【力扣周赛】第 355 场周赛(构造&二分答案&异或前缀 状态压缩⭐)
文章目录
- Q1:6921. 按分隔符拆分字符串(双指针)
- Q2:6915. 合并后数组中的最大元素(倒序遍历+贪心)
-
- 代码优化
- Q3:6955. 长度递增组的最大数目
-
- 解法1——构造⭐
- 解法2——排序 + 二分⭐(!重要!有启发性!)
- Q4:2791. 树中可以形成回文的路径数(异或&哈希表)⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
-
- 补充:相关题目
-
- 1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
- 1371. 每个元音包含偶数次的最长子字符串
- 1542. 找出最长的超赞子字符串
- 成绩记录
Q1:6921. 按分隔符拆分字符串(双指针)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/split-strings-by-separator/description/
1 <= words.length <= 100
1 <= words[i].length <= 20
words[i] 中的字符要么是小写英文字母,要么就是字符串 ".,|$#@" 中的字符(不包括引号)
separator 是字符串 ".,|$#@" 中的某个字符(不包括引号)
用双指针手动切分每个 word 加入答案列表即可。
class Solution {
public List<String> splitWordsBySeparator(List<String> words, char separator) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList();
for (String word: words) {
int n = word.length();
for (int r = 0, l = 0; r < n; ++r) {
if (word.charAt(r) == separator) {
if (r > l) ans.add(word.substring(l, r));
l = r + 1;
} else if (r == n - 1) ans.add(word.substring(l, n));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Q2:6915. 合并后数组中的最大元素(倒序遍历+贪心)
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
贪心地尽量先合并后面的元素。
因为先合并前面的可能会导致数字变大不能继续合并。 e.g. 3,4,5 变成 7,5之后就不能合并了;但是变成3,9之后可以继续合并成12。
使用 long 是防止在原数组上计算时溢出。
class Solution {
public long maxArrayValue(int[] nums) {
long[] ans = new long[nums.length];
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
ans[i] = nums[i];
}
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > 0; --i) {
if (ans[i] >= ans[i - 1]) ans[i - 1] += ans[i];
}
return Arrays.stream(ans).max().getAsLong();
}
}
代码优化
也可以用 cur 存储当前结果,省去额外的 long 数组。
class Solution {
public long maxArrayValue(int[] nums) {
long ans = nums[nums.length - 1], cur = ans;
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i > 0; --i) {
if (cur >= nums[i - 1]) cur += nums[i - 1];
else cur = nums[i - 1];
ans = Math.max(ans, cur);
}
return ans;
}
}
Q3:6955. 长度递增组的最大数目
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-number-of-groups-with-increasing-length/description/
提示:
1 <= usageLimits.length <= 10^5
1 <= usageLimits[i] <= 10^9
解法1——构造⭐

证明讲解可见:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1n8411m7Fs/
class Solution {
public int maxIncreasingGroups(List<Integer> usageLimits) {
// 从小到大排序
Collections.sort(usageLimits);
long ans = 0, s = 0;
for (int v: usageLimits) {
s += v;
// 如果像让当前的 ans + 1,就需要 s 足够组成 1 ~ ans + 1 的等差数列
if (s >= (ans + 2) * (ans + 1) / 2) {
// 每次来一个新的数字,且它的数量足够,那么就可以多构造出 1 组
ans++;
}
}
return (int)ans;
}
}
解法2——排序 + 二分⭐(!重要!有启发性!)
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-number-of-groups-with-increasing-length/solutions/2355580/pai-xu-er-fen-tu-jie-ban-by-yzq-a-smlx/
设可以组成 k 个序列。
二分答案。检查答案是否合理的过程是:将 usageLimits 从大到小进行排序,之后枚举。
数量少的元素可以补给数量大的元素,但是反过来不行。
class Solution {
public int maxIncreasingGroups(List<Integer> usageLimits) {
Collections.sort(usageLimits, (a, b) -> b - a); // 降序排序
int l = 0, r = usageLimits.size();
while (l < r) {
int mid = l + r + 1>> 1;
if (check(usageLimits, mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
boolean check(List<Integer> usageLimits, int k) {
int gap = 0;
for (int v: usageLimits) {
// 数量少的可以补给数量大的,所以降序排序后枚举
gap = Math.min(gap + v - k, 0);
if (k > 0) k--; // k是当前需要的数量
}
return gap >= 0;
}
}
Q:为什么要先使用数量多的元素?
A:因为数量多的元素即使数量大于组成序列个数 k,也最多只能使用 k 个,否则会重复。而数量小的元素可以放在任意不同的序列中而不会发生重复。
Q4:2791. 树中可以形成回文的路径数(异或&哈希表)⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
相似原题链接:https://loj.ac/p/6681
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-paths-that-can-form-a-palindrome-in-a-tree/
提示:
n == parent.length == s.length
1 <= n <= 10^5
对于所有 i >= 1 ,0 <= parent[i] <= n - 1 均成立
parent[0] == -1
parent 表示一棵有效的树
s 仅由小写英文数字组成
注意题目要求的是路径可以重新排列成回文串而不是要求路径组成了回文串。(即对字母的顺序没有要求,只对字母的数量有要求)。
重要:可以排列成回文串等价于最多一个字母出现奇数次,其余字母出现偶数次。
class Solution {
List<Integer>[] g;
String s;
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
long ans = 0;
public long countPalindromePaths(List<Integer> parent, String s) {
int n = parent.size();
this.s = s;
g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
g[parent.get(i)].add(i);
}
cnt.put(0, 1); // 放入一条【空路径】
dfs(0, 0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int x, int xor) {
for (int y: g[x]) {
int bit = 1 << (s.charAt(y) - 'a');
int y_xor = xor ^ bit;
ans += cnt.getOrDefault(y_xor, 0); // 自己和自己异或是0
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
// 和只有1位数字不一样的异或,结果上只有1位数字是1
ans += cnt.getOrDefault(y_xor ^ (1 << i), 0);
}
cnt.merge(y_xor, 1, Integer::sum);
dfs(y, y_xor);
}
}
}
注意在 dfs 之前要现在 cnt 中添加一条空路径。
我们在 dfs 过程中计算的是从根节点到各个节点的 xor。如果两条路径可以组成一条合理的路径有两种情况:1.两条路径的 xor 相同;2.两条路径的二进制表示只有一个位置不同。
补充:相关题目
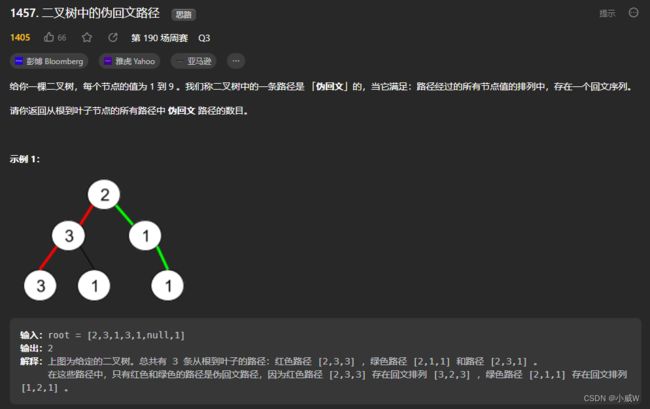
1457. 二叉树中的伪回文路径
https://leetcode.cn/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree/
提示:
给定二叉树的节点数目在范围 [1, 10^5] 内
1 <= Node.val <= 9
这道题目相对简单一些,只需要判断从根节点到叶子节点的路径能否排列成回文串。
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int pseudoPalindromicPaths (TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, int xor) {
xor ^= 1 << root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (xor == 0 || (xor & (xor - 1)) == 0) ++ans;
return;
}
if (root.left != null) dfs(root.left, xor);
if (root.right != null) dfs(root.right, xor);
}
}
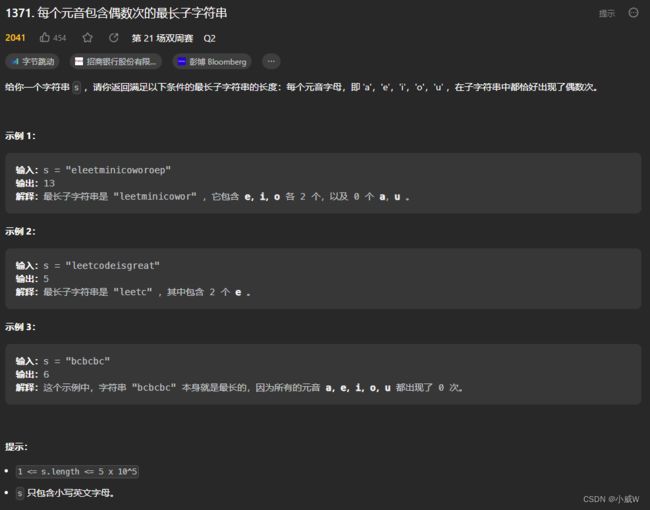
1371. 每个元音包含偶数次的最长子字符串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-longest-substring-containing-vowels-in-even-counts/
使用异或前缀,记录每一种状态出现的第一个位置,当出现了之前出现过的状态时,可以尝试更新答案。
class Solution {
public int findTheLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0, xor = 0;
String vowels = "aeiou";
Map<Integer, Integer> idx = new HashMap<>();
idx.put(0, -1); // 0的位置是-1
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
// 如果是元音
if (vowels.indexOf(ch) != -1) {
xor ^= 1 << (ch - 'a');
}
// 记录每个状态第一次出现的位置
if (idx.containsKey(xor)) {
ans = Math.max(i - idx.get(xor), ans);
} else idx.put(xor, i);
}
return ans;
}
}
1542. 找出最长的超赞子字符串
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-longest-awesome-substring/
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 10^5
s 仅由数字组成
可以变成回文子串:异或值至多有 1 个 1。
class Solution {
public int longestAwesome(String s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0, xor = 0;
int[] idx = new int[1 << 10];
Arrays.fill(idx, n);
idx[0] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
xor ^= 1 << (s.charAt(i) - '0');
// 前缀一致,出现次数全是偶数
if (idx[xor] != n) ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[xor]);
// 前缀只有一位不一样,只有一个次数是奇数
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; ++j) {
int x = xor ^ (1 << j);
if (idx[x] != n) ans = Math.max(ans, i - idx[x]);
}
if (idx[xor] == n) idx[xor] = i;
}
return ans;
}
}
成绩记录
T3、T4 做不出来是正常的(