【C#】异步编程自定义任务调度器TaskScheduler介绍
【C#】多线程基础
【C#】ThreadPool与Task
文章目录
- 一、TaskScheduler是什么?
- 二、自定义TaskScheduler的具体实现
-
- 1.程序文件结构
- 2.前端代码
- 3.自定义调度器代码
- 4.测试结果
- 三、LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler介绍
- 四、总结
一、TaskScheduler是什么?
有时需要创建一组共享相同配置的Task对象,为避免机械地将相同的参数传给每个Task构造器,可创建一个任务工厂来封装通用的配置。System.Threading.Tasks命名空间定义了一个TaskFactory类型和一个TaskFactory类型。
要创建一组返回void的任务,就创建一个TaskFactory对象;要创建一组具有特定返回类型的任务,就构造一个TaskFactory,并通过泛型TResult实参传递任务的返回类型。
var cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
TaskFactory _taskFactory = new TaskFactory(
cts.Token,
TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent,
TaskContinuationOptions.AttachedToParent,
TaskScheduler.Default);
以上代码演示了如何创建一个TaskFactory,其构造函数中所有参数都有默认值。其中TaskScheduler对象负责执行调度的任务。
FCL提供了两个派生自TaskScheduler的类型:线程池任务高度器(thread pool task scheduler),和同步上下文任务调度器(synchronization context task scheduler)。默认情况下,所有应用程序使用的是前者,这个任务调度器将任务调度给线程池的工作者线程。后者适合提供了图形用户界面(GUI)的应用程序,如WPF,SliverLight和Windows Store应用程序。它将所有的任务都调度给应用程序的GUI线程,使所有任务代码都能成功更新UI组件,该调度器不使用线程池,可通过TaskScheduler.FromCurrentSynchronizationContext()获得对同步上下文任务调度器的引用。
在有特殊的任务调度需求的情况下,可以定义自己的TaskScheduler派生类。本文中我们就实现一种简单任务调度器。
二、自定义TaskScheduler的具体实现
本调度器中维护一个Task列表,在调度器中开辟一个线程,在线程中始终循环读取该列表,顺序执行列表中的任务。其中要注意的是,任务调度针对的是未开始执行的任务。
1.程序文件结构
2.前端代码
在前端代码中放置一个Button和一个TextBox控件,Button触发Task创建,TextBox控件中显示Task执行结果。
MainWindow.xaml文件代码:
<Window x:Class="CustomTaskScheduler.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="160" Width="500">
<Grid>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="10">
<Button Content="AutoAddTasks" Click="AutoAddTasks" Height="35" Margin="10"/>
<TextBox x:Name="AutoAddTextBox" Height="70" Width="290" TextWrapping="Wrap"/>
StackPanel>
Grid>
Window>
前端后台代码MainWindow.xaml.cs:
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
//定义一个taskfactory,采用了自定义调度程序
private readonly TaskFactory _customTaskFactory =
new TaskFactory(new TaskSchedulerBase<DynamicQueueScheduler>());
//点击按钮后,依次建立三个Task,会根据自定义调度程序进行调度
private void AutoAddTasks(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Task1,这里传入了AsyncState为”A"
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
this.Dispatcher.Invoke(new Action(delegate
{
this.AutoAddTextBox.Text += "Task1 Executed Successed" + '\n';
}));
}, "A");
//Task2,这里传入了AsyncState为”B"
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
this.Dispatcher.Invoke(new Action(delegate
{
this.AutoAddTextBox.Text += "Task2 Executed Successed" + '\n';
}));
}, "B");
//Task3,这里传入了AsyncState为”C"
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
this.Dispatcher.Invoke(new Action(delegate
{
this.AutoAddTextBox.Text += "Task3 Executed Successed" + '\n';
}));
}, "C");
}
}
3.自定义调度器代码
创建一个任务调度器接口,IScheduler.cs文件代码:
public interface IScheduler
{
void Add(Task t);
void Remove(Task t);
IEnumerable<Task> GetTasks();
}
创建TaskScheduler泛型派生类,类型参数T需要继承自IScheduler接口,TaskSchedulerBase.cs文件代码:
public class TaskSchedulerBase<T> : TaskScheduler where T : IScheduler, new ()
{
private readonly Thread _processThread;
private readonly object _lock = new object();
public TaskSchedulerBase()
{
_processThread = new Thread(this.Process);
_processThread.Start();
UnobservedTaskException += new EventHandler<UnobservedTaskExceptionEventArgs(
TaskSchedulerBase_UnobservedTaskException);
}
private void Process()
{
//这里一直循环读取任务列表,依次执行列表中的任务,并将任务从列表中移除(所有Task是在同一个线程中执行的)
while (true)
{
var firstTask = GetScheduledTasks().FirstOrDefault();
if (null != firstTask)
{
try
{
//在当前线程执行task,即Process所在线程,所以队列里的所有task只能依次执行
TryExecuteTask(firstTask);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
throw;
}
finally
{
//这里建议把移除任务的操作放在任务开始执行之前,因为任务开始执行后,对任务的调度已没有意义
TryDequeue(firstTask);
}
}
}
}
private T _scheduler = new T();
public T Scheduler
{
get { return _scheduler; }
}
protected override void QueueTask(Task task)
{
lock (_lock)
{
Scheduler.Add(task);
}
}
protected override bool TryDequeue(Task task)
{
lock (_lock)
{
Scheduler.Remove(task);
}
return true;
}
protected override bool TryExecuteTaskInline(Task task, bool taskWasPreviouslyQueued)
{
if (taskWasPreviouslyQueued)
{
if (TryDequeue(task))
{
return base.TryExecuteTask(task);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return base.TryExecuteTask(task);
}
}
protected override IEnumerable<Task> GetScheduledTasks()
{
lock (_lock)
{
return Scheduler.GetTasks();
}
}
private void TaskSchedulerBase_UnobservedTaskException(object sender, UnobservedTaskExceptionEventArgs e)
{
if (null != e.Exception)
{
if (null != e.Exception.InnerExceptions)
{
foreach (var exception in e.Exception.InnerExceptions)
{
Console.WriteLine("TaskSchedulerBase_UnobservedTaskException",
exception);
}
}
}
e.SetObserved();
}
}
IScheduler接口的具体实现,DynamicQueueScheduler.cs:
public class DynamicQueueScheduler : IScheduler
{
protected List<Task> _queue = new List<Task>();
public void Add(Task t)
{
if (Contains(t, out Task oldTask))
{
_queue.Remove(oldTask);
}
_queue.Add(t);
}
public void Remove(Task t)
{
_queue.Remove(t);
}
public IEnumerable<Task> GetTasks()
{
return _queue.ToArray();
}
public virtual bool Contains(Task t, out Task oldTask)
{
bool result = false;
oldTask = null;
foreach (var task in _queue)
{
//调度逻辑:如果当前Task列表中存在与新建Task的AsyncState相同的Task,则删除列表中对应Task
if (null != t.AsyncState && t.AsyncState.Equals(task.AsyncState))
{
oldTask = task;
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
4.测试结果
调度逻辑:如果当前Task列表中存在与新建Task的AsyncState相同的Task,则删除列表中对应Task。
这里做一个测试:在文件MainWindow.xaml.cs中建立三个Task时,按AsyncState的不同做4组测验:
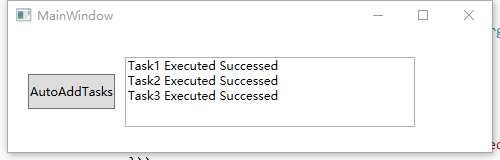
- 如果传入的AsyncState分别为"A",“B”,“C”,即三个Task的AsyncState完全不同,三个Task会全部执行,输出结果:
- 如果传入为"A",“A”,“B”,Task2的AsyncState与Task1相同,则Task2会顶掉Task列表中的Task1,只执行Task2和Task3,输出结果:

- 如果传入为"A",“B”,“B”,则Task3会顶掉Task2,只执行Task1和Task3,输出结果:

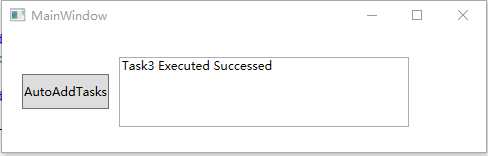
- 如果传入"A",“A”,“A”,则Task2会顶掉Task1,Task3会顶掉Task2,最终结果为:
以上所有测试都是连续向任务队列中添加任务,在添加新任务的时候,上一个任务还没有开始执行。如果添加任务时,上一个任务正在执行,则调度器不再起作用:
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("task 1 start execute, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
Thread.Sleep(50);
Console.WriteLine("task 1 end execute, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
}, "A");
//Thread.Sleep(40);
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("task 2 execute success, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
Thread.Sleep(50);
Console.WriteLine("task 2 end execute, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
}, "A");
//Thread.Sleep(40);
_customTaskFactory.StartNew((c) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("task 3 execute success, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
Thread.Sleep(50);
Console.WriteLine("task 3 end execute, Thread id: " + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());
}, "A");
//连续添加任务时的输出结果
task 3 execute success, Thread id: 10
task 3 end execute, Thread id: 10
//取消//Thread.Sleep(40);注释后的输出结果
task 1 start execute, Thread id: 10
task 1 end execute, Thread id: 10
task 2 execute success, Thread id: 10
task 2 end execute, Thread id: 10
task 3 execute success, Thread id: 10
task 3 end execute, Thread id: 10
三、LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler介绍
微软提供了一些任务调度器,这里简单介绍下LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler,其调度策略是:不允许超过n(n可设定)个任务同时并行执行。直接继承自TaskScheduler基类,相比于上述便于扩展的自定义调度器较易理解。代码如下:
public class LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler : TaskScheduler
{
// Indicates whether the current thread is processing work items.
[ThreadStatic]
private static bool _currentThreadIsProcessingItems;
// The list of tasks to be executed
private readonly LinkedList<Task> _tasks = new LinkedList<Task>(); // protected by lock(_tasks)
// The maximum concurrency level allowed by this scheduler.
private readonly int _maxDegreeOfParallelism;
// Indicates whether the scheduler is currently processing work items.
private int _delegatesQueuedOrRunning = 0;
//通过构造函数传入最大并行数
public LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler(int maxDegreeOfParallelism)
{
if (maxDegreeOfParallelism < 1) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("maxDegreeOfParallelism");
_maxDegreeOfParallelism = maxDegreeOfParallelism;
}
// Queues a task to the scheduler.将一个task加入调度器队列
protected sealed override void QueueTask(Task task)
{
// Add the task to the list of tasks to be processed. If there aren't enough
// delegates currently queued or running to process tasks, schedule another.
lock (_tasks) //这里加锁,如果while循环中的lock还没有释放,新任务无法添加进队列
{
_tasks.AddLast(task);
if (_delegatesQueuedOrRunning < _maxDegreeOfParallelism)
{
++_delegatesQueuedOrRunning;
//每次加入task时,如果当前正在执行的线程数小于最大并行数,执行下述方法,在该方法中新开一个线程
NotifyThreadPoolOfPendingWork();
}
}
}
// Inform the ThreadPool that there's work to be executed for this scheduler.
private void NotifyThreadPoolOfPendingWork()
{
ThreadPool.UnsafeQueueUserWorkItem(_ =>
{
// Note that the current thread is now processing work items.
// This is necessary to enable inlining of tasks into this thread.
_currentThreadIsProcessingItems = true;
try
{
// Process all available items in the queue.
while (true)
{
Task item;
lock (_tasks)
{
// When there are no more items to be processed,
// note that we're done processing, and get out.
if (_tasks.Count == 0)
{
--_delegatesQueuedOrRunning;
break;
}
// Get the next item from the queue
item = _tasks.First.Value;
//先从队列中删除该任务,然后再执行,如果task开始执行后,存在于队列中已没有意义
_tasks.RemoveFirst();
}
// Execute the task we pulled out of the queue
base.TryExecuteTask(item);
}
}
// We're done processing items on the current thread
finally { _currentThreadIsProcessingItems = false; }
}, null);
}
// Attempts to execute the specified task on the current thread.
protected sealed override bool TryExecuteTaskInline(Task task, bool taskWasPreviouslyQueued)
{
// If this thread isn't already processing a task, we don't support inlining
if (!_currentThreadIsProcessingItems) return false;
// If the task was previously queued, remove it from the queue
if (taskWasPreviouslyQueued)
// Try to run the task.
if (TryDequeue(task))
return base.TryExecuteTask(task);
else
return false;
else
return base.TryExecuteTask(task);
}
// Attempt to remove a previously scheduled task from the scheduler.
protected sealed override bool TryDequeue(Task task)
{
lock (_tasks) return _tasks.Remove(task);
}
// Gets the maximum concurrency level supported by this scheduler.
public sealed override int MaximumConcurrencyLevel { get { return _maxDegreeOfParallelism; } }
// Gets an enumerable of the tasks currently scheduled on this scheduler.
protected sealed override IEnumerable<Task> GetScheduledTasks()
{
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
Monitor.TryEnter(_tasks, ref lockTaken);
if (lockTaken) return _tasks;
else throw new NotSupportedException();
}
finally
{
if (lockTaken) Monitor.Exit(_tasks);
}
}
}
另外还提供了OrderedTaskScheduler调度器,一次只允许一个任务执行,所有任务顺序执行。其派生自LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler,n为1。
源码参考1
源码参考2
四、总结
本文主要实现了一个简单的自定义任务调度器,本实现中将DynamicQueueScheduler类中的Contains()方法设置了为虚函数,今后可以自定义DynamicQueueScheduler派生类,重新实现Contains(),以适应更加复杂的任务调度场景。并简单介绍了LimitedConcurrencyLevelTaskScheduler调度器。