXX = x( bestII, : );
for i = ( pNum + 1 ) : pop % Equation (4)
A=floor(rand(1,dim)*2)*2-1;
if( i>(pop/2))
x( sortIndex(i ), : )=randn(1)*exp((worse-pX( sortIndex( i ), : ))/(i)^2);
else
x( sortIndex( i ), : )=bestXX+(abs(( pX( sortIndex( i ), : )-bestXX)))*(A'*(A*A')^(-1))*ones(1,dim);
end
x( sortIndex( i ), : )
= Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
c=randperm(numel(sortIndex));
b=sortIndex(c(1:20));
for j = 1 : length(b) % Equation (5)
if( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )>(fMin) )
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )=bestX+(randn(1,dim)).*(abs(( pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) -bestX)));
else
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) =pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )+(2*rand(1)-1)*(abs(pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )-worse))/ ( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )-fmax+1e-50);
end
x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : )
= Bounds( x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( b(j) ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) );
end
for i = 1 : pop
if ( fit( i ) < pFit( i ) )
pFit( i ) = fit( i );
pX( i, : ) = x( i, : );
end
if( pFit( i ) < fMin )
fMin
= pFit( i );
bestX = pX( i, : );
end
end
Convergence_curve(t)=fMin;
end
% Application of simple limits/bounds
function s = Bounds( s, Lb, Ub)
% Apply the lower bound vector
temp = s;
I = temp < Lb;
temp(I) = Lb(I);
% Apply the upper bound vector
J = temp > Ub;
temp(J) = Ub(J);
% Update this new move
s = temp;完整代码获取方式,后台回复关键词。
关键词:SCSSA