MYBATIS动力
MYBATIS
三层架构
在文献中看到的framework被翻译为框架Java常用框架:
- SSM三大框架: Spring + SpringMVC + MyBatis
- SpringBoot
- SpringCloud
等。。

ORM:对象关系映射
O(Object): JVM中的java对象
R(Relational):关系型数据库
M(Mapping):映射’
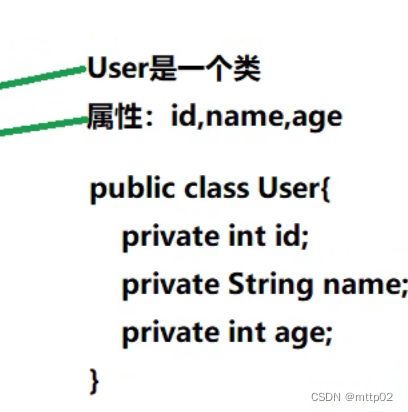
:像User这样的类,有特殊的称呼:
有的人把它叫做: pojo(普通java类)有的叫做: bean(豆子)
有的叫做: domain(领域模型)
mybatis开发步骤
2.开发步骤
*第一步:打包方式jar
*第二步:引入依赖
- mybatis依赖- mysql驱动依赖
*第三步:编写mybatis核心配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
注意:
第一:这个文件名不是必须叫做mybatis-config.xml,可以用其他的名字。只是大家都采用这个名字。第二:这个文件存放的位置也不是固定的,可以随意,但一般情况下,会放到类的根路径下
mybatis-config.xml文件中的配置信息.不理解没关系,先把连接数据库的信息修改以下即可。其他的别动。
*第四步:编写XxxxMapper. xml文件
在这个配置文件当中编写SQL语句。
这个文件名也不是固定的,放的位置也不是固定,我们这里给它起个名字,叫做:CarMapper . xml把它暂时放到类的根路径下。
*第五步:在mybatis-config.xml文件中指定XxxxMapper.xml文件的路径:
注意:resource属性会自动从类的根路径下开始查找资源。*第六步:编写MyBatis程序。

在MyBatis当中,负责执行SQL语句的那个对象叫做什么呢?
:sqlSession
SqlSession是专门用来执行SQL语句的,是一个Java程序和数据库之间的一次会话。
要想获取SqLSession对象,需要先获取SqLSessionFactory对象,通过SqlSessionFactory工厂来生产SqLSession对象。
怎么获取SqlSessionFactory对象呢?
需要首先获取SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象。
通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象的build方法,来获取一个SqlSessionFactory对象。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder --> SqlSessionFactory --> sqlsession
//获取SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//获取SqlSessionFactory对象
InmputStrean is a Resources.getRiesourceAsStrean("mybatis-config.xm1 "); // Resounces. getResounceAsStream默认就是从类的根路径下开始查找资源。
sqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
//获取SqlSession对象
sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Junit
@Test
public void testsum(){
//单元测试中有两个重要的概念:
//一个是:实际值(被测试的业务方法的真正执行结果)
//一个是:期望值(执行了这个业务方法之后,你期望的执行结果是多少)
MathService mathService = new MathService();
//获取实际值
int actual = mathService.sum( a: 1,b: 2);//期望值
int expected = 3;
//加断言进行测试
Assert.assertEquals(expected,actual) ;
引入Juint
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
2.7 引⼊⽇志框架logback
启⽤标准⽇志组件,只需要在mybatis-config.xml⽂件中添加以下配置:【可参考mybatis⼿册】
mybatis常见的集成的日志组件有哪些呢?
SLF4(沙拉风)﹔沙拉风是一个日志标准,其中有一个框架叫做logback,它实现了沙拉风规范。
LOG4J
L0G4J2
STDOUT_LOGGING
注意:log4j log4j2 logback都是同一个作者开发的。
集成logback日志框架。
logback日志框架实现了slf4j标准。(沙拉风:日志门面。日志标准。)
第一步:引入logback的依赖。
ch.qos.logback
logback-classic 1.2.11
第二步:引入Iogback所必须的xml配置文件。
这个配置文件的名字必须叫做: logback.xml或者logback-test.xml,不能是其它的名字。这个配置文件必须放到类的根路径下。不能是其他位置。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmins="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/PON/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd ">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.powernode</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-002-crud</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!--mybatis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--logback依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>
严格意义上来说:如果使用POJO对象传递值的话,#{ }这个大括号中到底写什么?
写的是get方法的方法名去掉get,然后将剩下的单词首字母小写,然后放进去。
例如:getUsername() -->#{username}
例如:getEmail() -->#{email}
注意:占位符#{} ,大括号里面写: pojo类的属性名
insert into t_car(id, car_num , brand , guide_price , produce_time ,car_type)values(null, #{carNum}, #{brand}, #{guidePrice}, #{produceTime}, #{carType}
删除操作
CarMappper.xml文件
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from t_car where id = #{afdsafdsa}
delete>
CarMappper
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
sqlsession sqlsession = sqlsessionUtil.openSession();
//执行SQL语句
int count = sqlSession.delete( statement:"deleteById",parameter:59)
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
改操作
<update id="updateById ">
update t_car set
car_num=#{},
brand=#{},
guide_price=#{},
produce_time=#l},
car_type=#{},
where
id = #{}
update>
sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtil.openSession(;
//准备数据
Car car = new Car( id:4L,carNum: "9999",brand:"凯美瑞",guidePrice: 30.3
produceTime: "1999-11-10" , carType:"燃油车")
//执行SQL语句
int count = sqlSession.update( statement: "updateById", car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlsession.close();
查操作
<select id="selectById" resultType="com. powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car ">
select
id ,
car_num as carNum ,
brand ,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime ,
car_type as carType
from
t_carwhere
id = #{id}
select>
resultType="com. powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car "
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
sqlsession sqlSession = sqlsessionUtil.openSession();
//执行DQL语句。查询。根据id查询。返回结果一定是一条。
// mybatis底层执行了select语句之后,一定会返回一个结果集对象:ResultSet
//JDBC中叫做ResultSet,接下来就是mybatis应该从ResultSet中取出数据,封装java对象。
Object car = sqlSession.selectOne( statement: "selectById" ,parameter:1);
system.out.println(car);
sqlsession.close();
}
查询所有
xml改id,其他不变
@Test
public void testSelectAll(){
sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionutil.openSession();
//执行SQL语句
List<0bject> cars = sqlSession.selectList( statement: "selectAll");
//遍历
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
mybatis中transactionManager标签:
1.作用:配置事务管理器。指定mybatis具体使用什么方式去管理事务。
2.type属性有两个值:
第一个:JDBC:使用原生的JDBC代码来管理事务。
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
…
conn.commit();
第二个:MANAGED: mybatis不再负责事务的管理,将事务管理交给其它的JEE(JavaEE)容器来管理。
例如: spring
配置具体的数据库连接池参数
<property name=" poolMaximumActiveConnections" value="3"/>
<property name="poolTimeToWait" value="2000"/>
<property name="poolMaximumCheckoutTime" value="10000"/>
<property name=" poolMaximumIdleConnections" value="5"/>