Springboot-加载静态资源(最后重点)
简介
位置与优先级
位置
spring boot的静态资源:
- static目录:css、js、图片等
- templates目录:html页面
优先级
spring boot默认将/**静态资源访问映射到以下目录:
classpath:/static
classpath:/public
classpath:/resources
classpath:/META-INF/resources
这四个目录的访问优先级:META-INF/resources > resources > static > public
即:这四个路径下如果有同名文件,则会以优先级高的文件为准。
其对应的配置方法为:application.yml。默认配置如下:
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/
其实,它还与application.yml的下边这个配置有关,两者联合起来控制路径
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /**
HTML放置位置的区别
HTML文件放到templates目录下
推荐将html页面放置在templates目录,原因如下:
templates目录下的html页面不能直接访问,需要通过服务器内部进行访问,可以避免无权限的用户直接访问到隐私页面,造成信息泄露。
HTML文件放到static目录下
这样用户可以通过两种方法获得到html页面:
直接访问.html资源
通过controller跳转
就像上边说的一样,当直接访问.html资源时,用户可以访问到无权访问的页面。
templates和static目录都是项目创建时自带的!!!!!!
HTML存放于templates目录(推荐)
步骤1:引入thymeleaf 依赖(视图解析),这里的页面必须通过controller跳转才能访问
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
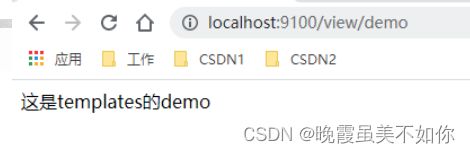
步骤2:写一个简单的HTML,放置到templates路径
this is title
这是templates 的demo !!!!!!
步骤3:编写Controller
package com.example.demo.views;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("view")
public class ViewController {
@GetMapping("demo")
public String demo() {
return "demo";
}
}
需要注意:必须使用@Controller,不能使用@RestController。
因为@RestController返回的是 JSON,且不走SpringMVC的视图解析流程,所以跳不到html那里。
测试
HTML存放于static目录(不推荐)
法1:直接访问.html资源
步骤1:将html放到static目录
法2:通过controller跳转
步骤1:确保没有thymeleaf依赖
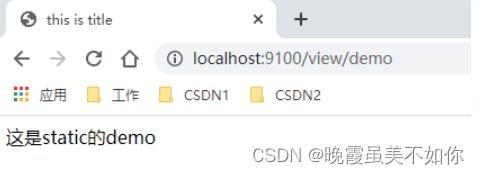
步骤2:将html放置到static路径
this is title
这是static的demo
步骤3:编写controller
package com.example.demo.views;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("view")
public class ViewController {
@GetMapping("demo")
public String demo() {
return "/demo.html";
}
}注意:返回的字符串前边必须带“/” 。
测试
说明
也可以如下操作,结果是一样的:
application.yml配置前后缀:
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.html
controller这样写:
package com.example.demo.views;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("view")
public class ViewController {
@GetMapping("demo")
public String demo() {
return "demo";
}
}自己包下的静态资源导入到Springboot中
Springboot,默认的静态资源映射是这样的
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/以下两种方法都会使得Springboot默认的静态资源映射失效
第一种方法
修改成这样子
spring:
web:
resources:
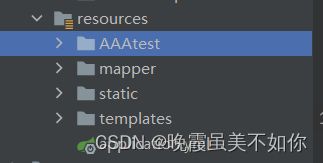
static-locations: classpath:/这样就代表我们resources下的都注册到Springboot静态资源下了(templates还是不能直接访问地址,因为他加载了thymeleaf 依赖(视图解析)。
结果
第二种方法,通过类实现
package com.example.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
/**
* 设置静态资源映射
*
* @param registry
*/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
log.info("开始进行静态资源映射...");
registry.addResourceHandler("/AAAtest/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/AAAtest/");
}
}
结果
两种方法都会使得默认配置失效!!!!!
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/