图论 并查集 模拟 位运算—题841、127、684、685、657、31、463、1356 C++实现与有向图 无向图 并查集总结
文章目录
- 841.钥匙和房间
-
- DFS
- BFS
- 127. 单词接龙
- 684.冗余连接
- 685.冗余连接II
- 657. 机器人能否返回原点
- 31.下一个排列
- 463. 岛屿的周长
-
- 解法1
- 解法2
- 1356. 根据数字二进制下 1 的数目排序
-
- 解法1
- 解法2
- 注意点
图论:题841、127
并查集:题684、685
模拟:题657、31、463
位运算:题1356
841.钥匙和房间
-
这道题是有向图,图1的所有节点都是连接的,而图二中的节点2 是孤立的,不能进入所有房间。孤立问题可以用并查集的方式去解决,但本题是有向图。
图2中,0号房间拿到1、3号房间的钥匙,可以去1、3号房间;1号房间拿到0、1、3号房间的钥匙,可以去0、1、3号房间;2号房间只能拿到2号房间的钥匙;3号房间拿到0号房间的钥匙,可以去0号房间,只有2号房间是孤立的。

-
在有向图中,即使所有节点都是链接的,依然不能从0出发遍历所有边,如下,节点0只能去节点5。所以本题是一个有向图搜索全路径的问题。 只能用**深搜(DFS)或者广搜(BFS)**来搜索路径。
DFS
-
确认递归函数,参数
需要传入二维数组rooms来遍历,当前的key,和记录走过的房间的布尔类型的一维数组visited。 -
确认终止条件
在递归中,处理当前访问的节点,还是处理下一个要访问的节点?这决定终止条件怎么写。首先明确,本题中要处理的是visited数组,需要记录哪些房间是访问过的。visited数组默认元素都是false,如果遇到访问过的节点把元素标记为true。
- 如果是处理当前访问的节点,当前节点在visited数组是 true ,说明访问过该节点,那就终止本层递归,否则在visited数组标记为true。
- 如果是处理下一个要访问的节点,那么就不需要终止条件,而是在 搜索下一个节点的时候,直接判断 下一个节点是否是我们要搜的节点。
- 处理目前搜索节点出发的路径
终止条件的两种写法决定了两种不一样的递归写法。通常有递归就有回溯,但是这道题是搜索所有路径,不需要回溯,只要遍历过的节点都标记,例如题797.所有可能的路径。当搜索一条可行路径的时候,就需要回溯操作了。没有回溯的话,就没法“调头”。
写法1,处理当前节点
class Solution {
public:
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
//写法1 处理当前节点
vector<bool> visited(rooms.size(), false);
dfs(rooms, visited, 0);
//检查是否都访问到了
for(int i : visited)
{
if(i == false) return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
//写法1 处理当前节点
void dfs1(const vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<bool>& visited, int key)
{
//如果访问过房间 终止本层递归
if(visited[key]) return;
//没有访问过,标记该房间为true
visited[key] = true;
//获取当前房间的钥匙 进行下一轮的递归
vector<int> keys = rooms[key];
for(int key : keys) dfs1(rooms, visited, key);
}
};
写法2,处理下一个节点
class Solution {
public:
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
vector<bool> visited(rooms.size(), false);
//DFS写法2 处理下一个要访问节点
visited[0] = true;//0号房间肯定被访问过
dfs2(rooms, visited, 0);
//检查是否都访问到了
for(int i : visited)
{
if(i == false) return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
void dfs2(const vector<vector<int>>& rooms, vector<bool>& visited, int key)
{
//写法2是处理下一个节点
//遍历所有路径不需要终止条件 标记访问过的节点即可
//获取当前房间的钥匙
vector<int> keys = rooms[key];
for(int key : keys)
{
if(visited[key] == false)
{
visited[key] = true;
dfs2(rooms, visited, key);
}
}
}
};
BFS
class Solution {
public:
bool canVisitAllRooms(vector<vector<int>>& rooms) {
//BFS
return bfs(rooms);
}
private:
bool bfs(const vector<vector<int>>& rooms)
{
vector<int> visited(rooms.size(), 0);
visited[0] = 1;//0号房间开始 肯定被访问过
queue<int> que;//模拟房间的遍历
que.push(0);//0号房间开始
while(!que.empty())
{
//访问当前房间
int key = que.front(); que.pop();
//获取当前房间的钥匙
vector<int> keys = rooms[key];
for(int key : keys)
{
//如果该钥匙对应的房间没有被访问过
if(!visited[key])
{
que.push(key);//该房间入队列
visited[key] = 1;//标记房间
}
}
}
//检查是否都访问到了
for(int i : visited)
{
if(i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
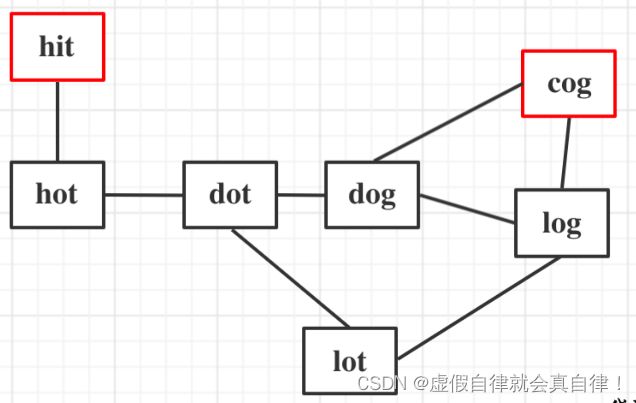
127. 单词接龙
- 本题只需要求出最短路径的长度就可以了,不用找出路径——无向图求最短路径,广搜BFS最合适,从起点中心向四周扩散搜索,BFS找到终点就是最短路径
- 本题的关键在于,图中的线是如何连在一起的?起点和终点的最短路径长度?
- 图中的线是如何连在一起的——如果单词只差一个字符就相连,需要判断
- 起点和终点的最短路径长度——BFS,到达终点就是最短路径。使用深搜的话,还需要选择最短的路径。
- 本题是一个无向图,需要用标记位,标记着节点是否走过,否则就会死循环
- 本题给出集合是数组型的,可以转成set结构,查找更快一些
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
// 将vector转成unordered_set,提高查询速度
unordered_set<string> wordset(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());
// 如果endWord没有在wordSet出现,直接返回0
if(wordset.find(endWord) == wordset.end()) return 0;
// 记录word是否访问过 684.冗余连接
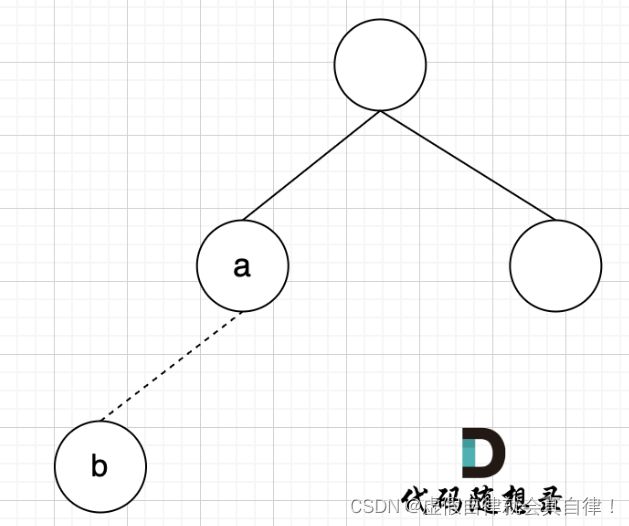
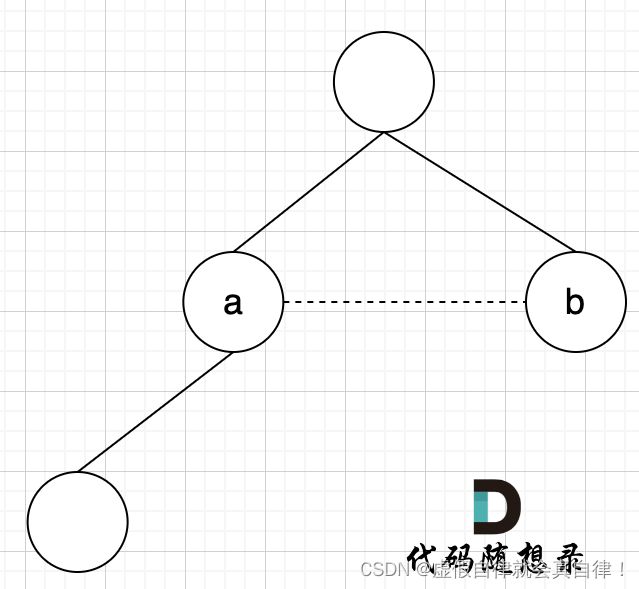
- 题目要求:1)删去的一条边使得结果图是一个有着N个节点的树,即只有一个根节点;2 )如果有多个答案,则返回二维数组中最后出现的边。
- 从前向后遍历每一条边,优先让前面的边连上,边的两个节点如果不在同一个集合,就加入集合(即:同一个根节点)
- 如果节点a 和节点b 不在同一个集合,将两个 节点连在一起,加入集合,图1。如果边的两个节点已经出现在同一个集合里,说明着边的两个节点已经连在一起了,再加入这条边一定就出现环了,图2。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
init();
for(int i=0; i<edges.size(); i++)
{
if(isSame(edges[i][0], edges[i][1])) return edges[i];
else join(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
return {};
}
private:
//构造并查集
int n = 1005; //节点数量3 到1000
//C++中的一种数据结构
vector<int> father = vector<int> (n, 0);
//并查集初始化
void init()
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) father[i] = i;
}
//并查集里 寻找根节点
//相当于判断节点是否出现在集合中
int find(int root)
{
return root == father[root] ? root : father[root] = find(father[root]);
}
//判断 两个节点是否找到同一个根
//相当于判断两个节点是否出现在同一个集合
bool isSame(int node1, int node2)
{
node1 = find(node1);
node2 = find(node2);
return node1 == node2;
}
//两个节点连接 node2->node1
void join(int node1, int node2)
{
node1 = find(node1);
node2 = find(node2);
if(node1 == node2) return;
father[node2] = node1;
}
};
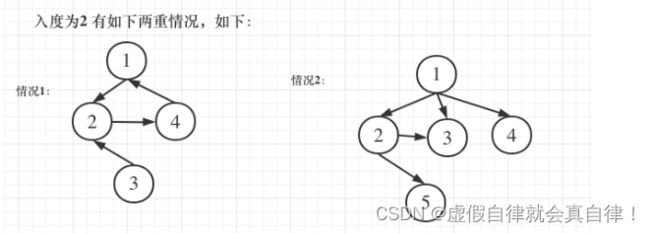
685.冗余连接II
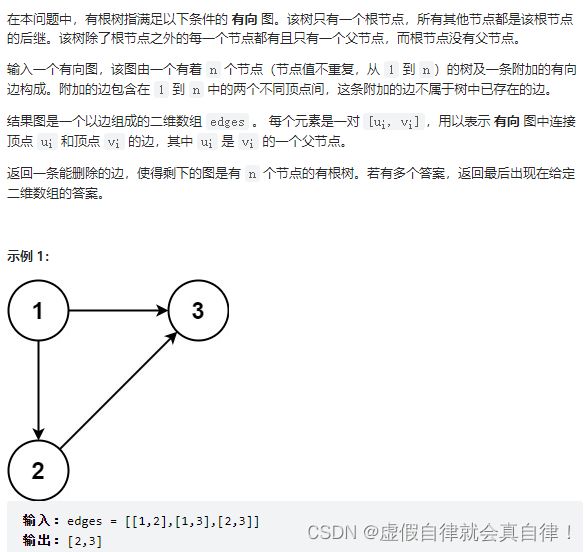

-
题目的意思是题中的图原本是一棵树,只不过在不增加节点的情况下多加了一条边。还有如果存在多便可以删除的情况下,要删顺序靠后的边。
-
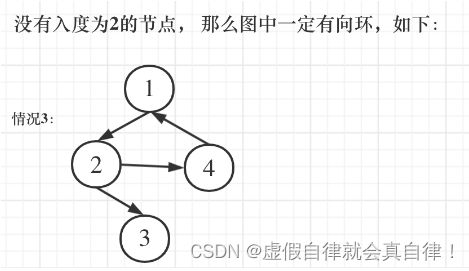
情况1中,节点2来源于节点1和节点3,上层节点和下层节点。情况2中,节点3来源于节点1和节点2,父节点和同层节点。情况3中,没有入度为2的点,图中一定出现了有向环。因此,首先要计算节点的入度,也就是计算edges[i][1]。不考虑出度是因为出度没有意义,一个父节点有多个出度。
-
步骤
- 计算节点的入度,也就是计算edges[i][1]。
- 当节点入度为2时,要删除 指向该节点的两条边其中的一条。同时,要判断删除这个边,图是否为树,如果是。删除的边就是所求结果。
- 还要注意从后向前遍历,要保证存在多边可以删除时,删除的是顺序靠后的边。
- 当没有入度为2的情况时,存在有向环,构成环的边就是要删除的边。
- 两个关键的函数,一个是判断删除边后图是否为树,另一个是存在有向环时,要找到需要删除的边。
- 并查集,判断有向图能否构成树:在添加图之前,两个点所在的边 能够在并查集里找到相同的根,那么这条边加到图中得到的新图一定不是树。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findRedundantDirectedConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int inDegree[N] = {0};//记录节点入度
n = edges.size();//边的数量
//1.计算节点的入度
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
inDegree[edges[i][1]]++;
}
vector<int> vec;//记录入度为2的边
//2.找入度为2的节点所对应的边,要倒序,优先返回最后出现在二维数组中的答案
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--)
{
if(inDegree[edges[i][1]] == 2) vec.push_back(i);
}
//3.处理情况1和2 入度为2的节点
//两条边中 要判断删除哪个边可以构成树
if(vec.size() > 0)
{
if(isTreeAfterRemoveEdge(edges, vec[0])) return edges[vec[0]];
else return edges[vec[1]];
}
//4.处理情况3 没有入度为2的节点 有有向环
return getRemoveEdge(edges);
}
private:
static const int N = 1010;//题目二维数组大小的在3到1000范围内
int father[N];//并查集 数组
int n;//边的数量
//构造并查集的相关函数
void init()//初始化
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) father[i] = i;
}
//并查集寻根
int find(int root)
{
if(root == father[root]) return root;
return father[root] = find(father[root]);
//return root == father[root] ? root : father[root] = find(father[root]);
}
//将node2->node1 这条边加入并查集
void join(int node1, int node2)
{
node1 = find(node1);
node2 = find(node2);
if(node1 == node2) return;
father[node2] = node1;
}
//判断是否同根
bool isSame(int node1, int node2)
{
node1 = find(node1);
node2 = find(node2);
return node1 == node2;
}
//有向图如果存在有向环,找到有向环中要删除的边,使其变成树
vector<int> getRemoveEdge(const vector<vector<int>>& edges)
{
init();//初始化并查集
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
//找到有向环 两个节点同根->有向环
if(isSame(edges[i][0], edges[i][1])) return edges[i];
//不同根 则连接两节点
join(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
return {};
}
//删一条边之后判断是不是树
bool isTreeAfterRemoveEdge(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int deleteEdge)
{
init();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(i == deleteEdge) continue;
//有向环 一定不是树
if(isSame(edges[i][0], edges[i][1])) return false;
join(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
return true;
}
};
657. 机器人能否返回原点
假设机器人位置(x,y),初始为0,然后:
if (moves[i] == ‘U’) y++;
if (moves[i] == ‘D’) y–;
if (moves[i] == ‘L’) x–;
if (moves[i] == ‘R’) x++;
最后判断一下x,y是否回到了(0, 0)位置就可以了。

class Solution {
public:
bool judgeCircle(string moves) {
int x= 0 , y = 0;
for(int i=0; i<moves.size(); i++)
{
if(moves[i] == 'U') y++;
if(moves[i] == 'D') y--;
if(moves[i] == 'L') x++;
if(moves[i] == 'R') x--;
}
if(x == 0 && y == 0) return true;
return false;
}
};
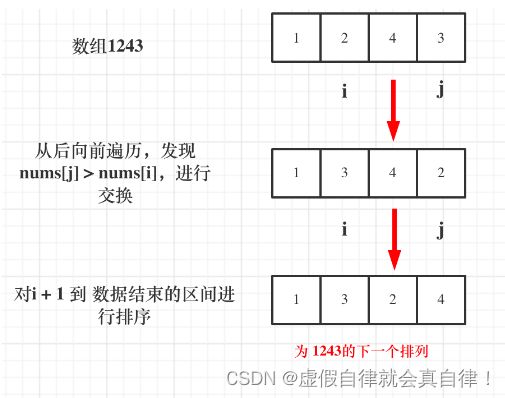
31.下一个排列
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i=nums.size()-1; i>=0; i--)
{
for(int j=nums.size()-1; j>i; j--)
{
if(nums[j] > nums[i])
{
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
reverse(nums.begin() + i + 1, nums.end());
return;
}
}
}
//此时整个数组是倒序的,反转一下便可
reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end());
}
};
463. 岛屿的周长


解法1
计算出总的岛屿数量,因为有一对相邻两个陆地,边的总数就减2,那么在计算出相邻岛屿的数量就可以了,如图:
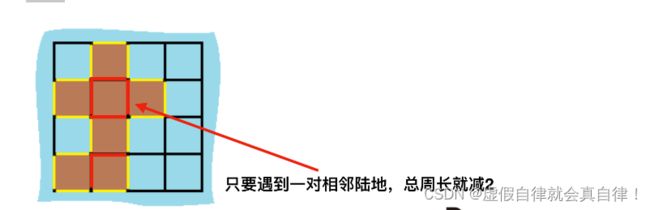
写法1是直接计算边长,遇到一个岛屿,边长+4,遇到一个相邻岛屿,边长-2
class Solution {
public:
int islandPerimeter(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
//解法1
return round2(grid);
}
private:
//解法1 写法1
int round1(const vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
int result1 = 0;
for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++)//遍历行
{
for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++)//遍历列
{
if(grid[i][j] == 1)//遇到岛屿
{
result1 += 4;//累加边长
if(i > 0 && grid[i-1][j] == 1) result1 -= 2;
if(j > 0 && grid[i][j-1] == 1) result1 -= 2;
}
}
}
return result1;
}
};
写法2是统计岛屿数量与相邻岛屿数量,周长 = 岛屿数量4 - 相邻岛屿数量2(公共边)
class Solution {
public:
int islandPerimeter(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
//解法1 周长 = 岛屿数量*4 - 相邻岛屿数量*2(公共边)
return round2(grid);
}
private:
//解法1 写法2
int round2(const vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
int land = 0;
int neiborland = 0;
for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++)//遍历行
{
for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++)//遍历列
{
if(grid[i][j] == 1)//遇到岛屿
{
land++;//累加边长
if(i > 0 && grid[i-1][j] == 1) neiborland++;
if(j > 0 && grid[i][j-1] == 1) neiborland++;
}
}
}
return land*4 - neiborland*2;
}
};
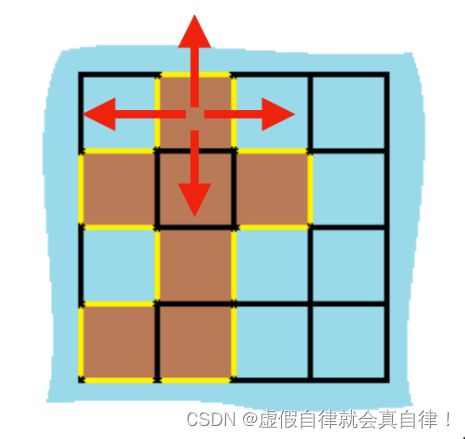
解法2
遍历每一个空格,遇到岛屿,看其上下左右四个方向是否为边界或者水域,如果遇到水域或者出界的情况,就可以计算边了,如图:
class Solution {
public:
int islandPerimeter(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
//解法2
return round3(grid);
}
private:
int round3(const vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
//当前地图上下左右方向的情况
int direction[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1};
int result3 = 0;
for(int i=0; i<grid.size(); i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<grid[0].size(); j++)
{
if(grid[i][j] == 1)
{
for(int k=0; k<4; k++)
{
int x = i + direction[k][0];
int y = j + direction[k][1];
if(x < 0
|| x >= grid.size()
|| y < 0
|| y >= grid[0].size()
|| grid[x][y] == 0) result3++;
}
}
}
}
return result3;
}
};
1356. 根据数字二进制下 1 的数目排序
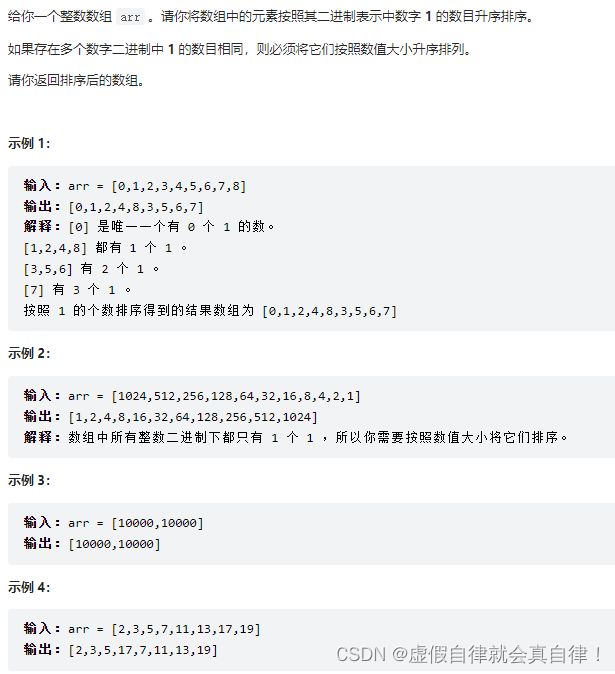

考察如何计算一个数的二进制中1的数量
解法1
挨个计算1的数量,最多就是循环n的二进制位数,32位。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortByBits(vector<int>& arr) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), compare);
return arr;
}
private:
static bool compare(int a, int b)
{
//解法1
int bita = bitCount1(a);
int bitb = bitCount1(b);
//如果二进制1的数量相同,比较数值大小
if(bita == bitb) return a < b;//升序
return bita < bitb;
}
static int bitCount1(int n)
{
int count = 0; // 计数器
while (n > 0) {
if((n & 1) == 1) count++; // 当前位是1,count++
n >>= 1 ; // n向右移位
}
return count;
}
};
解法2
只循环n的二进制中1的个数次,计算12的二进制1的数量为例,如图所示:
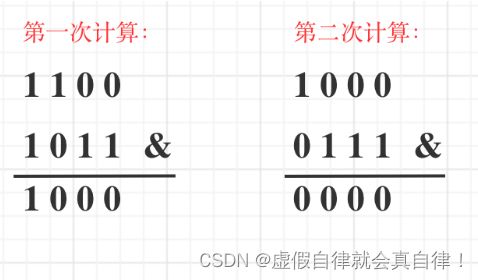
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortByBits(vector<int>& arr) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), compare);
return arr;
}
private:
static bool compare(int a, int b)
{
//解法2
int bita = bitCount2(a);
int bitb = bitCount2(b);
//如果二进制1的数量相同,比较数值大小
if(bita == bitb) return a < b;//升序
return bita < bitb;
}
static int bitCount2(int n)
{
int count = 0;
while(n)
{
n &= (n - 1);// 清除最低位的1
count++;
}
return count;
}
};
注意点
- 有向图,搜索全路径,深搜(DFS)或者广搜(BFS);并查集可以判断有向图在加边之后图是否为树
- 无向图,求最短路径,广搜
- 并查集定义:并查集集是一种维护集合的数据结构,并查集支持两个操作
- ① 合并:合并两个集合。在合并的过程中,只对两个不同的集合进行合并,如果两个元素在相同的集合中,那么就不会对它们进行操作。这就保证了在同一个集合中一定不会产生环,即并查集产生的每一个集合都是一棵树
- ② 查找:判断两个元素是否在一个集合。
- 并查集是用数组实现的,
int father[N];n,其中 father[i] 表示元素 i 的父亲结点,而父亲结点本身也是这个集合内的元素(1 ≤ i ≤ N) - 并查集可以解决什么问题呢?
主要解决集合问题,两个节点在不在一个集合,也可以将两个节点添加到一个集合中。 - 并查集主要有三个功能。
- 寻找根节点,函数:find(int u),也就是判断这个节点的祖先节点是哪个
- 将两个节点接入到同一个集合,函数:join(int u, int v),将两个节点连在同一个根节点上
- 判断两个节点是否在同一个集合,函数:isSame(int u, int v),就是判断两个节点是不是同一个根节点
例如 father[1] = 2 就表示元素 1 的父亲结点是元素 2 ,以这种父系关系来表示元素所属的集合。另外,如果 father[i] = i ,则说明元素 i 是该集合的根结点,但对同一个集合来说只存在一个根结点,且将其作为所属集合的标识。
-
并查集判断有向图在加边前后能否构成树
在添加图之前,两个点所在的边 能够在并查集里找到相同的根,那么这条边加到图中得到的新图一定不是树。 -
并查集模板如下,看题目情况修改模板中的 n
int n = 1005; // n根据题目中节点数量而定,一般比节点数量大一点就好
vector<int> father = vector<int> (n, 0); // C++里的一种数组结构
// 并查集初始化
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
father[i] = i;
}
}
// 并查集里寻根的过程
int find(int u) {
return u == father[u] ? u : father[u] = find(father[u]); // 路径压缩
}
// 判断 u 和 v是否找到同一个根
bool isSame(int u, int v) {
u = find(u);
v = find(v);
return u == v;
}
// 将v->u 这条边加入并查集
void join(int u, int v) {
u = find(u); // 寻找u的根
v = find(v); // 寻找v的根
if (u == v) return ; // 如果发现根相同,则说明在一个集合,不用两个节点相连直接返回
father[v] = u;
}